Method for introducing radish chromosomes into cabbage
A chromosome and chromosome number technology, applied in the field of cabbage distant hybridization and utilization, can solve problems such as the inability of chromosomes to be transferred, and achieve the effects of overcoming the obstacles of distant hybridization, avoiding genetic burden, and improving the efficiency of transfer and selection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
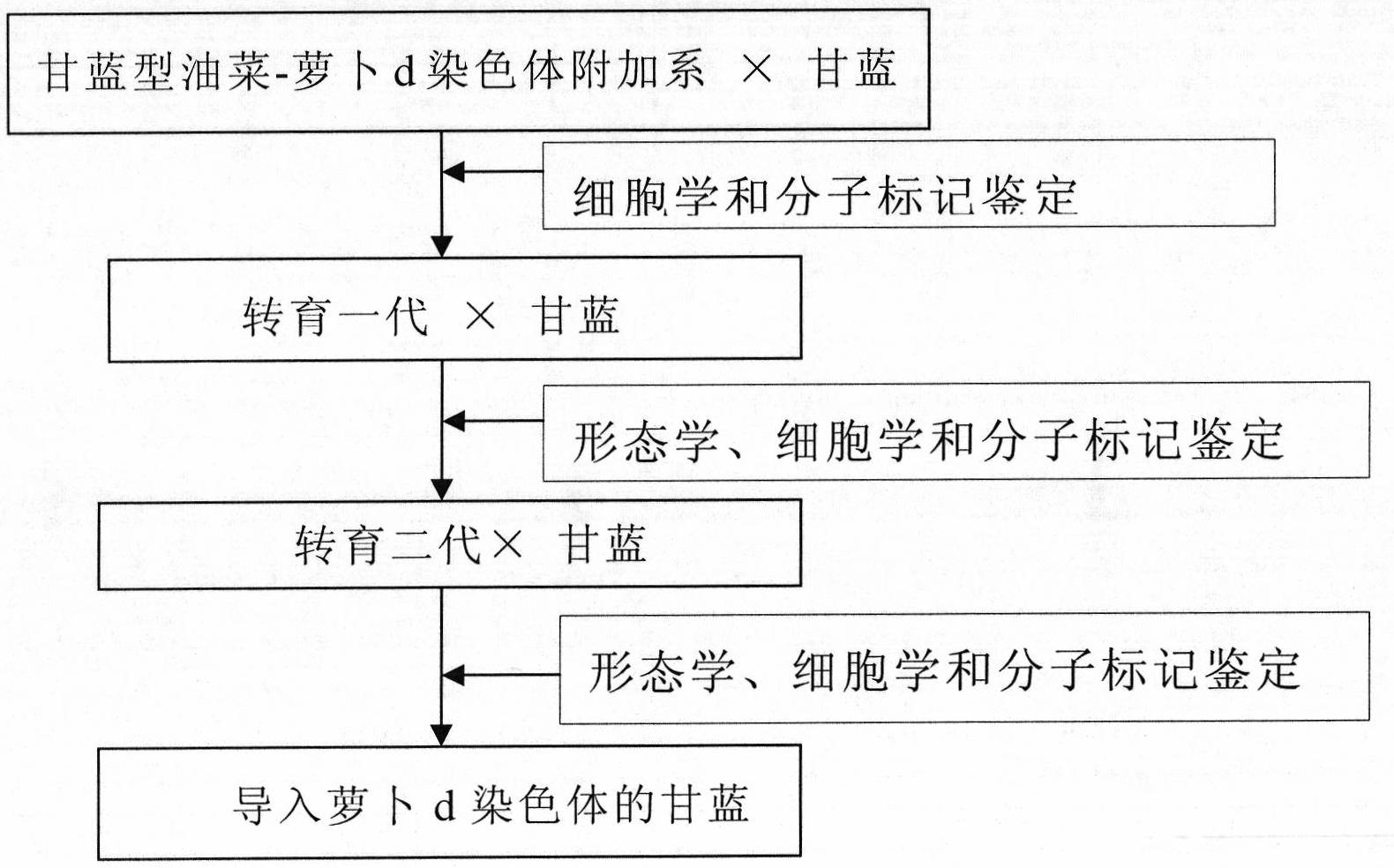
[0024] Such as figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0025] 1. Cross-pollination and ovary cultivation: take Brassica napus-radish d chromosome addition line as female parent, cabbage (commercially available to buy, variety or homozygous inbred line can be applied to the present invention, without specific limitation) Cross-pollinate the male parent. 2 to 3 days before flowering, the flowering branches of the parents were bagged and isolated separately. The female parent is emasculated at the bud stage, and the pollen of the male parent is taken and applied to the stigma of the female parent. The ovaries 7-15 days after pollination were taken for tissue culture. Medium: 1 / 2MS+inositol (10g / L)+nicotinic acid (100mg / L)+VB6(100mg / L)+VB1(1g / L)+IAA(1.5mg / L)+sucrose (50g / L ), pH=5.8. After cultivating for about a month, the seeds in the ovary are basically mature, and one generation is obtained.
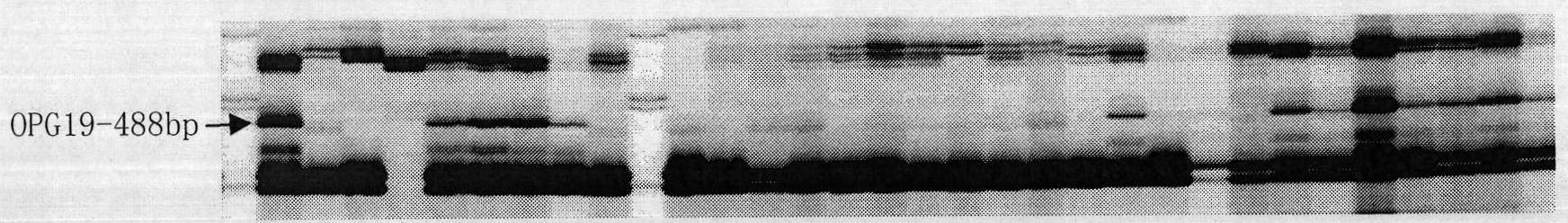
[0026] 2. Identification of the first generation of transfer: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com