Method for detecting nucleic acid mass of sample
A detection method and sample technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of indetermination of the degree of influence and inability to detect the degradation of DNA, and achieve the effect of expanding the range of reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
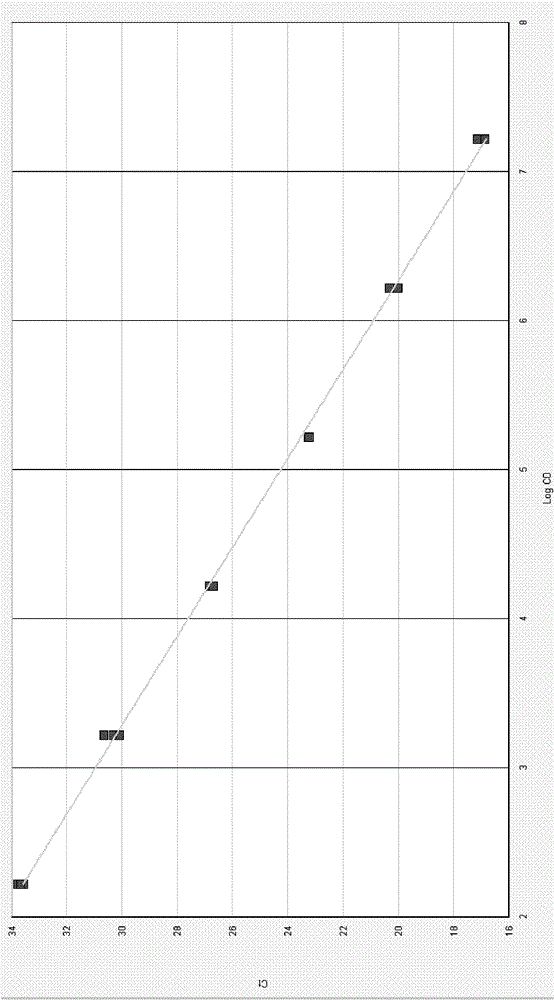
[0050] Embodiment 1: Evaluate the degradation situation of biological sample with the method of the present invention
[0051] Experimental scheme: In a 25ul fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction system, there are 2 primers for amplifying the RPPH1 gene (the nucleotide sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 respectively) and 1 FAM-labeled probe (The nucleotide sequence is respectively shown in SEQ ID No.3);
[0052] 2 primers for amplifying the Fas gene (its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.4 and SEQID No.5 respectively) and 1 HEX-labeled probe (its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.6 respectively) shown);
[0053] 2 primers for amplifying internal control IPC1 (its nucleotide sequences are shown in SEQ ID No.7 and SEQ ID No.8 respectively) and 1 TAMRA-labeled probe (its nucleotide sequences are shown in SEQ ID No .9);
[0054] 2 primers for amplifying internal control IPC2 (its nucleotide sequences are shown in SEQ ID No.10 and SEQ ID ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2: Evaluate biological samples affected by inhibitors with the method of the present invention
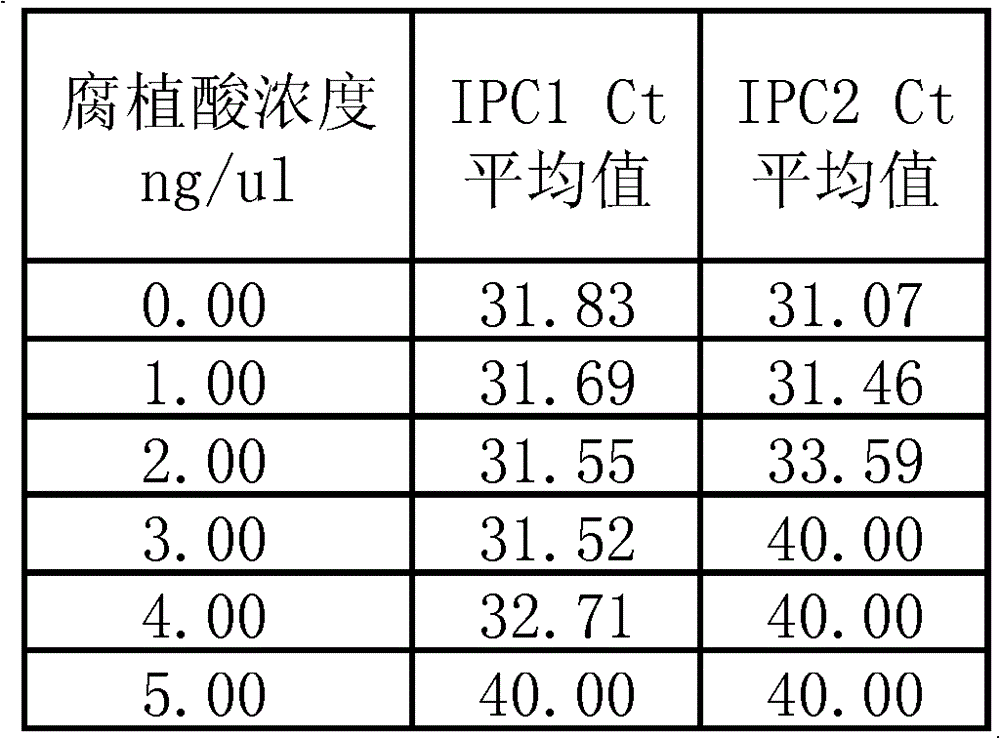
[0064] Referring to Example 1, to simulate actual samples, the PCR inhibitor humic acid (Humic acid), which is widely present in soil, plants and other environments, is added to the fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction system of Example 1, and all systems contain the same human The amount of genomic DNA, and the obtained Ct value of the reaction reflects the extent to which the PCR system is subjected to inhibitors. The data are shown in Table 2:
[0065] Table 2, method evaluation sample of the present invention is influenced by inhibitor
[0066]
[0067] The data in Table 2 shows that in PCR, the same inhibitor concentration has different degrees of inhibition on IPC fragments of different lengths, and the inhibition degree of long fragments is greater than that of small fragments. For example, in the presence of 3ng / ul humic acid, the Ct value of IPC1 is...
Embodiment 3
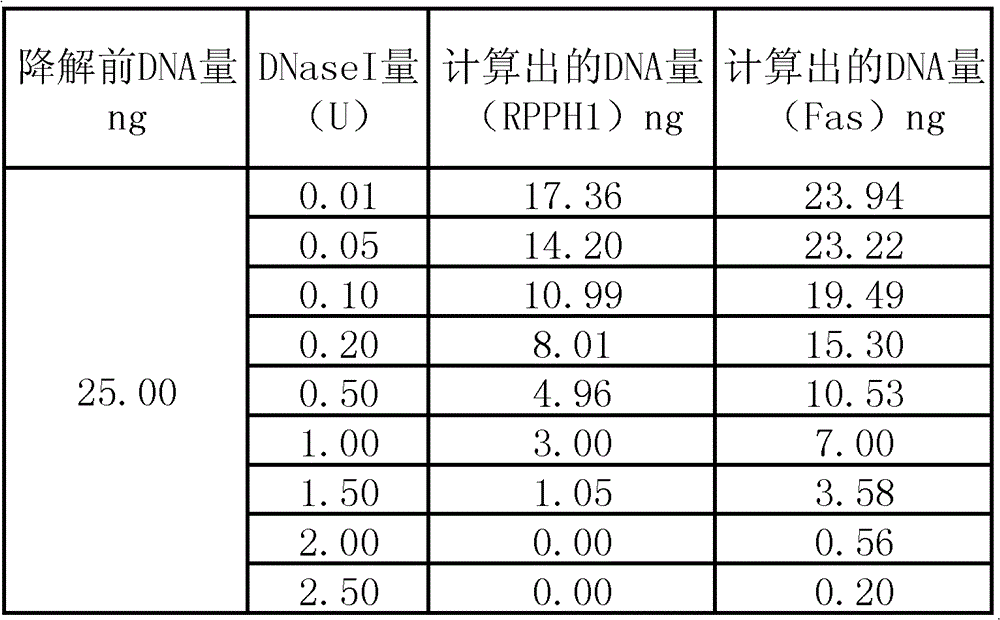
[0069] Embodiment 3: Evaluate the degradation situation of biological sample with the method of the present invention
[0070] Select 2 DNA fragments (non-overlapping regions) in the human gene TH01 (intron1 of human tyrosine hydroxylasegene), the nucleotide sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID No.23 and SEQ ID No.24 respectively, and with reference to Example 1, perform fluorescence Quantitative PCR detection. Amplification reagent components include:
[0071] (1) 2 primers for amplifying TH01 gene (its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.13 and SEQ ID No.14 respectively) and 1 FAM-labeled probe (its nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No.14) IDNo.15), the product is 135bp;
[0072] (2) 2 primers for amplifying TH01 gene (its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.16 and SEQ ID No.17) and 1 HEX-labeled probe (its nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No.17) IDNo.18), the product is 313bp;
[0073] (3) 2 primers for amplifying the internal control IPC1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com