Eupatorium adenophorum replacement control method by utilizing dolichos lablab L
A kind of E. japonica and alternative control technology, applied in the field of biological control, can solve the problems of weak competitiveness, poor control effect, slow growth, etc., and achieve the effects of wide ecological adaptability, good coverage, and increased fertility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
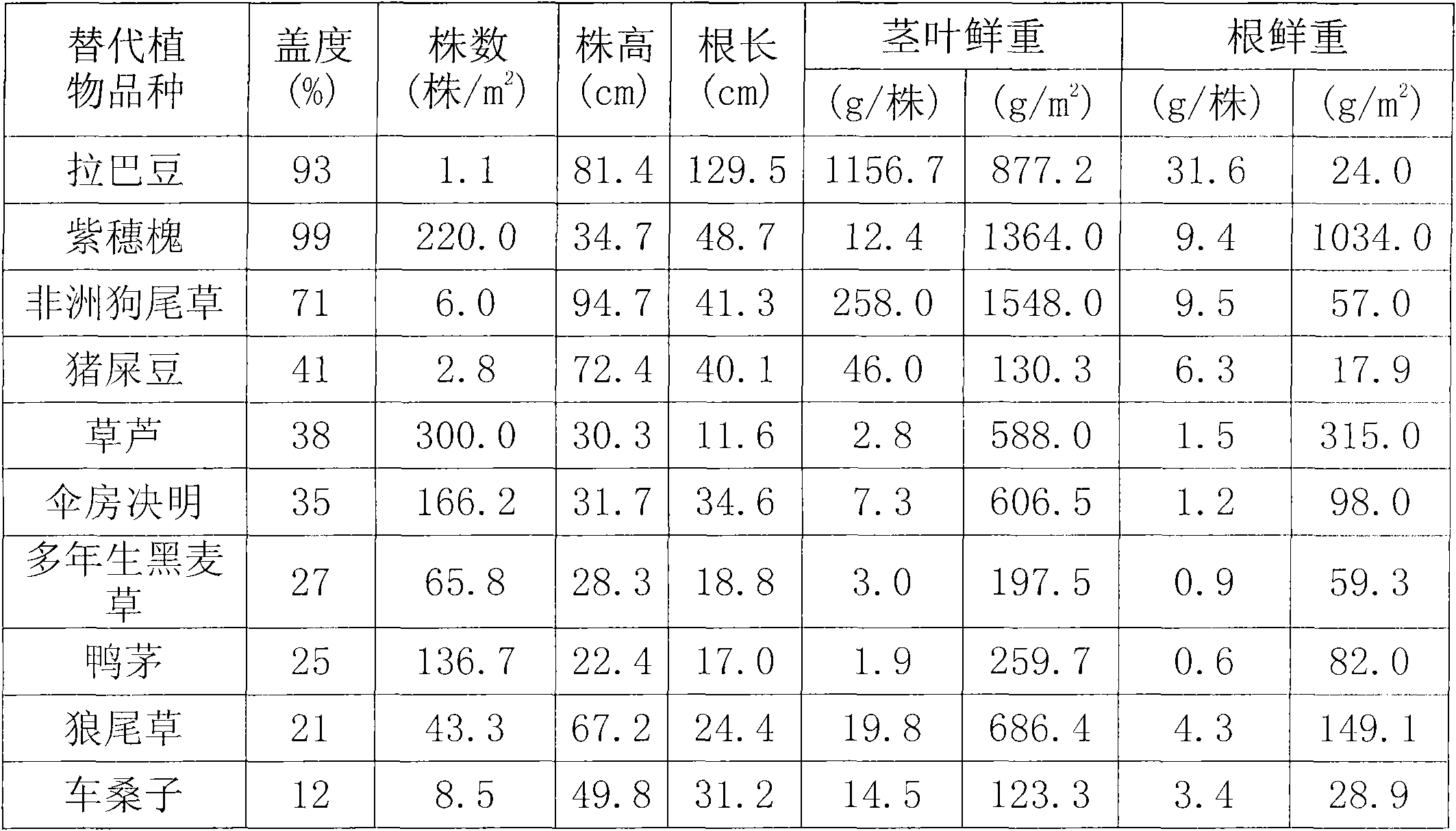
[0023] Embodiment 1: alternative plant ecological adaptability test
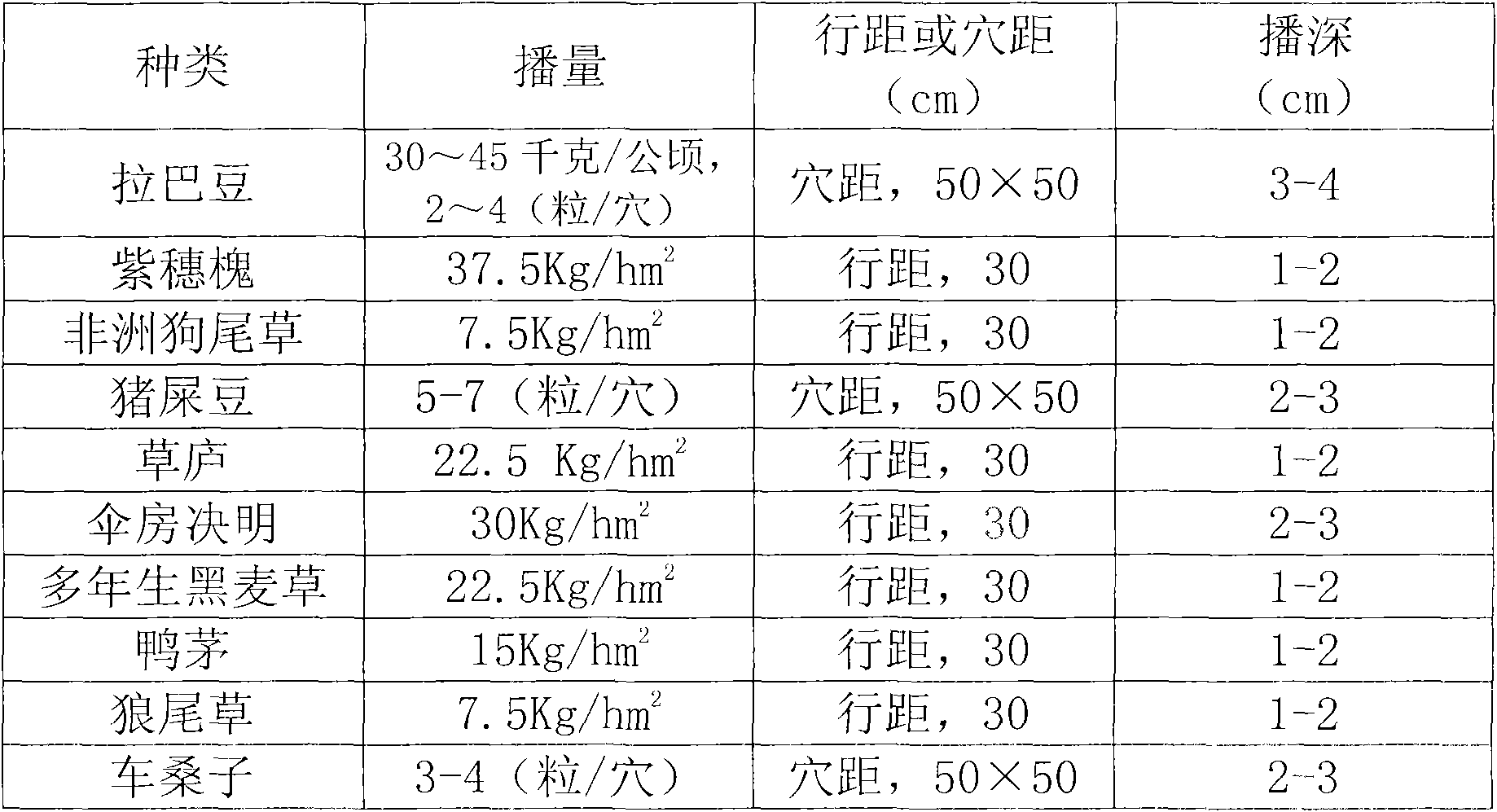
[0024] The substituted plants for the test were Labrador (provided by the Beijing representative office of the American Bailv Group), Amorpha fruticosa, African foxtail, pig dung bean, grass hut, corymbose cassia, perennial ryegrass, duck's grass, pennisetum, carnation Mulberries. The test was carried out in Chitu Village, Huishui County, Guizhou Province. The test site is located at 26.2° north latitude, 106.3° east longitude, and an altitude of about 1000m. The frost-free period is about 270 days. The annual average temperature is 14-16°C. The monthly average temperature is 4-6°C, the annual extreme maximum temperature is between 34.0-36.0°C, the extreme minimum temperature is between -6.0--9.0°C, and the annual average annual precipitation is 1100-1300mm. It is rainy, and the drought is severe from August to October.
[0025] Table 1 planting method for testing alternative plants
[0026]
[0027] T...
Embodiment 2
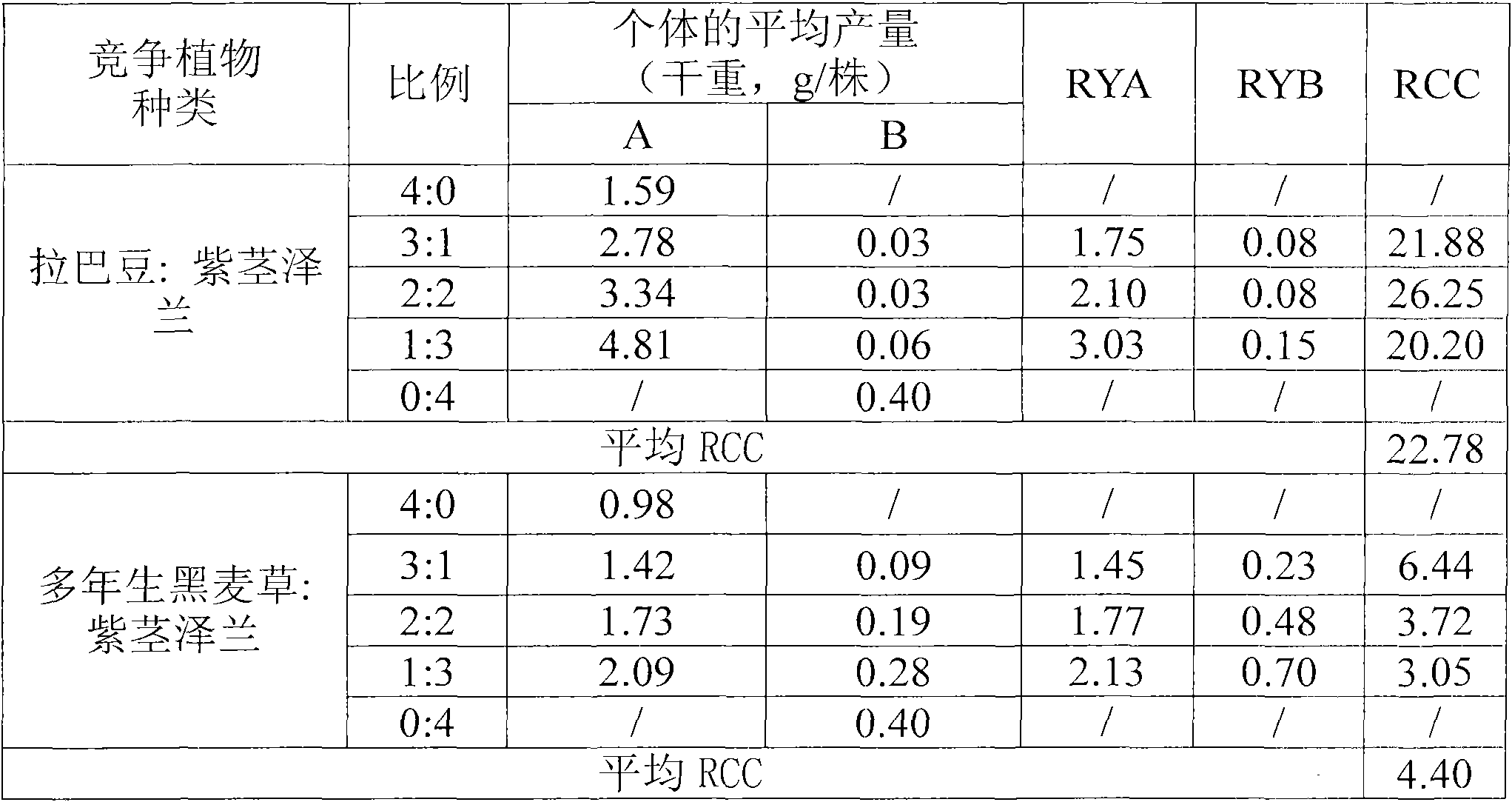
[0032] Embodiment 2: the competition test of substitute plant and Eupatorium adenophorum
[0033] The experiment was conducted outdoors in Shazi Township, Zhenning County, Guizhou Province. The species of substitute plants were Labrador and perennial ryegrass (control species), and their competition objects were Eupatorium adenophorum. The test pots are plastic pots with a diameter of 18 cm and a height of 14.8 cm. Each pot contains 2000 g of soil from the Eupatoria adenophorum invasion site. The soil is acidic yellow soil with an organic matter content of 15.6 g / Kg. Sowing on May 26, 2010, the replacement plant was sown 1 cm deep, and Eupatorium adenophorum was sown on the soil surface, and then the soil was kept moist. When the seedlings were 2-3 cm high, the replacement plant and Eupatorium adenophorum were planted in each pot. The number of plants was reserved according to the ratio of 4:0, 3:1, 2:2, 1:3 and 0:4 respectively. Fertilizers were not applied throughout the g...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: field experiment of preventing and controlling Eupatoria adenophorum by Raba bean
[0040] The test was carried out in Shazi Township, Zhenning County, Guizhou Province, about 100Km away from the site of Example 1, and to the southwest. The climate, altitude and soil texture are similar to the Huishui test site, and there was no severe drought in the test year.
[0041] The experimental site is a gentle slope mountain with a slope of 20°, and a small number of young peach trees are planted, with a density of 1 tree / 43.5m 2 , canopy density is less than 0.69. The number of Eupatorium adenophorum before site preparation (division number) was 71.7 plants / m 2 . The sowing time was May 1, 2010, when the soil moisture was good. First cut down Eupatorium adenophorum on the ground, and then divide the treatment of completely digging out the roots of Eupatorium adenophorum and the treatment of retaining the roots of Eupatorium adenophorum (that is, cutting trea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com