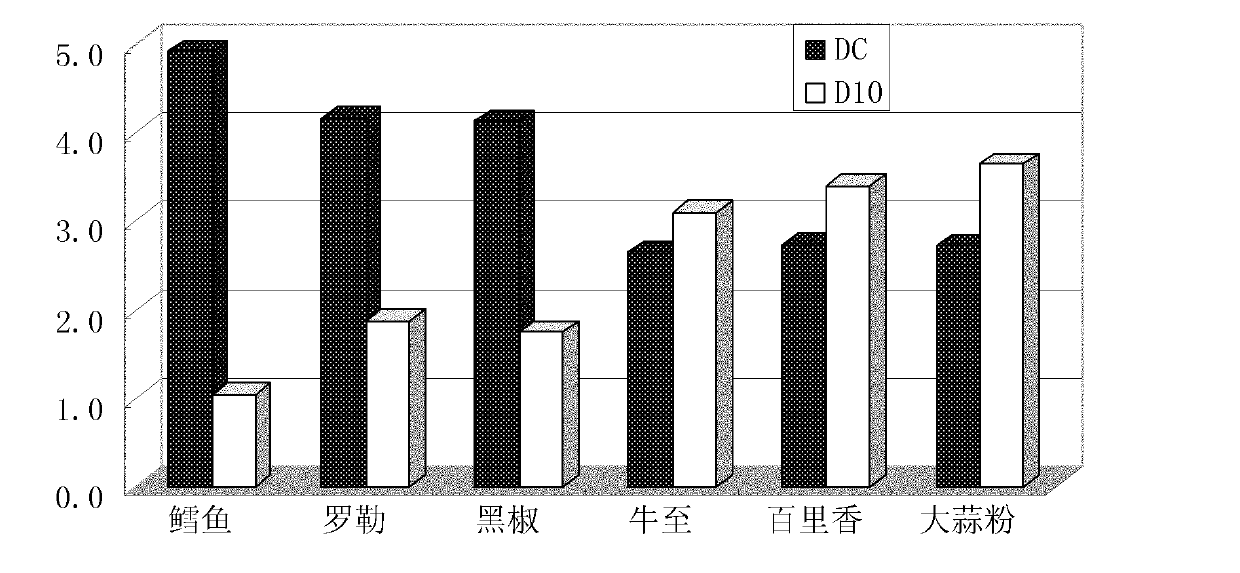
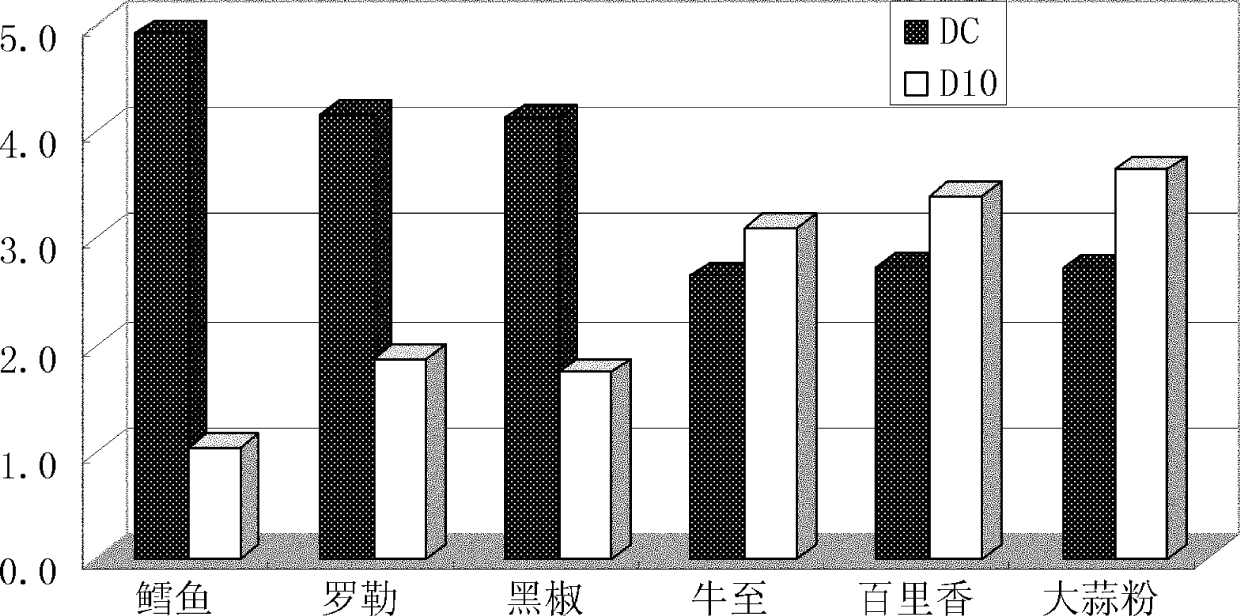
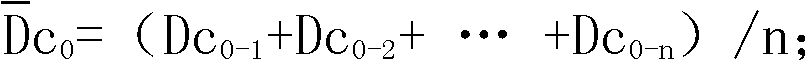Method for judging irradiation of product and dosage thereof
A product, irradiation technology, used in dosimeters, measuring devices, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, etc., can solve the problems of undetermined radiation dose, false negatives, false positives, etc., to reduce false negative results. Probability, accurate and rapid judgment, and the effect of improving detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0058] Example 1: Beet sample irradiation and dose determination:
[0059] Select five batches of unirradiated sugar beet samples in advance according to the method of the first step above, and each batch is divided into two parts, and a total of 5 parts of each batch are taken for detection, and obtained: log(DEFT 0-1 ) = 6.48, log(APC 0-1 ) = 7.08, D C0-1 =log(DEFT 0-1 )-log(APC 0-1 )=-0.6,...,D C0-2 =-0.49,D C0-3 =-0.71,D C0-4 =-0.55,D C0-5 = -0.65, calculate
[0060] The other five samples in the five batches passed the sugar beet irradiation dose (ranging from 0 to 0.8kGy, 0.8>2×0.28) survival test, respectively: D 10-1 =0.24kGy,D 10-2 = 0.34kGy, D 10-3 =0.26kGy,D 10-4 = 0.30kGy, D 10-5 = 0.26kGy, calculate
[0061] 1) Beet sample 1 under inspection:
[0062] DEFT / APC method test results: log(DEFT)=6.29, log(APC)=4.32, Dc=1.97, because According to criterion 1, the sample has been treated with a dose greater than 0.28 / 2 = 0.14 kGy.
[0063] 2) B...
example 2
[0067] Example 2: Irradiation of yellow line fish samples and its dose determination:
[0068] Select five batches of unirradiated yellow-haired fish samples in advance according to the method of the first step above, each batch is divided into two parts, and one part of each batch is taken for a total of 5 parts for testing, and it is obtained: log(DEFT 0-1 ) = 10.65, log(APC 0-1 ) = 8.34, D C0-1 =log(DEFT 0-1 )-log(APC 0-1 )=2.31,...,D C0-2 =2.2,D C0-3 =2.40,D C0-4 =2.32,D C0-5 = 2.32, calculate
[0069] The other five samples in the five batches passed the survival test of yellow line fish irradiation dose (ranging from 0 to 4.0 kGy, 4.0>2×1.42), respectively: D 10-1 = 1.42kGy, D 10-2 = 1.30kGy, D 10-3 = 1.46kGy, D 10-4 = 1.44kGy, D 10-5 = 1.48kGy, calculate
[0070] 1) Sample 1 of the inspected yellow line fish:
[0071] DEFT / APC method test results: log(DEFT)=10.45, log(APC)=6.84, Dc=3.61, because According to criterion 2, it cannot be judged whe...
example 3
[0076] Example 3: Irradiation and dose determination of black pepper samples:
[0077] Select five batches of unirradiated black pepper samples in advance according to the method of the first step above, each batch is divided into two parts, and one part of each batch is taken for a total of 5 parts for detection, and it is obtained: log(DEFT 0-1 ) = 6.92, log(APC 0-1 ) = 5.77, D C0-1 =log(DEFT 0-1 )-log(APC 0-1 )=1.15,...,D C0-2 =1.18,D C0-3 =1.20,D C0-4 =1.08,D C0-5 = 1.14, calculate
[0078] Another five samples in the five batches passed the black pepper class irradiation dose (range is 0~6.0kGy, 6.0>2×2.39) survival test, respectively: D 10-1 =2.39kGy,D 10-2 =2.44kGy,D 10-3 =2.22kGy,D 10-4 =2.31kGy, D 10-5 = 2.59kGy, calculate
[0079] 1) Detected black pepper sample 1
[0080] DEFT / APC test results: log(DEFT)=6.9, log(APC)=4.41, Dc=2.49, because According to criterion 3, it cannot be judged whether the sample has been treated with a dose > 2.0 kGy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com