Method for analyzing genetic diversity of shellfish by using fAFLP (Fluorescent Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism) labeling technology
A technology of genetic diversity and marker technology, applied in the field of analysis of shellfish genetic diversity using fAFLP marker technology, can solve the problems of enzyme digestion, pre-amplification, selective amplification without providing a reaction system, etc., to achieve gene diversity and The effect of large Shannon information index, high proportion of polymorphic sites, and many amplification sites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
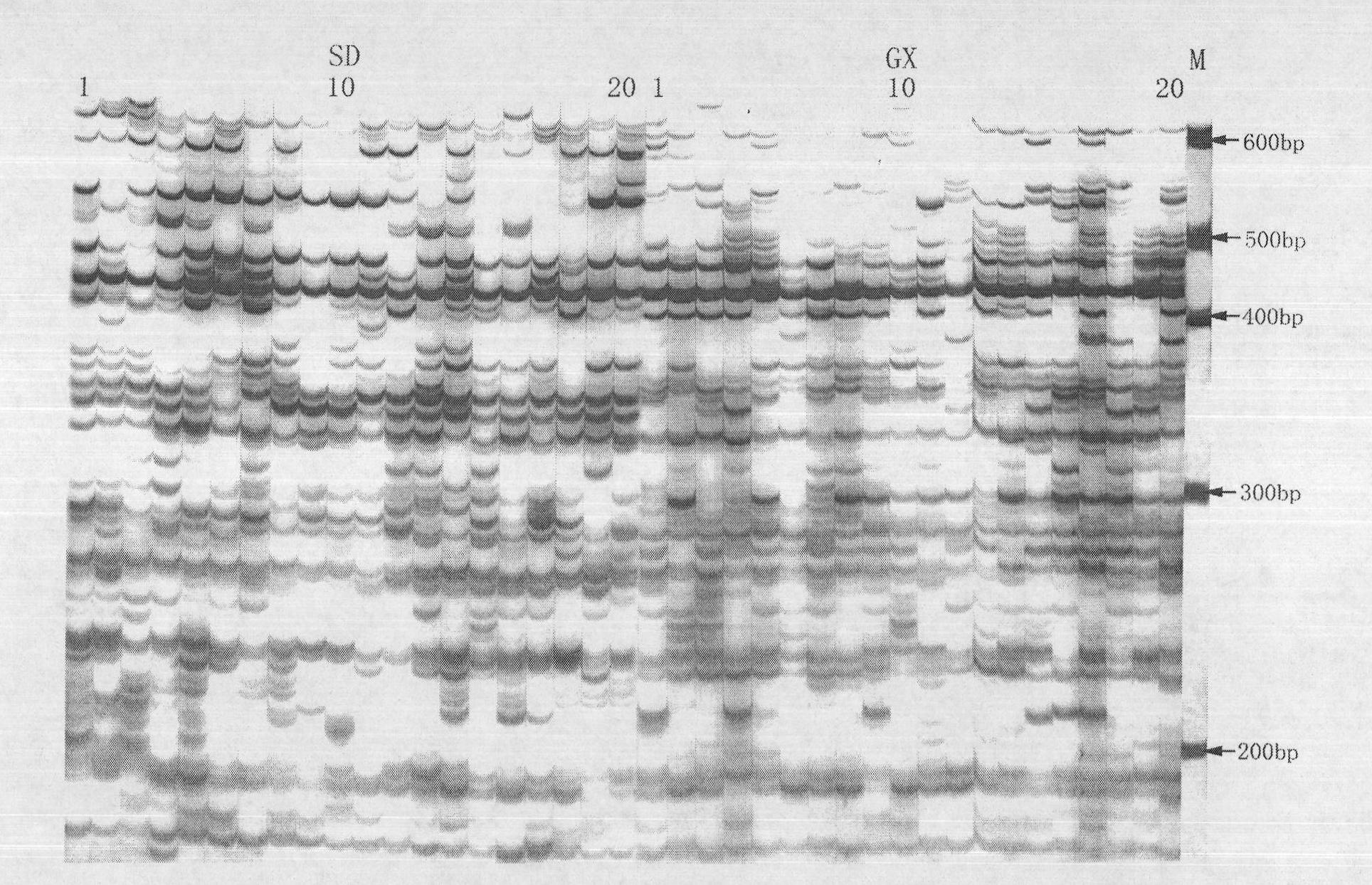
[0023] The advantages of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples of silver staining and fluorescent labeling methods for detecting AFLP diversity in different geographical populations of clams.
[0024] (1) Extraction of high-quality DNA: In July 2006, 20 adductor muscles of clams Shandong population (abbreviated as SD) and Guangxi population (abbreviated as GX) were taken, and genomic DNA was extracted with phenol / chloroform method, and 1% agar Sugar gel electrophoresis and ultraviolet spectrophotometer were used to detect the purity and integrity of DNA, and the concentration of DNA in all samples was adjusted to 100ng / μL.
[0025] (2) Restriction endonuclease digestion of DNA: digest with EcoR I and Mse I two endonucleases. The digestion mixture for each DNA sample includes: DNA 100ng, Ms...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com