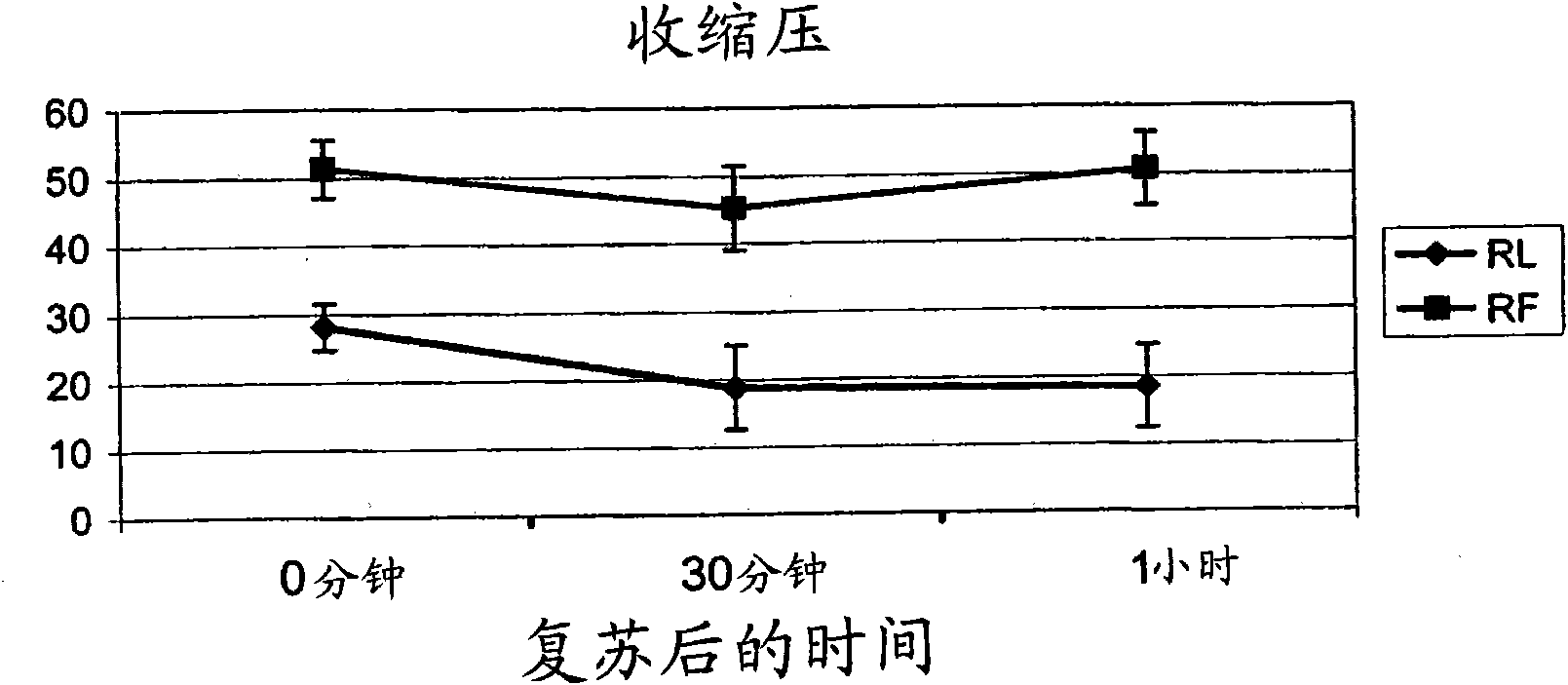
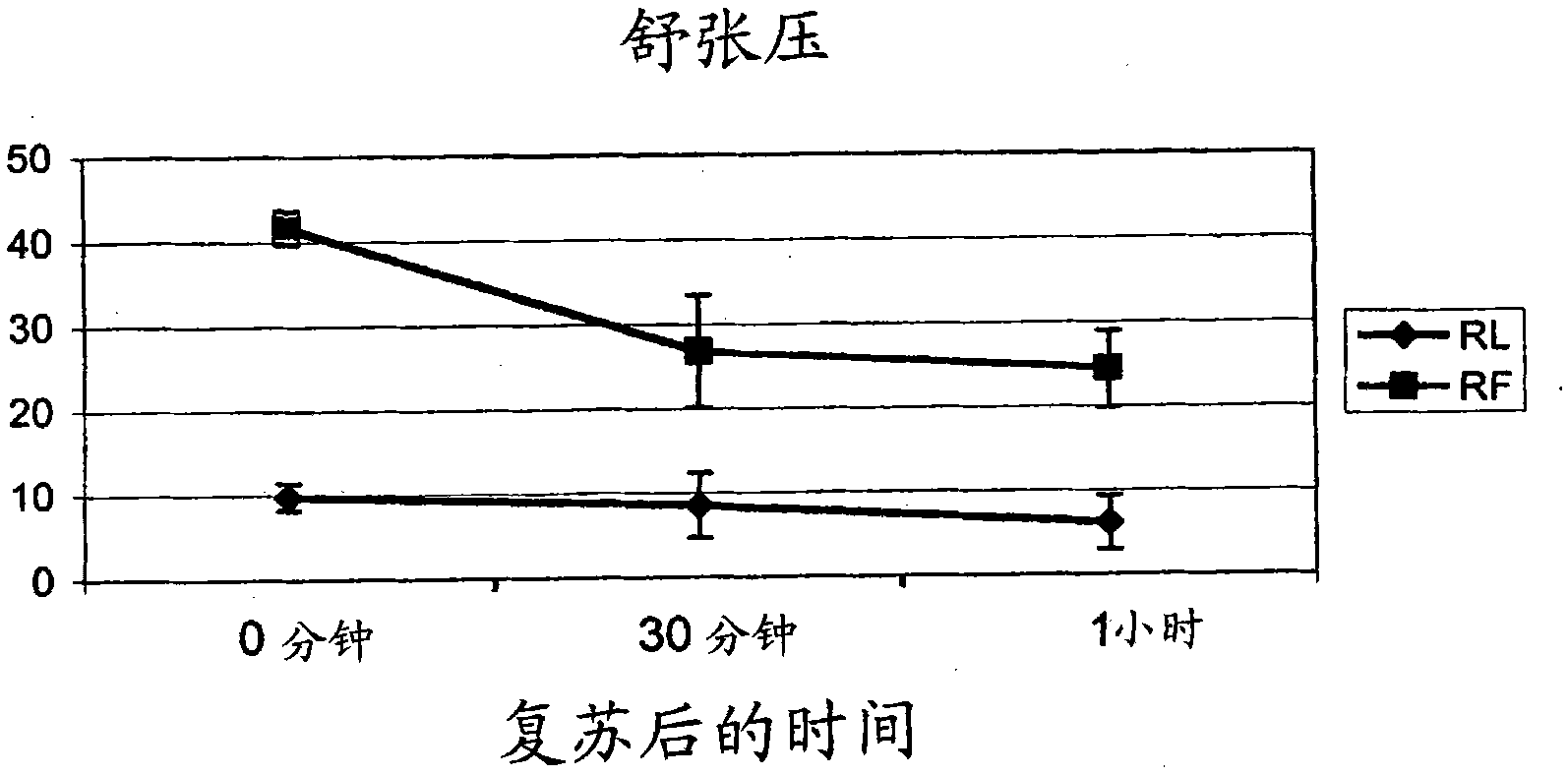
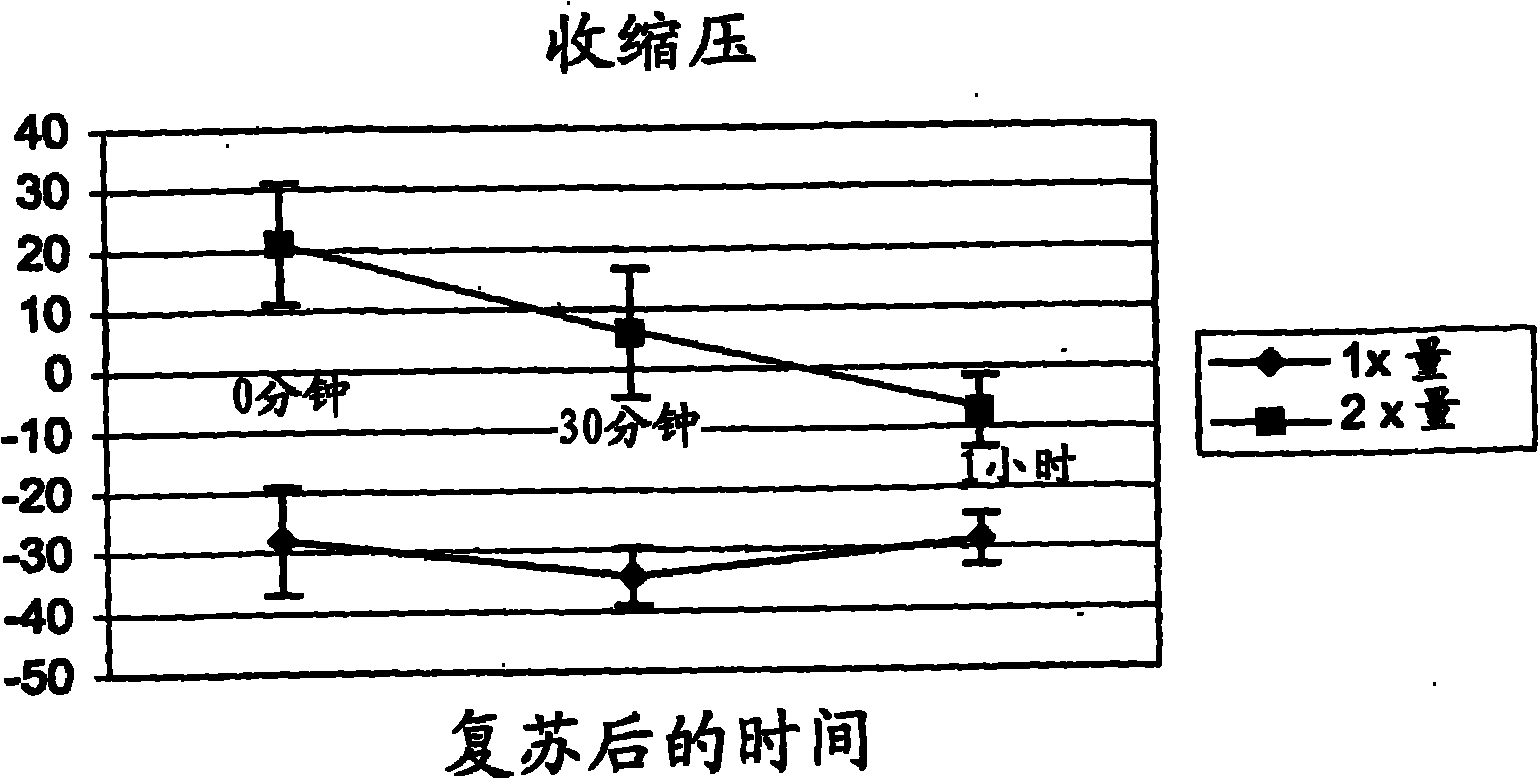
Resuscitation fluid
A technology for resuscitation fluid and blood, applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of high price and short storage life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] Preparation of resuscitation fluid
[0050] Resuscitation fluids are prepared by mixing lipid components, an aqueous carrier, and any other ingredients to form an emulsion. Common mixing methods include, but are not limited to, stirring, shaking, vibrating, and sonication. In one embodiment, by using A preformed lipid emulsion is mixed with an aqueous carrier and other ingredients to form a resuscitation fluid.
[0051] In order to increase the oxygen content in the resuscitation fluid, by making pure oxygen or oxygen content be 21% to 100% (volume / volume), preferably 40% to 100% (volume / volume), more preferably 60% to 100% (volume / volume), most preferably 80% to 100% (volume / volume) gas bubbled through the resuscitation fluid for more than 30 seconds, preferably 1 minute to 15 minutes, more preferably 1 minute to 5 minutes, can oxygenate the resuscitation fluid . The oxygenation time for a particular composition of resuscitation fluid can be determined experiment...
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Methods and Materials
[0066] Lipid Emulsion: 20% Intralipid (marketed by Baxter International Inc., Deerfield, IL) was used as a model lipid emulsion. It consisted of 20% soybean oil, 1.2% egg yolk phospholipids, 2.25% glycerol, water and sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 8.
[0067] Determination of Intralipid Oxygen Content: Place samples of distilled water, Ringer's Lactate (RL) and Intralipid (20%) (1ml each) in 2.0ml tubes in contact with air for 30 minutes before dissolved gas analysis . A 50 [mu]L volume withdrawn from each of these liquids was injected into a 37[deg.]C Sievers cleanup vessel containing 36ml of a mildly acidic solution consisting of 32ml 1M HCL and 4ml 0.5M ascorbic acid. The solution was continuously purged with high purity helium to convey any oxygen released by the sample to a mass spectrometer (HP 5975) for direct gas analysis. The signals generated at m / z=32 when injecting RL and lipid emulsion samples were integrated usin...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2: Oxygen content of resuscitation fluid
[0074] 20% I.V. Fat Emulsion (marketed by Baxter International Inc., Deerfield, IL) was used as sample recovery fluid (RF). The composition is 20% soybean oil, 1.2% egg yolk phospholipid, 2.25% glycerin, water and sodium hydroxide adjusted to pH 8. Oxygen content in RF was determined by mass spectrometry. As shown in Table I, the oxygen content of RF was almost twice that of Ringer's lactate (RL), the standard resuscitation fluid perfused during massive blood loss. The oxygen content of RL is comparable to that of water. As shown in Table II, the oxygen content of RF was increased five-fold by bubbling oxygen through the resuscitation fluid for about 1 minute. After oxygen loading, the oxygen content of RF compares favorably to that of blood with a minimum acceptable hemoglobin level (ie, 7.0 g / dl). Table III shows the theoretical oxygen content of RF with higher lipid content.
[0075] Table I. Ringer's Lactate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com