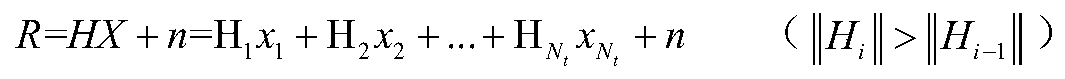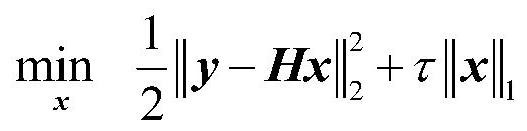Patents
Literature
51results about How to "Improve signal detection performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of transmitting reference signal and transmitter using the same
ActiveUS20090238064A1Low peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR)High cross-correlation propertyModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource block
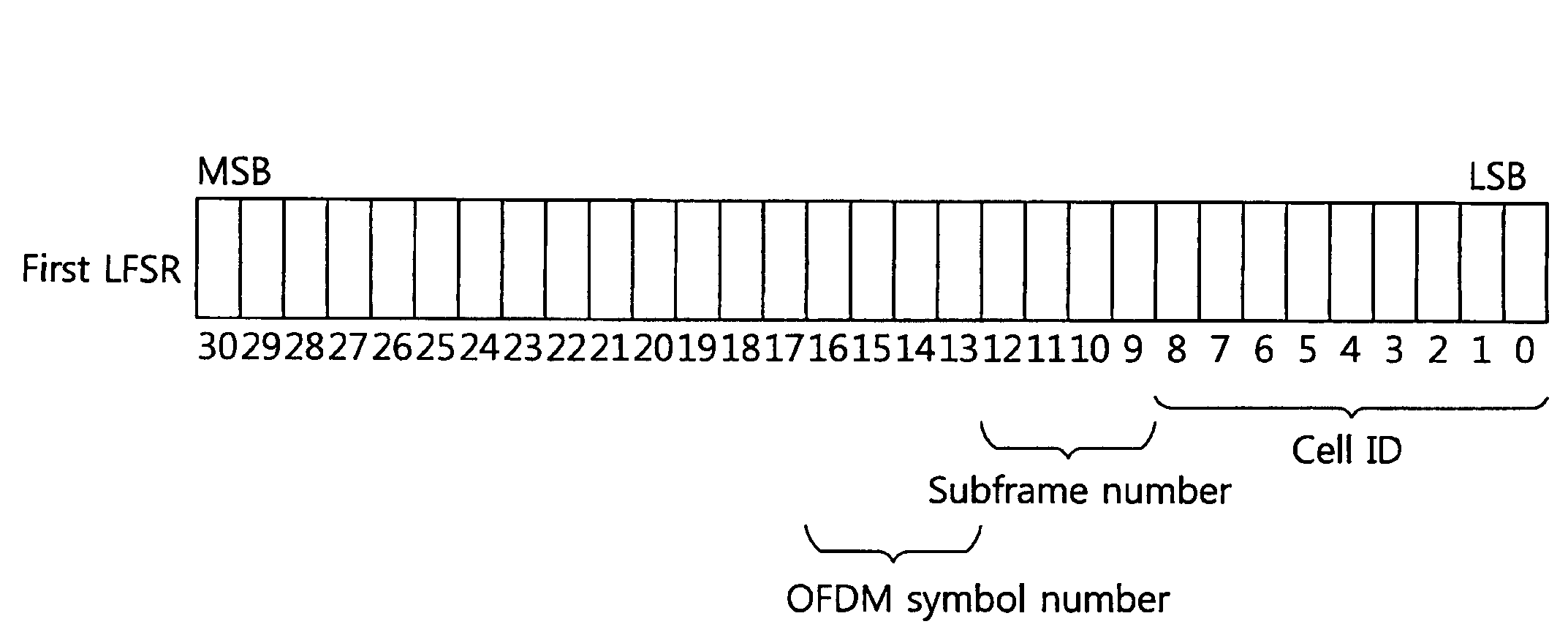
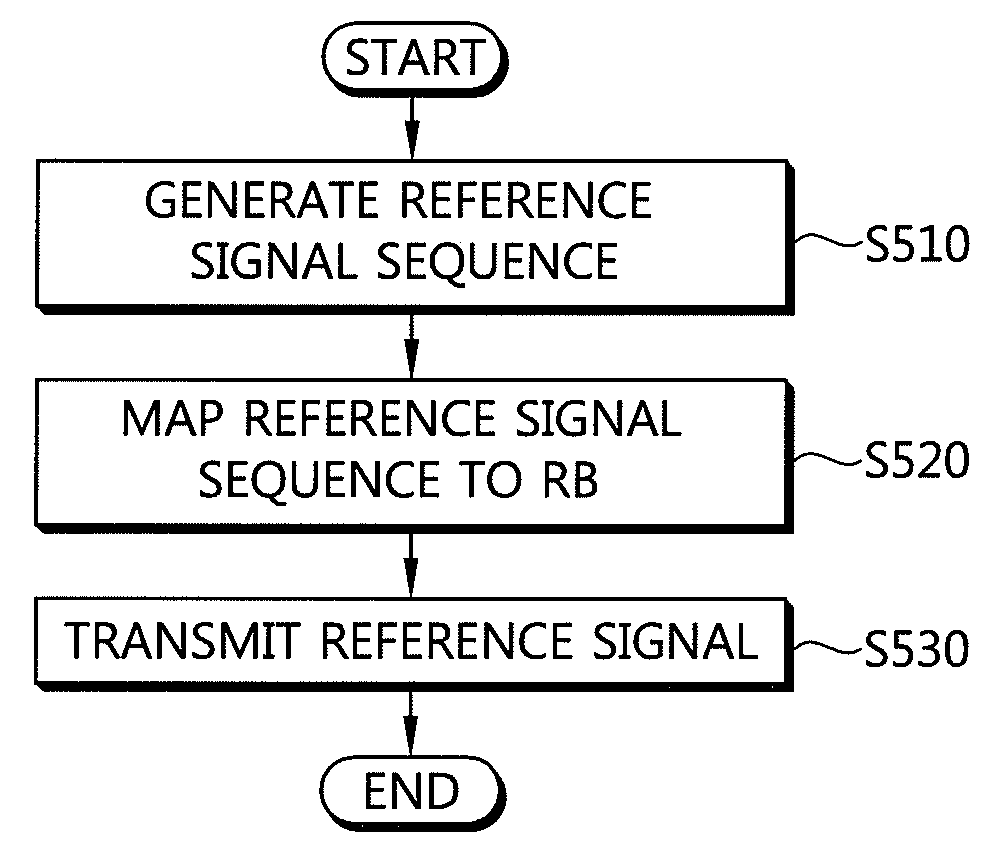
A method and apparatus of transmitting a reference signal in a wireless communication system is provided. A reference signal sequence is generated by using a pseudo-random sequence. A portion or entirety of the reference signal sequence is mapped to at least one resource block and is transmitted. The pseudo-random sequence is generated by a gold sequence generator which is initialized with initial values obtained by using cell identifier. The reference signal provides low PAPR and high cross correlation characteristic.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method of transmitting reference signal and transmitter using the same
ActiveCN101682419AEffective transmit powerImprove signal detection performanceEnergy efficient ICTTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource block
A method and apparatus of transmitting a reference signal in a wireless communication system is provided. A reference signal sequence is generated by using a pseudo-random sequence. A portion or the entirety of the reference signal sequence is mapped to at least one resource block, and is transmitted. The pseudo-random sequence is generated by a gold sequence generator which is initialized with initial values obtained by using cell identifier. The reference signal provides low PAPR and high cross correlation characteristic.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
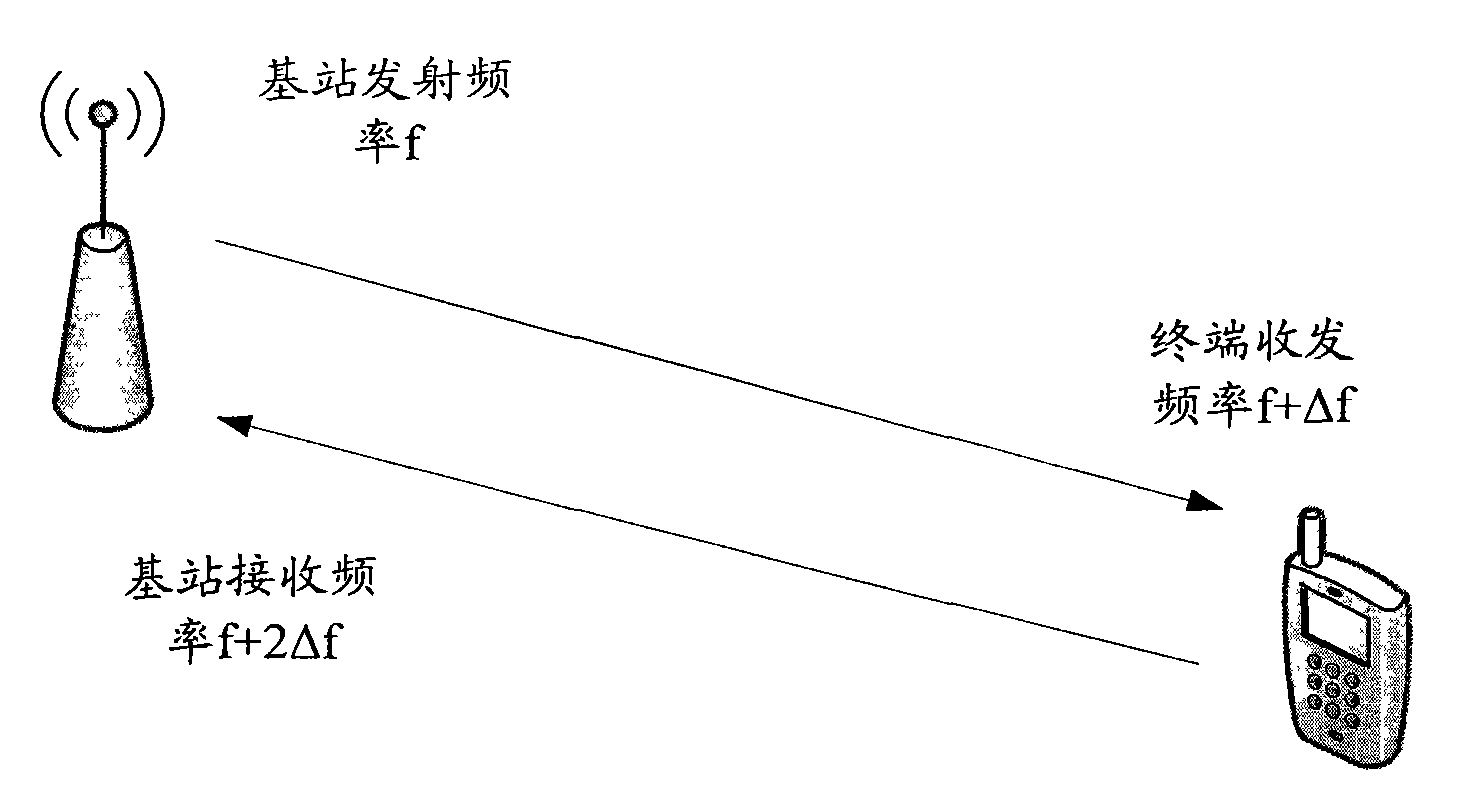
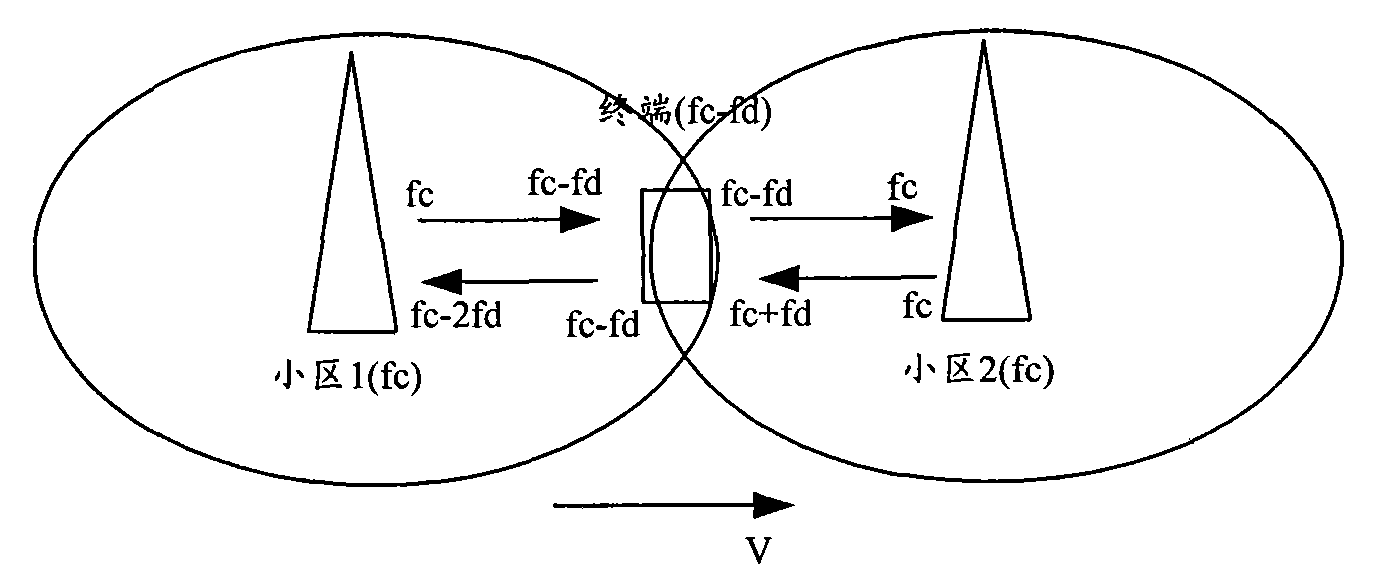
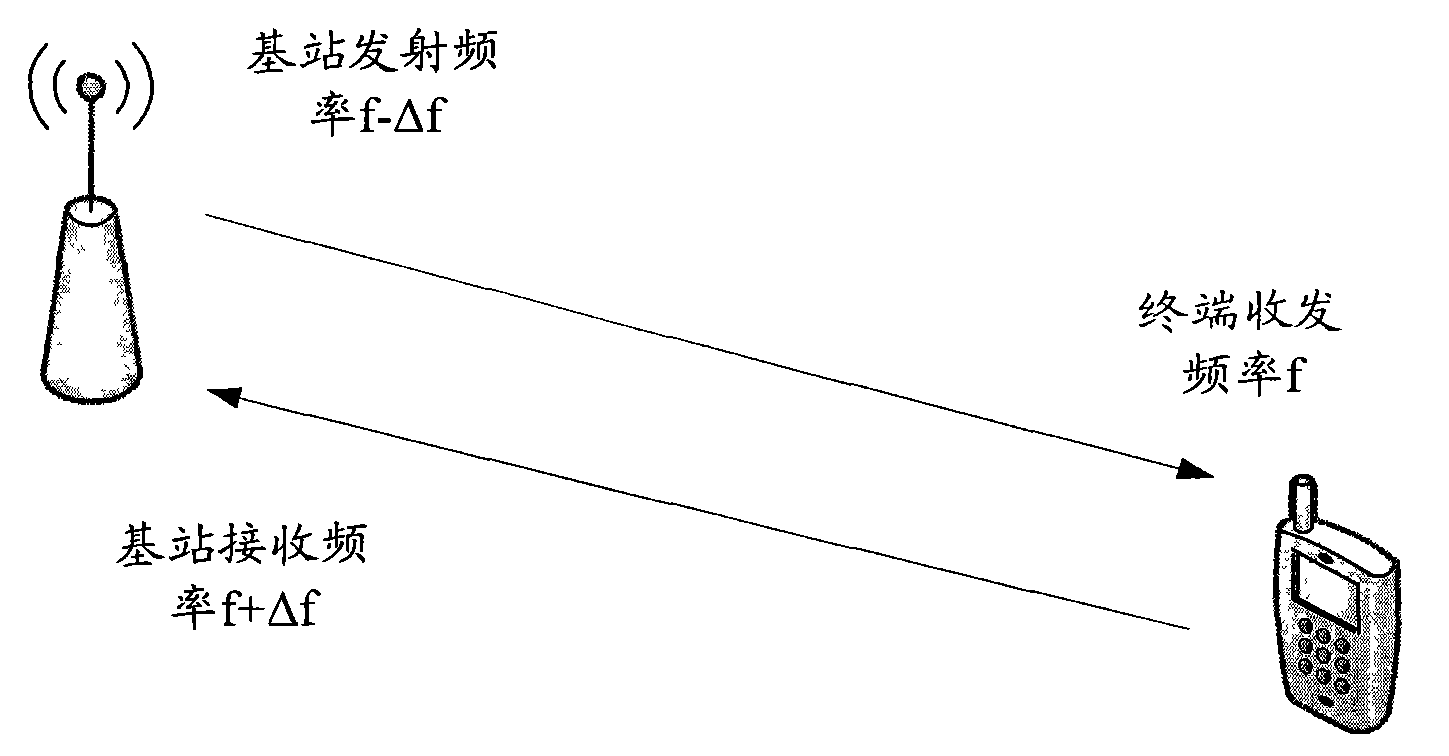
Method and device for pre-calibrating frequency deviation
ActiveCN101958744AImprove signal detection performanceModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmission for post communicationFrequency deviationBase station
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for pre-calibrating frequency deviation, comprising the following steps of: estimating an uplink frequency deviation value of a terminal, and obtaining a history uplink frequency deviation pre-calibration value used by the frequency deviation pre-calibration on the terminal; determining a current uplink frequency deviation pre-calibration value of the terminal according to the history uplink frequency deviation pre-calibration value, wherein the current uplink frequency deviation pre-calibration value is closer to the uplink frequency deviation value in comparison with the history uplink frequency deviation pre-calibration value; and pre-calibrating the frequency deviation of the terminal by utilizing the current uplink frequency deviation pre-calibration value. The embodiment of the invention further discloses a base station. The invention can efficiently improve the signal detection performance of the terminal.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method of transmitting reference signal and transmitter using the same
ActiveUS7729237B2Lower ratioHigh propertyModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource block
A method and apparatus of transmitting a reference signal in a wireless communication system is provided. A reference signal sequence is generated by using a pseudo-random sequence. A portion or entirety of the reference signal sequence is mapped to at least one resource block and is transmitted. The pseudo-random sequence is generated by a gold sequence generator which is initialized with initial values obtained by using cell identifier. The reference signal provides low PAPR and high cross correlation characteristic.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Line spectrum detection method by coherent accumulation of frequency domains
InactiveCN102353952AEasy to detectImprove signal detection performanceWave based measurement systemsNoise fieldTime correlation
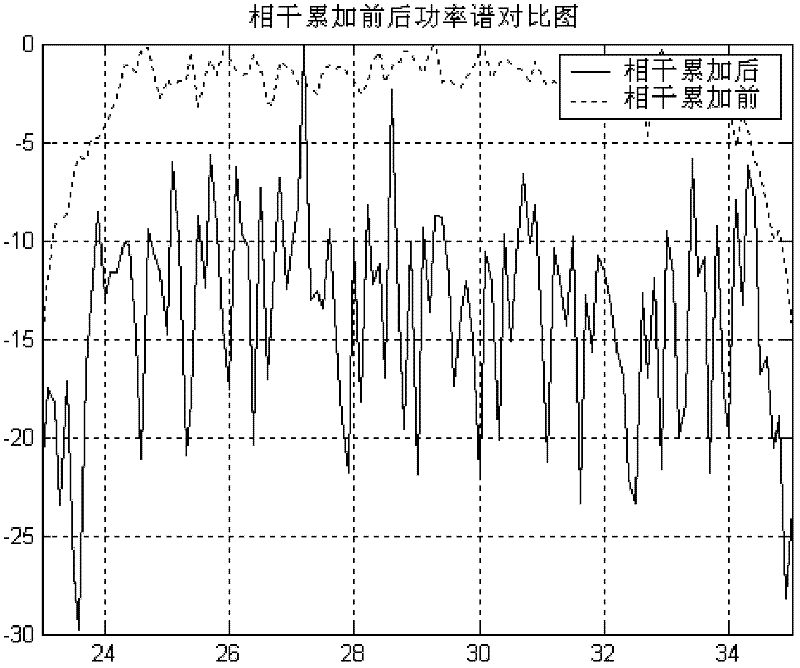
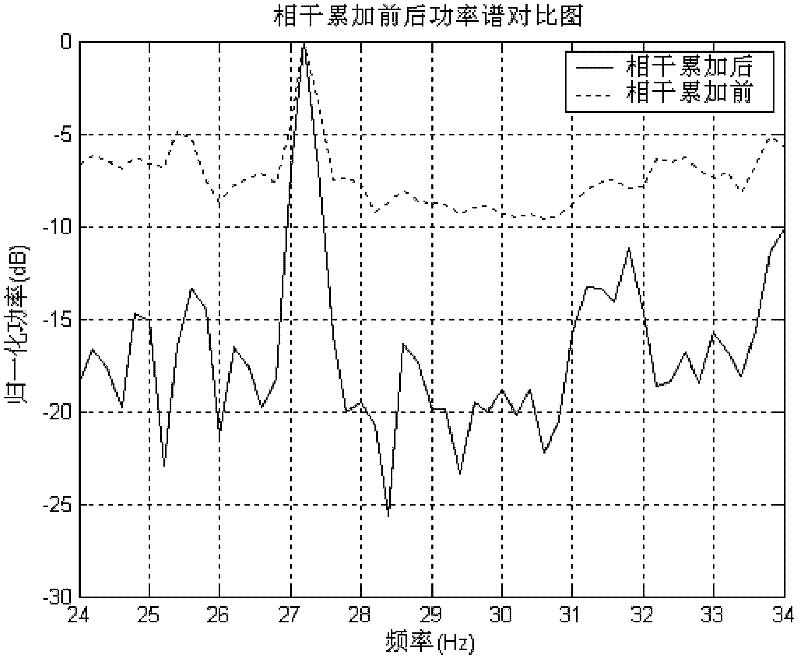
The invention provides a line spectrum detection method by coherent accumulation of frequency domains. According to the invention, the method comprises the following steps that: step one, on the basis of time correlation characteristics of a signal field and a noise field, segment processing is carried out on a receiving signal, so that there are time delays between all segments of the signal and a time delay amount is greater than a correlation radius of the noise and is less than a correlation radius of the signal; step two, each the signal segment is internally divided into a plurality of sub data segments and it is allowed that there are overlapping parts of data of all the segments; step three, time delay compensation is carried out on the signal; step four, signals of all the segments are accumulated to obtain an output signal of coherent accumulation; step five, power equalization is carried out on outputs of all correlation accumulations, so that a power spectrum estimated by the method provided in the invention is obtained. According to the invention, coherence of signals is utilized; and phase compensation is carried out on signals, wherein there are time delay differences between all the signals; therefore, same phase addition of the signals is formed; however, because the phase of the noise is random, there is no formed same phase addition for the noise, so that a detection capability on a weak signal can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Self-adaption ultrasonic beamforming method and system based on channel data
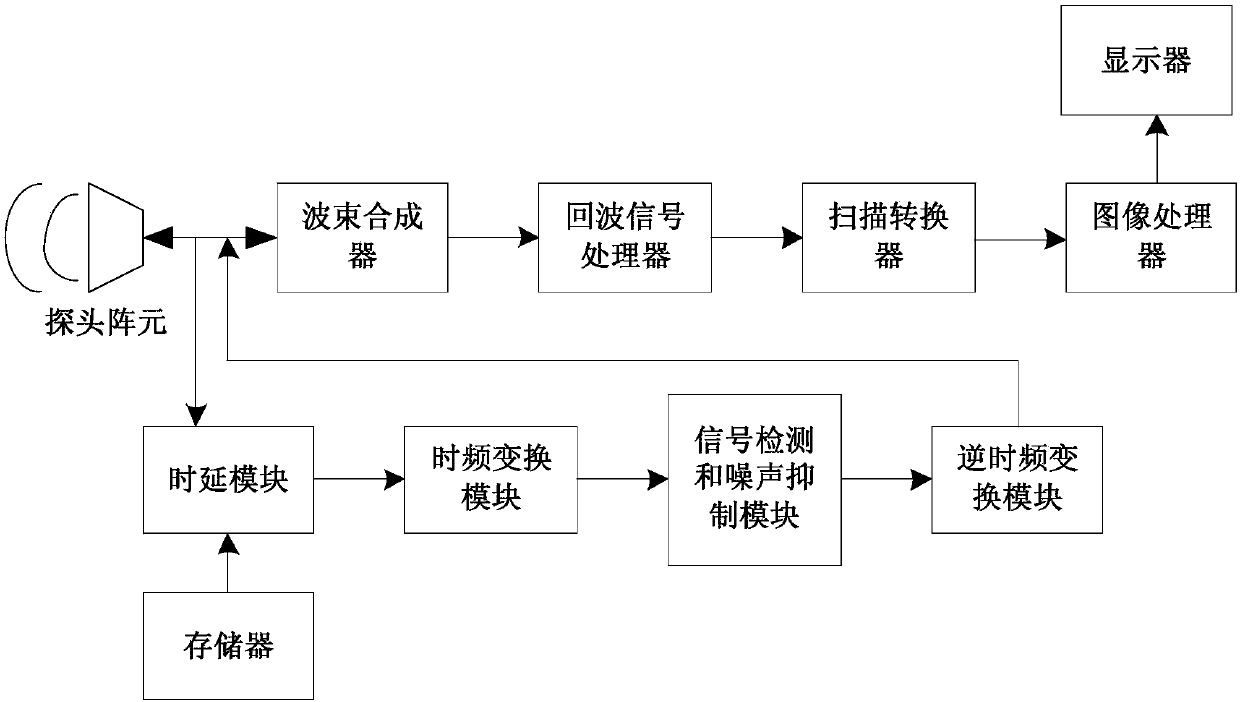
ActiveCN107789008AIncreased Noise Removal EfficiencyImprove removal efficiencyInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic image/data processingSonificationSynthesis methods
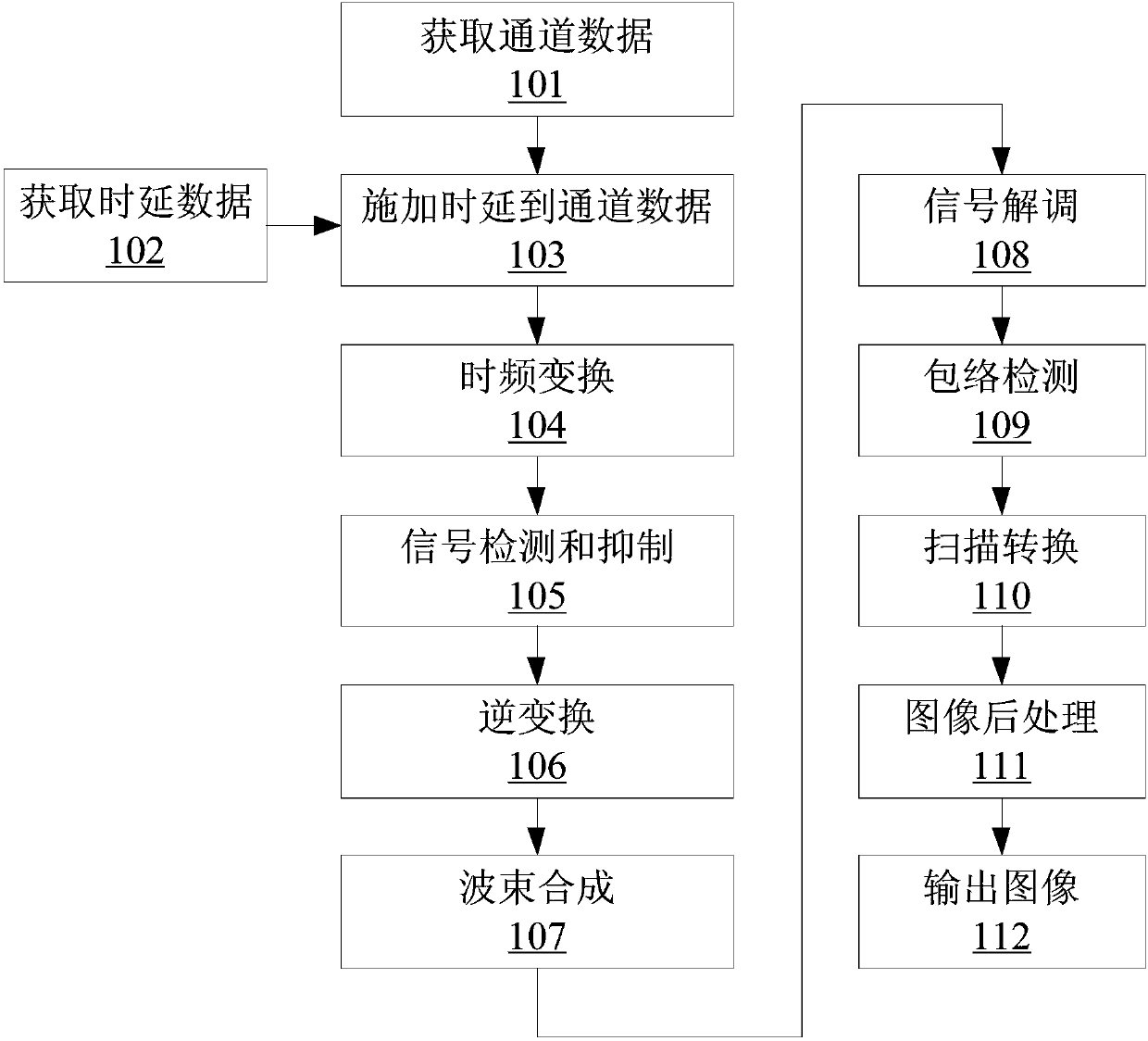
The invention discloses a self-adaption ultrasonic beamforming method and system based on channel data. Unwished sidelobes can be removed, noise generated by the channel data can be stored, and the removing efficiency is high. The method comprises the steps of conducting multiple times of ultrasonic emission, and obtaining first channel data according to corresponding multiple echo signals; obtaining time delay data corresponding to each focus point; regarding each focus point, applying the corresponding time delay to the first channel data to obtain vector data; conducting discrete time-frequency transformation on one or multiple vectors in the vector data to generate frequency domain signals; conducting inverse transformation on each vector in the frequency domain signals which are subjected to noise suppression to obtain second channel data; conducting beamforming on the obtained second channel data; conducting signal demodulation, envelope detection, scanning conversion and image postprocessing on signals which are subjected to beamforming in sequence to generate a frame of image.
Owner:SASET CHENGDU TECH LTD
Method of transmitting reference signal and transmitter using the same
ActiveUS20100195481A1Lower ratioHigh propertyModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource block
A method and apparatus of transmitting a reference signal in a wireless communication system is provided. A reference signal sequence is generated by using a pseudo-random sequence. A portion or entirety of the reference signal sequence is mapped to at least one resource block and is transmitted. The pseudo-random sequence is generated by a gold sequence generator which is initialized with initial values obtained by using cell identifier. The reference signal provides low PAPR and high cross correlation characteristic.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Radar device
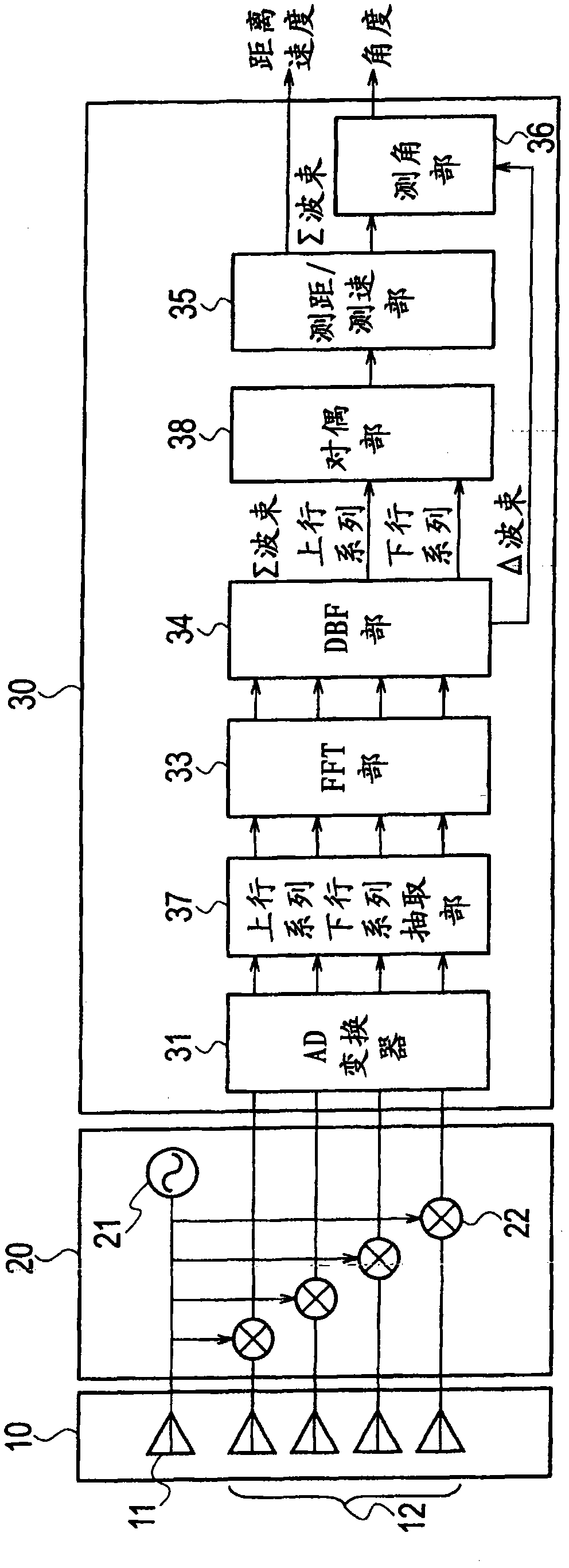
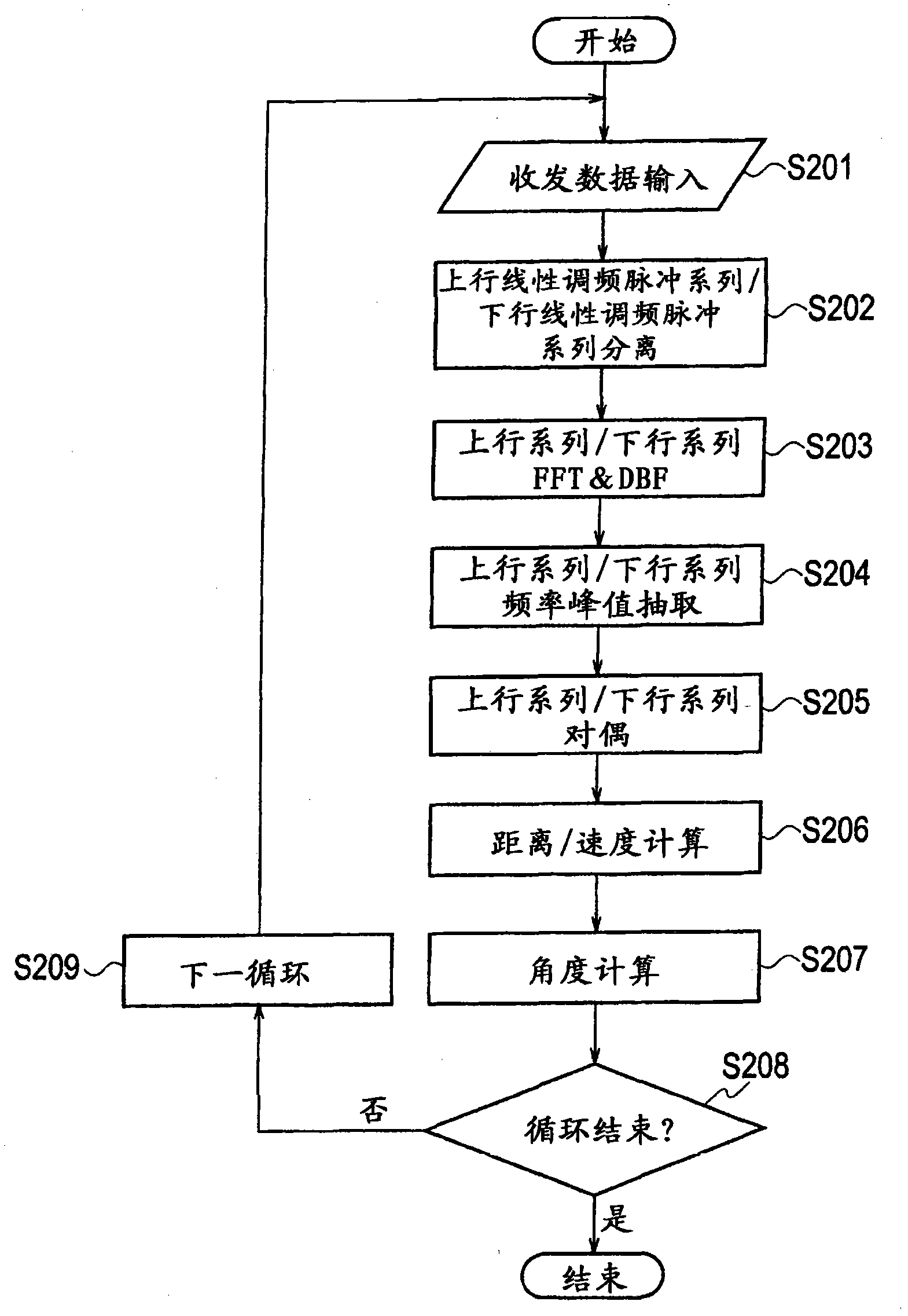
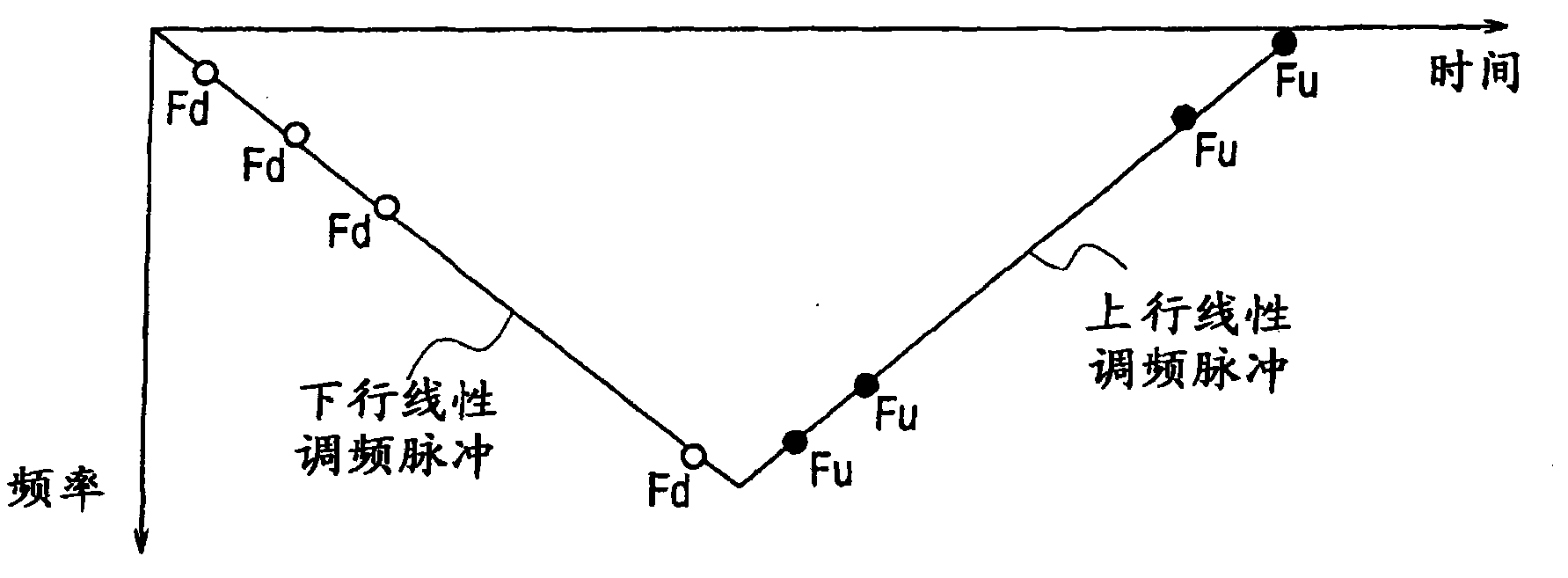
InactiveCN101971050AImprove signal detection performanceReduce mistakesMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverRadar
Provided is a device equipped with a transceiver (20) whereby sweep signals subjected to FMCW modulation is transmitted at least twice, an FFT unit (32) whereby at least two rounds of sweep signals received in response to transmission from the transceiver are subjected to fast Fourier transforms, and an MRAV processing unit (35a) whereby beat frequencies corresponding to each of the at least two rounds of sweeps by the transceiver are calculated on the basis of at least two rounds of sweep signals obtained by performing Fourier transforms in the FFT unit, whereby velocities are calculated on the basis of beat frequency differences and time differences that are calculated, and whereby distances are calculated on the basis of velocities and beat frequencies that are calculated, thereby making calculations of distances and velocities of a plurality of targets.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Signal detection method suitable for large-scale MIMO system
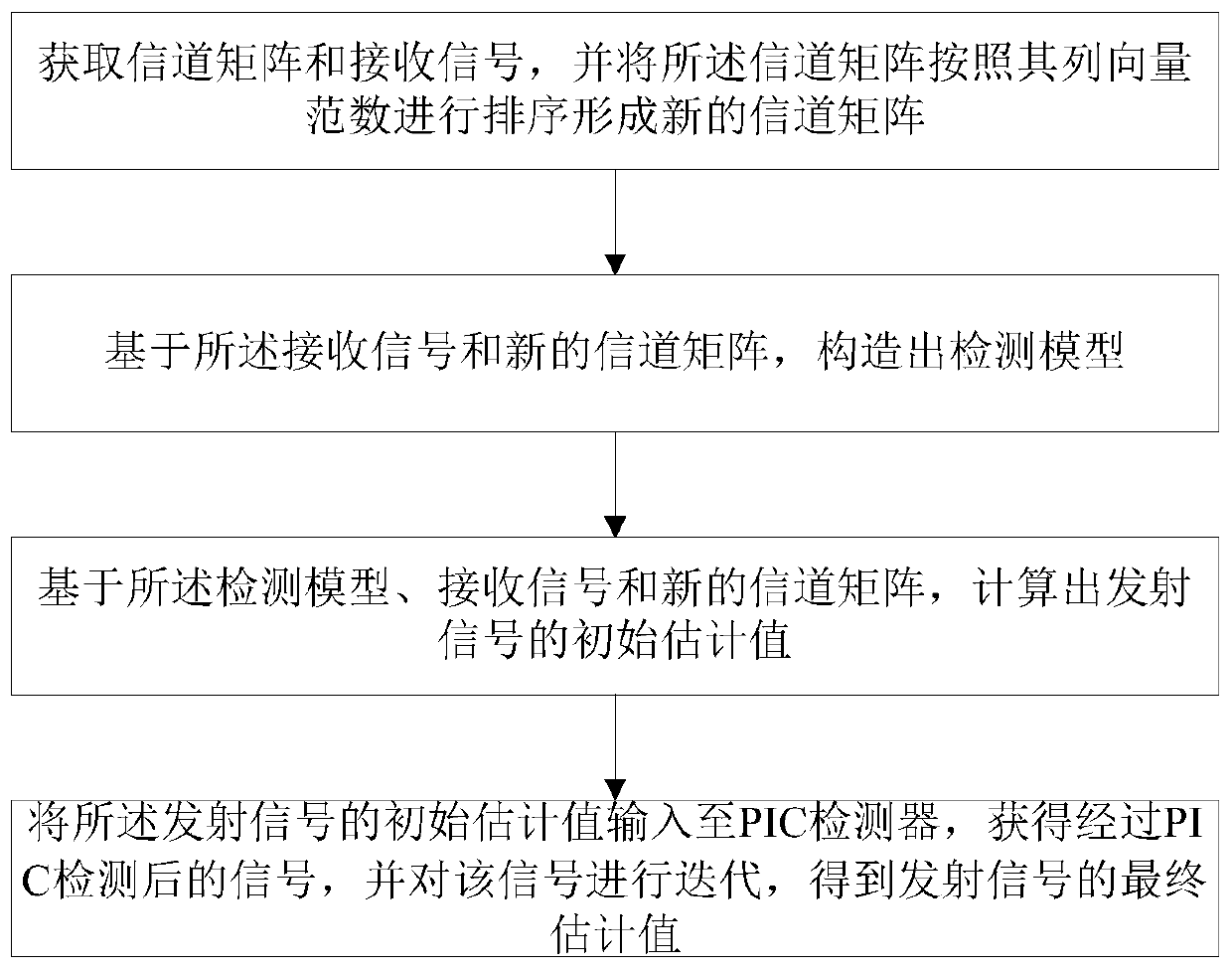
ActiveCN109951214AImprove signal detection performanceReduce bit error rateSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringAlgorithmColumn vector
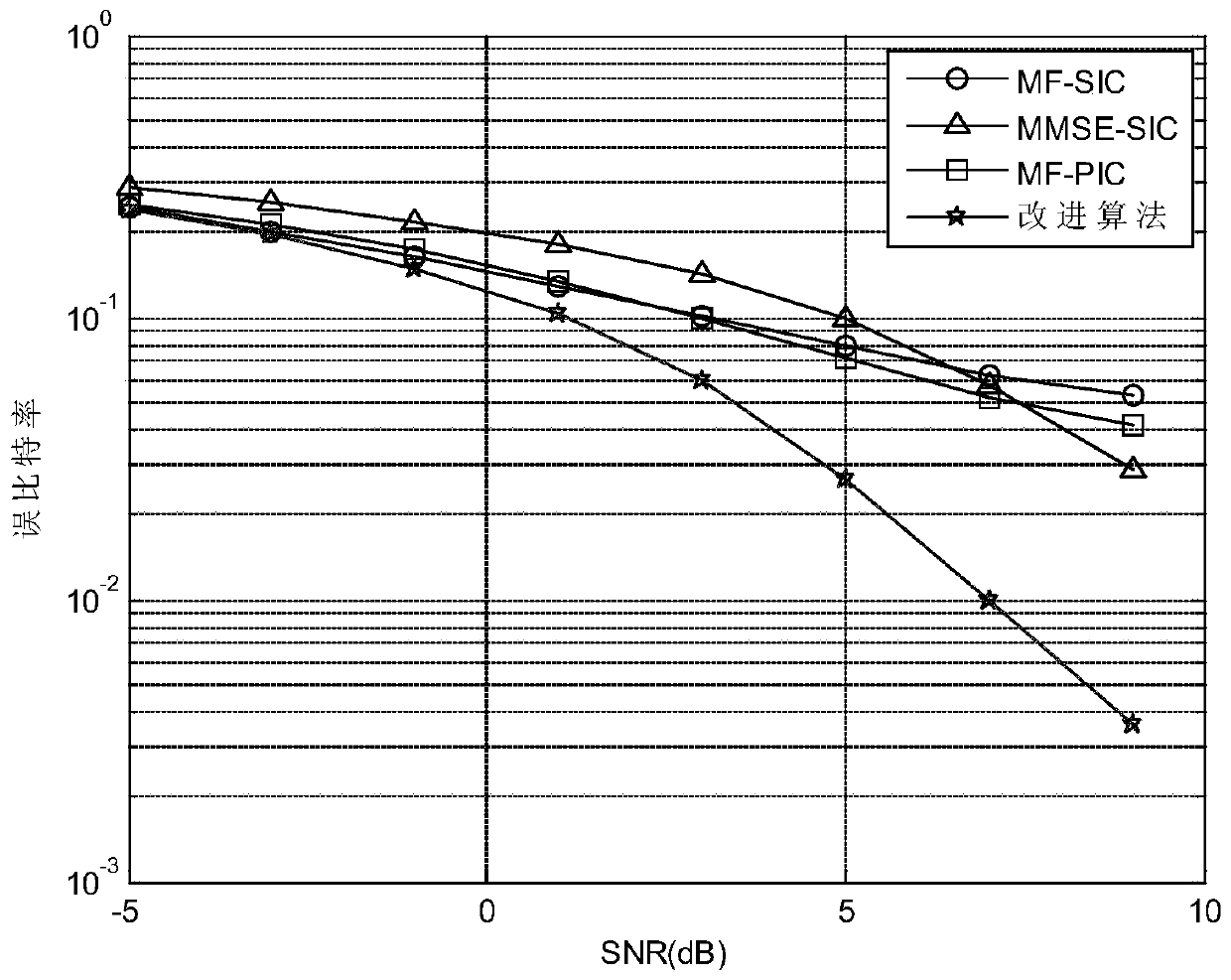
The invention discloses a signal detection method suitable for a large-scale MIMO system, and the method comprises the steps: S1, obtaining a channel matrix and a received signal, and carrying out thesorting of the channel matrix according to the column vector norm, so as to form a new channel matrix; S2, constructing a detection model based on the received signal and a new channel matrix; S3, onthe basis of the detection model, the received signal and the new channel matrix, calculating an initial estimation value of the transmitted signal; and S4, inputting the initial estimation value ofthe transmitted signal into a PIC detector to obtain a signal subjected to PIC detection, and performing iteration on the signal to obtain a final estimation value of the transmitted signal. The complexity of the algorithm can be effectively reduced, and the bit error rate is obviously lower than that of a traditional nonlinear signal detection algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Signal interference filtering method and related device
ActiveCN103997473AImprove signal detection performanceEasy to operateTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCholesky decompositionLookup table
The embodiment of the invention discloses a signal interference filtering method and a related device. The device comprises a searching module, a correcting module and a filtering module. The searching module is used for carrying out parameter estimation in a selected area in the time-frequency domain to obtain estimation parameters, and the estimation parameter serve as an index for searching for compensation factors from a preset compensation factor lookup table, wherein the compensation factor lookup table comprises the various preset estimation parameters and the corresponding compensation factors. The correcting module is used for calculating an autocorrelation matrix corresponding to interference data in the selected area, and correcting the diagonal element of the autocorrelation matrix on the basis of the compensation factors. The filtering module is used for carrying out Cholesky decomposition on the corrected autocorrelation matrix to obtain a whitening matrix, and carrying out interference filtering on received signals in the selected area through the whitening matrix. By adopting the signal interference filtering method and the related device, interference on the signals in the selected area is effectively eliminated, the signal detection performance is improved, and operation is simple.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method
InactiveCN104878102AEasy to operateSlow down the speed of color developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementYolkPlant Germ Cells
The invention relates to a positioning and marking method for embryonic-period primordial germ cells (PGCs), in particular to a bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method. The bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method includes the steps of fixing collected various periods of embryo samples of the bastard halibuts by a 4% PFA solution; using a PBS (phosphate buffer saline) solution with 50% of deionized formamide to preserve the embryo samples at the temperature of -20 DEG C, and subjecting the fixed and preserved embryo samples to oolemma removing, gradient methanol dewatering and rewatering; after rewatering, washing the various periods of embryo samples with PBS buffering liquid without RNA ( ribonucleic acid) enzyme, pre-hybridizing at the temperature of 62-65 DEG C for 2-4 hours; after hybridization, adding a hybridization solution with bastard halibut RNA probes into the various periods of embryo samples subjected to pre-hybridization for hybridizing overnight at the temperature of 62-65 DEG C; after hybridization, subjecting the various periods of embryo samples to washing, antibody incubation and rewashing, keeping away from light, and developing colors to achieve marking for tracking and positioning of the embryonic-period primordial germ cells of the bastard halibuts. The bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method has the advantages that the problems that yolks and oolemma of the samples hybridized in situ conventionally are difficult to strip and a background color is too deep after color developing detection are solved, and operation steps are simplified.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
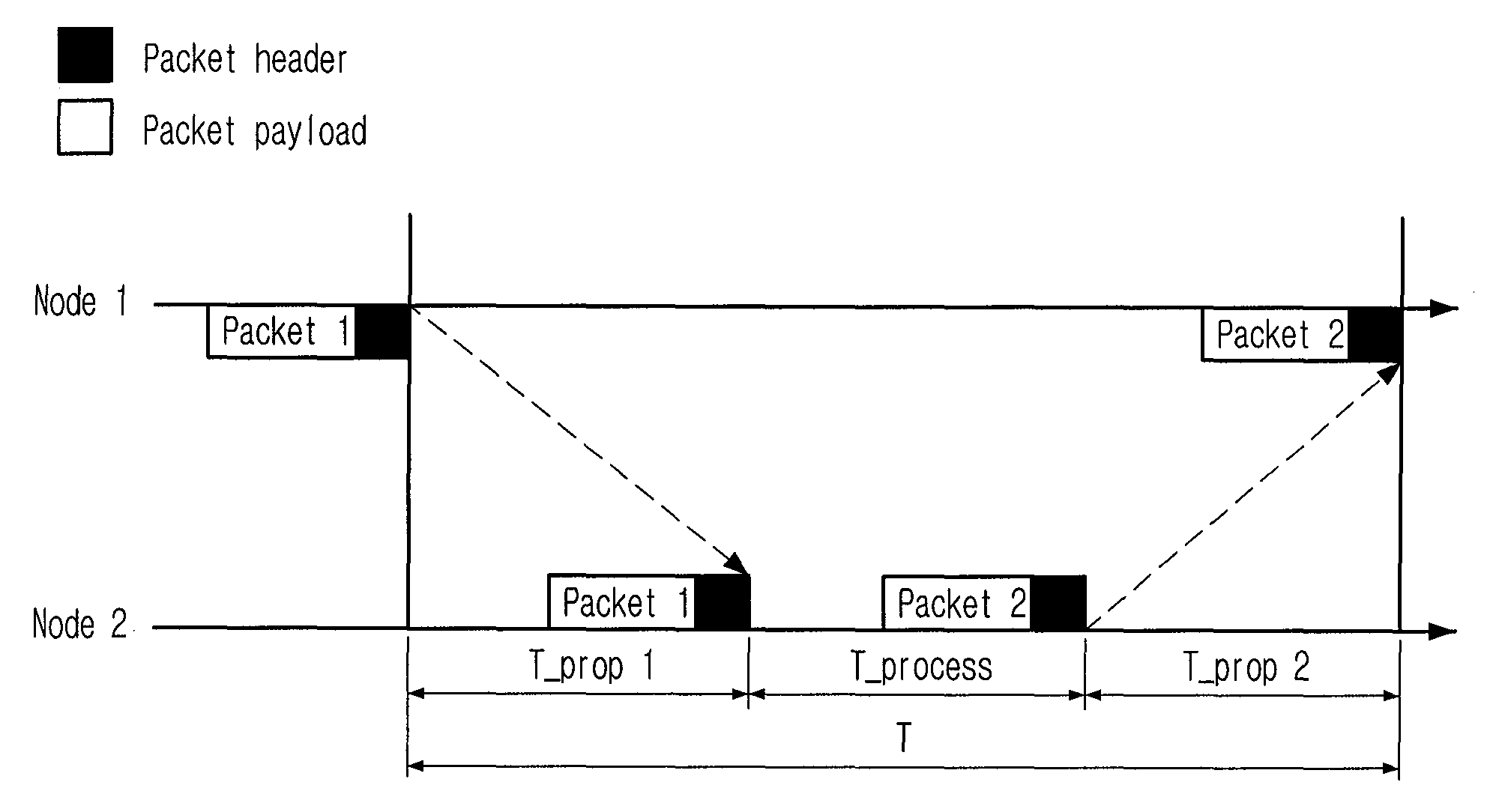
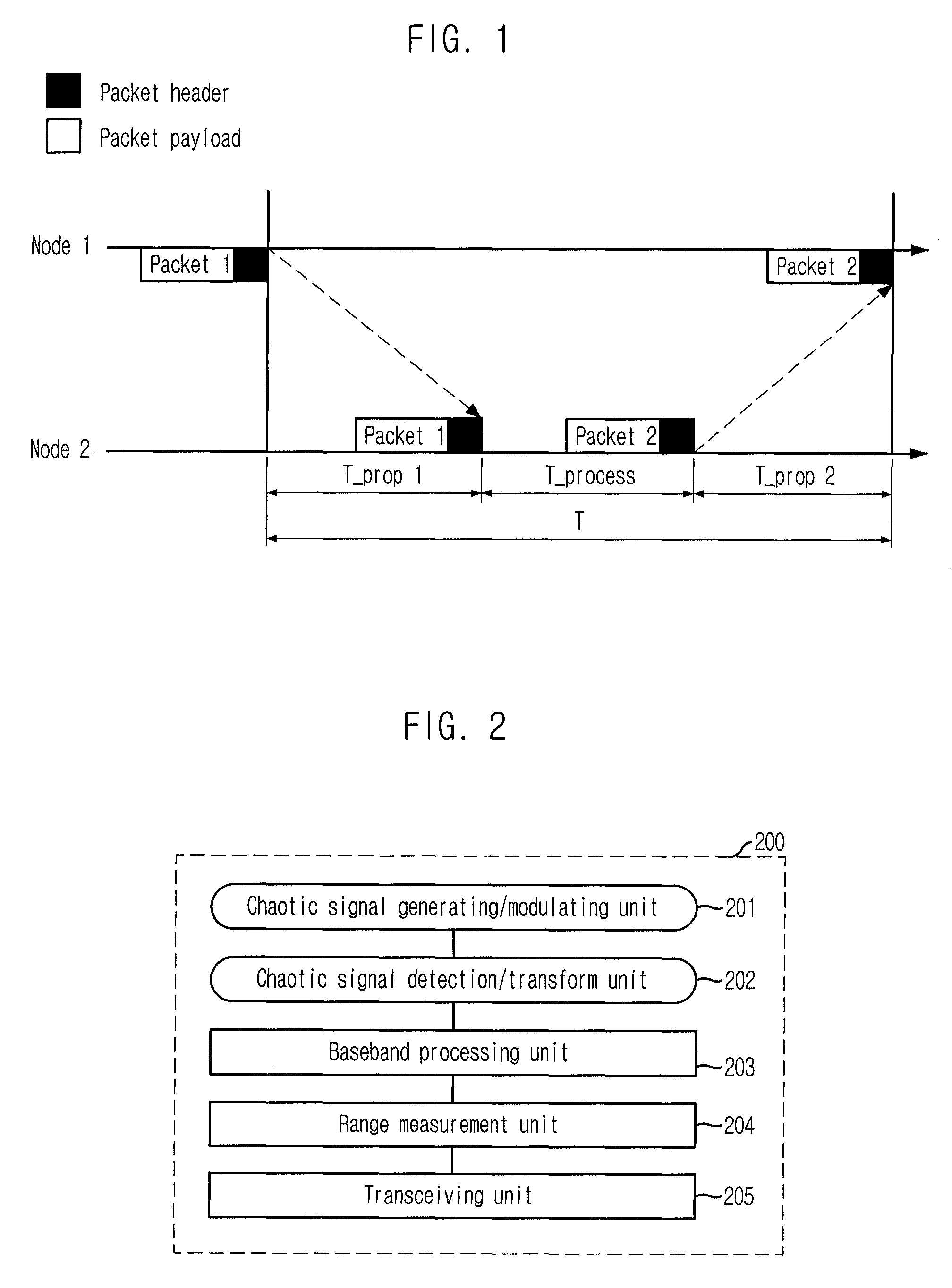
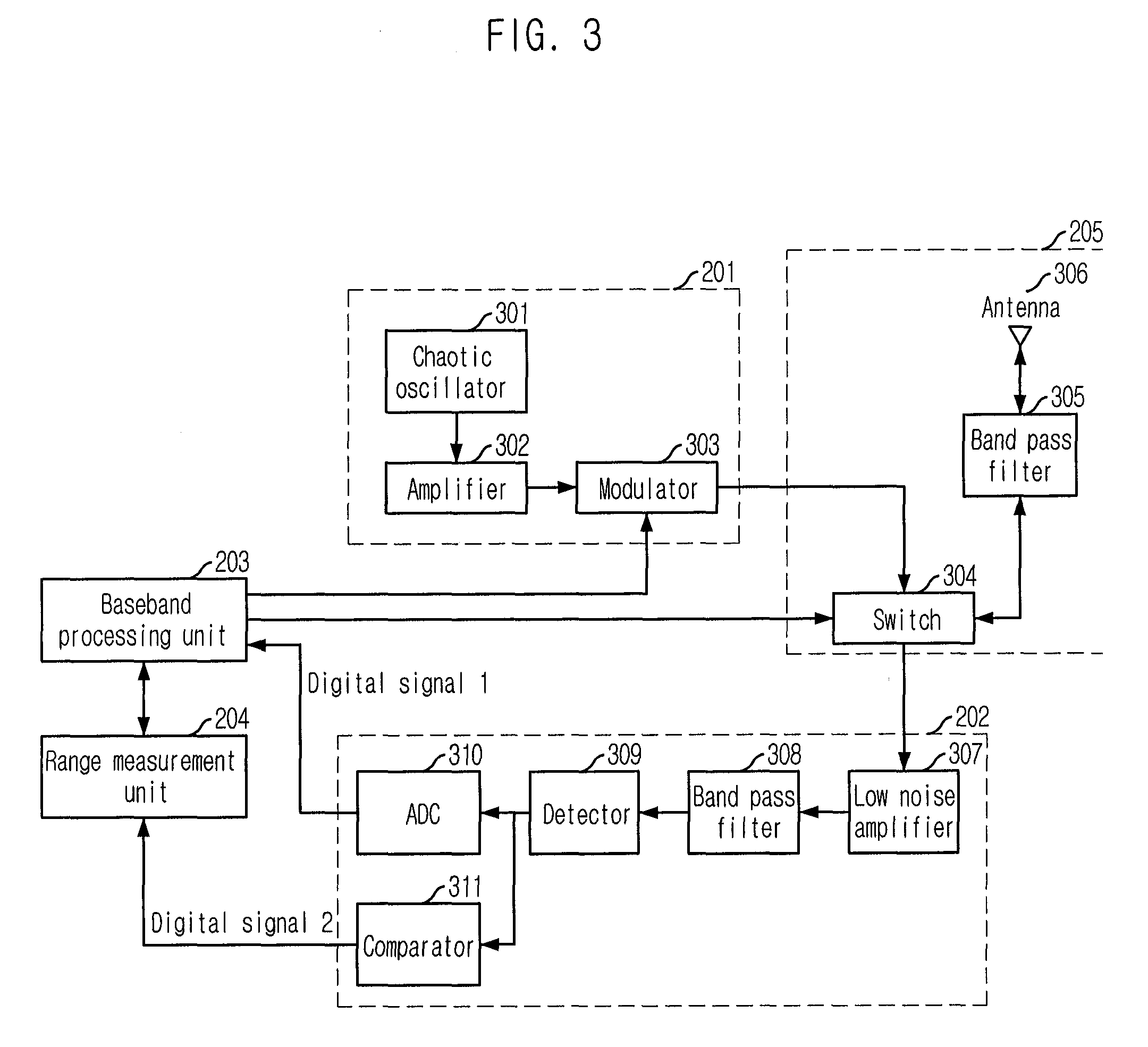
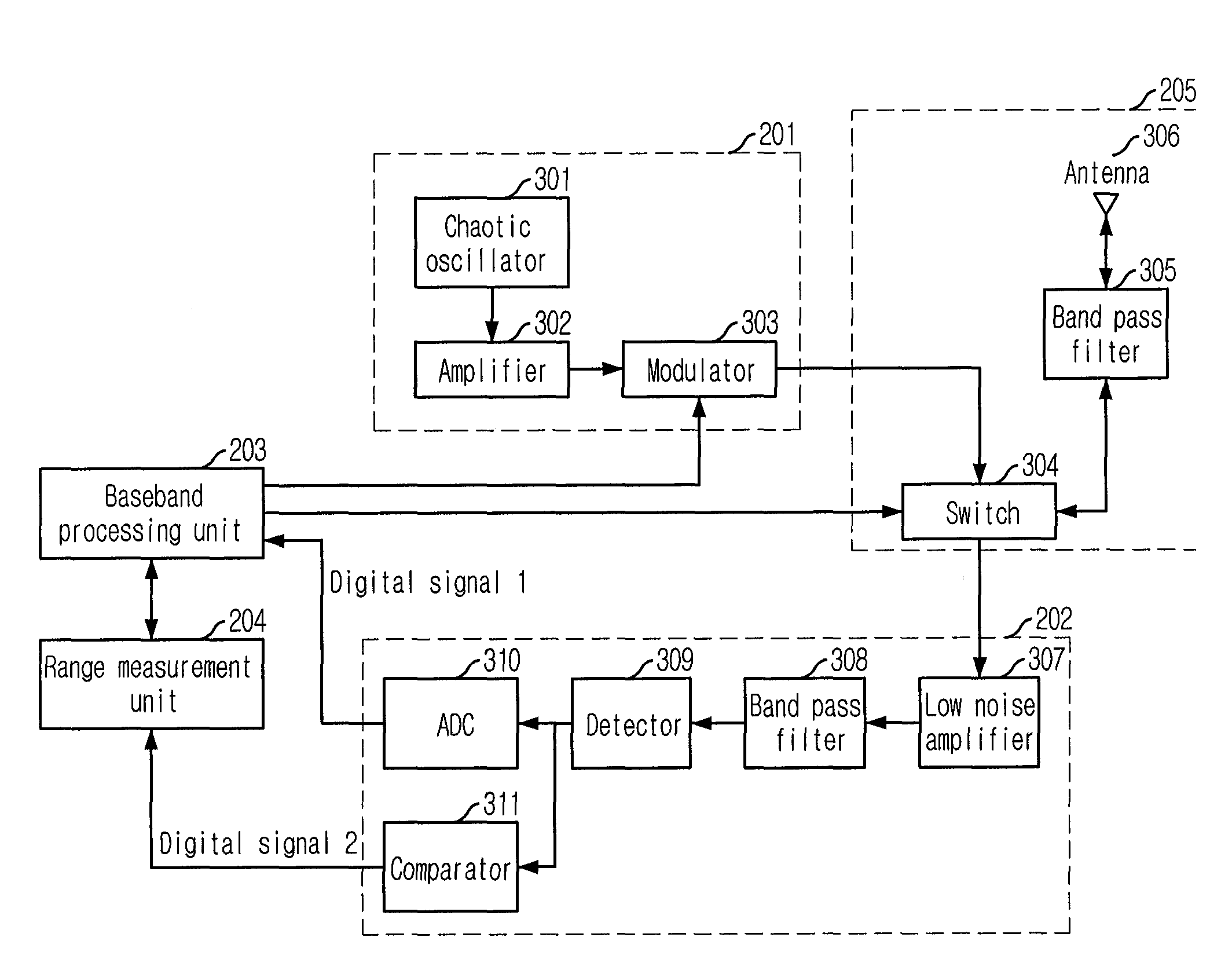
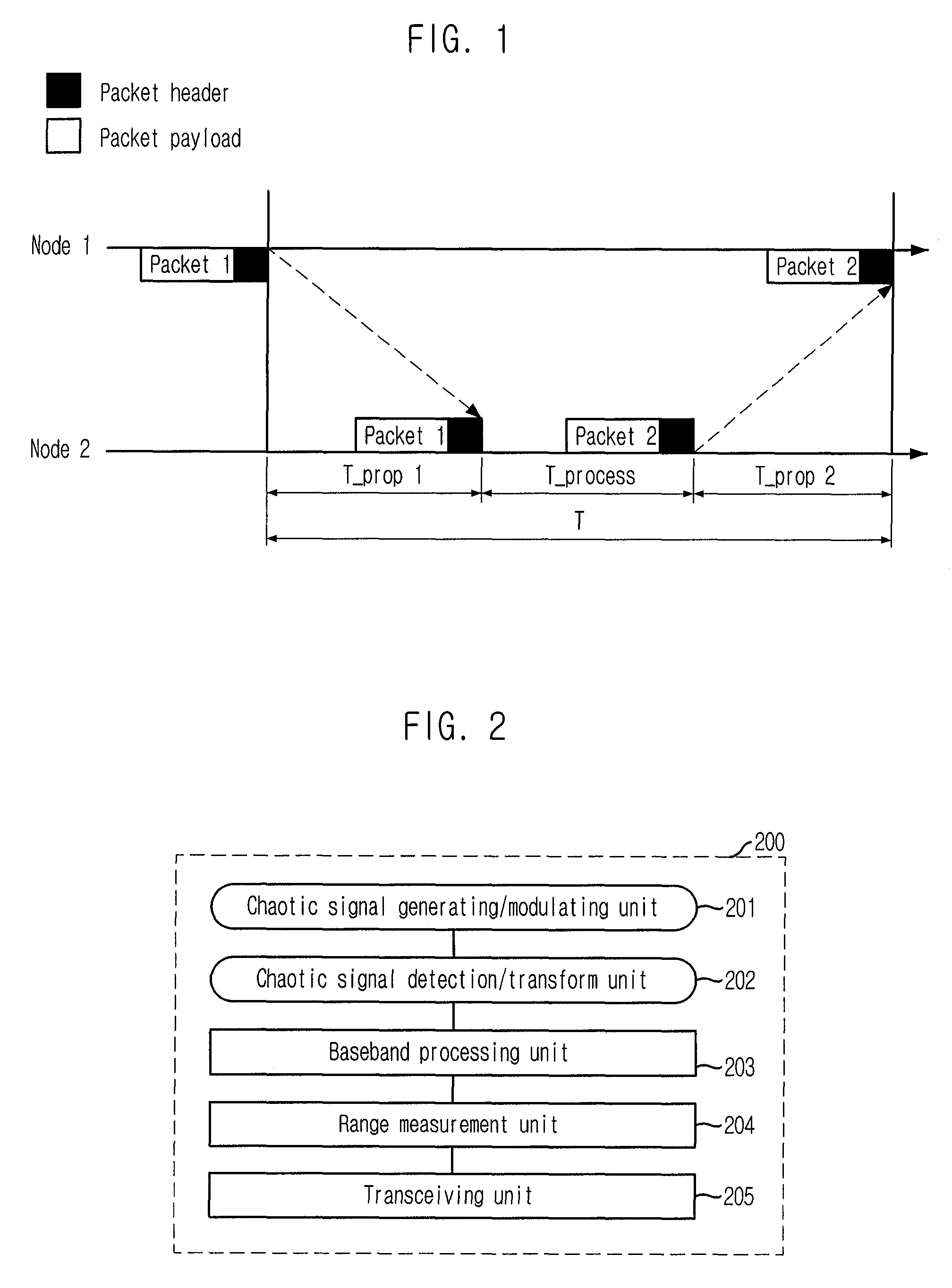
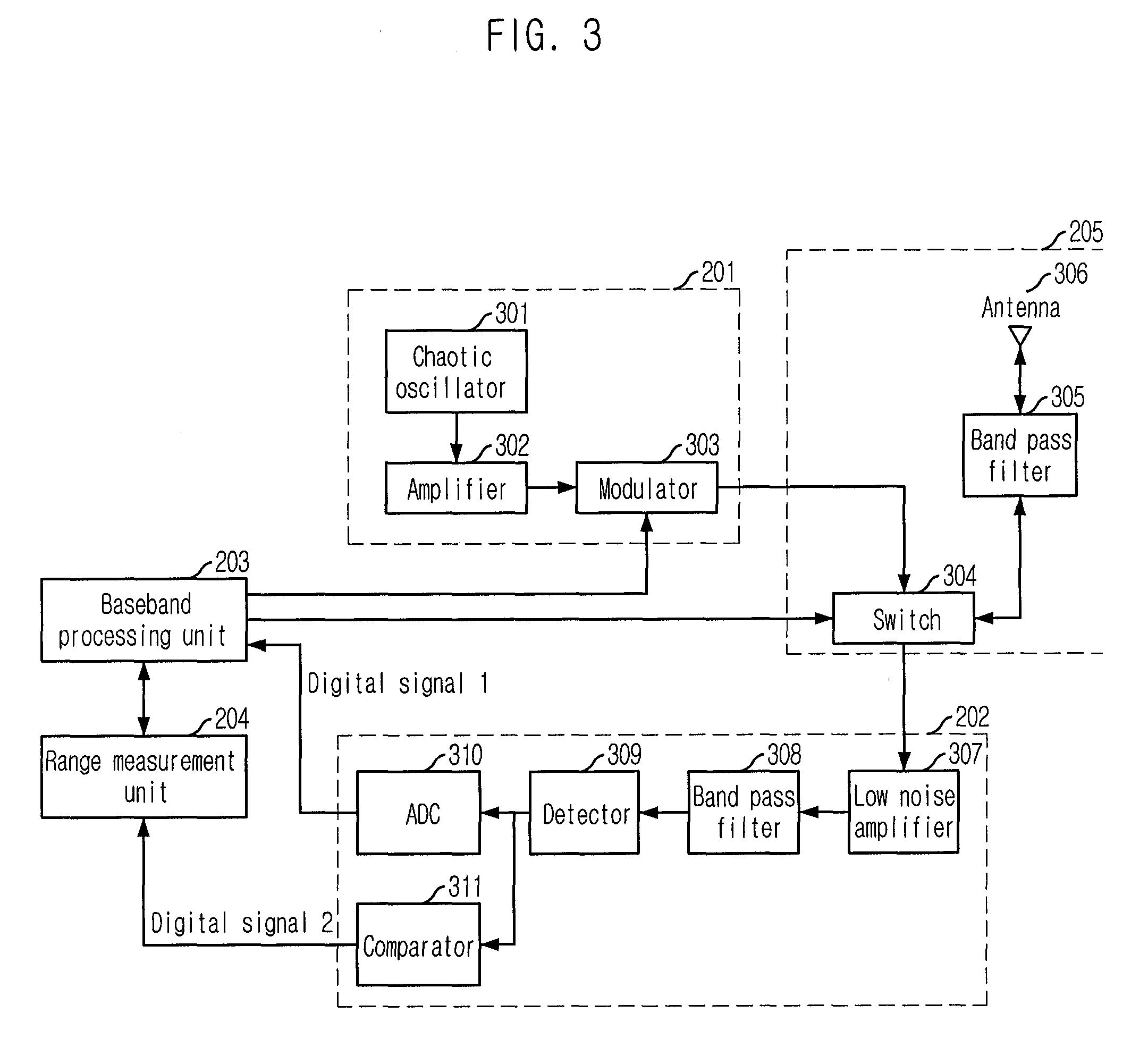
Range Measurement Apparatus and Method Using Chaotic Uwb Wireless Communication
InactiveUS20080226072A1Easy to controlImprove signal detection performanceModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationUltra-widebandLeading edge
Provided is a range measurement apparatus and method based on chaotic ultra wideband (UWB) wireless communication. The apparatus includes a chaotic signal generating / modulating unit for generating / modulating chaotic signals and outputting them to a transceiving unit; a transceiver for transceiving radio signals; a detector for detecting the radio signals in forms of voltage signals; a transformer for sampling the analog voltage signals and outputting first digital signals of a predetermined level; a comparator for comparing levels of the analog voltage signals with a threshold value and outputting second digital signals; and a range measurement unit for calculating a leading edge, which is a moment when initial data of a packet payload arrive, by using the binary signals from transformation of the first digital signals based on the threshold and the second digital signals, and performing range measurement based on the leading edge. This research is applied to chaotic UWB wireless communication.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
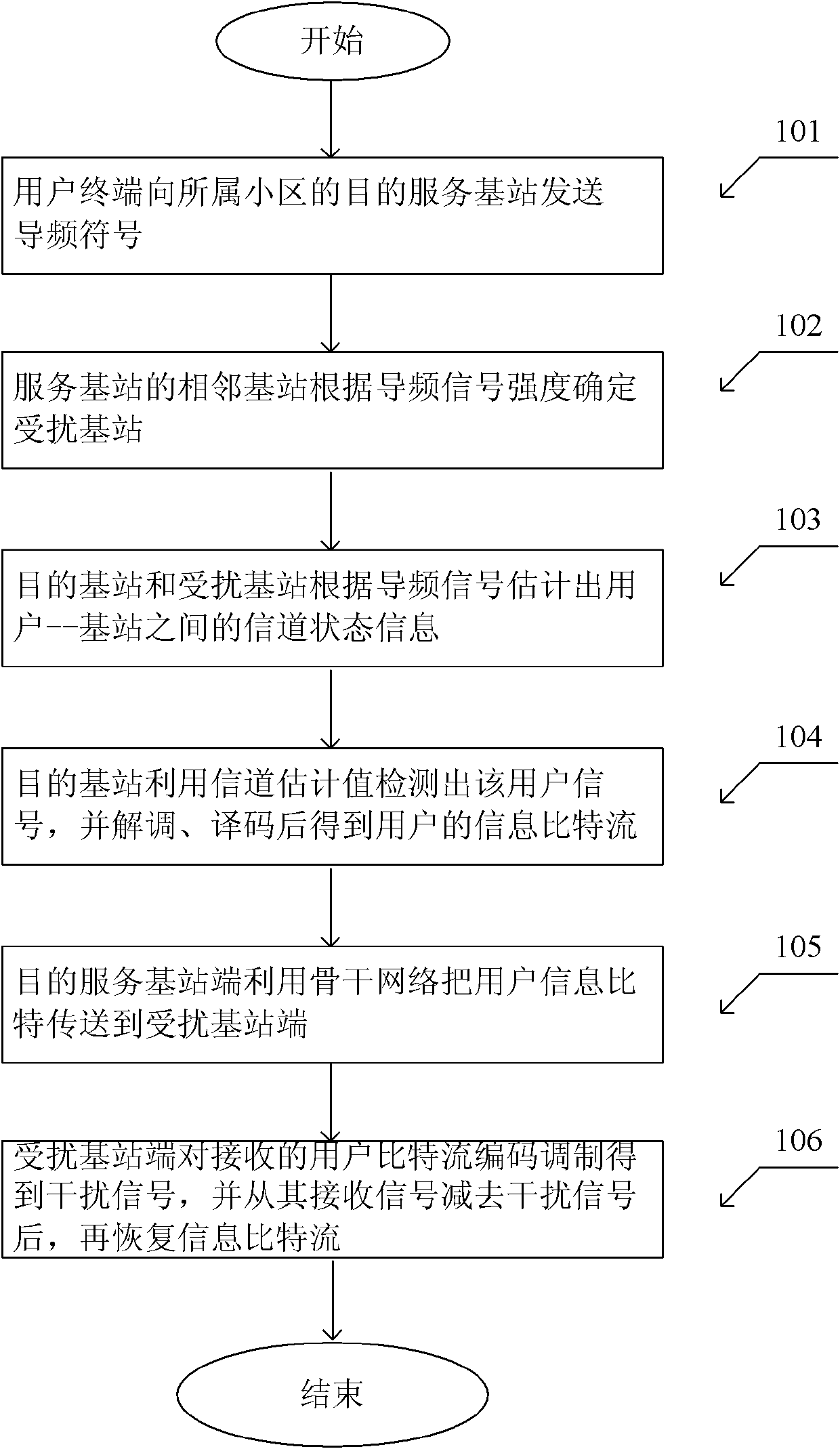
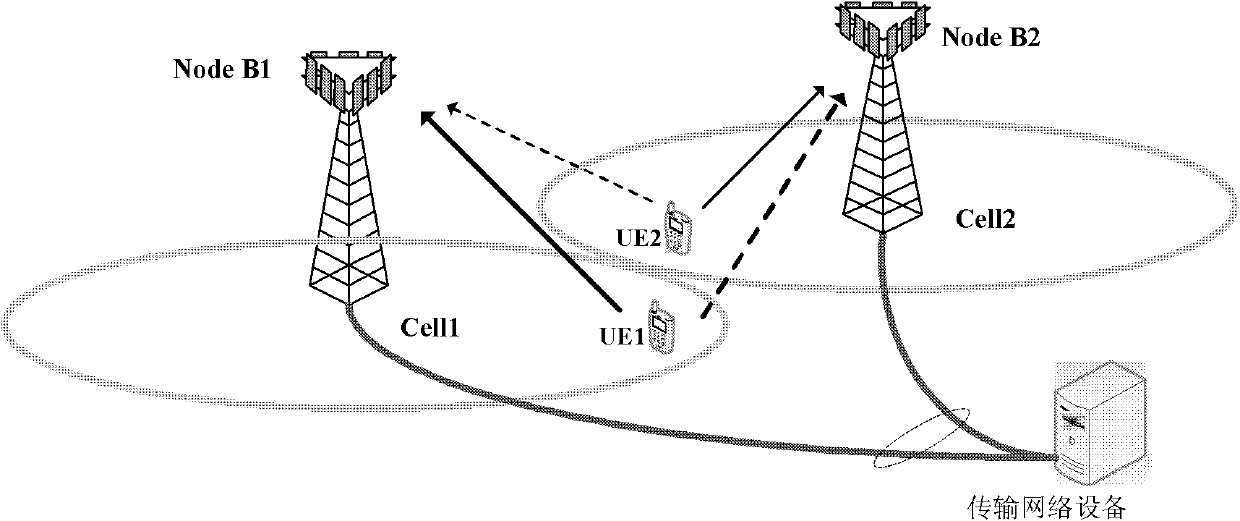
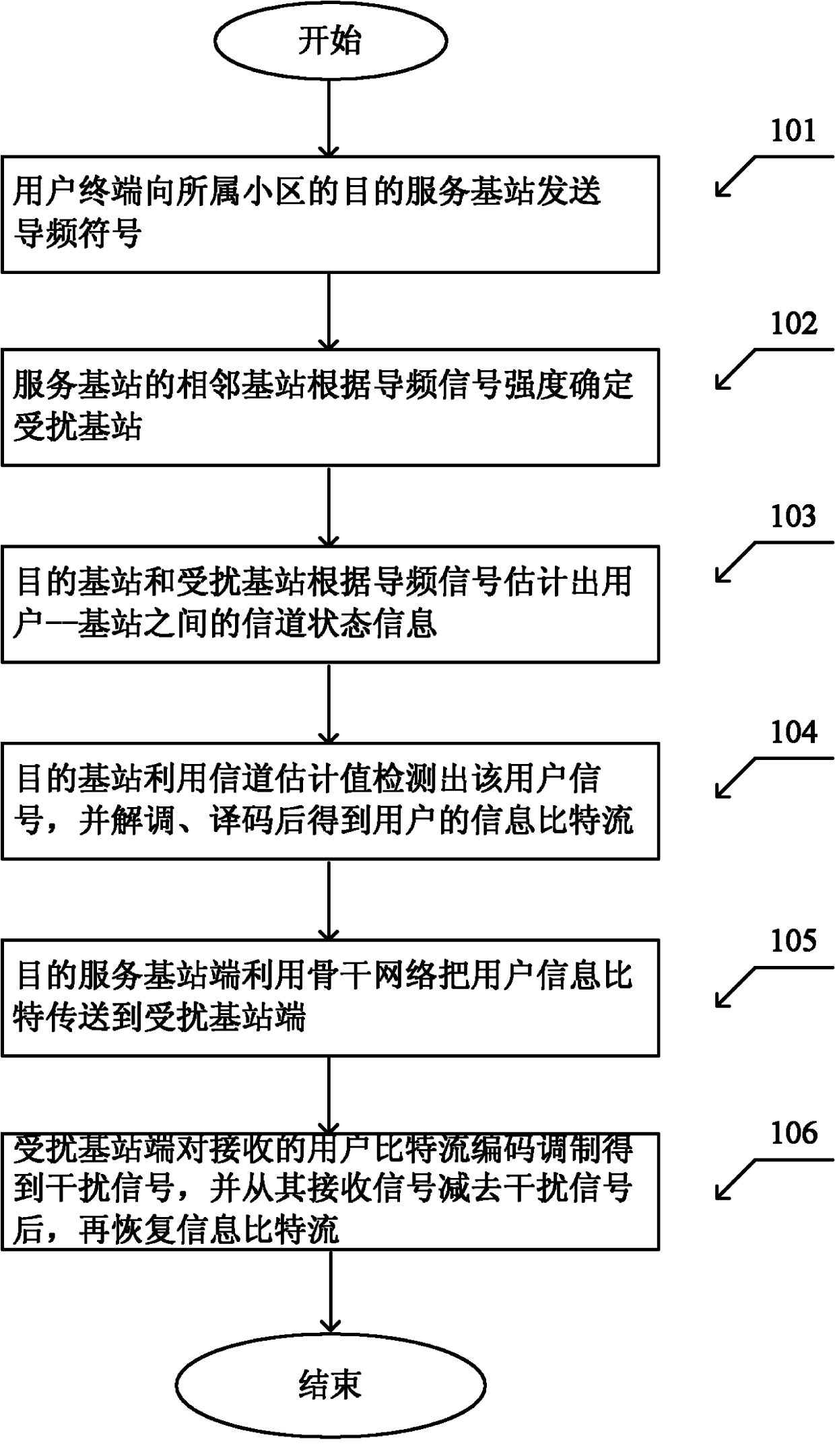
Interference elimination method of multi-cell base station cooperation
InactiveCN102170304AImprove signal detection performanceReduced transfer rate requirementsSpatial transmit diversityError preventionSystem capacityInterference elimination
The invention provides an interference elimination method of multi-cell base station cooperation, belonging to the wireless information transmission field. When a user terminal located in the edge of the cell communicates with the target service base station thereof, the terminal causes interference to the base stations of the adjacent cells. In the invention, the service base station terminal is used to detect the user signal, and transmit the information bit to the interfered base station after demodulation and coding; and at the interfered base station terminal, the interference is rebuilt in accordance with the received user information bit flow, and is deleted from the received signal, after that, the information is recovered. Compared to the general base station cooperation method, by the interference elimination method of the invention, the transmission rate requirement between the cooperative base stations is reduced, and the system capacity is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
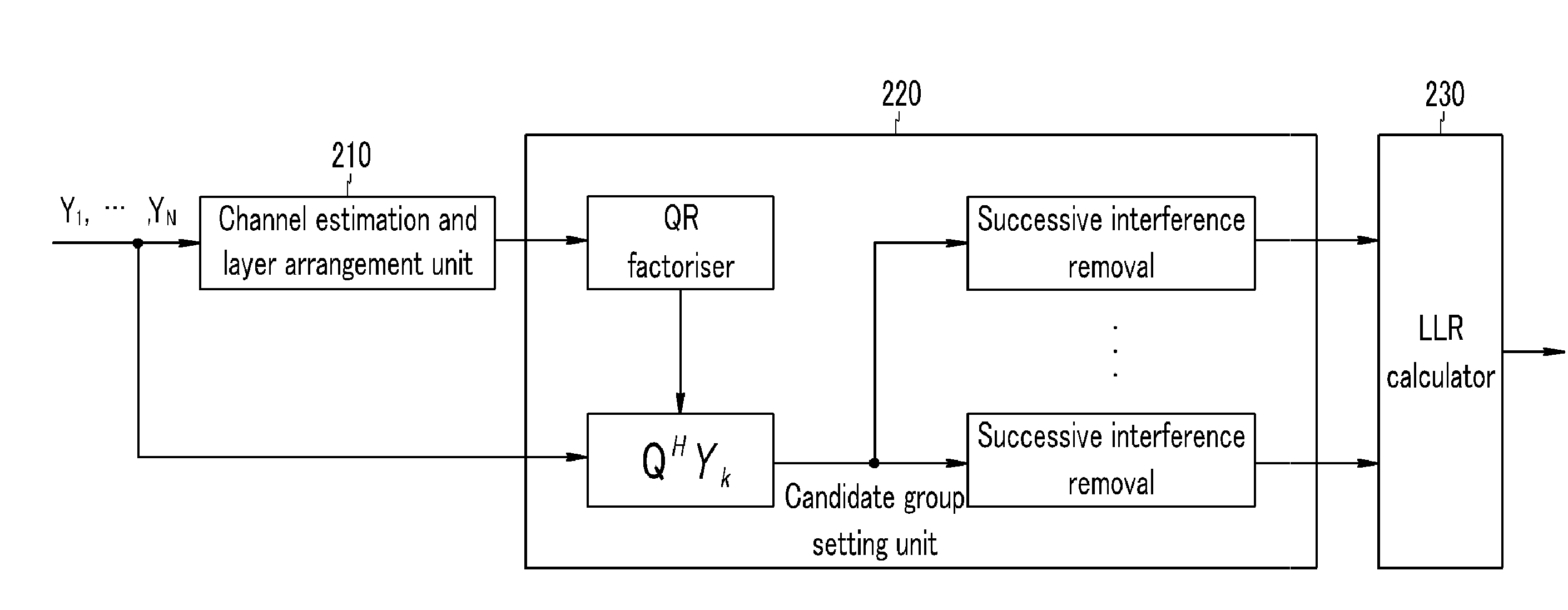
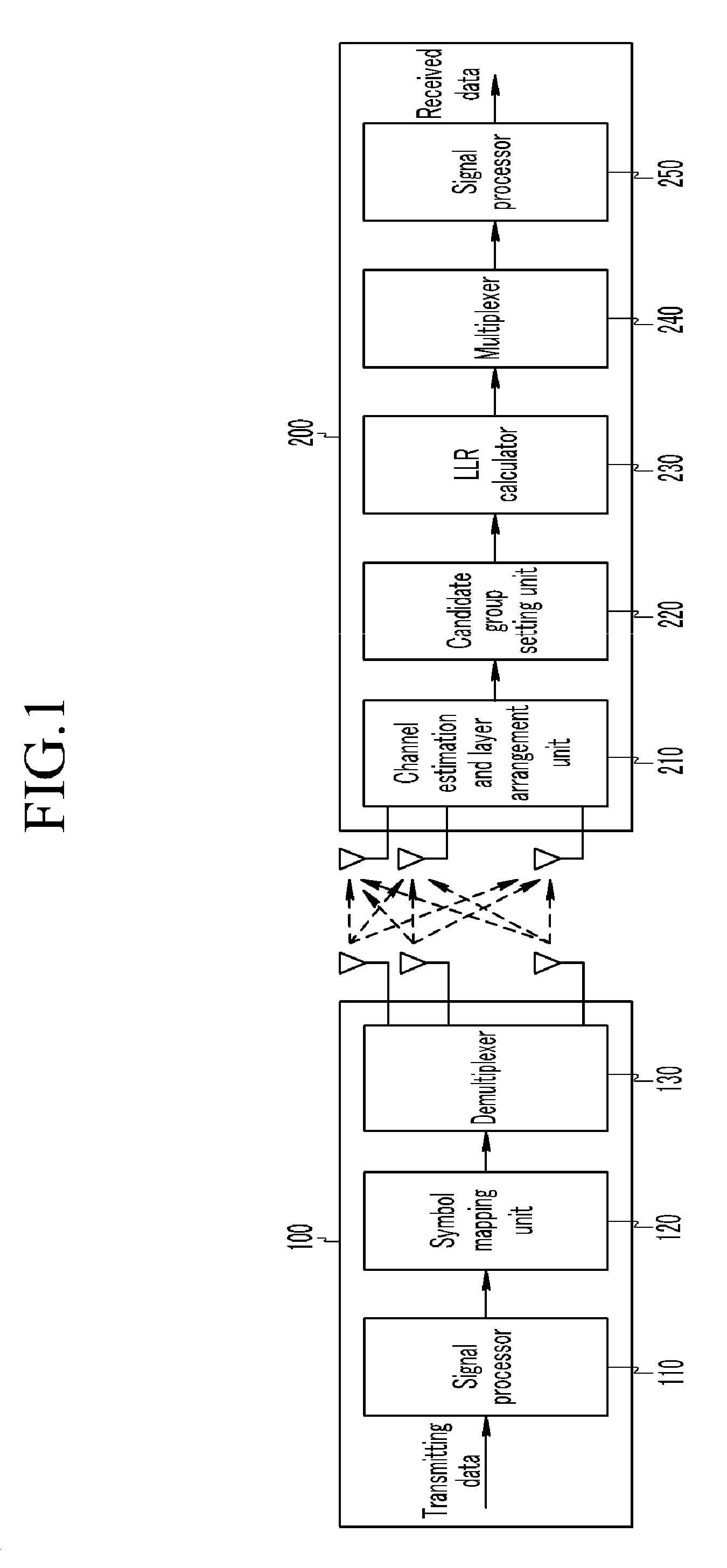
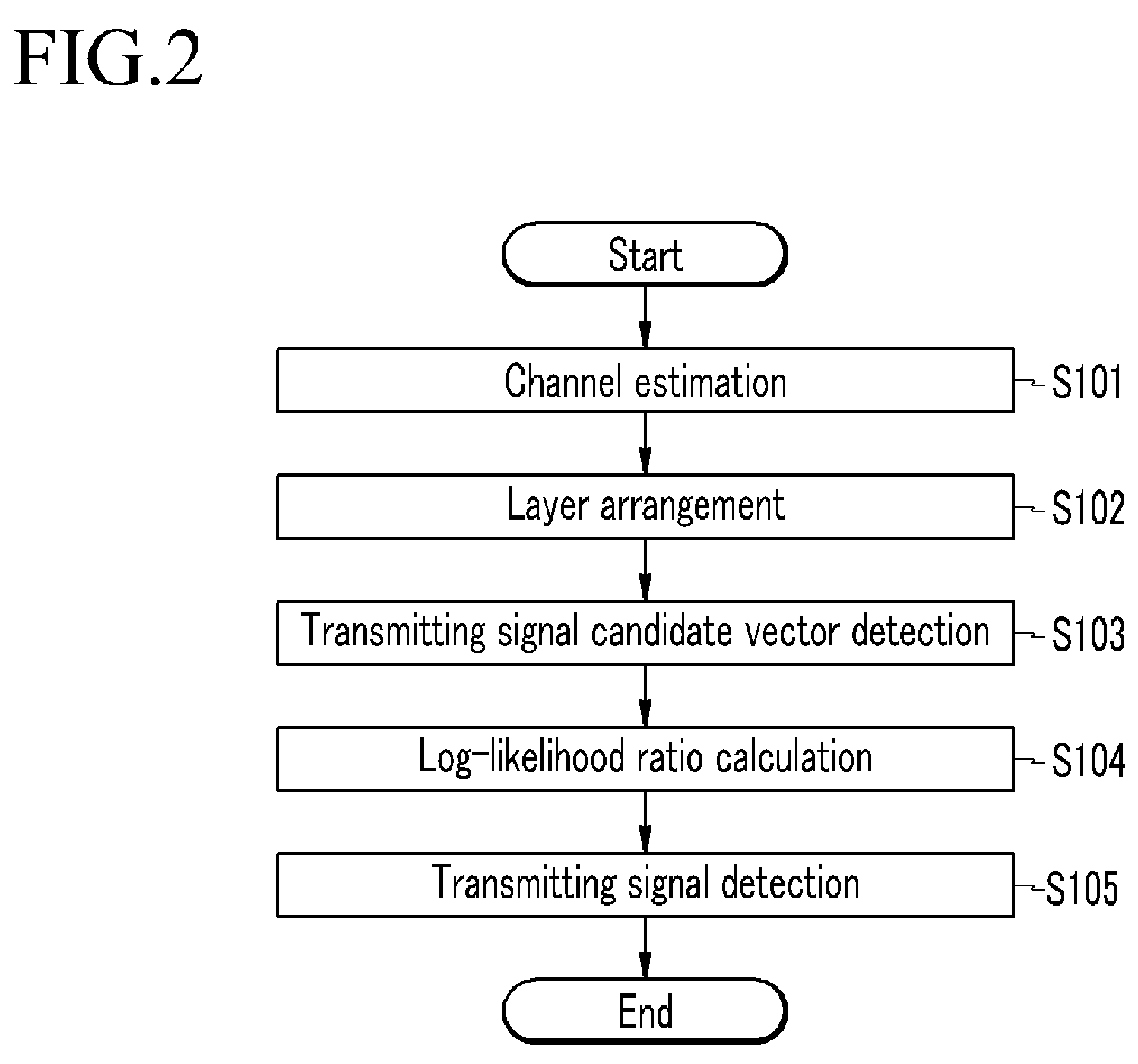
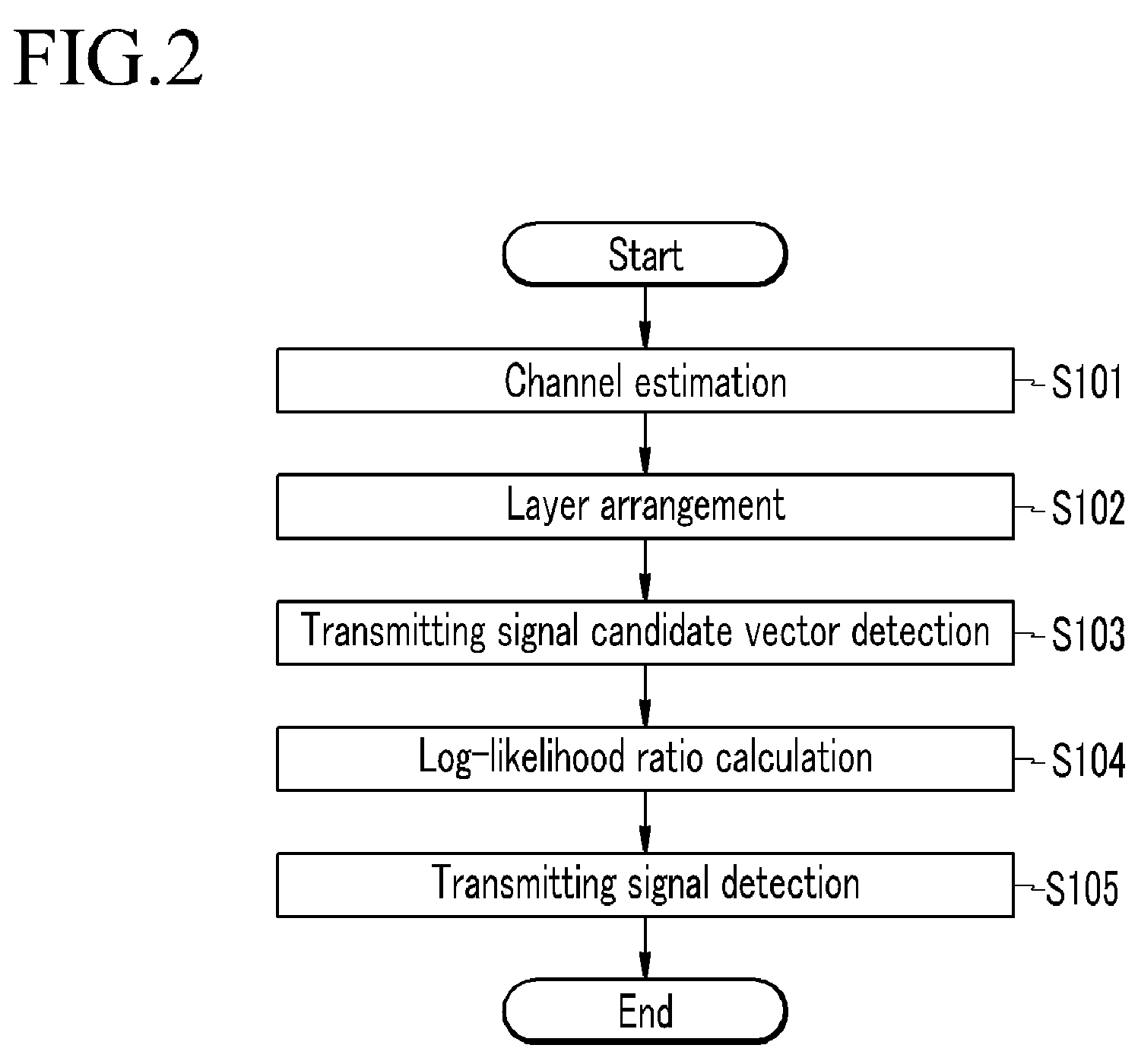
Log likelihood ratio calculation method, transmit signal detection method, and receiver
ActiveUS20090052593A1Reduce complexityImproved transmitting signal detection performanceOther decoding techniquesAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLogitDependability
The present invention relates to a log-likelihood ratio calculation method, a transmitting signal detection method, and a receiver. The present invention estimates a channel on the basis of the received signal and rearranges a plurality of layers. Further, at the time of rearrangement of the layers, a symbol of a layer having the lowest reliability is considered for every constellation dot, and the successive interference for the remaining layers is removed corresponding to the constellation dots of the layer having the lowest reliability to set the transmitting symbol candidate vector. Furthermore, a log-likelihood ratio for every bit of the plurality of layers is calculated using the transmitting symbol candidate vector to decode the channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
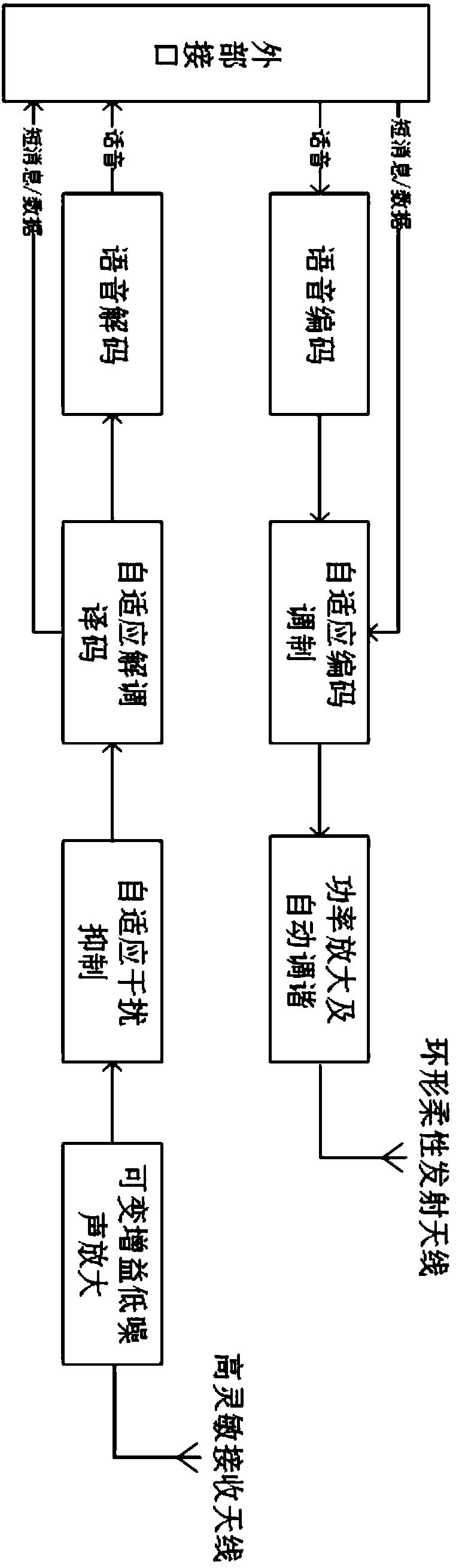
Wireless transmission subsystem for VLF through-the-earth communication
ActiveCN108564959AImprove stabilityHigh energySpatial transmit diversitySpeech analysisLow noiseWireless transmission
The invention discloses a wireless transmission subsystem for VLF through-the-earth communication, comprising a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter first adaptively encodes and modulates speech codes and short messages or data to obtain a VLF modulated output signal, and sends the VLF modulated output signal to a flexible transmitting antenna for transmission after power amplification andautomatic tuning. The flexible transmitting antenna is configured to generate and transmit a VLF signal of a predetermined carrier frequency. In the receiver, a highly sensitive receiving antenna anda variable-gain low-noise amplifying unit form a weak signal detecting circuit to receive the VLF signal from the transmitter. The VLF signal is subjected to adaptive interference suppression processing, then is subjected to demodulation and channel error correction decoding, and finally is sent to an external interface through voice decoding and the like. In summary, the wireless transmission subsystem enhances the energy of weak signals, achieves normal communication requirements, improves the stability of through-the-earth communication, and provides a new way for mine disaster communication.
Owner:湖南正申科技有限公司
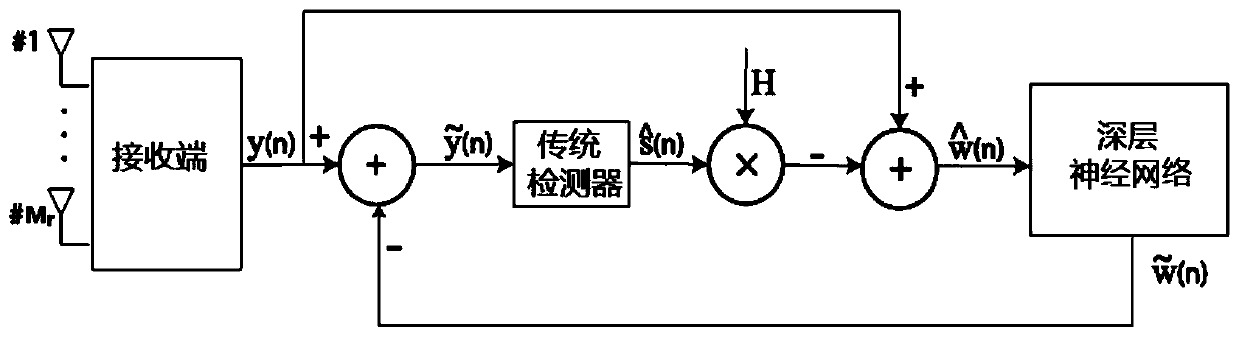
Time-varying OFDM system signal detection method based on deep learning
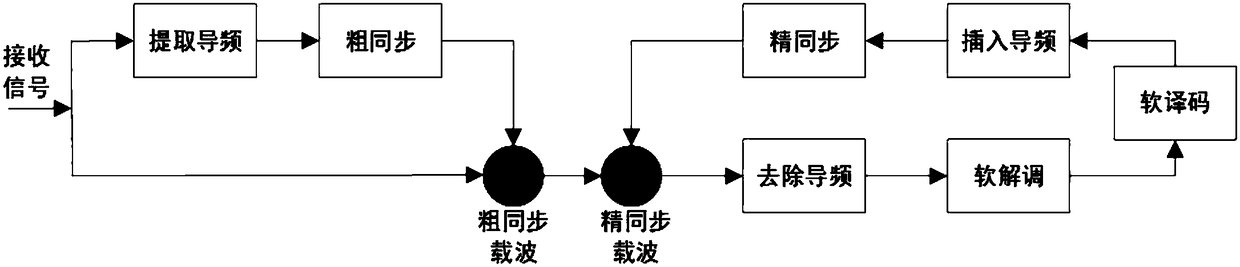
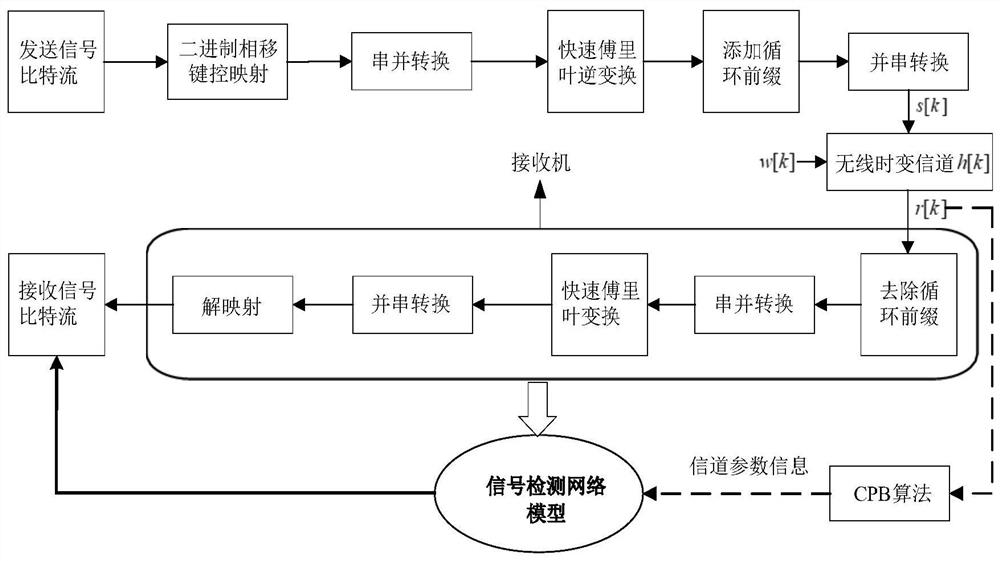
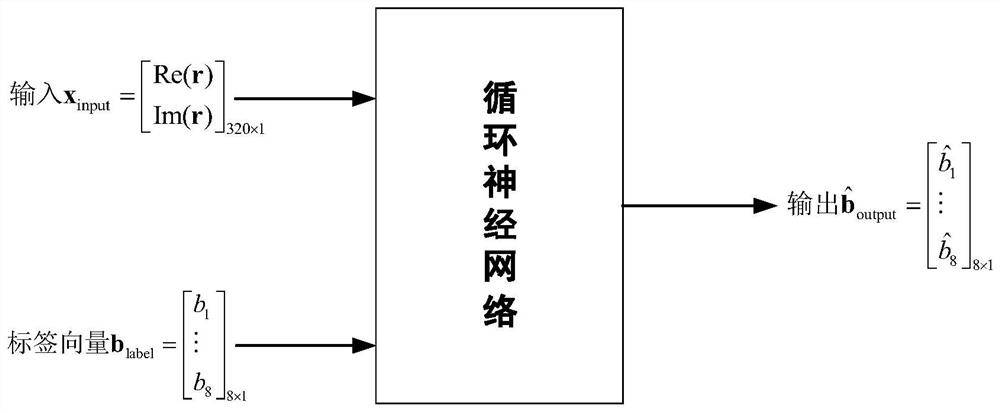
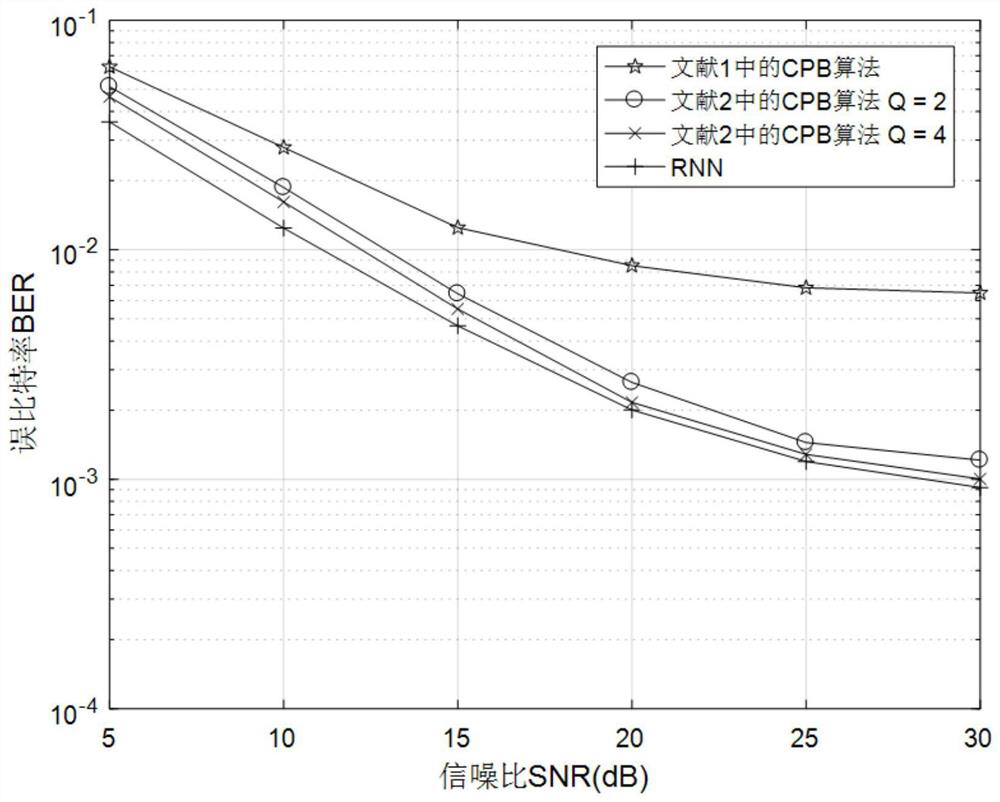
ActiveCN111669344ASimplify Receiver ArchitectureImproved signal detection performanceChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsNetwork modelReceiver
The invention provides a time-varying OFDM system signal detection method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a signal detection network model input data set; constructing a signal detection network model; presetting training and testing parameters before network training; and training the network by adopting a mode of generating training data and test data on line, feeding the test data into a signal detection network, generating predicted sending data bits by the signal detection network model according to a fed feature vector, and comparing the predicted sending data bits with real sending data bits to test the current performance of the network. The method is applied to a fast time-varying OFDM system. By combining a deep learning method andutilizing the advantages of a recurrent neural network in time sequence processing, the receiver architecture is simplified, the signal demodulation is successfully realized, the signal detection performance in the fast time-varying OFDM system is improved, the system realization complexity is effectively reduced, and the bit error rate performance of the whole system is also improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Ultra-short baseline positioning method and device based on three-dimensional array and electronic equipment
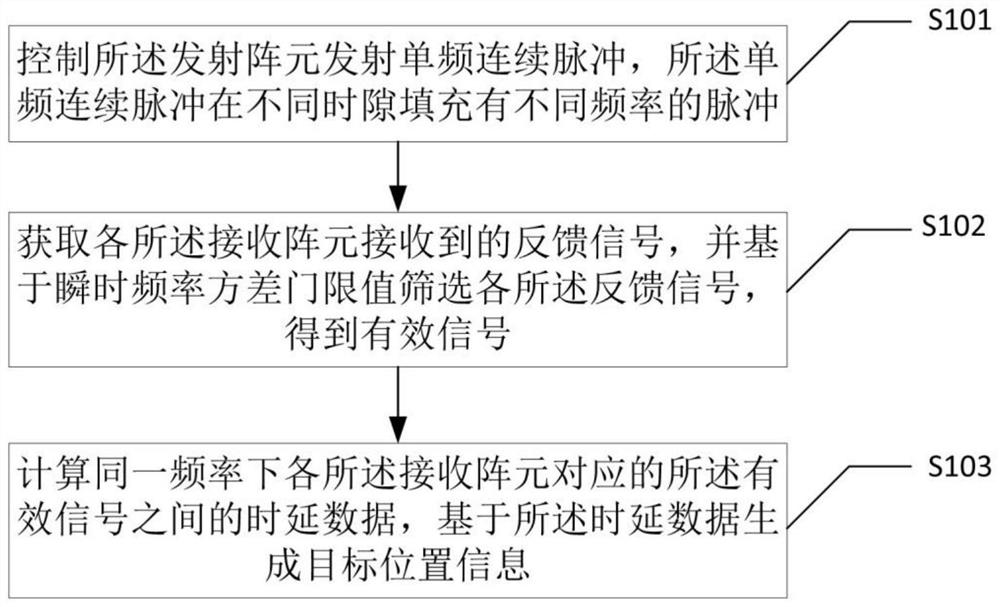
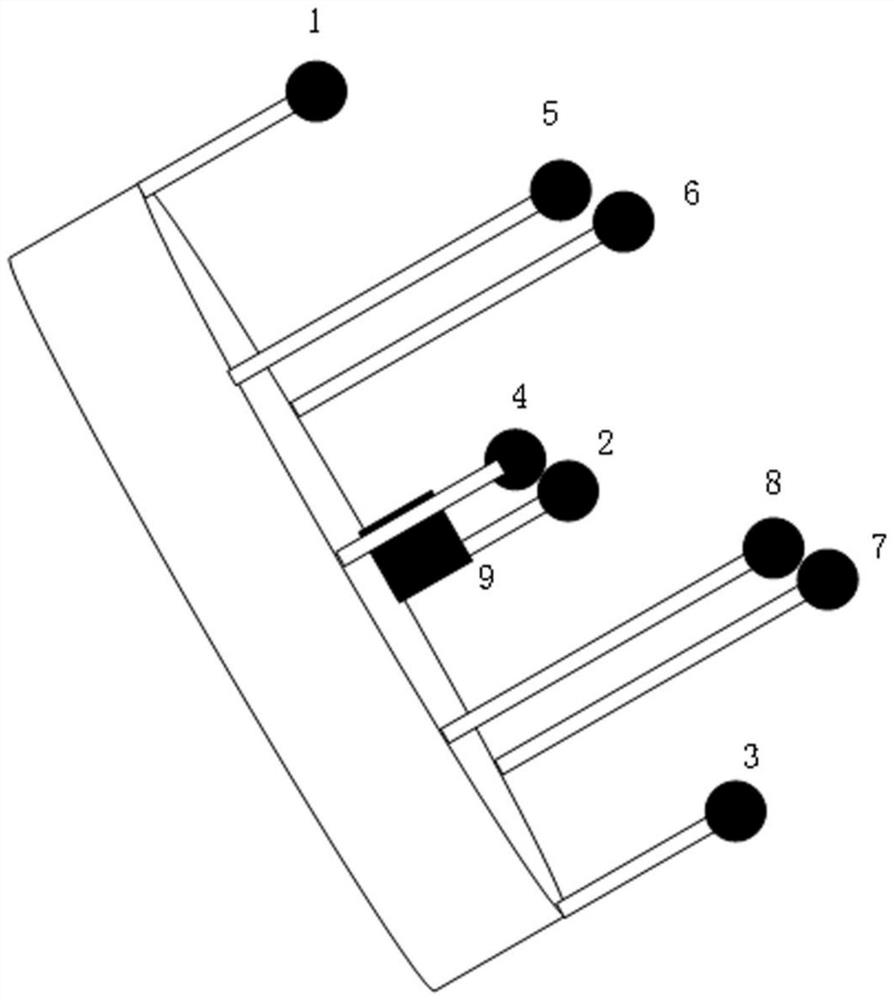
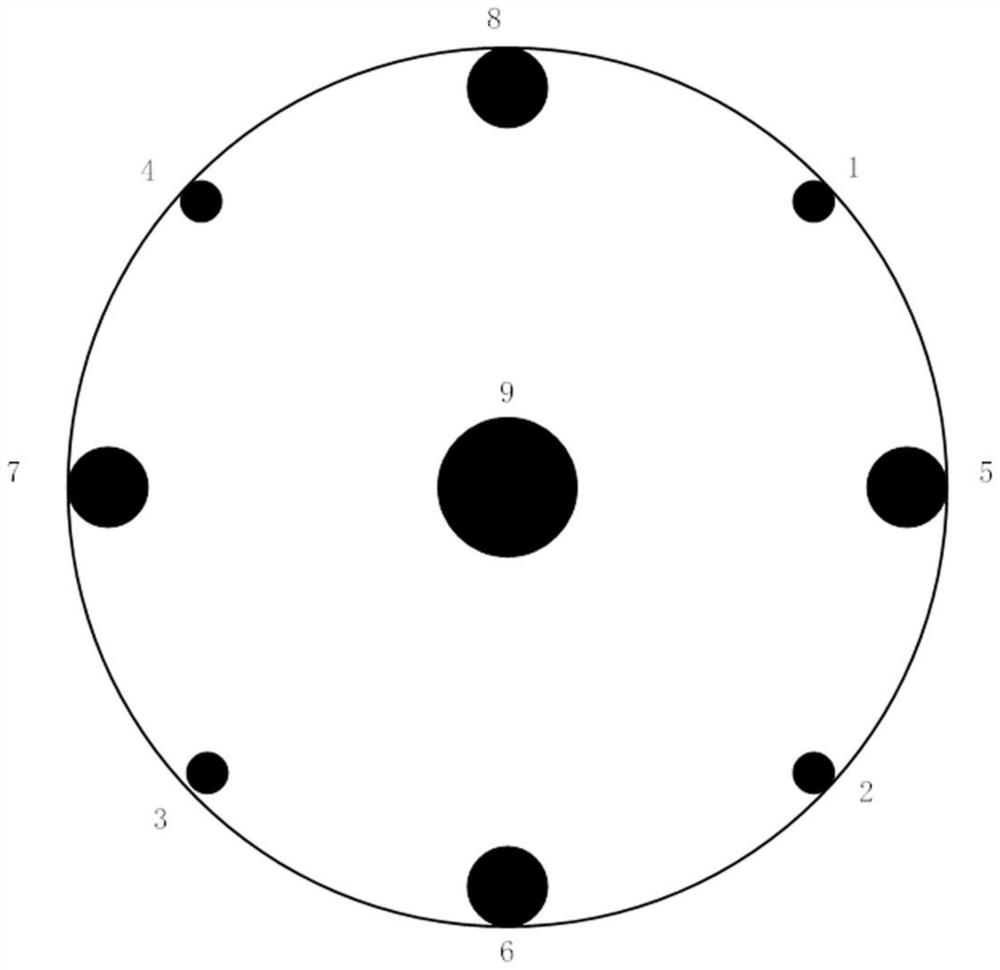
PendingCN114791597AIncrease redundancyAdd dimensionAcoustic wave reradiationTelecommunicationsArray element
The invention discloses an ultra-short baseline positioning method and device based on a three-dimensional array and electronic equipment, and the method comprises the steps: controlling a transmitting array element to transmit a single-frequency continuous pulse, and enabling the single-frequency continuous pulse to be filled with pulses with different frequencies at different time slots; feedback signals received by the receiving array elements are obtained, and the feedback signals are screened based on the instantaneous frequency variance threshold value to obtain effective signals; and calculating time delay data between the effective signals corresponding to the receiving array elements under the same frequency, and generating target position information based on the time delay data. According to the invention, the feedback pulse signals are received through the three-dimensional array formed by the plurality of cross arrays in different planes, one dimension is added in the vertical direction, the redundancy of array elements is improved, and the positioning precision is further improved.
Owner:苏州澜声科技有限公司
Signal amplification circuit, metallic detector formed by signal amplification circuit and signal amplification method
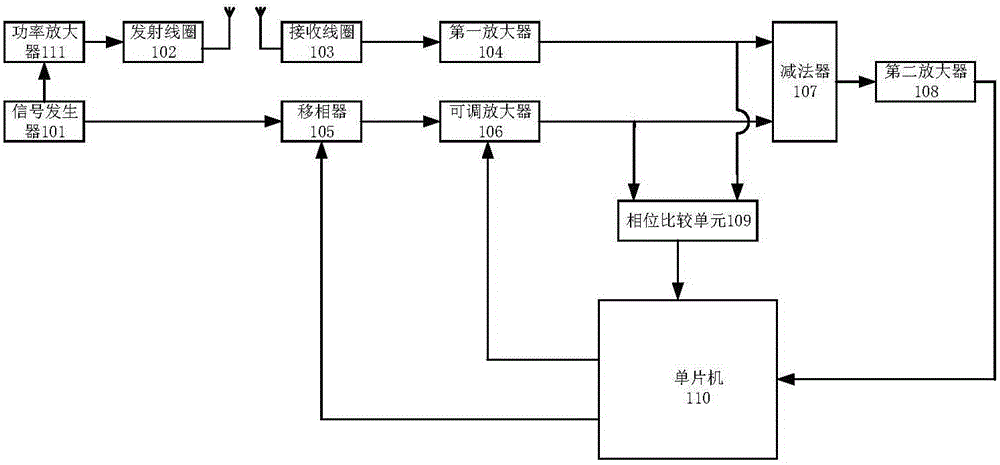
PendingCN105846824AImprove signal detection performanceFewer false negativesAnalogue-digital convertersElectric/magnetic detectionMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
The invention discloses a signal amplification circuit, a metallic detector formed by the signal amplification circuit and a signal amplification method based on the circuit. The signal amplification circuit comprises a signal generator for generating electromagnetic signals and referential signals, an emission coil for emitting electromagnetic signals, a reception coil for receiving sensed signals, a first amplifier for amplifying output signals of the reception coil, a phase shifter for shifting the phases of the referential signals, an adjustable amplifier for amplifying the referential signals, a phase comparison unit for comparing the output signals of the first amplifier with the output signals of the adjustable amplifier, a subtractor which subtracts the output signals of the adjustable amplifier from the output signals of the first amplifier, a second amplification unit for amplifying the signals output by the subtractor, and a single-chip microcomputer which controls the phase shifter and the adjustable amplifier and receives the output signals of the second amplification unit. The detector formed by the signal amplification circuit has substantially improved detection capability.
Owner:DONGGUAN HUADUN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
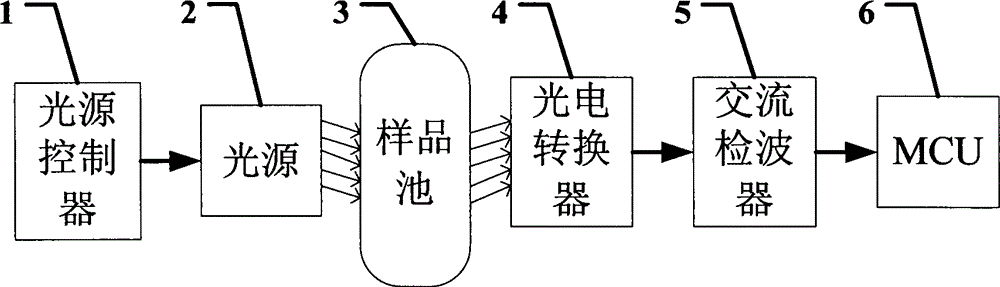
Water quality detection system based on AC detection
InactiveCN104034671AImprove signal detection performanceImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsWater qualityPhotoelectric conversion
The invention discloses a water quality detection system based on AC detection. The water quality detection system is characterized by comprising a light source controller, a light source, a sample cell, a photoelectric converter, an AC detector and an MCU, wherein the light source controller outputs an alternating voltage or current driving signal to drive the light source to work, the light source emits an initial AC optical signal with an amplitude consistent with the driving signal under the driving of the light source controller, the photoelectric converter can convert a residual optical signal absorbed by the sample cell into an electric signal consistent with residual light intensity, the AC detector is used for filtering an interference signal, detecting a useful electric signal and outputting detection results to the MCU, and the MCU calculates the concentration of a target substance in the sample cell through operation. The water quality detection system is not influenced by backlight, the dark current of the photoelectric converter and bias of a circuit, can effectively improve signal detection capability and has detection accuracy far higher than that of a common DC detection system.
Owner:苏州威阳环保科技有限公司
Data transmitting method and base station control system
InactiveCN101577611ASolve the problem of particularly high power control requirementsEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityHigh level techniquesControl systemDiversity scheme
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmitting method and a base station control system. The data transmitting method comprises the following steps: adjacent base stations with multiple antennas determine data to be transmitted by each antenna and a transmitting mode; and at least one antenna of the adjacent base stations on the same time-frequency resource transmits the same data to a user terminal in the same mode. The technical scheme of the embodiment of the invention solves the problem that different cells adopt transmit diversity or multiplex and have particularly high requirement on power control in the prior art, has low requirement on the power control of each base station and is easy to implement, and moreover, the user terminal obtains multi-path gaining and improves the signal detection performance.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
SSTMV minimum variance beam forming method for wideband radar
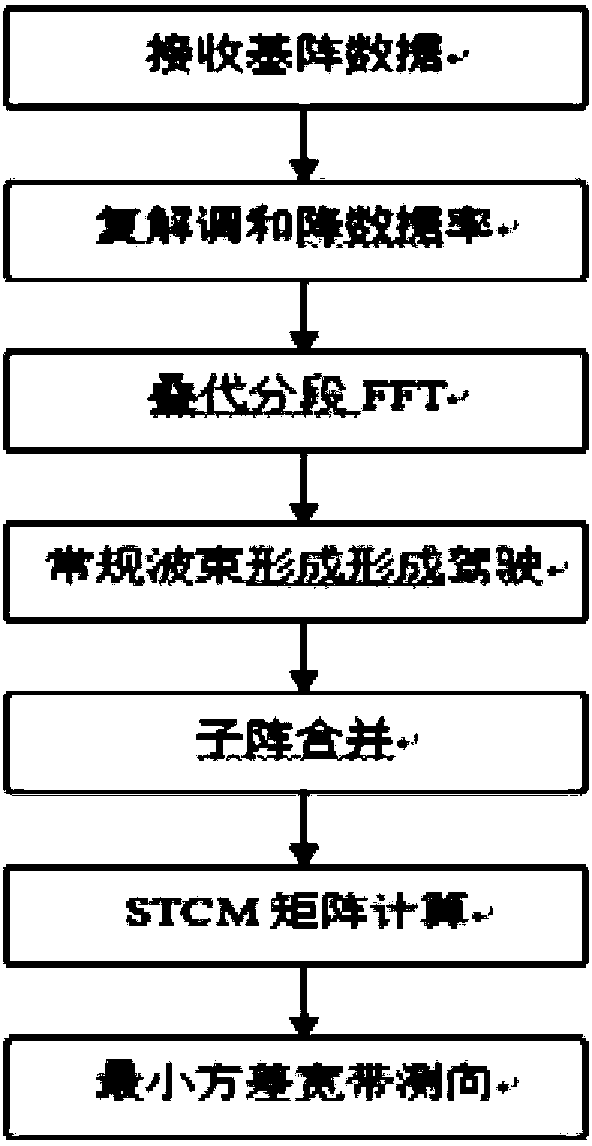
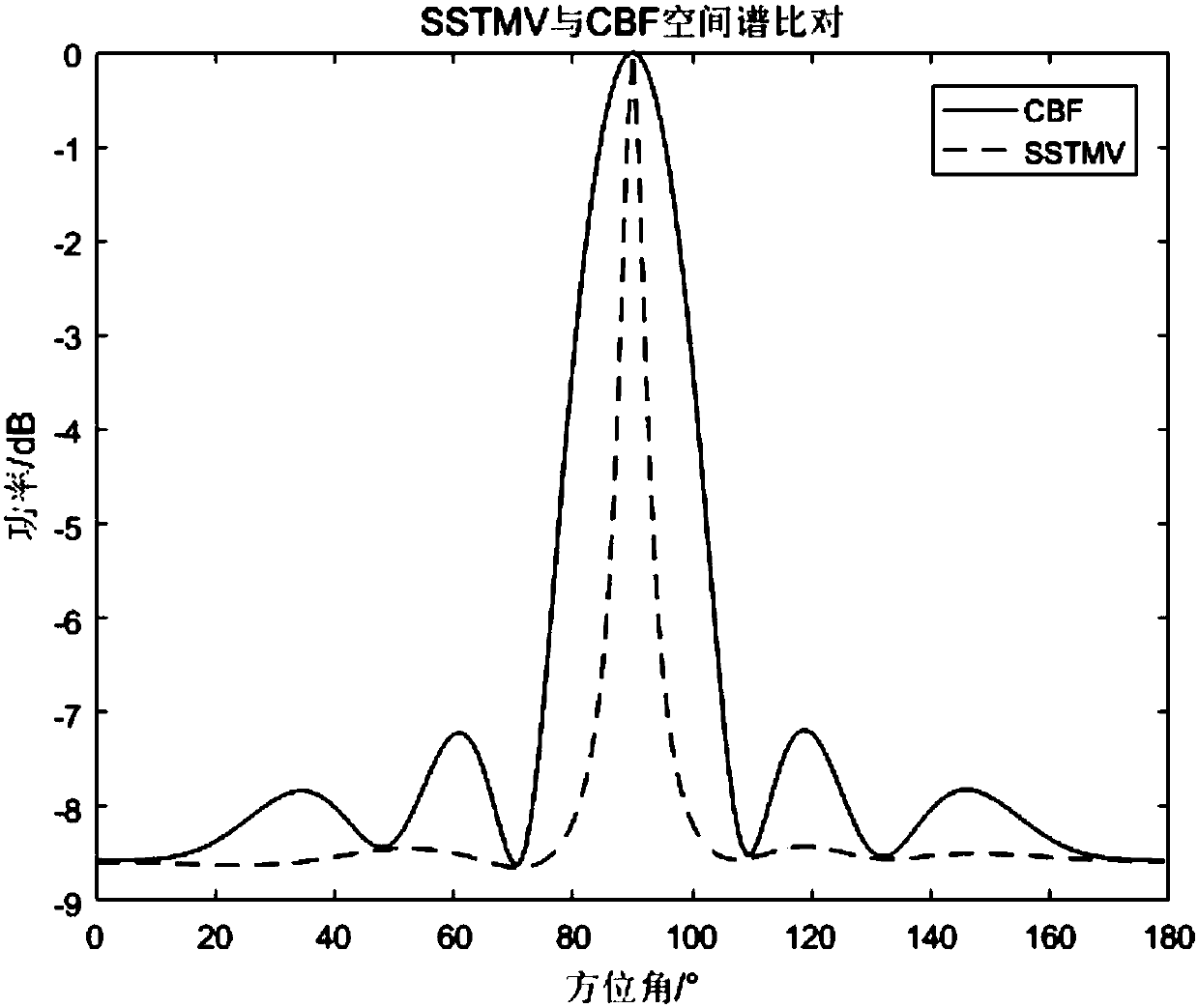
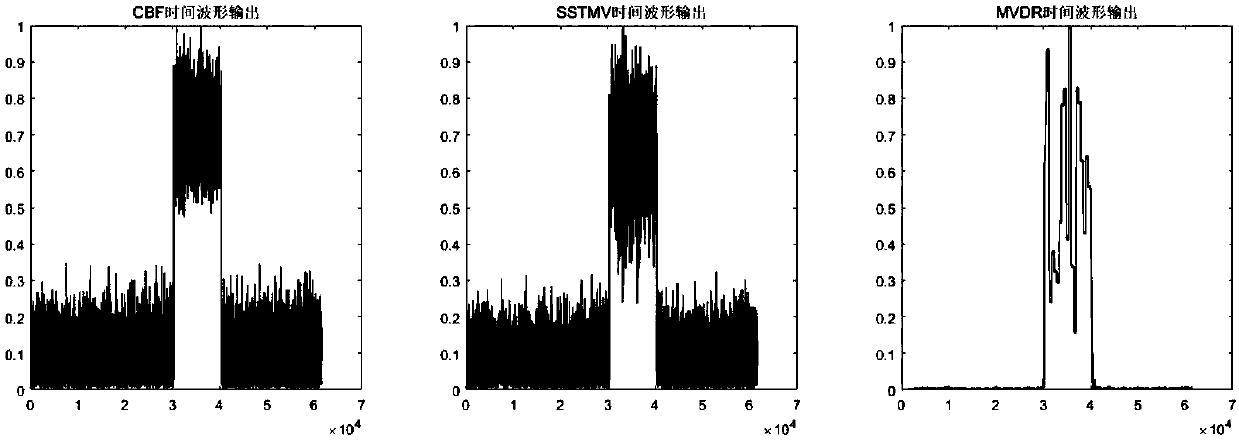
InactiveCN107783081AImprove performanceImprove spatial resolutionWave based measurement systemsWideband radarCovariance matrix
The invention discloses an SSTMV minimum variance beam forming method for wideband radar. Array data is obtained by an antenna of the wideband radar, iterative segmentation and FFT conversion are conducted on the array data to obtain array frequency domain data, and conventional beam forming treatment is conducted on the array frequency domain data through a weighting vector for conventional beamforming; sub-array division and combination are conducted on the array frequency domain data obtained after conventional beam forming treatment to obtain sub-array data; calculation and accumulation of an STCM driving covariance matrix are conducted on the sub-array data, and the beam forming of a minimum variance wideband direction-finding algorithm is conducted through the obtained STCM matrix to obtain the minimum variance beam. By means of the method, the radar space resolution capacity can be effectively improved, good performance can be presented under a small number of periods without accumulating or modifying too large number of periods due to the coherent accumulation characteristic of SSTMB, and the method greatly reduces the calculation amount of the algorithm and is suitable for the wideband radar.
Owner:杭州睿达汽车科技有限公司
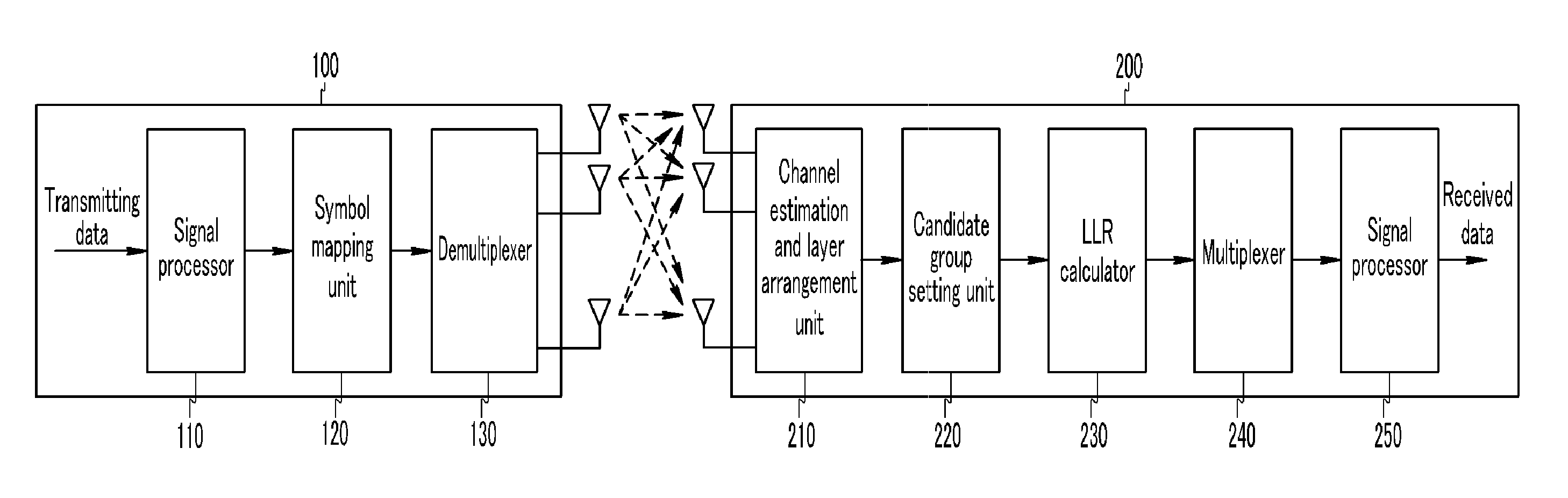
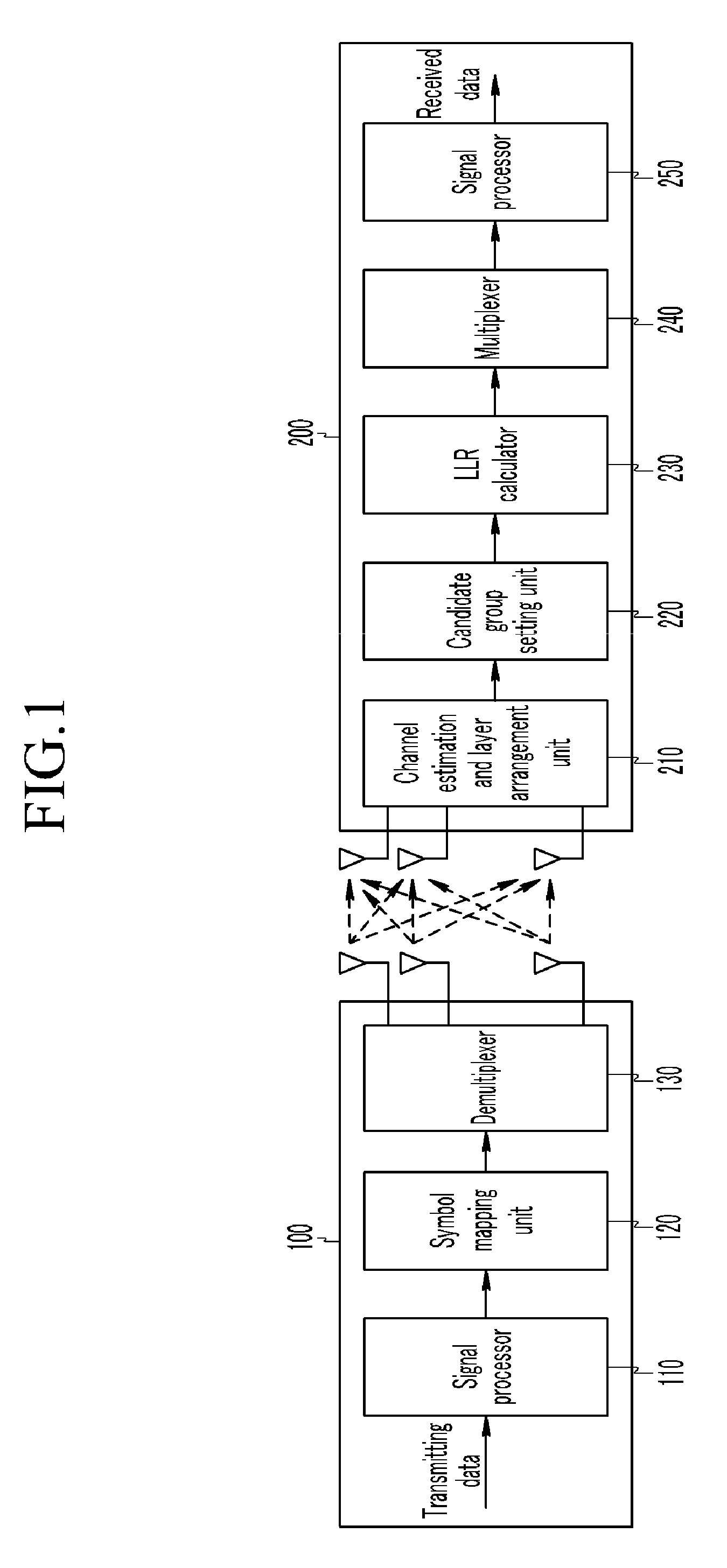
Channel estimation method and device
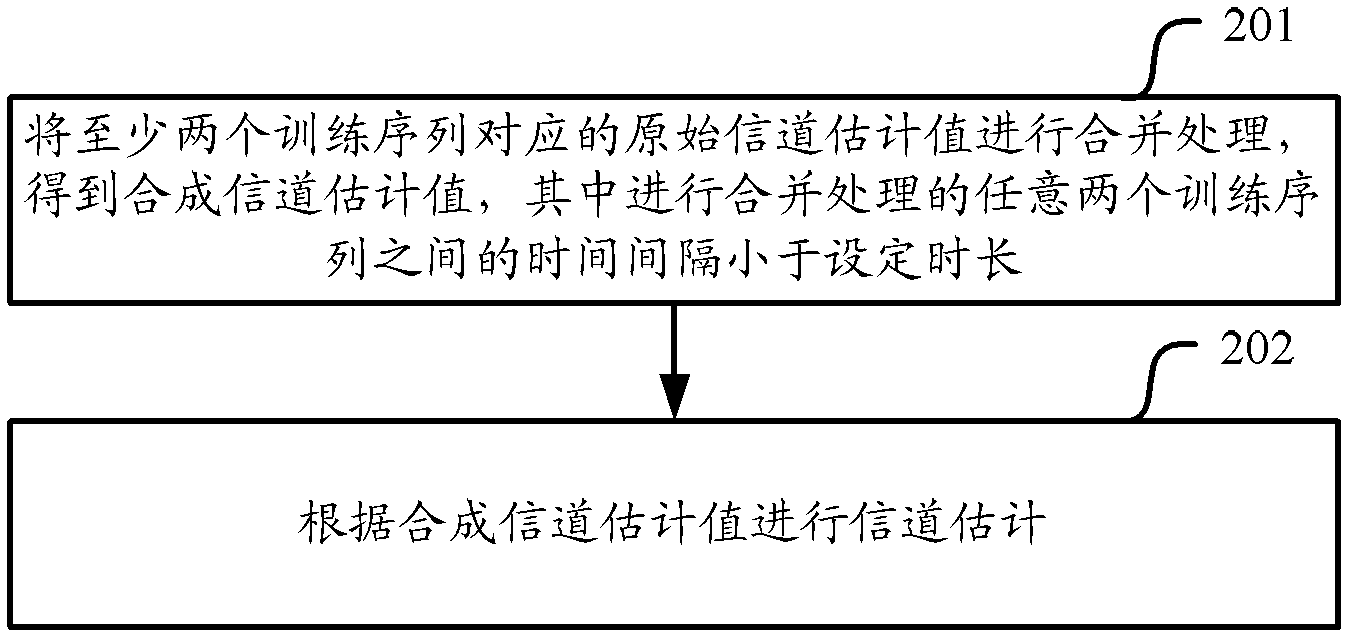
InactiveCN103220238AImprove accuracyImprove signal detection performanceBaseband system detailsAlgorithmEstimation methods
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, in particular to a channel estimation method and device. The channel estimation method and device is used for solving the problem that performance of signal detection is reduced due to the fact that an existing channel estimation method is low in accuracy. According to the channel estimation method and device, original channel estimation values corresponding to at least two training sequences are merged to obtain a merged channel estimation value and then channel estimation is carried out according to the merged channel estimation value, wherein the time interval between any two training sequences treated with merging processing is smaller than a predetermined length of time. Due to the fact that the channel estimation is carried out according to the merge channel estimation value obtained through the merging processing, accuracy of the channel estimation is improved, and the performance of the signal detection is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
Range measurement apparatus and method using chaotic UWB wireless communication
InactiveUS8175274B2Easy to controlImprove signal detection performanceModulated-carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingLeading edgeUltra-wideband
An apparatus for measuring a range based on a chaotic ultra wideband (UWB) wireless communication technology is disclosed. The Apparatus includes a chaotic signal generating / modulating unit, a transceiving unit, a detecting unit, a transform unit, a comparison unit, and a range measurement unit. The transform unit converts the analog voltage signal from the detecting unit into digital signals based on a first sampling period. The comparison unit compares the analog voltage signal from the detecting unit with a predetermined threshold value and to output a comparison signal. The range measurement unit is configured to calculate a time point corresponding to a leading edge, which is a moment when initial data of a packet payload arrive, by using the digital signals based on the threshold value and by using the comparison signal, and to perform a range measurement calculation based on the time point corresponding to the leading edge.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
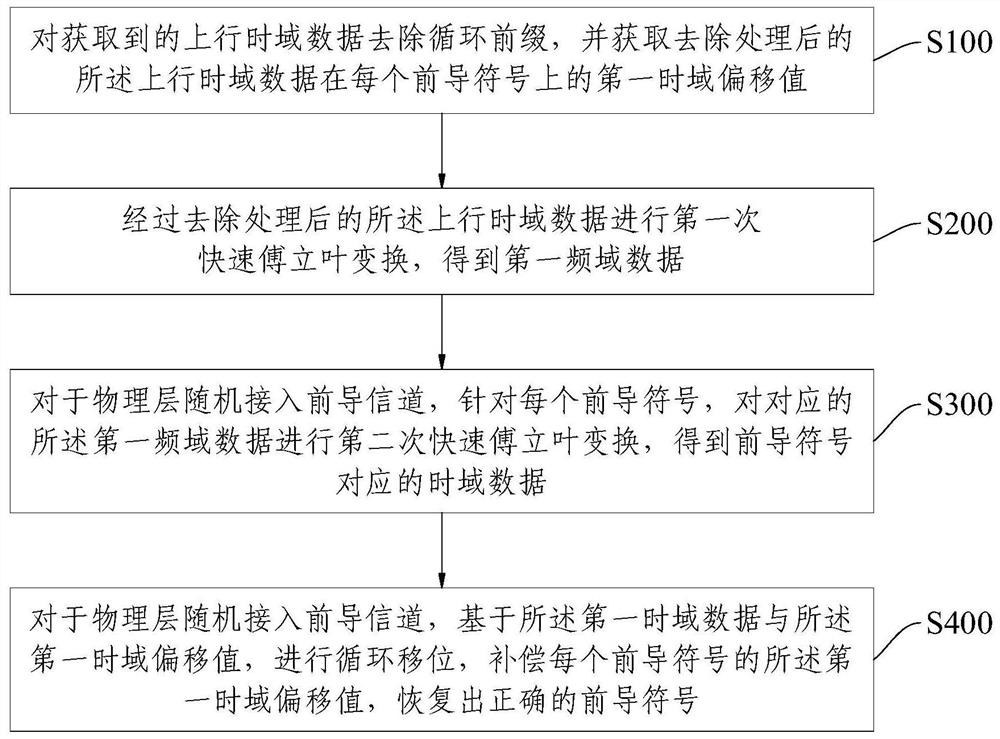
5G uplink physical layer channel processing method, device, equipment and product
ActiveCN114039713ASave storage spaceSimplify complexityMulti-frequency code systemsPilot signal allocationTime domainTelecommunications
The present invention provides a 5G uplink physical layer channel processing method, device, equipment and product, and relates to the technical field of communications. The method comprises the following steps: removing a cyclic prefix from acquired uplink time domain data, and acquiring a first time domain offset value of the uplink time domain data after removal processing on each preamble symbol; performing first fast Fourier transform on the uplink time domain data subjected to removal processing to obtain first frequency domain data; performing second fast Fourier transform on the corresponding first frequency domain data to obtain time domain data corresponding to the preamble symbol; and performing cyclic shift based on the first time domain data and the first time domain offset value, compensating the first time domain offset value of each preamble symbol, and recovering a correct preamble symbol. According to the invention, the detection time delay of the PRACH channel is reduced, the detection efficiency is improved, and the correctness of PRACH detection is ensured, so that the user perception is improved.
Owner:INSPUR SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD
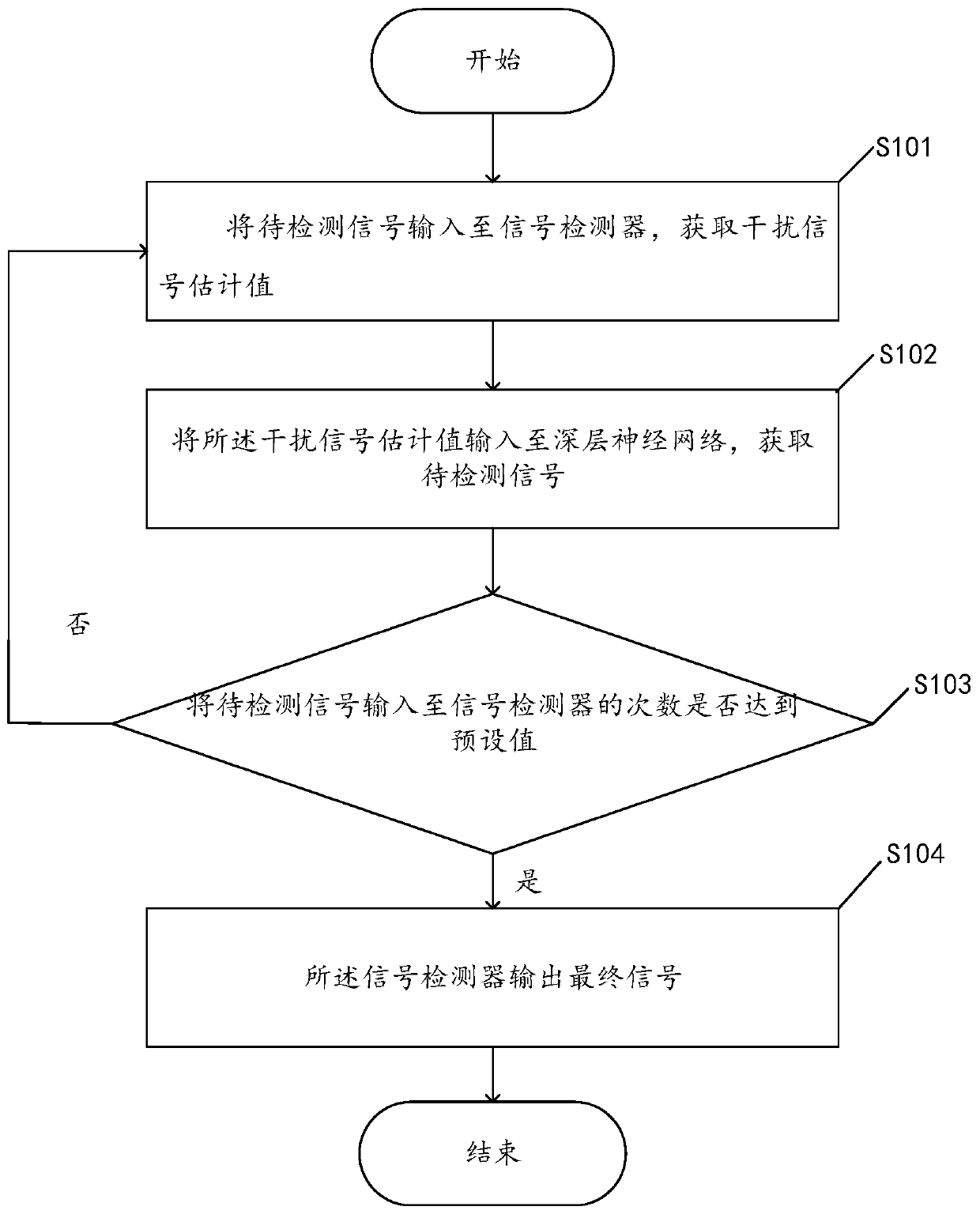
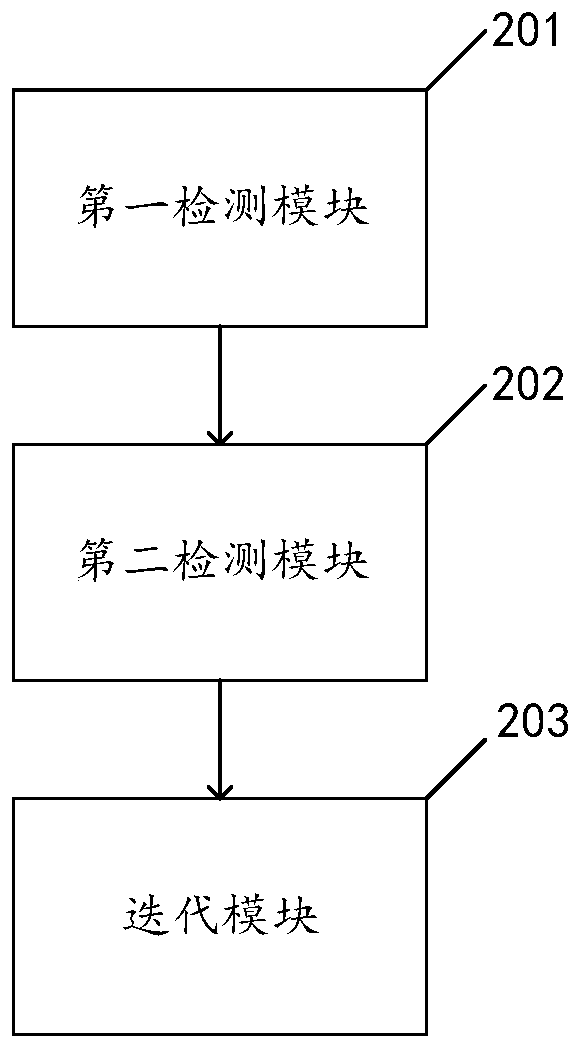
Iterative intelligent signal detection method based on neural network
ActiveCN110474663AImprove signal detection performanceEasy to detectError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio transmissionPattern recognitionNerve network
The invention discloses an iterative intelligent signal detection method based on a neural network, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, inputting a to-be-detected signal to a signal detector, and obtaining an interference signal estimation value; 2, inputting the interference signal estimation value into a deep neural network to obtain the to-be-detected signal; and step 3, repeatingthe step 1 and the step 2 for several times, and outputting a final signal by the signal detector. The invention further provides an iterative intelligent signal detection device and equipment based on the neural network, and a storage medium. By adopting the method and the device, the signal detection performance in a scene subjected to complex dynamic related interference can be improved.
Owner:南方电网互联网服务有限公司
Log likelihood ratio calculation method, transmit signal detection method, and receiver
InactiveUS8040980B2Reduce complexityImprove signal detection performanceOther decoding techniquesAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLogitDependability
The present invention relates to a log-likelihood ratio calculation method, a transmitting signal detection method, and a receiver. The present invention estimates a channel on the basis of the received signal and rearranges a plurality of layers. Further, at the time of rearrangement of the layers, a symbol of a layer having the lowest reliability is considered for every constellation dot, and the successive interference for the remaining layers is removed corresponding to the constellation dots of the layer having the lowest reliability to set the transmitting symbol candidate vector. Furthermore, a log-likelihood ratio for every bit of the plurality of layers is calculated using the transmitting symbol candidate vector to decode the channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Method and device for pre-calibrating frequency deviation
ActiveCN101958744BImprove signal detection performanceModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmission for post communicationEngineeringFrequency deviation
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
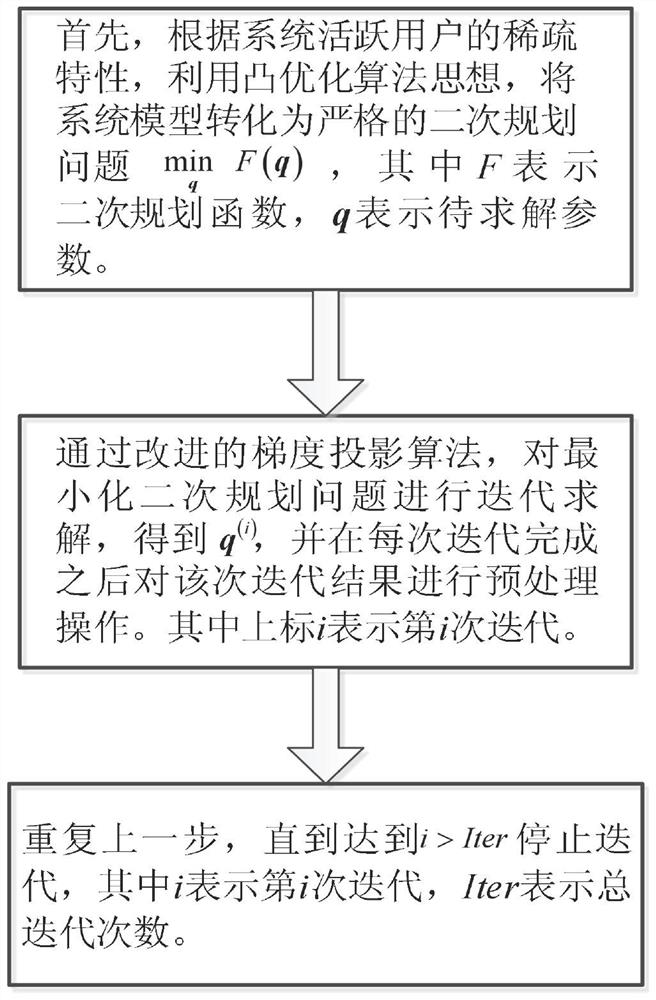
Signal detection method for low-complexity mimo-noma system based on improved gradient projection method
ActiveCN109474388BFast convergenceImprove signal detection performanceRadio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAlgorithm convergenceNoma
The invention discloses a low-complexity MIMO-NOMA system signal detection method based on an improved gradient projection method, and relates to wireless communication technology. According to the sparse characteristics of the active users of the system, the system model is transformed into a strict quadratic programming problem by using the idea of convex optimization algorithm; then the problem is solved iteratively, and the results of each iteration are preprocessed to achieve the goal of active users and Its signal is effectively detected. The invention breaks through the problem of slow convergence speed of the algorithm in the traditional detection method, performs preprocessing operation on each iteration result, not only can make the detection result converge quickly, but also can detect the active user set, the realization process is simple, and the application range is wide .
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
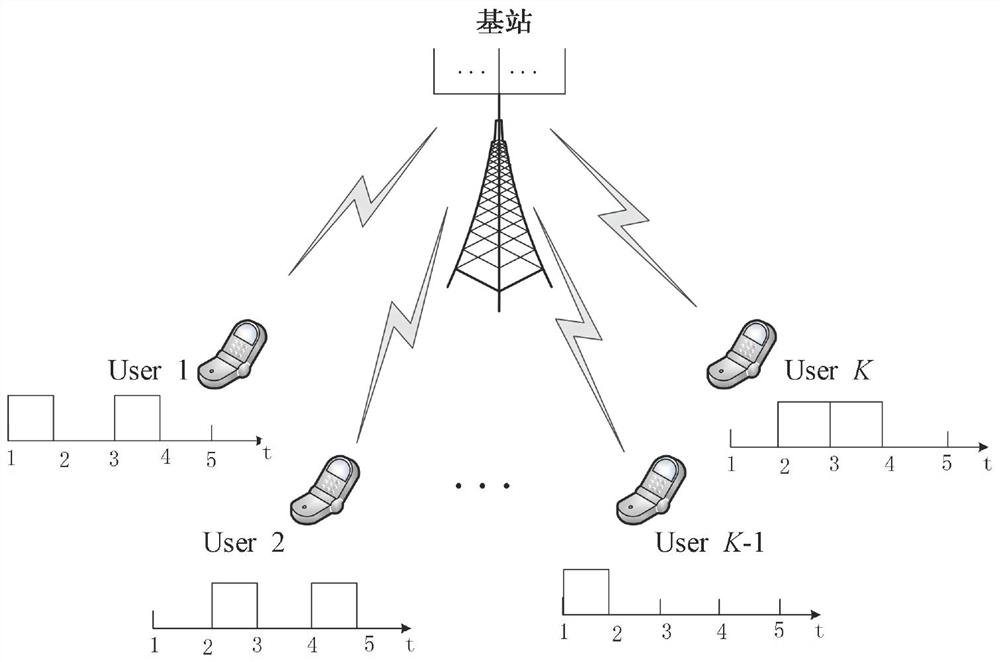
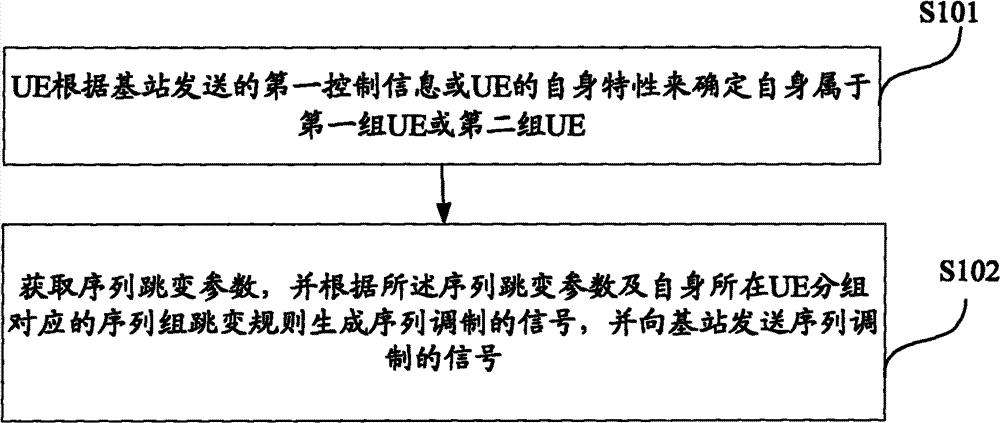
Transmission method and device of signals for sequence modulation
ActiveCN102123502BImprove signal detection performanceInterference randomizationWireless communicationUser equipmentVIT signals
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Satellite-borne ADS-B group signal receiving and processing method
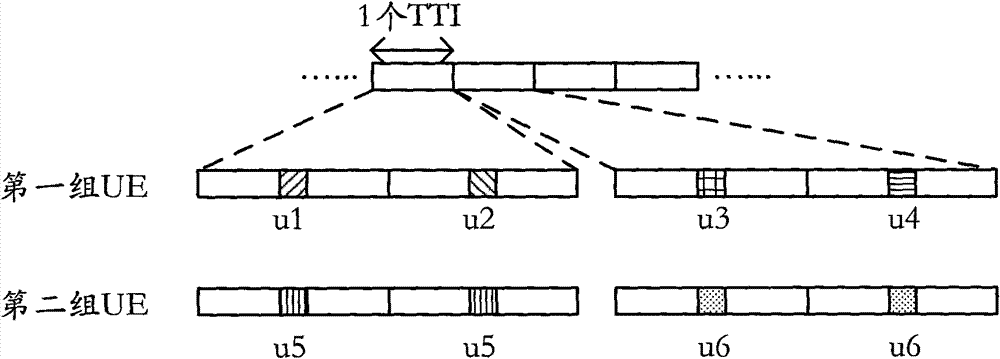
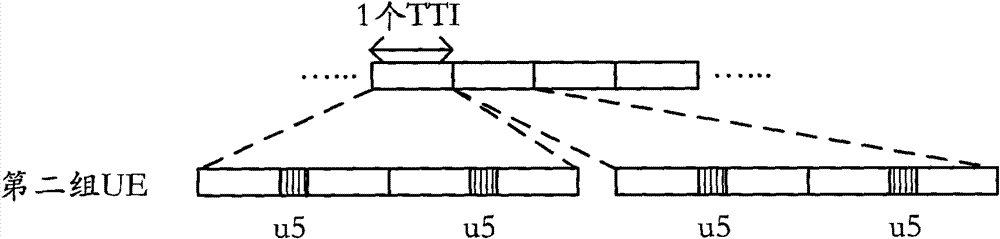
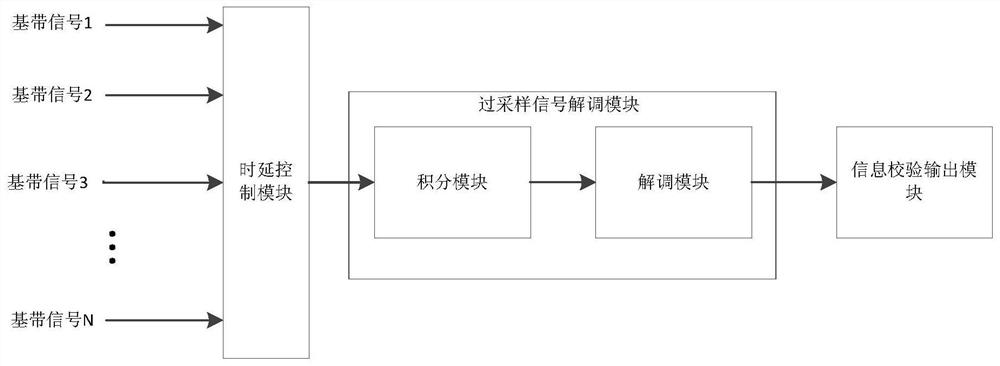
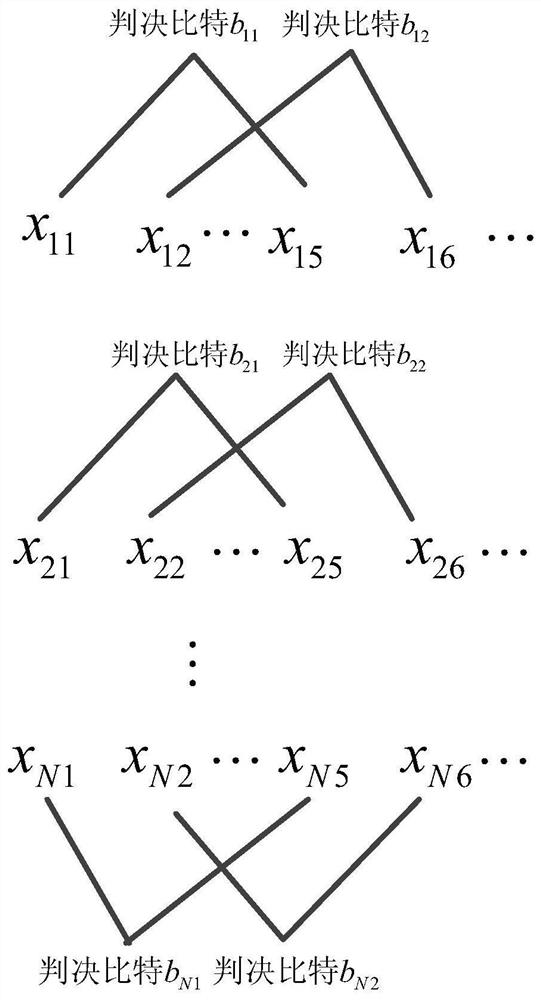
ActiveCN112468214AReduce resource usageEliminate burst detection effectsRadio transmissionEngineeringOversampling
The invention discloses a satellite-borne ADS-B group signal receiving and processing method, and the method employs a signal processing method and a time division multiplexing structure under oversampling for the characteristics of a group ADS-B signal. The demodulation structure comprises a group signal delay control module, an oversampling demodulation module and an information verification output module. The group signal delay control module completes the function of converting parallel signals into serial signals by controlling the delay of the parallel group signals; the oversampling demodulation module carries out sliding correlation on the oversampling signal and a local standard pulse signal and then demodulates the oversampling signal to obtain demodulation information of the oversampling signal; and the information verification output module screens the demodulated repeated information and confirms the correctness of the demodulated information through CRC verification. According to the invention, the resource consumption is reduced by improving the clock utilization rate in the demodulation of the ADSB group signals, and the detection performance of the system on the ADSB signals is greatly improved because the received signals do not need to be subjected to burst detection in the oversampling demodulation process.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com