Imaging structure of fixed star sensor
A stellar sensor and imaging technology, which is applied in the field of deep space navigation sensors, can solve the problems of increased difficulty in processing and assembly, high difficulty in aspheric processing and assembly, and achieve the goals of reducing processing and assembly difficulty, protecting windows, and saving costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
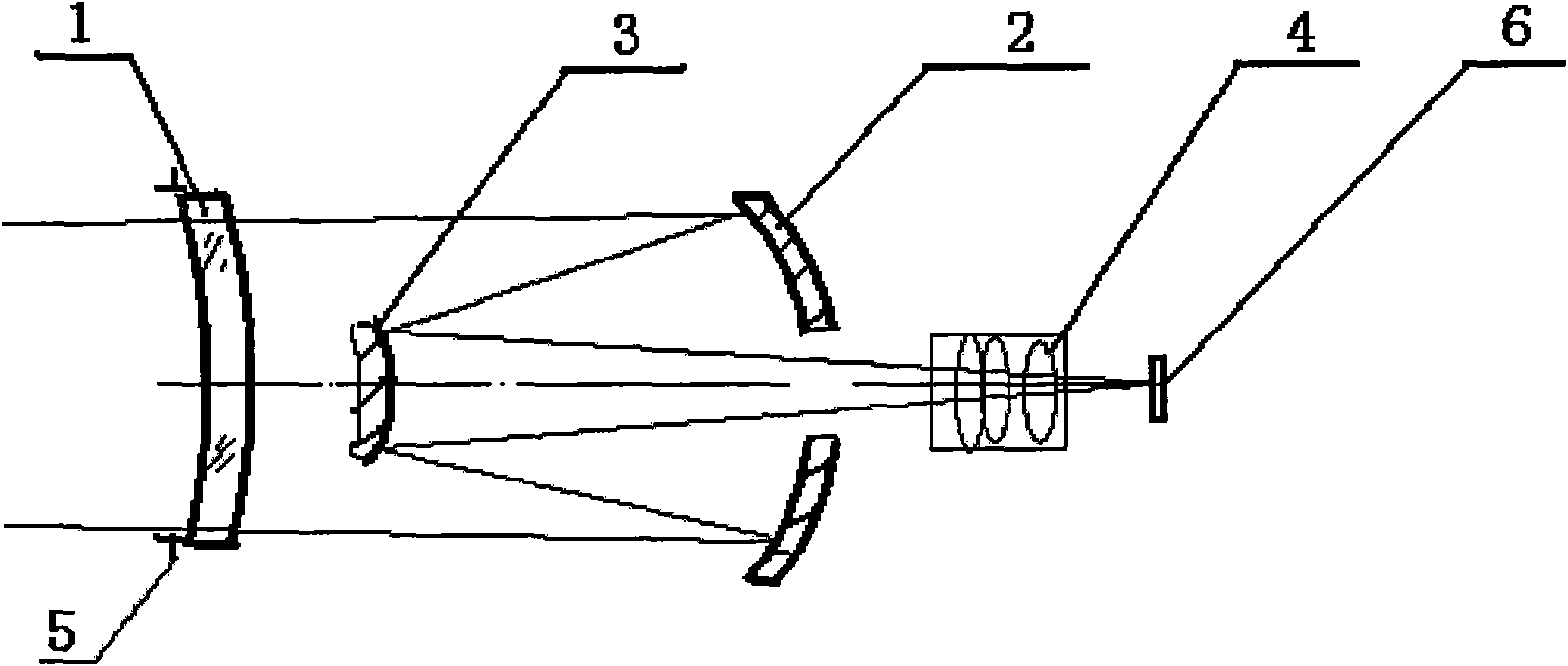
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, a stellar sensor imaging structure, the leftmost is the correction mirror 1, followed by the secondary mirror 3, the primary mirror 2, the correction mirror group 4, and the focal plane detector 6. The diaphragm 5 is installed on the first optical surface or the second optical surface of the correction mirror 1; a circular hole is opened in the center of the main mirror 2, and the center of the hole is located in the center of the main mirror 2, and the diameter is the smallest on the basis of its optical aperture The outer expansion is 6 mm to accommodate the correction lens group 4 to pass through the hole or to satisfy that the light from the secondary mirror 3 does not block.
[0021] The distance between the last optical surface of the correction mirror group 4 and the photosensitive surface of the focal plane detector 6 should be greater than 5 mm to meet the detector installation requirements. In this embodiment, the correction mirror g...
Embodiment 2
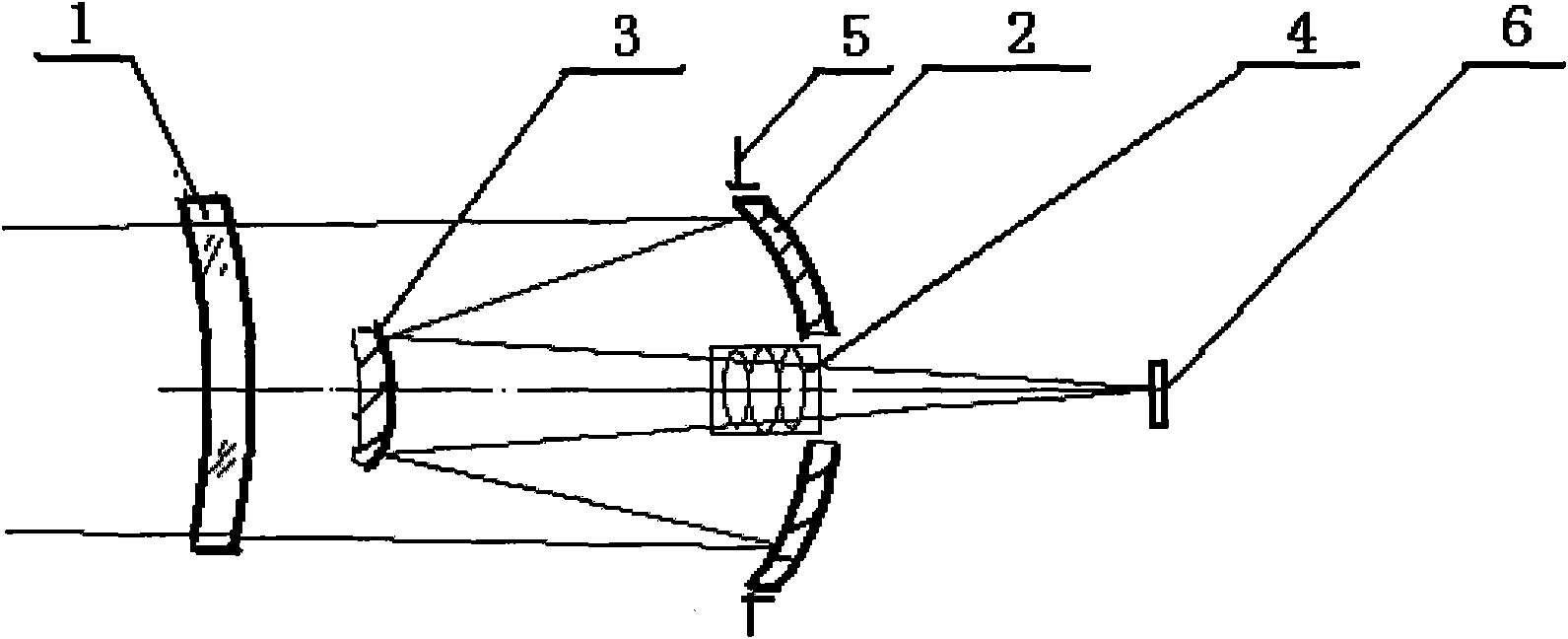
[0030] Such as figure 2 As shown, the diaphragm 5 is installed on the reflective surface of the main mirror 2, and the position of the diaphragm 5 can also be moved back and forth a small amount along the direction of the optical axis to complete the design of the present invention. The correction mirror group 4 is located at the center of the circular hole of the main mirror 2 and on the left side of the main mirror 2 .
Embodiment 3
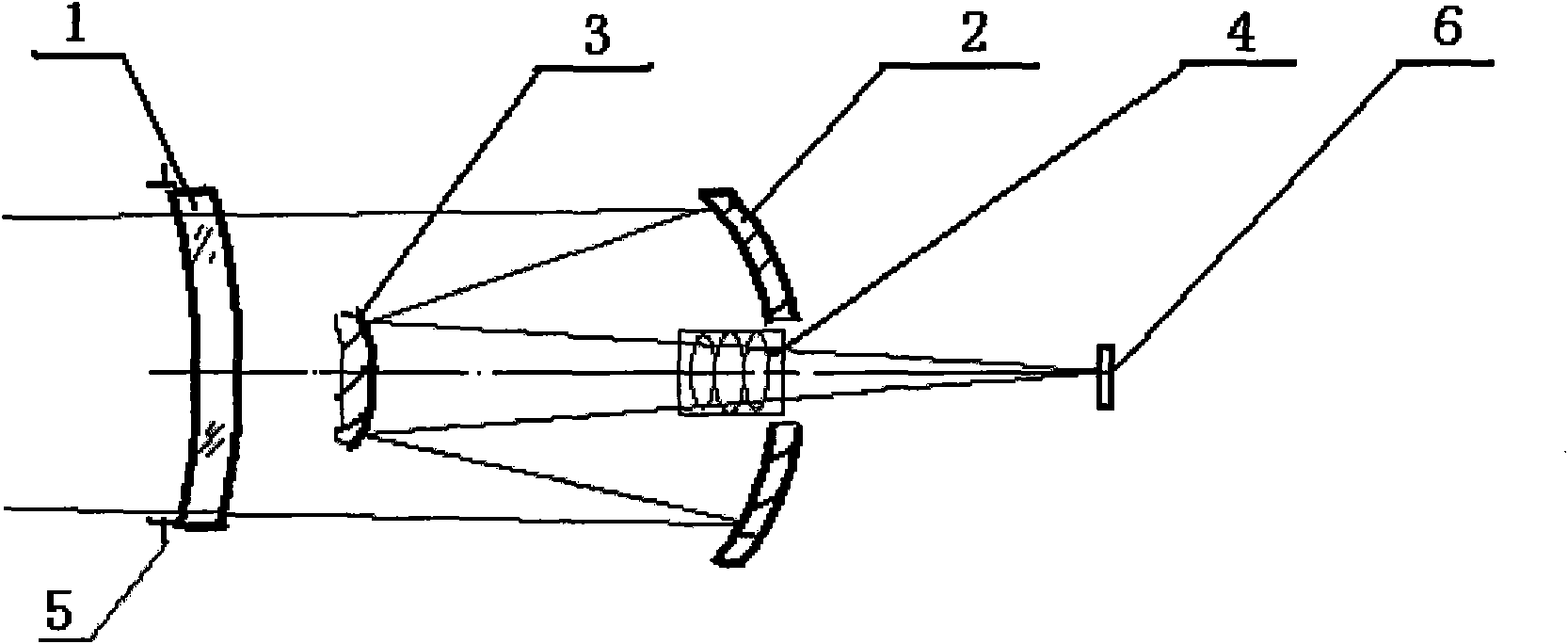
[0032] Such as image 3 As shown, the diaphragm 5 is installed on the first optical surface or the second optical surface of the aberration correcting mirror 1 , and the correcting mirror group 4 is located at the center of the circular hole of the main mirror 2 and on the left side of the main mirror 2 . The focal length f of the optical system is 500mm, and the relative aperture is The field of view is 1.6°.
[0033] The correcting mirror group 4 of the system described in this embodiment comprises 4 spherical lenses, 401, 402, 402, 404, and the lens material of the correcting mirror group 4 is glass of the same brand, such as K9, QK3, etc., and this embodiment uses K9 glass.
[0034] Its structural parameters are as follows:
[0035] Radius of curvature Center spacing Glass material
[0036] 401 First face 33.23875 4.000000 K9
[0037] 401 Second face 18.30291 2.800000
[0038] 402 First face 316.41161 4.215735 K9
[0039] 402 Second face -23.28973 16....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com