Method for identifying time-varying structure modal frequency based on time frequency distribution map
A time-frequency distribution, time-varying modal technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as difficult adaptation, different results of the same algorithm, no physical meaning, etc., to achieve strong applicability performance and anti-noise interference, easy to use effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
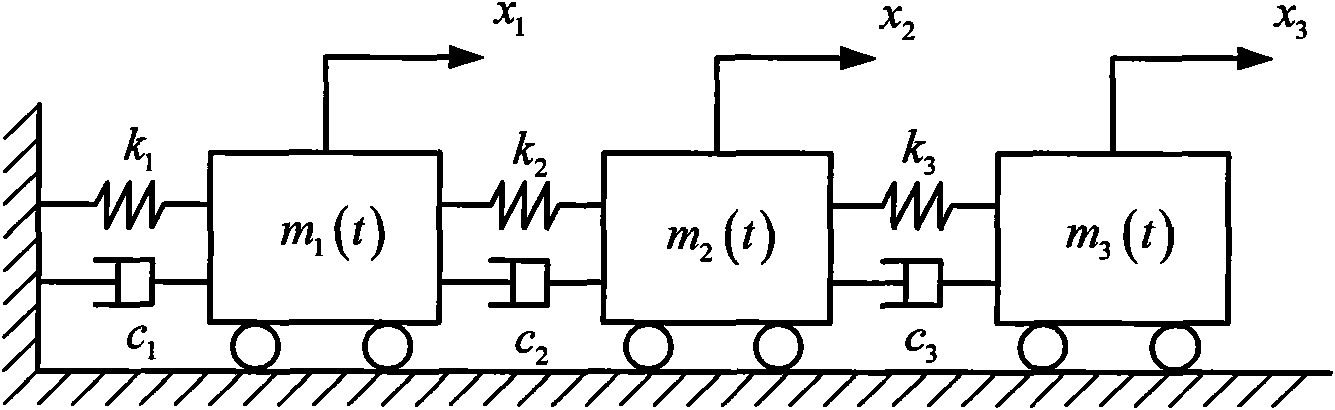
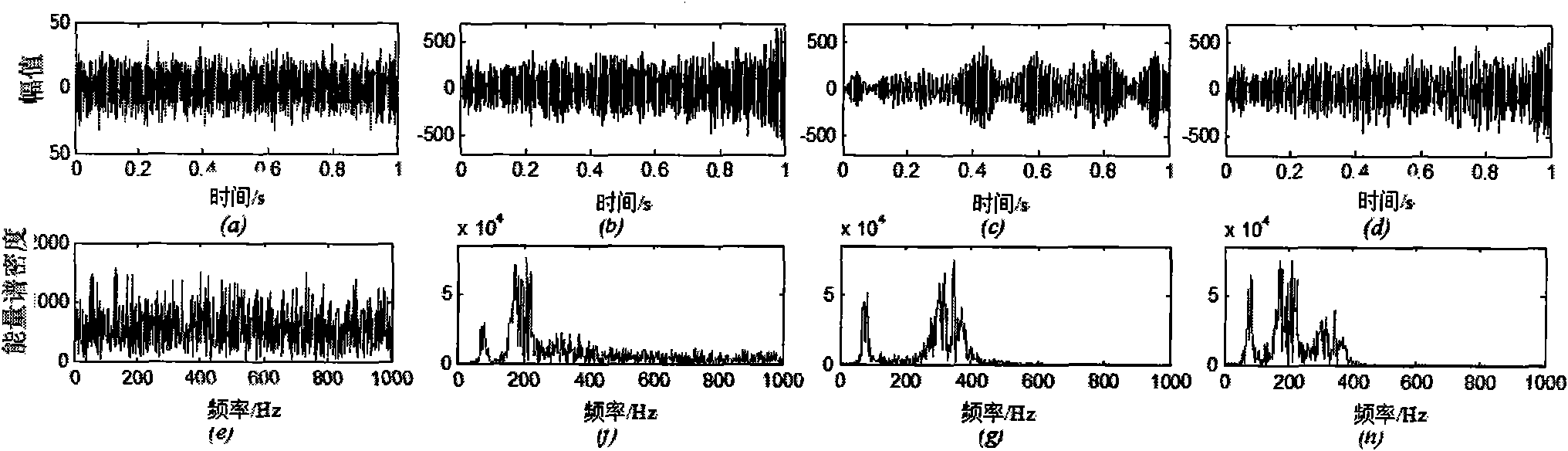
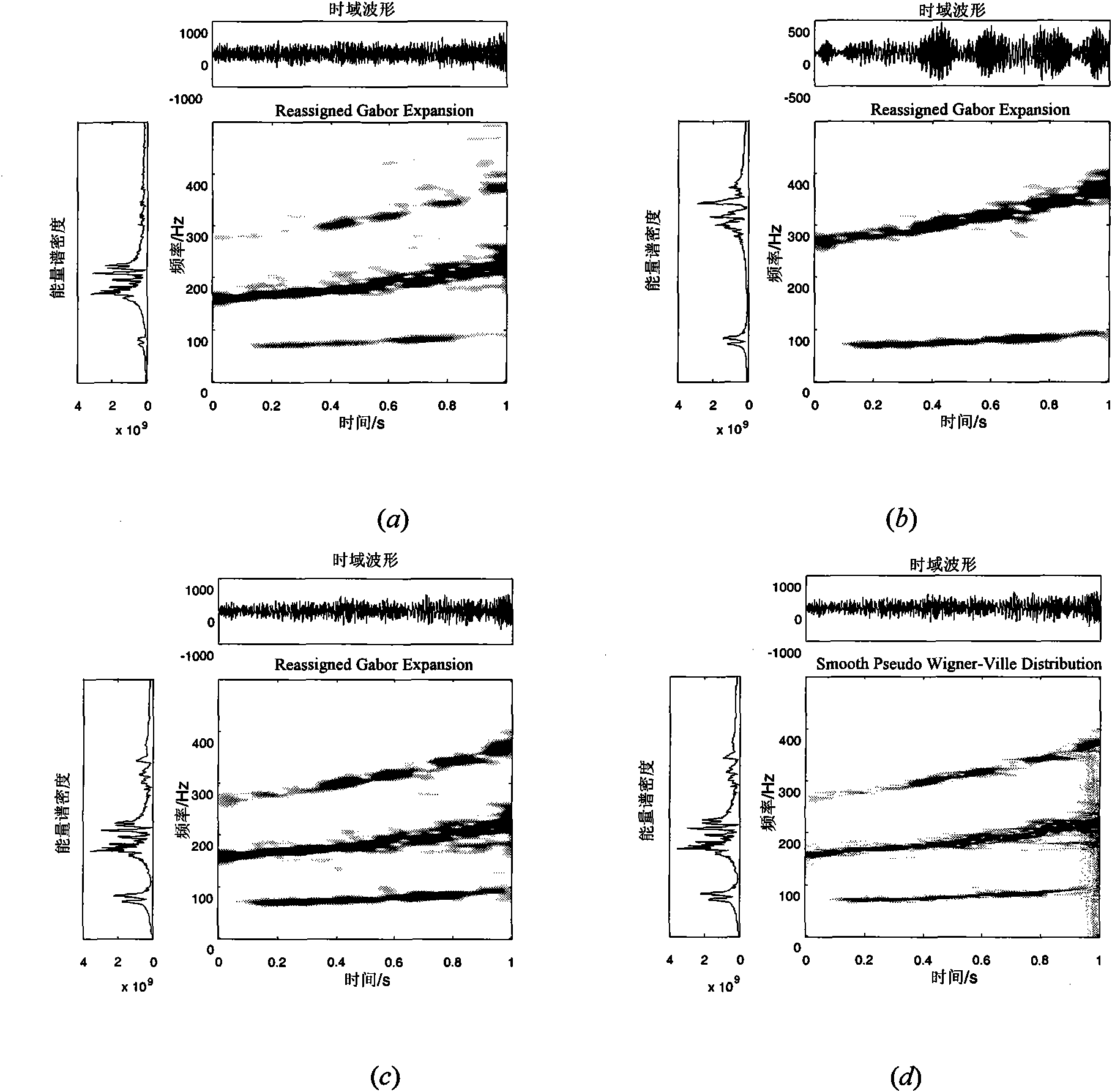
[0044] The invention proposes and realizes a weighted non-linear least square time-varying structural mode frequency identification method with the energy time-frequency distribution coefficient as the weighting coefficient. The present invention will be further described through an example of a randomly excited three-degree-of-freedom time-varying structure.
[0045] figure 1 A three-degree-of-freedom spring-damper-mass system is shown. The parameter of the three-degree-of-freedom system is k 1 =k 2 =k 3 =10 5 , c 1 = 1.0, c 2 =0.5,c 3 =0.5, the initial mass is m 1 (0)=0.2, m 2 (0)=0.1, m 3 (0)=0.1. The dynamic governing equation of the system is:
[0046] M ( t ) x · · + C x · ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com