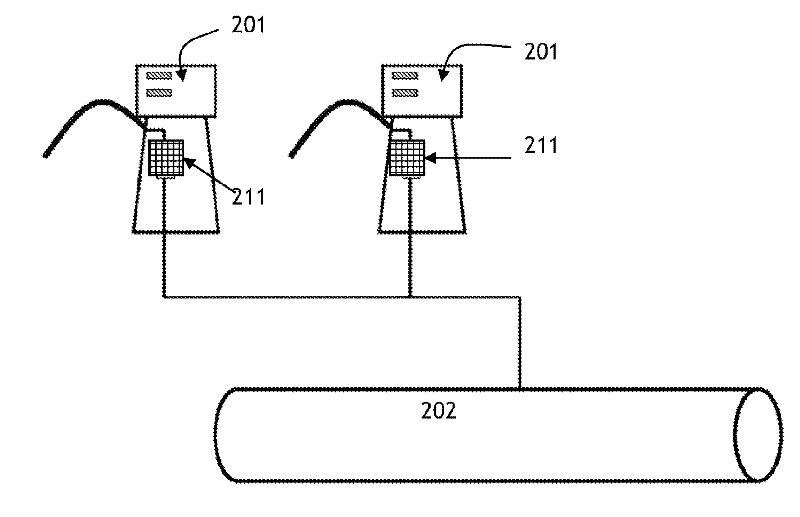
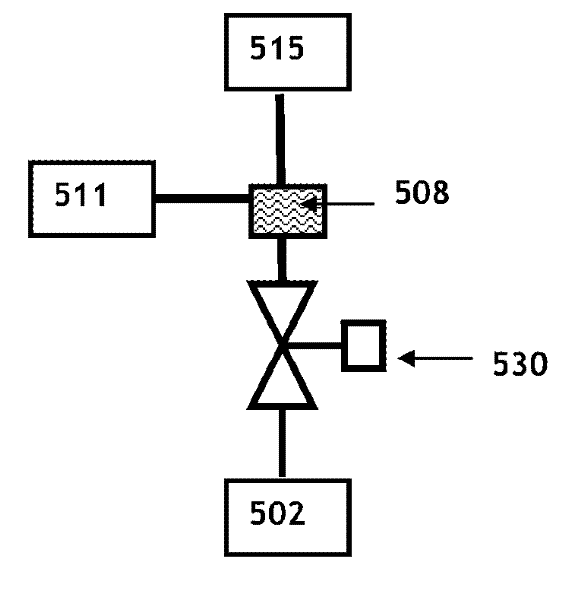
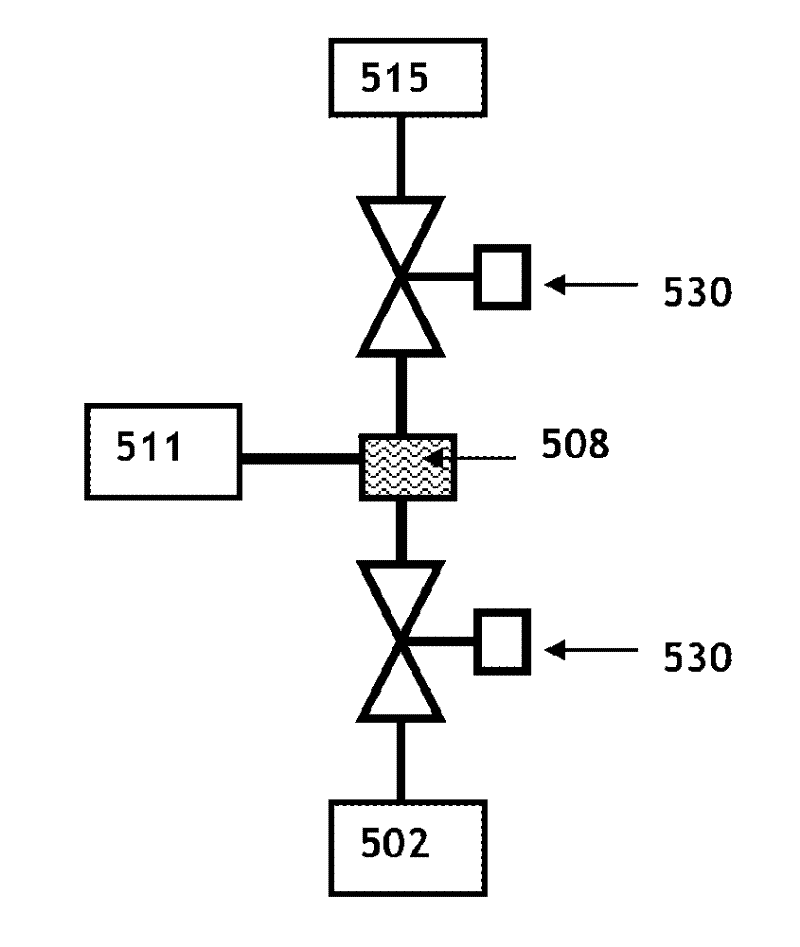
Fuel vapor management system with proportioned flow splitting
A technology of fuel vapor and management system, which is applied in the field of fuel vapor management system with proportional split flow, which can solve the problems of carbon bed not regenerating, low efficiency, increasing the size of tank and regenerative vacuum pump, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0057] Example 1 : If 70oF, 9 psi fuel is delivered at 10 gpm from UST to refuel a vehicle initially containing 60oF, 9 psi fuel, then the air and gasoline vapors will exit the vehicle at a rate of approximately 10.6 gallons per minute. If the vapor management system is operating at 80% recovery efficiency and an A / L ratio of 1.1, the system can extract 26.6% hydrocarbon vapor at 11 gpm. The return vapor stream can be split to send 3.4 gal / min to the vapor collection device and 7.6 gal / min back to the UST. Approximately 1.1 liters of honeycomb activated carbon are required to adsorb the 19 grams of hydrocarbons delivered to it over the course of two minutes. After refueling is complete, the tank can be purged with purge air at a flow rate of 0.9 gallons per minute at an operating pressure of 250 mbar in less than one minute. Under the above operating conditions, a gauge pressure of -6 inches of water can be maintained within the UST.
example 2
[0058] Example 2 : If six vehicles are refueled simultaneously at three dispenser units by delivering fuel at 70oF with a Reid vapor pressure of 7 psi at 60 gpm, each initially containing 80oF, Reid vapor With fuel at a pressure of 9 psi, air and gasoline vapors would be expelled from all vehicles at a rate of approximately 56.5 gpm. If the vapor management system is operating at 100% recovery efficiency and an A / L ratio of 1.2, the vapor management system can extract air and vapor at 20.6% concentration at 72 gpm. If the vapor management system is operating with a single diverter on the vapor return manifold, the return vapor flow can be split to send 23.6 gallons per minute to six groups of vapor collection devices (the amount to each group is 3.9 GPM) and 48.4 GPM back to UST. Approximately 1.4 liters of honeycomb activated carbon are required to adsorb the 22.7 grams of hydrocarbons sent to each adsorber over a period of two minutes. After refueling is complete, each t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com