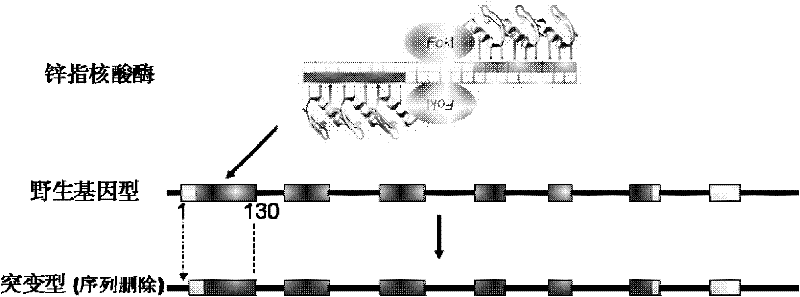
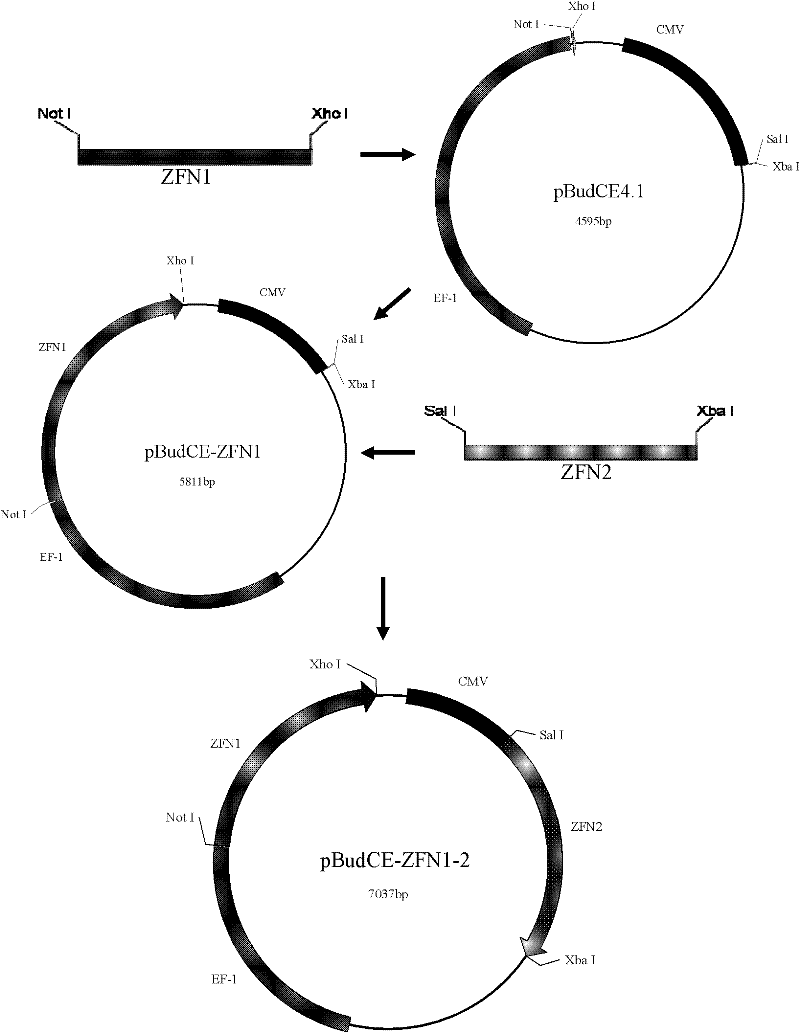
Method for knocking out cattle beta-lactoglobulin gene by using zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs)
A technology of zinc finger nuclease and lactoglobulin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of inability to obtain positive single cell clones, high risk, long cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying the biosafety evaluation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1Z
[0034] Screening and knockout efficiency of embodiment 1 ZFN expression vector
[0035] 1. Screening of ZFNs
[0036] BLG (NC_007309.4) gene sequence information was obtained from the NCBI website, and the ZFNs design was completed by Sigma Company, and the designed ZFNs sites were located on exons 1 and 2. ZFNs-Set1 and ZFNs-Set 2 act on the first exon, and ZFNs-Set 3 acts on the second exon. The DNA sequences they act on are:
[0037] ZFNs-Set 1: CC CAGGCCCTCATTGTC ACCC AGACCATGAAGGGCCTG GA;
[0038] ZFNs-Set 2: AG GCCCTCATTGTCAC CCAGACC ATGAAGGGCCTGGAT AT;
[0039] ZFNs-Set 3: CC CAGAGTGCCCCCCTGAGA GTGTA TGTGGAGGAGCTGAA GC.
[0040] The underlined parts are zinc finger protein binding sequences, and the middle part is the FokI endonuclease cleavage site. The corresponding three ZFNs expression vectors are: PZFN1 / PZFN2-set 1, PZFN1 / PZFN2-set 2 and PZFN1 / PZFN2-set 3. All three expression vectors can function in yeast, refer to Doyon et al., Nat Biotechnol, (...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 Obtaining of Single Cell Clones and Identification of Gene Knockout Clones
[0054] 1. Obtaining of single cell clones
[0055] Using the AMAXA electroporation instrument to electrotransfer bovine fibroblasts, using optimized electrotransfer parameters T-016, the gene transfection efficiency can reach more than 90%. The transfected genetic material is mRNA, and the half-life in the cell is about 8 hours. There will be no random insertion into the cell genome when the DNA is transfected, which has a good guarantee for the genetic stability of the animal. At the same time, there will be no random integration of resistance genes, which meets the requirements of biological safety.
[0056] Specific operation method: using the plasmid pBudCE-ZFN1-2 as a template, the in vitro transcribed mRNA was recovered and purified with a kit from Applied Biosystems, and eluted with DEPC water to make the final concentration about 500 ng / μl. The mRNA corresponding to a pair o...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Preparation of embryos of gene knockout single-cell clones and cloned cattle
[0061] 1. Preparation of knockout cattle
[0062] The specific process includes:
[0063] (1) Holstein cow fetal fibroblast culture
[0064] Fetal ear tissues of 40-day-old Holstein cows were taken, and the bovine fetal fibroblast cell line was established through primary culture, subculture, freezing and other in vitro culture operations.
[0065] (2) Gene knockout single cell clone
[0066] The acquisition of gene knockout single cell clones is the same as in Example 2.
[0067] (3) Transgenic cloned embryo preparation and embryo transfer
[0068] Collect the ovaries of adult cattle from the slaughterhouse, take follicles with a diameter of 2-8 mm, and recover the cumulus-oocyte-complex with uniform shape and compact structure, and divide the cumulus-oocyte-complex into 50-60 pieces Put each hole into a four-well plate containing maturation solution (M199+10% fetal bovine ser...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com