Detection-information-fusion-based wireless sensor network deterministic deployment method
A wireless sensor and information detection technology, applied in network planning, network topology, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as lack of effective methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Equilateral triangle deployment method
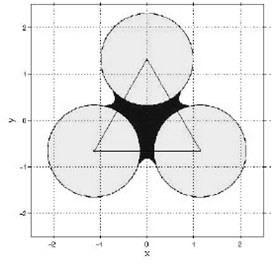
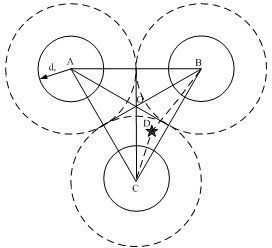
[0034] In the deterministic deployment strategy of wireless sensor networks, the equilateral triangle deployment method is a common deployment method. The so-called equilateral triangle deployment method refers to the arrangement of sensor nodes in an equilateral triangle manner, such as figure 1 Shown. figure 1 Among them, the center position of the three circles is the deployment position of the sensor node. The sensing range of the sensor node is the circle with the sensor node as the center and radius r. If the cooperative information processing capability (ie, physical coverage) between sensor nodes is not considered, When the distance d between the target and at least one sensor node is not greater than r, the target can be detected, otherwise it cannot be detected. figure 1 The middle circular area is the sensing range of a single sensor node, and the black area between the circles is the area that can be sensed ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Embodiment 2: Square deployment mode
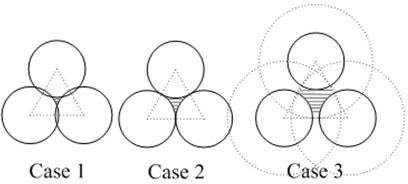
[0063] Similar to the equilateral triangle deployment method, the square deployment method requires the sensor nodes to be arranged in a square manner, such as Image 6 Shown. There are also three situations in square deployment, such as Figure 7 Shown. Case1 indicates that the sensing ranges of sensor nodes have intersections, Case2 indicates that the sensing ranges of sensor nodes are just tangent, and Case3 indicates that the sensing ranges of sensor nodes do not have intersections. As the separation distance between sensor nodes becomes larger, the area that needs to use cooperative information processing to detect targets becomes larger, such as Figure 7 Part of the horizontal line area.
[0064] When the number of sensor nodes for detecting information fusion is K=2, the optimal linear unbiased estimation method is used to calculate the estimated value of the target feature parameter θ And parameter estimation error The follo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com