Method of increasing specificity of nucleic acid hybridization using zwitterionic compound
A nucleic acid hybridization and zwitterion technology, which is applied in the field of improving nucleic acid hybridization specificity with zwitterionic compounds, and can solve the problem of low hybridization specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1: Influence of CAPS on Nucleic Acid Hybridization Specificity in Multiplex PCR
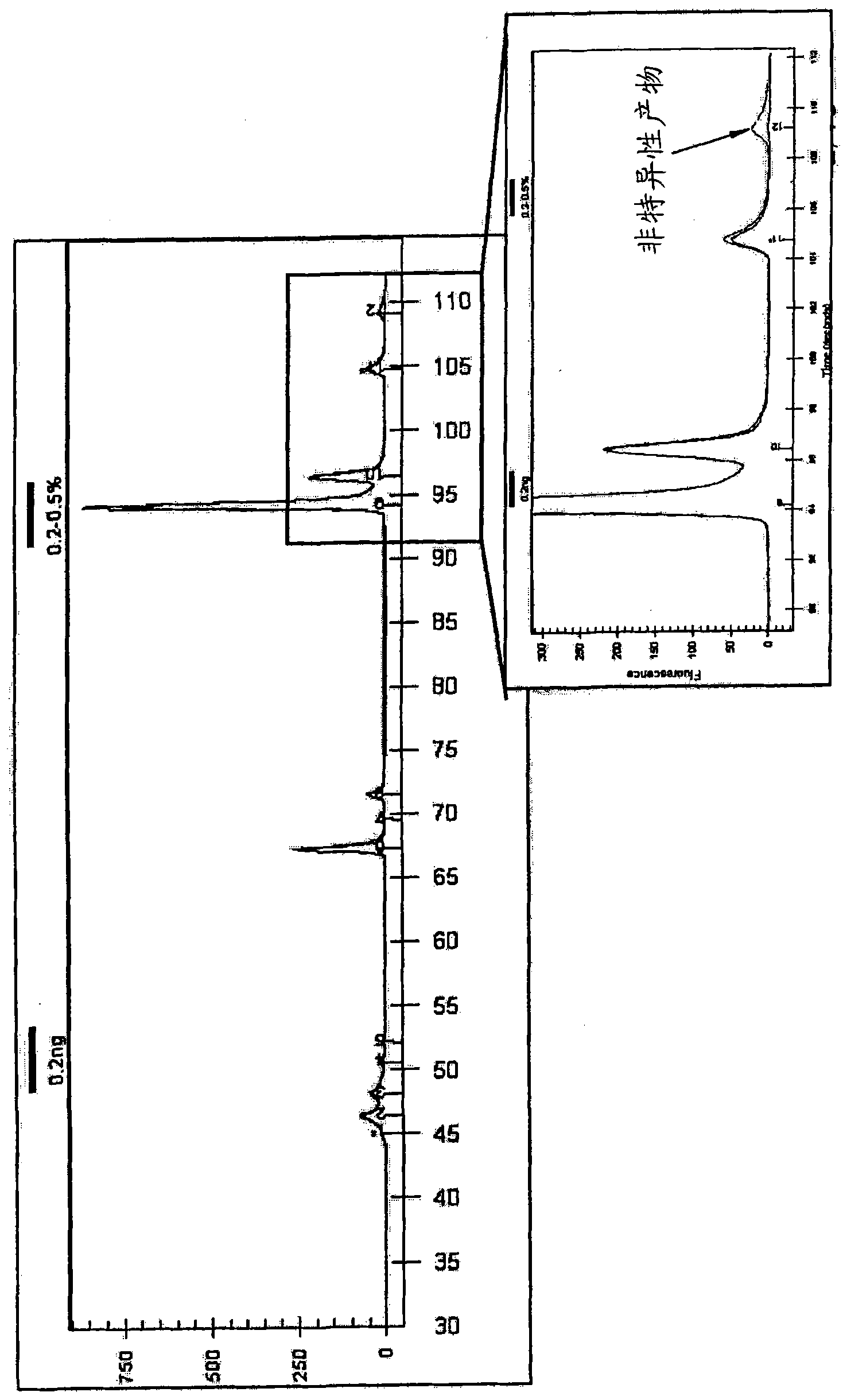
[0052] Genomic DNA (gDNA) was isolated from Haemophilus influenza (from Samsung Medical Center), a major pathogen of respiratory infection, and as a template for multiplex PCR, the isolated gDNA was used in an amount of 0.2 ng or 1 ng. 3-(cyclohexylamino)-1-propanesulfonic acid (CAPS), which is a zwitterionic compound according to an embodiment of the present invention, was used at a concentration of 0.5% or 1% to perform multiplex PCR. With GeneAmp PCR system 9700 (ABI), PCR mixture (template gDNA 0.2ng or 1ng, CAPS 0.5% or 1%, 1×Taq Pol buffer solution, dNTP mixture each 200 μ M, PCR primer each 400 nM (SEQ ID NO: 1 to SEQ ID NO: 10), and Taq Pol 5 units), at 95°C for 1 minute to completely denature the DNA, and then carry out 25 PCR cycles on the PCR mixture (95°C for 5 seconds, 62°C for 13 seconds, 72 °C for 15 seconds), and a final extension at 72°C for 1 minute, thus perform...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Influence of CAPSO and CHES on nucleic acid hybridization specificity in multiplex PCR
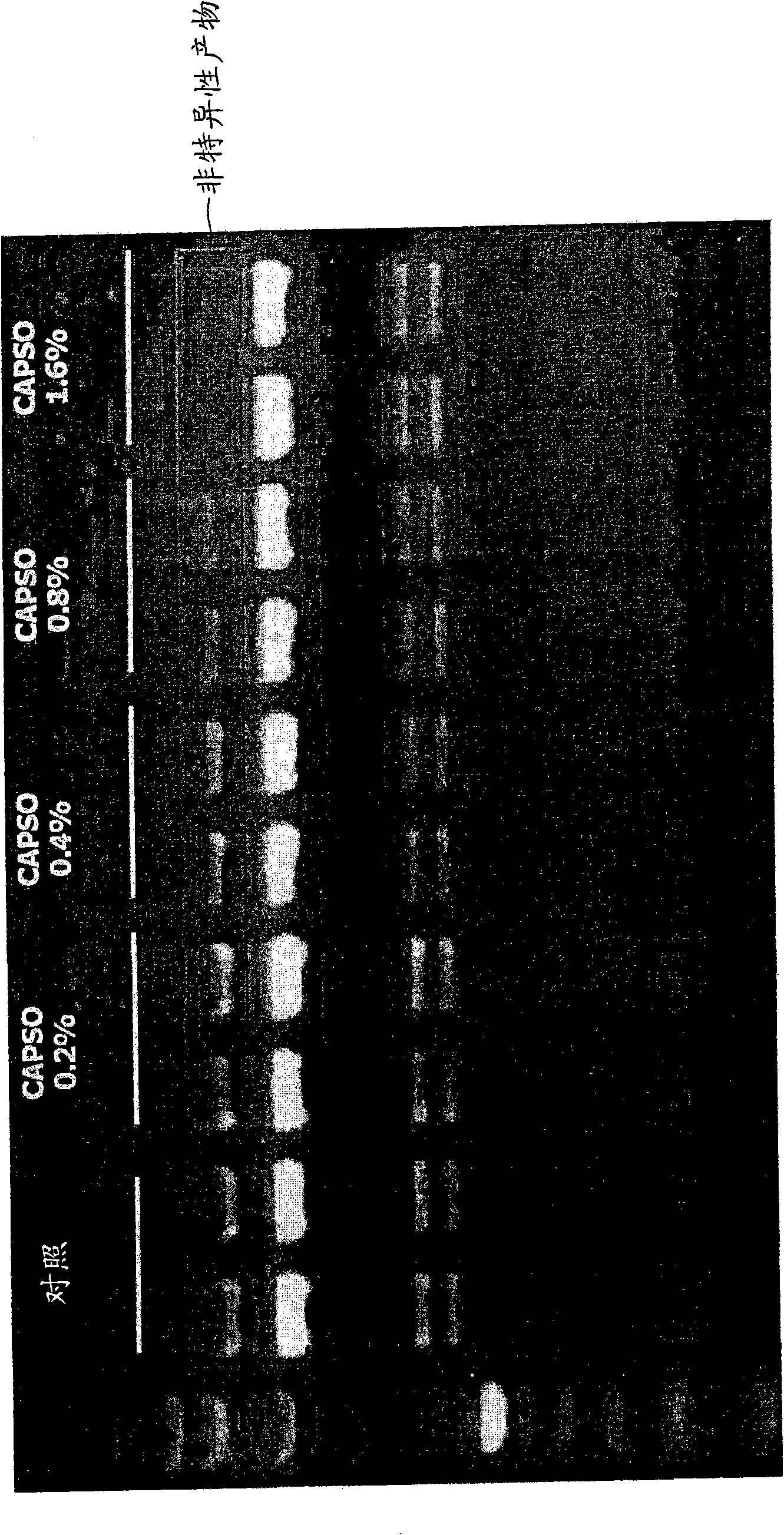
[0058] To study the nucleic acid hybridization specificity of different types of zwitterionic compounds in multiplex PCR, CAPSO and CHES were also used. The same experiment was performed in the same manner as in Example 1, except that CAPSO and CHES were added to the multiplex PCR at concentrations of 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.8% and 1.6%, respectively, and 1 ng of Haemophilus influenzae gDNA was used template.
[0059] image 3 A photograph showing the results of electrophoretic analysis of PCR products obtained when CAPSO was added to the multiplex PCR, showing a decrease in the yield of non-specific hybridization products. see image 3 , Multiplex PCR without CAPSO addition was performed on the control. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the intensity of non-specific hybridization product bands was significantly reduced with the addition of CAPSO compared to the case with...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3: Effect of Types of Zwitterionic Compounds on Nucleic Acid Hybridization Specificity in Multiplex PCR
[0061] Study of nucleic acid hybridization specificity of different classes of zwitterionic compounds in multiplex PCR using betaine. The same test was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that 2.5 μl (0.25×), 5 μl (0.5×), 10 μl (1 ×), and 15 μl (1.5×) of betaine were added to the multiplex PCR, and the Haemophilus influenzae gDNA template was used in amounts of 1 ng, 0.1 ng and 0.01 ng, respectively.
[0062] Figure 5 A photograph showing the results of electrophoretic analysis of PCR products obtained when betaine was added to multiplex PCR, showing a decrease in the yield of non-specific hybridization products. see Figure 5 , the control implements multiplex PCR without adding betaine, and the numbers "1", "2" and "3" refer to the amount of template gDNA used for PCR, for example, 1ng, 0.1ng and 0.01ng, respectively. Depend on Fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com