Carpesium fruit extract for preventing and controlling crop insects
A technology for extracts and plant-derived extracts, which is applied in the field of biological pesticide development to achieve the effects of reducing environmental risks, solving the problem of large dosage and various modes of action.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
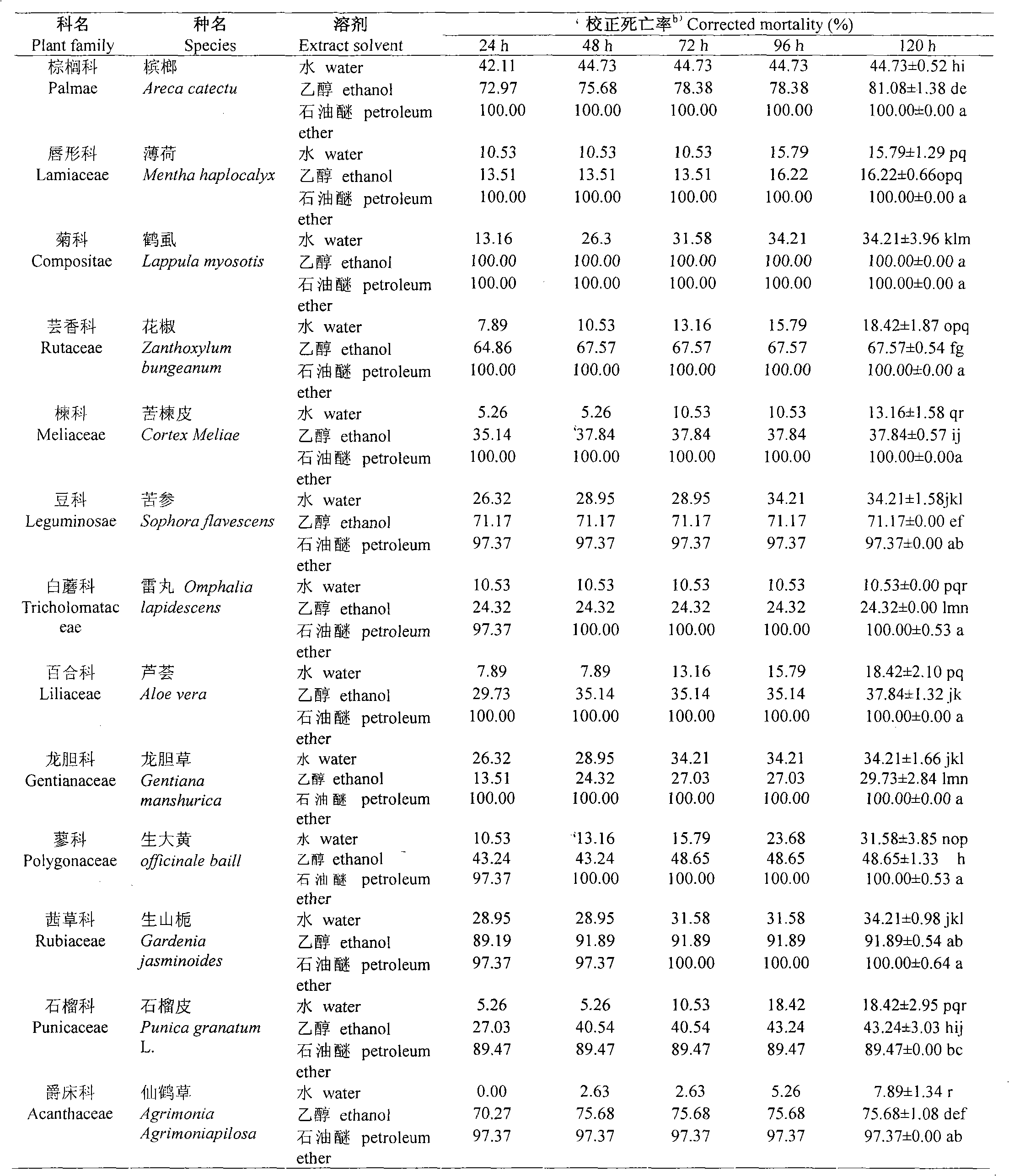
[0028] Indoor bioassay results (Table 1) show that 13 Chinese herbal medicines have good insecticidal effects on brown planthoppers, among which the crane lice was first reported for the control of agricultural pests, and it is a new type of plant-derived extract. The ethanol and petroleum ether extracts of crane lice have strong contact activity against brown planthopper, and can kill all test insects after 24 hours, but the contact activity of its water extract against brown planthopper is low, and the corrected mortality rate reaches 34.21% after 96 hours . It shows that the ethanol and petroleum ether extracts of crane lice have strong contact activity against brown planthopper.
[0029] Table 113 Contact activity of Chinese herbal medicine extracts on 3rd instar nymphs of brown planthopper a)
[0030] Table 1 Contact activity of extracts of 13 Chinese traditional herbal plants to the 3rd nymphs of Nilaparvatalugens
[0031]
[0032] a) The dosage is 0.8g / ml, the sam...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The indoor bioassay results (Table 2) showed that the ethanol and petroleum ether extracts of crane lice could kill all the tested SBPH after 24 hours. It shows that the ethanol and petroleum ether extracts of crane lice have strong contact activity against SBPH.
[0036] Table 2 The contact activity of crane lice extracts on the 3rd instar nymphs of SBPH
[0037] Table 2 Contact activity of extracts of Common Carpesium Fruit to the 3rd nymphs of Laodelphgax striatellus
[0038]
Embodiment 3
[0040] The indoor test results showed that the LC of the petroleum ether extract of the crane lice on the 3rd instar nymphs of the brown planthopper 50 The relative toxicity is 0.0038g / ml, and the relative toxicity is 21.7, which shows that the crane louse has a high contact activity to the brown planthopper.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com