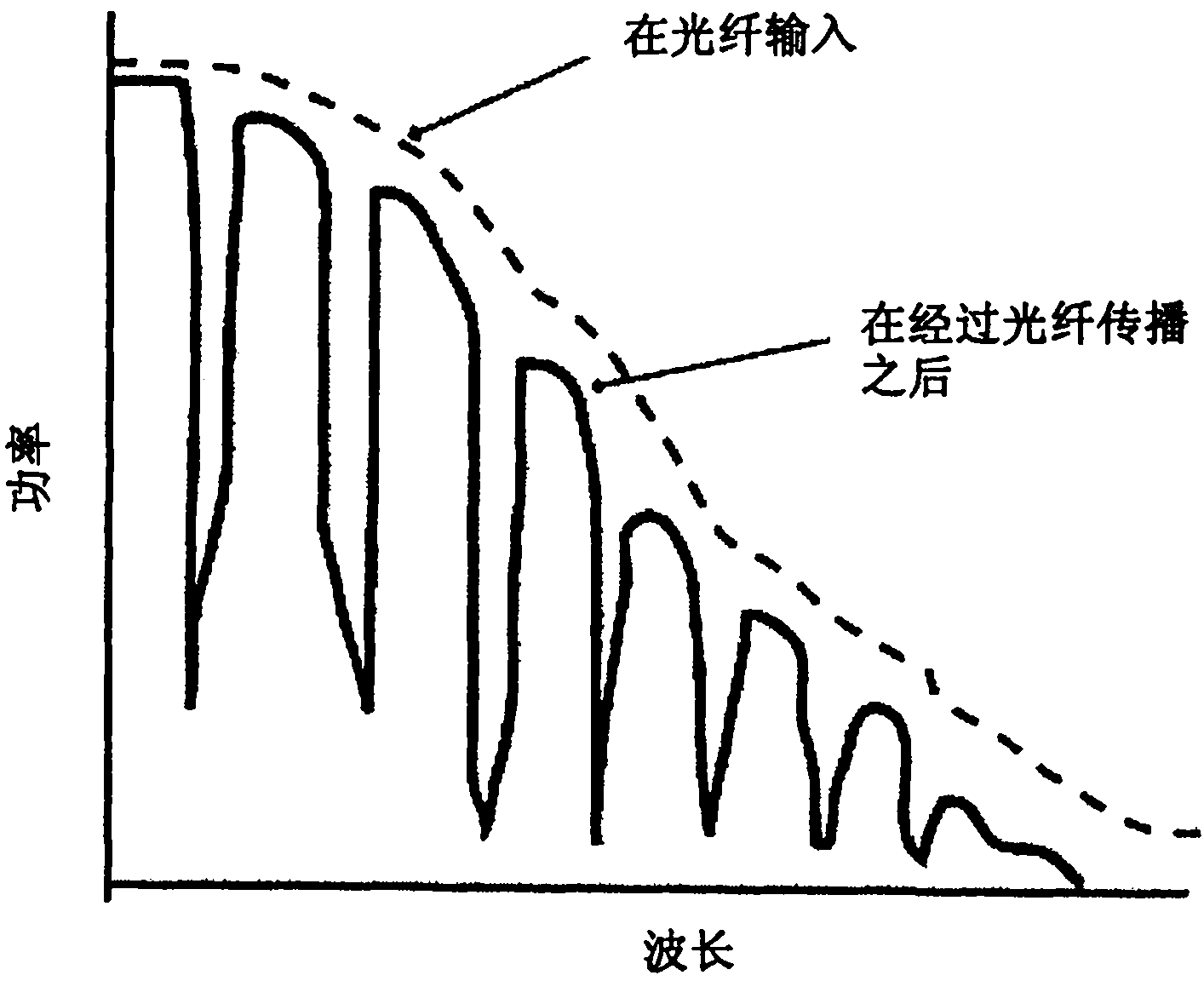
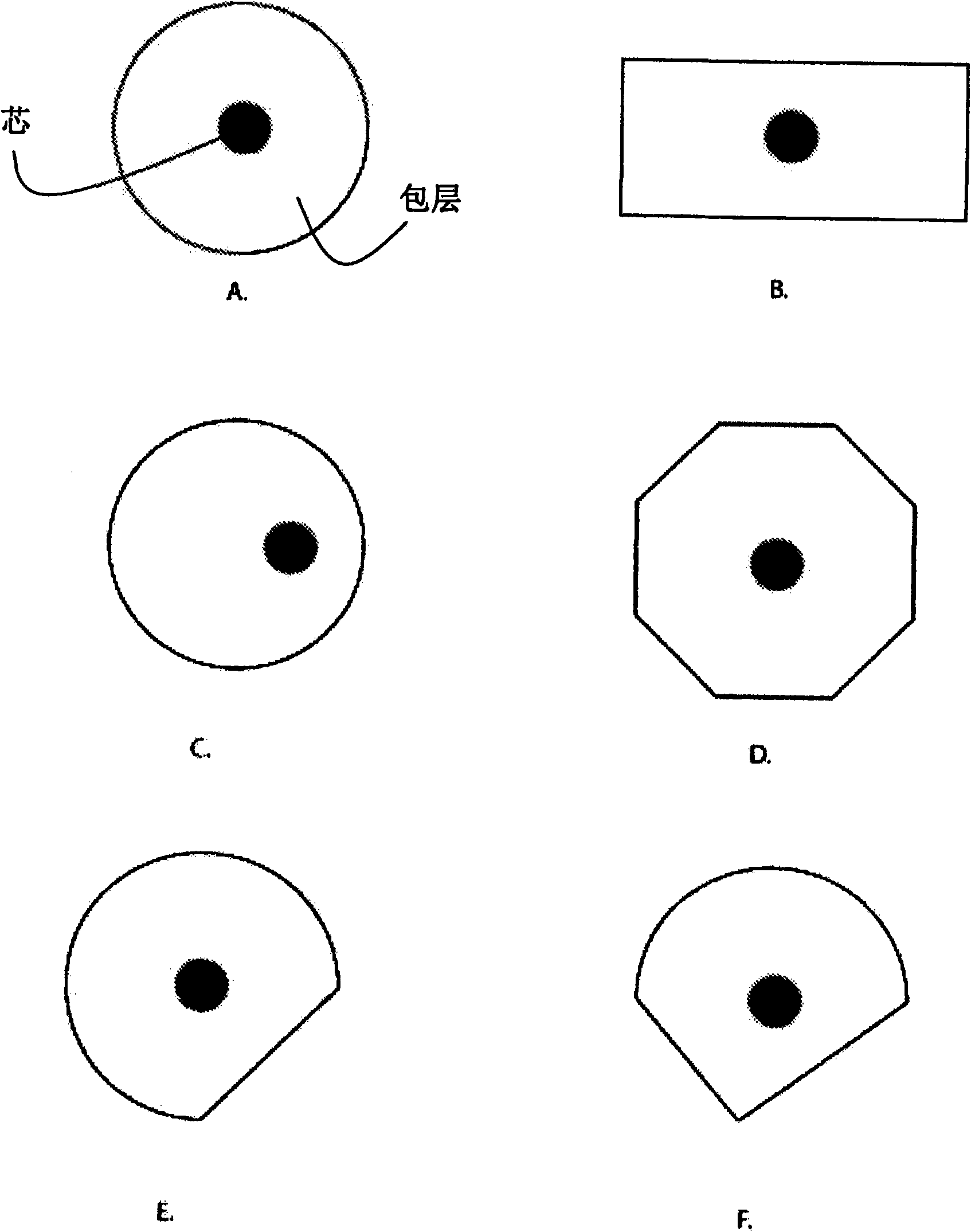
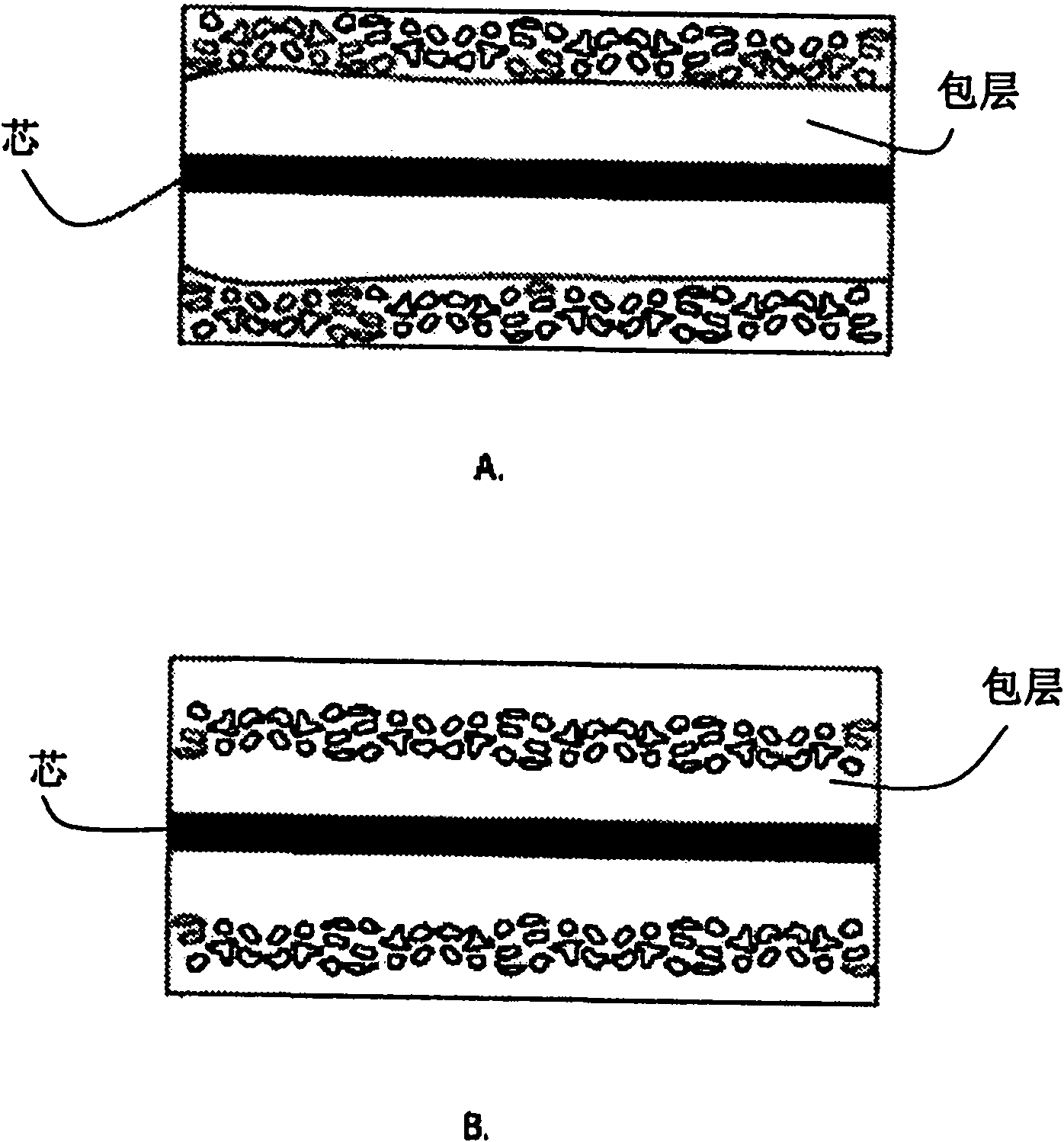
Active optical fiber and method for fabricating an active optical fiber
A technology of optical fiber and prefabricated parts, applied in the direction of cladding optical fiber, manufacturing tools, optical waveguide and light guide, etc., can solve the problems of pump loss, pump power leakage optical fiber, etc., and achieve the effect of improving absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] Figure 4 A longitudinal section of a tapered portion 11 of a double-clad active fiber according to one embodiment of the invention is shown. This part of the fiber comprises an active core 1 , an inner cladding 2 , and an outer cladding 3 . Also shown is the tapered curve or profile 6 of this portion of the fiber. The conical curve 6 of the outer cladding 3 of the optical fiber exhibits the diameter of the portion 11 of the optical fiber as a function of the position on the portion 11 of the optical fiber. exist Figure 4 In the example of , the conic curves for all three layers above follow a linear functional relationship, although other curves could be utilized. Considering the manufacturing method, an example can be considered where all the layers in this part of the fiber have the same functional dependence of the longitudinal curve. According to the invention, however, only the core 1 and the inner cladding 2 in which the pump power is propagated need to be tap...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com