Pichia pastoris gene knockout and resistance gene recovery carrier, and construction method and application thereof
A technology of Pichia pastoris and gene knockout, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems such as difficulty in taking into account the efficiency of screening marker recovery for resistance knockout efficiency, heavy screening workload of target clones in the knockout process, and long homologous arms. Achieve the effect of improving knockout efficiency, facilitating knockout of multiple genes, and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
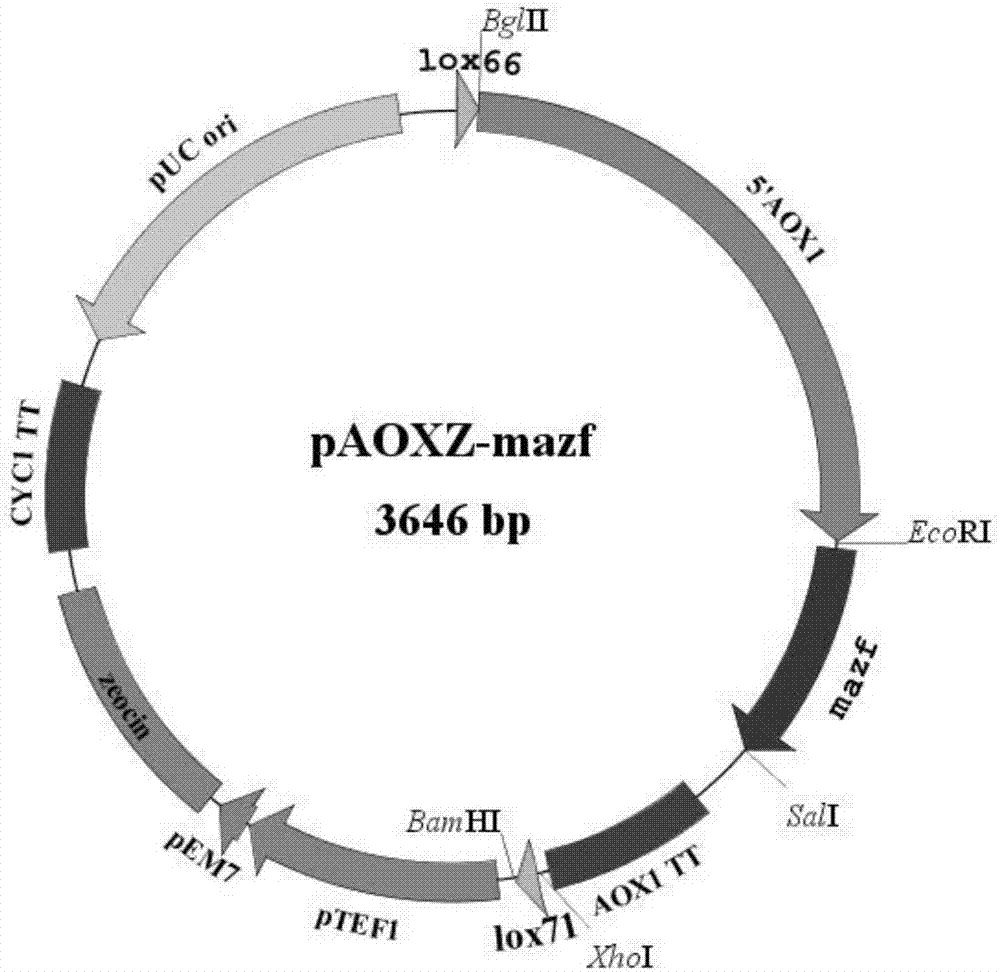
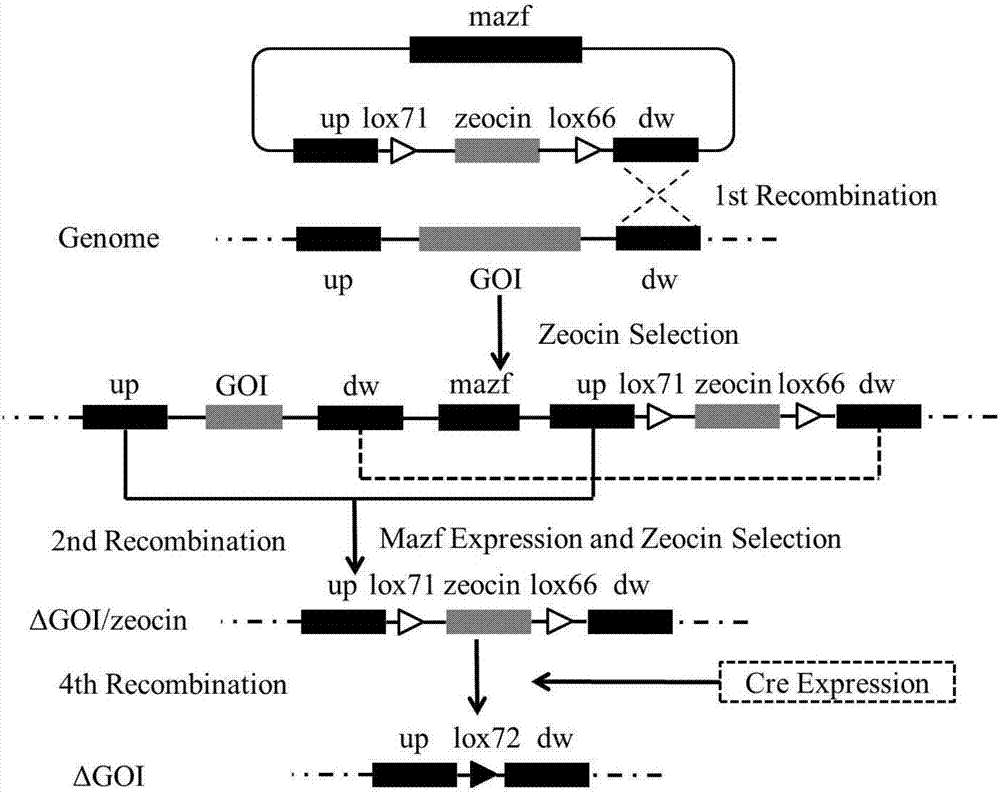
[0055] Example 1: A template vector pAOXZ-mazf for gene knockout of Pichia pastoris, such as figure 1 As shown, the template vector includes the mazf gene expression cassette and the bleomycin resistance gene expression cassette regulated by the Pichia methanol-type promoter AOX1;
[0056] The 5' end of the mazf expression cassette contains a restriction site A for inserting a homologous fragment downstream of the gene to be knocked out, and the 5' end of the restriction site contains a lox66 site recognized by the Cre-specific recombination system;
[0057] The 3' end of the mazf expression cassette contains a restriction site B for inserting the upstream homologous fragment of the gene to be knocked out, and the 3' end of the restriction site contains the lox71 site recognized by the Cre-specific recombination system;
[0058] The bleomycin resistance gene expression cassette is located between the 5' end of the lox66 site and the 3' end of the lox71 site; the restriction si...
Embodiment 2
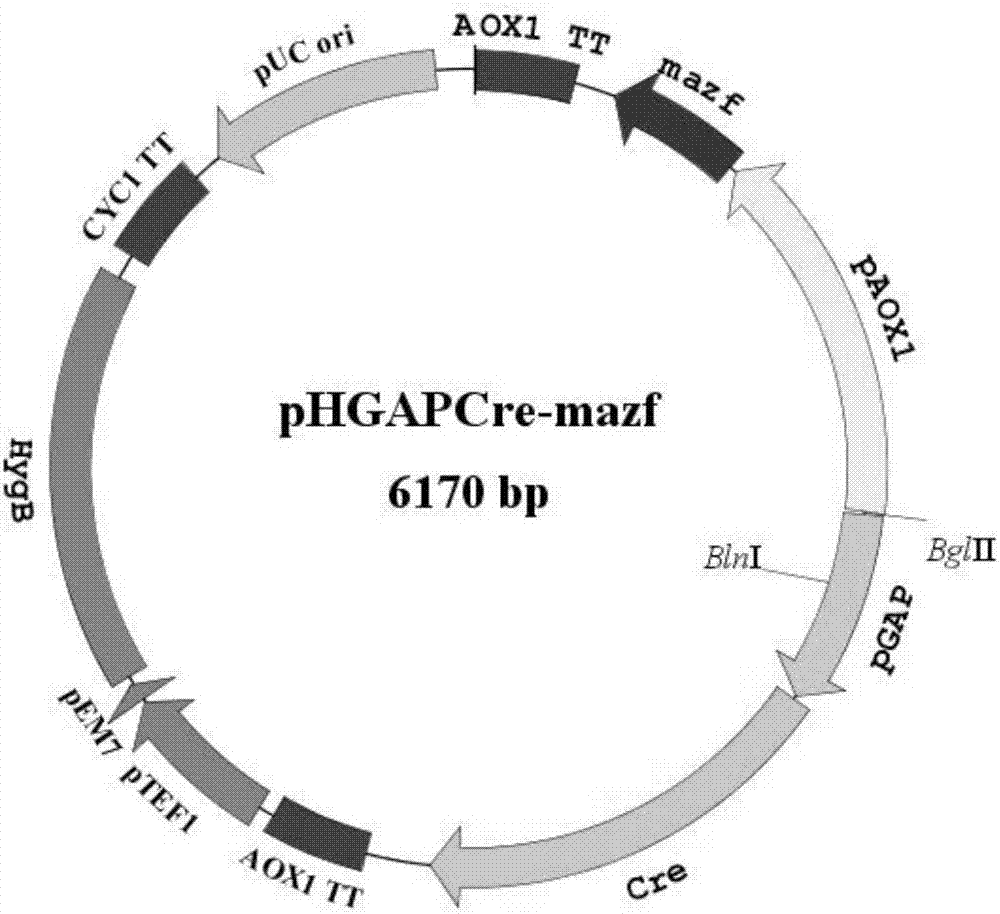
[0059] Embodiment 2: a kind of Pichia pastoris gene resistance gene recovery carrier pHGAPCre-mazf, such as figure 2 As shown, the recovered vector includes: the mazf gene expression cassette AOX1-mazf-AOX1TT regulated by the Pichia methanolic promoter AOX1, the Cre gene expression cassette GAP-Cre-AOX1TT constitutively expressed by the GAP promoter, and HygB resistance The gene expression cassette TEF1-HygB-CYC TT; the mazf gene expression cassette and the Cre gene expression cassette are in opposite directions on the pHGAPCre-mazf recovery vector; the GAP promoter contains at least one recovery vector in the pHGAPCre-mazf The only enzyme cleavage site present.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3: Construction of the template vector pAOXZ-mazf for Pichia pastoris gene knockout
[0061] (1) Using Escherichia coli DH5α cells as a template, using primers mazf-F and mazf-R to amplify the mazf gene by colony PCR, introducing EcoR I and Sal I restriction sites at both ends of the gene, agarose gel Recovery and purification after electrophoresis;
[0062] (2) Purify and recover after double digestion with EcoR I and Sal I, and then digest the commercialized vector pPICZA with EcoR I and Sal I (removing the Xho I restriction site of the vector itself) and gel the recovered vector in 3 :1 mixed, transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells through Takara's ligation kit Solution I at 16°C for 1 h, the clones were screened on an LLB plate containing 25 μg / mL zeocin, and the grown clones were randomly selected to extract plasmids After enzyme digestion verification, it was named pPICZA-mazf after sequencing verification;
[0063] (3) Using pPICZA-mazf ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com