Method for generating live yeast cell derivative (LYCD) through natural stacking fermentation
A technology of active yeast and natural accumulation, applied in the biological field, can solve the problem of not seeing active yeast cell derivatives
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A method for naturally accumulating fermentation to produce active yeast cell derivatives, comprising the following steps:
[0024] (1) The fermentation substrate is mainly crushed and gelatinized sorghum, and other raw materials can be used for solid-state fermentation. Gelatinization, cooling, adding traditional high-temperature Daqu, mixing evenly, stacking, accumulating and fermenting. The amount of koji, the degree of gelatinization of raw materials, and the degree of stacking fermentation are routinely adjusted according to the natural fermentation situation. Fermentation can be repeated multiple times;
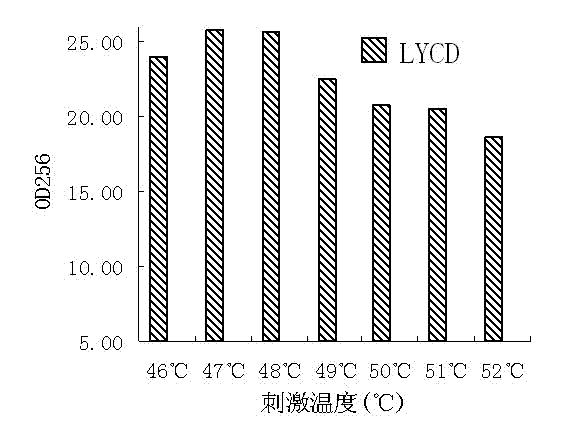
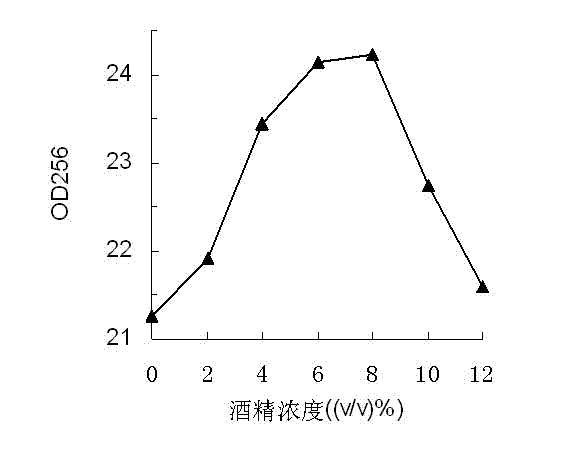
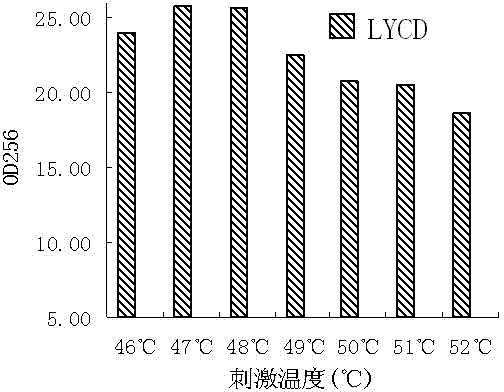
[0025] (2) Fermentation time: 3 to 7 days, the fermentation is terminated when the temperature of the fermentation substrate is 52°C and the alcohol concentration is 12% (v / v);
[0026] (3) Centrifuge at 2000g for 20min to collect the bacteria, wash once with sterile water, then add medium to continue culturing for 2h, centrifuge, freeze in liquid nitrogen to b...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A method for naturally accumulating fermentation to produce active yeast cell derivatives, comprising the following steps:
[0029] (1) The fermentation substrate is mainly crushed and gelatinized sorghum, and other raw materials can be used for solid-state fermentation. Gelatinization, cooling, adding traditional high-temperature Daqu, mixing evenly, stacking, accumulating and fermenting. The amount of koji, the degree of gelatinization of raw materials, and the degree of stacking fermentation are routinely adjusted according to the natural fermentation situation. Fermentation can be repeated multiple times;
[0030] (2) Fermentation time: 3 to 7 days, when the temperature of the fermentation substrate is 48°C and the alcohol concentration is 2% (v / v), the fermentation is terminated;
[0031] (3) Centrifuge at 2000g for 20min to collect the bacteria, wash once with sterile water, then add medium to continue culturing for 2h, centrifuge, freeze in liquid nitrogen to b...
Embodiment 3
[0033] A method for naturally accumulating fermentation to produce active yeast cell derivatives, comprising the following steps:
[0034] (1) The fermentation substrate is mainly crushed and gelatinized sorghum, and other raw materials can be used for solid-state fermentation. Gelatinization, cooling, adding traditional high-temperature Daqu, mixing evenly, stacking, accumulating and fermenting. The amount of koji, the degree of gelatinization of raw materials, and the degree of stacking fermentation are routinely adjusted according to the natural fermentation situation. Fermentation can be repeated multiple times;
[0035] (2) Fermentation time: 3 to 7 days, the fermentation is terminated when the temperature of the fermentation substrate is 46°C and the alcohol concentration is 4% (v / v);
[0036] (3) Centrifuge at 2000g for 20min to collect the bacteria, wash once with sterile water, then add medium to continue culturing for 2h, centrifuge, freeze in liquid nitrogen to br...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com