Radar device
A radar device, a technology of sweeping frequency signals, applied in measurement devices, directional multi-channel systems using radio waves, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of long cycle time, inability to calculate distance, speed and angle, and large integral number N, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of improving signal detection performance, improving signal detection performance, and reducing the impact of errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
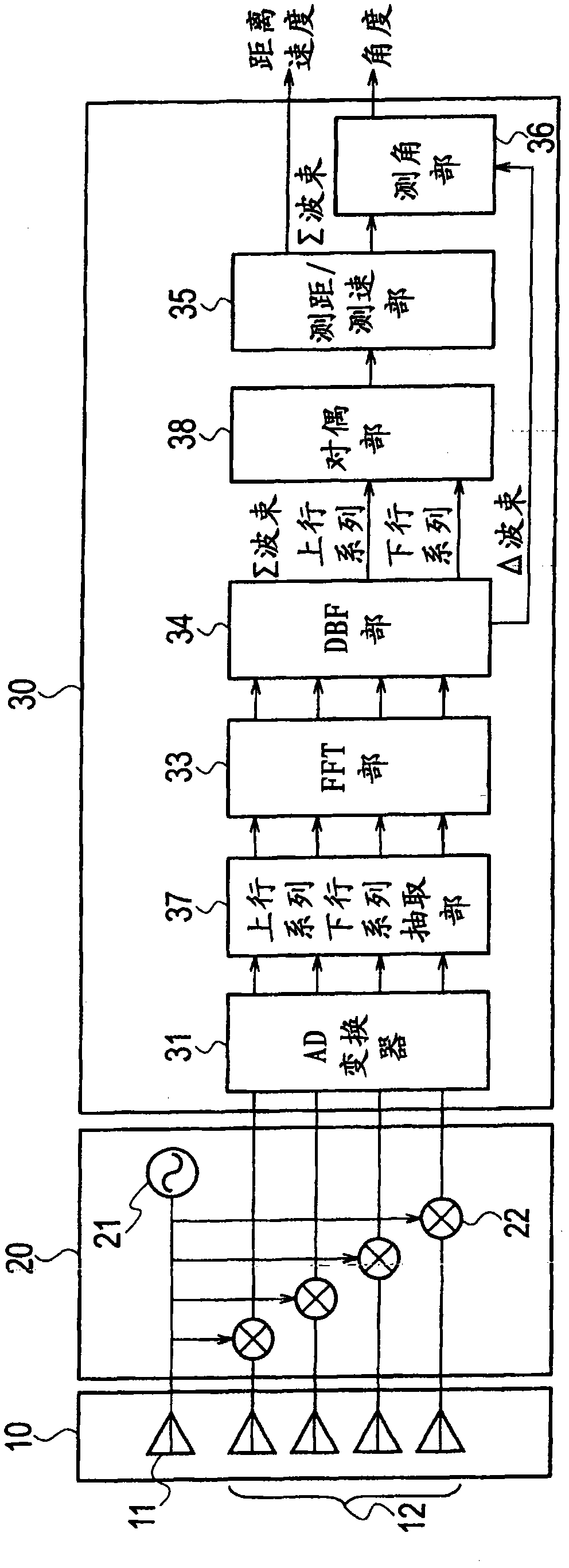
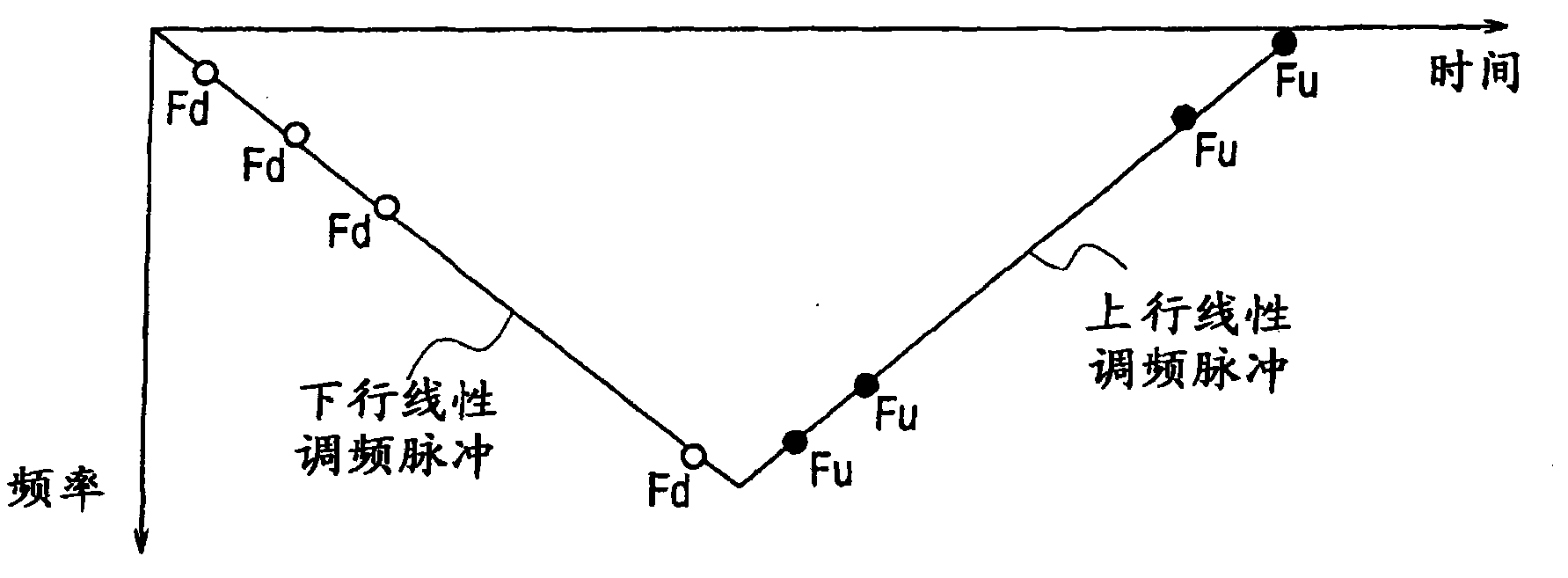
[0113] The radar device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention adopts the MRAV (Measurement Range after measurement Velocity) method in which the distance is calculated after the velocity is calculated from the beat frequency. Figure 7 It is a system diagram showing the configuration of the radar device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This radar device includes an antenna 10, a transceiver 20, and a signal processor 30a.
[0114] The antenna 10 is composed of an antenna radiating element 11 and a plurality of antenna receiving elements 12 . The antenna radiating element 11 converts a transmission signal as an electric signal from the transceiver 20 into an electric wave and sends it out to the outside. The plurality of antenna receiving elements 12 receive external radio waves, convert them into electrical signals, and send them to the transceiver 20 as received signals.
[0115] The transceiver 20 includes a transmitter 21 and a plurality of...
Embodiment 2
[0158] The radar device according to the second embodiment of the present invention employs a system in which a phase monopulse is combined with the MRAV system according to the above-mentioned first embodiment. The structure and the structure of the radar device involved in Embodiment 2 Figure 7 The configuration of the radar device according to the first embodiment shown is the same.
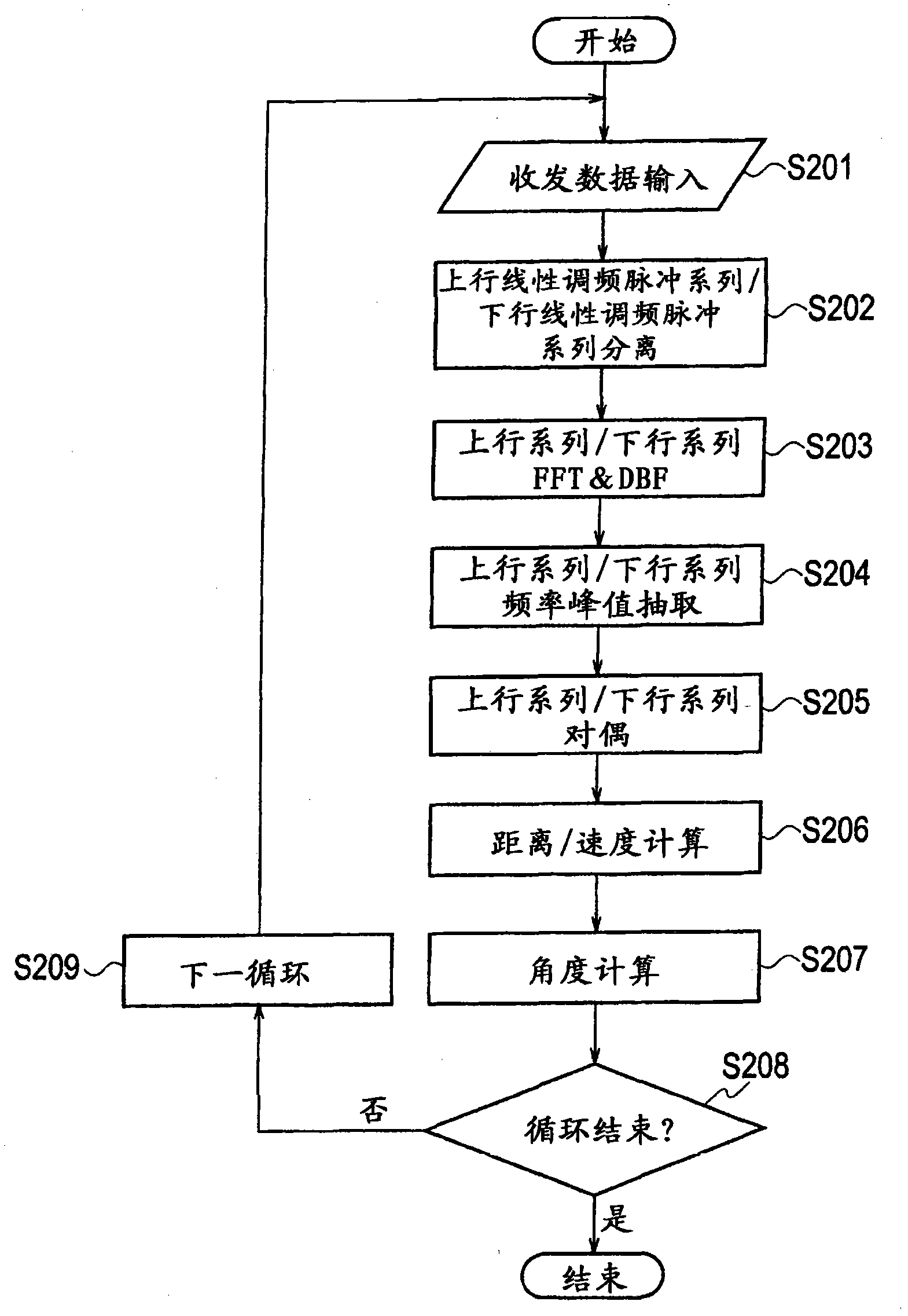
[0159] Figure 13This is a flowchart showing the operation of the radar device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, focusing on measurement processing for distance measurement, speed measurement, and angle measurement. In addition, for the Figure 8 The same or equivalent processing steps as the measurement processing related to the embodiment 1 shown in the flow chart of Figure 8 The same markup as used in . Hereinafter, description will be given mainly on parts different from the first embodiment.
[0160] In particular, when the PRF is the same and the number of sampli...
Embodiment 3
[0173] The radar device according to the third embodiment of the present invention uses an amplitude comparison monopulse instead of the phase monopulse of the radar device according to the second embodiment. The composition and the structure of the radar device involved in embodiment 3 Figure 7 The configuration of the radar device according to the first embodiment shown is the same. Hereinafter, the parts different from those in Embodiment 1 will be mainly described. In addition, the amplitude comparison monopulse (also referred to as amplitude monopulse) is described in "Supervisor Takashi Yoshida, 'Revised Radar Technology', Society of Electronics, Information and Communication, pp. 274-275 (1996)".
[0174] Using ∑(f) and ∑(f-1) and ∑(f+1) of the group before and after the frequency of the extracted target, compare the absolute value abs(∑(f-1)) and the absolute value abs(∑( f+1)), and the larger one is set as the absolute value abs(∑u).
[0175] Then, calculate the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com