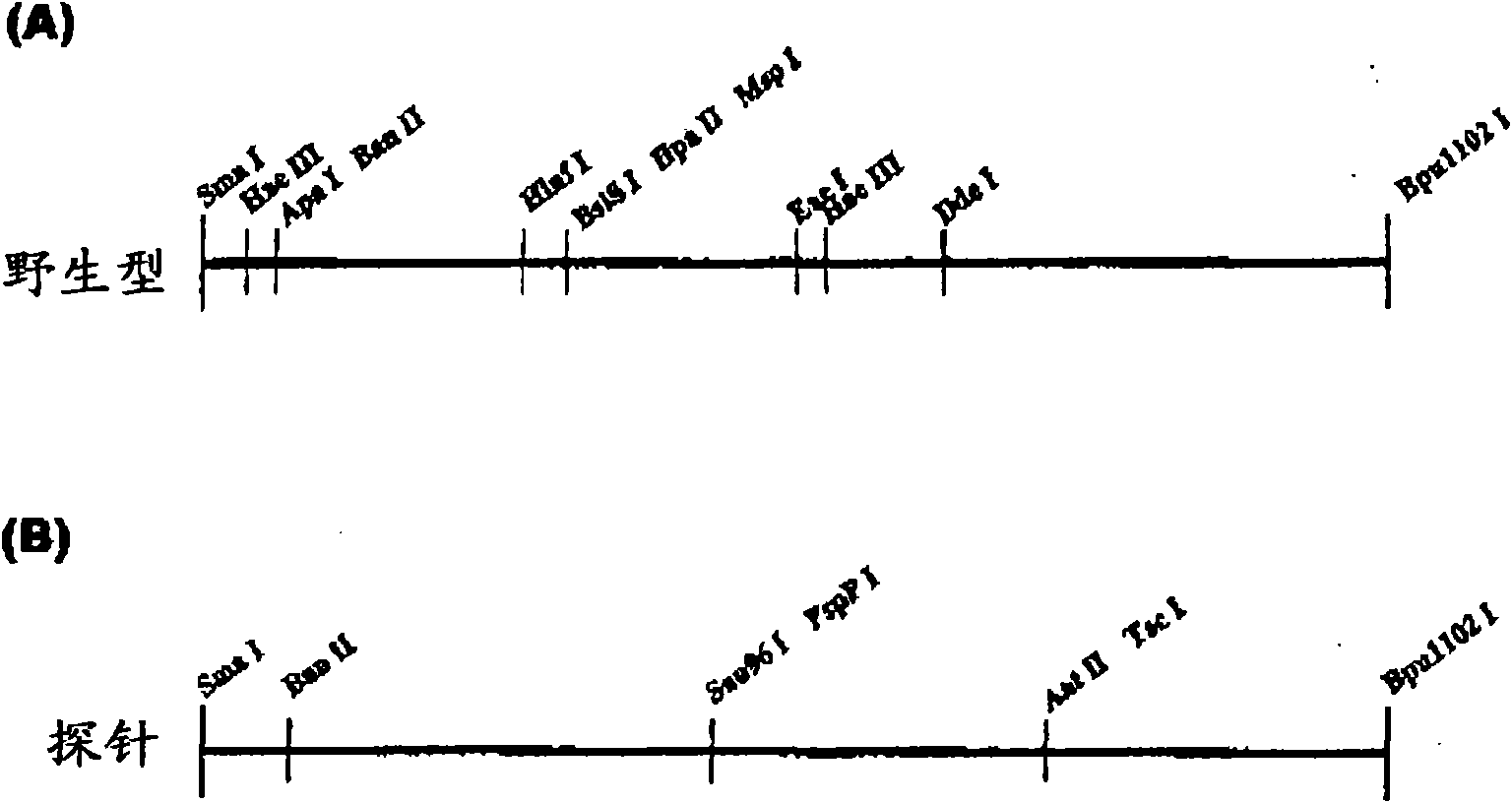
Non-human mammal model of epilepsy
A technology for non-human mammals and epilepsy, applied in the field of mutant genes, can solve the problems of low probability and time-consuming homologous recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0167] First, using rat brain QUICK-Clone cDNA (CLONTECH; MountainView, CA) as a template, two primers designed based on the existing cDNA sequence of rat Chrna4, namely, the forward primer (BN-rat CHRNA4cDNA-F ):
[0168] AGATCTCGCGAAGCTTCACCATGGCCAATTCGGGCACCGG (40-mer) (SEQ ID NO: 3) and
[0169] Reverse primer (rat CHRNA4cDNA-BX-R):
[0170] AGATCTAGATCAGCAAGCAGCCAGCCAGGGAGGCAGGA (38-mer) (SEQ ID NO: 4)
[0171] PCR was performed. The resulting PCR product was purified and subcloned into the pCRII-TOPO vector (Invitorogen; Carlsbad, CA). The obtained clone was sequenced to determine the base sequence of the cDNA of Chrna4. Among them, the base sequence information of rat is registered under the accession number L31620 (NCBI).
[0172] The resulting clones were mutated using the QuikChange Site-Specific Mutagenesis Kit (STRATAGENE; La Jolla, CA). First, use r845T846C-sen: CACACTGTGCATCTTCGTGCTGCTTTCTC (29-mer) (SEQ ID NO: 7) and r845T846C-ant: GAGAAAGCAGCACGAAGATGCACA...
Embodiment 2
[0179]As in Example 1, use r856C857T-sen: CGGTGCTGCTTTCTTTCACCGTCTTCCTG (29-mer) (SEQ ID NO: 10) and r856C857T-ant: CAGGAAGACGGTGAGAAGAAGCAGCACCG (29-mer) (SEQ ID NO: 11) to mutate the T at position 856 of the cDNA base sequence For C, mutate C at position 857 to T. The base sequence of the obtained mutant cDNA is shown in SEQ ID NO:12. Thus, the amino acid residue Ser at position p.286, which is homologous to the α4 subunit of the human neuronal acetylcholine receptor, was mutated to the amino acid residue Leu.
[0180] To c.104 to c.221 of the thus prepared mutated cDNA, a probe containing 118 bp of nucleotides shown in SEQ ID NO: 23 was prepared and introduced as in Example 1.
[0181] Using the mutated cDNA into which the probe was introduced as described above, a recombinant was prepared as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0183] As in Example 1, use sense primer rCHRNA-878insGCT-sen: GTCTTCCTGCTGCTGCTCATCACCGAGATC (30-mer) (SEQ ID NO: 13) and antisense primer rCHRNA-878insGCT-ant: GATCTCGGTGATGAGCAGCAGCAGGAAGAC (30-mer) (SEQ IDNO: 14) in cDNA A GCT is inserted between the 878th and 879th positions of the base sequence. The base sequence of the obtained mutant cDNA is shown in SEQ ID NO:15. Thus, an amino acid residue Leu was inserted between the amino acid residue Leu at position p.293 and the amino acid residue Ile at position p.294, which are homologous to the α4 subunit of the human neuronal acetylcholine receptor.
[0184] Using the mutated cDNA thus prepared, a recombinant was prepared as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com