Porous microspheres for medicine carriers, preparation method and medicine loading method
A technology of porous microspheres and drugs, applied in the field of drug loading, can solve the problems of uneven particle size and pore size distribution of porous microspheres, uncontrollable release, low drug activity, etc., achieve the same bumping speed, increase loading rate, and maintain The effect of biological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
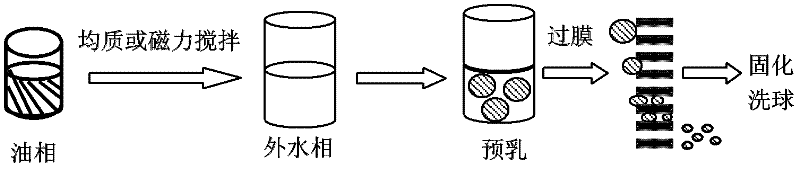
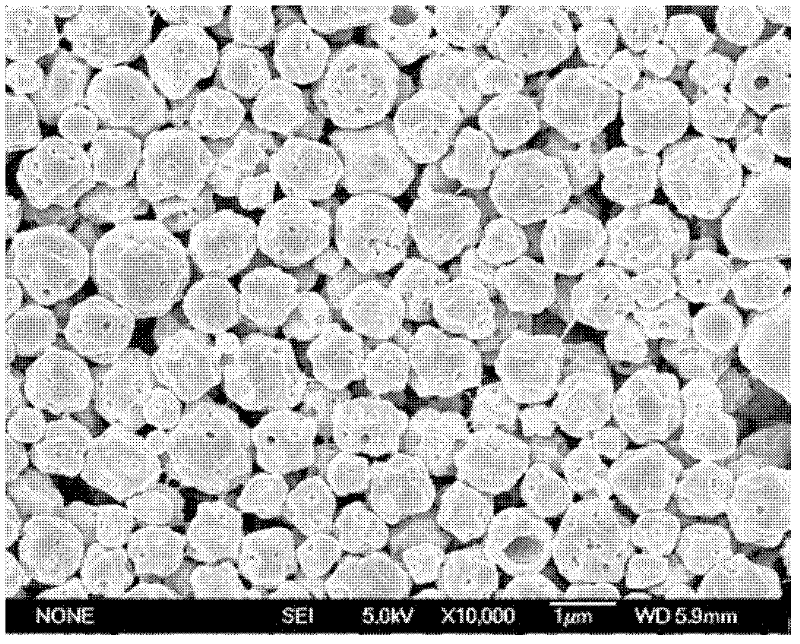
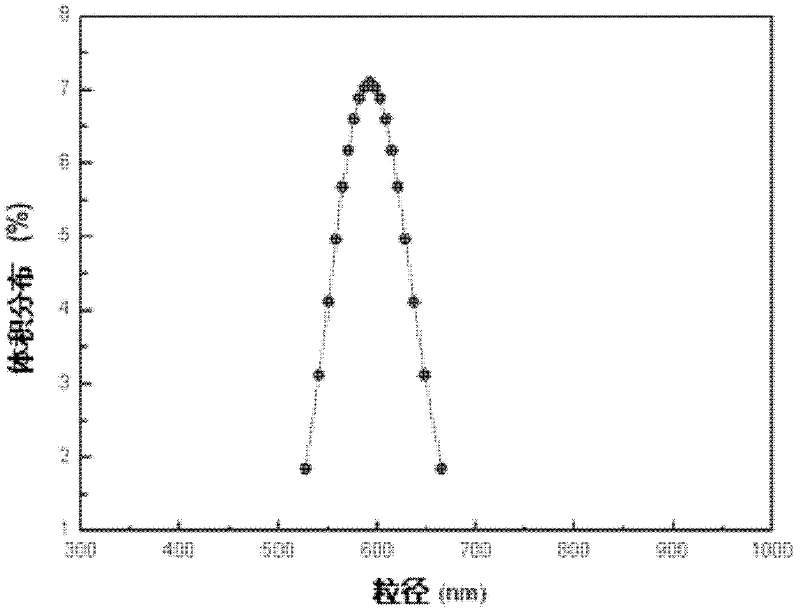
[0059] The hydrophilic microporous membrane with a pore size of 2.8 μm is soaked in water to fully wet the porous membrane. The molecular weight of 0.4g is 10,000 polylactic acid-polyethylene glycol copolymer (PELA) (the proportion of hydrophilic block is 4%) is dissolved in 8ml methylene chloride, as oil phase, this oil phase Join in the polyethylene glycol (PVA) aqueous solution of 1%wt of 80ml, the ratio of oil phase and water phase is 1: 10, magnetic stirring 300rpm stirs 1min and prepares pre-emulsion, then this pre-emulsion is under the operating pressure of 400kPa Pressed through a microporous membrane device (such as figure 1 ) to obtain an emulsion, and the membrane passing time of the emulsion is less than 10s, then the emulsion is stirred at room temperature for 24h to remove the organic solvent methylene chloride, and then centrifuged to obtain the drug-loaded microspheres. The obtained microspheres were vacuum-dried for 48 h to obtain finished microspheres. The ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The hydrophilic membrane with a pore size of 7.2 μm is soaked in water to fully wet the porous membrane. 0.7g of molecular weight is 50,000 polylactic acid-polyglycolic acid and polyethylene glycol copolymer (the proportion of hydrophilic block is 10%) dissolved in 10ml of chloroform, as the oil phase, the oil Phase is added in the PVA aqueous solution of 50ml 1.2%wt, and the ratio of oil phase and water phase is 1: 5, and magnetic stirring 300rpm stirs 1min to prepare pre-emulsion, and then this pre-emulsion is pressed through the microporous membrane under the operating pressure of 200kPa device to obtain an emulsion, and the membrane-passing time of the emulsion is less than 10s, and then the emulsion is stirred at room temperature for 24 hours to remove the organic solvent chloroform, and then centrifuged to obtain the drug-loaded microspheres. The obtained microspheres were vacuum-dried for 48 h to obtain finished microspheres. The dried microspheres were redisper...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The hydrophilic membrane with a pore size of 9 μm is soaked in water to fully wet the porous membrane. The molecular weight of 0.8g is 20,000 polylactic acid-polyethylene glycol copolymer (the proportion of hydrophilic block is 20%) is dissolved in 15ml carbon disulfide, as oil phase, this oil phase is added to 300ml of 1.4 In the PVA aqueous solution of %wt, the ratio of oil phase and water phase is 1: 20, magnetic stirring 300rpm stirs 1min to prepare pre-emulsion, then this pre-emulsion is pressed through the microporous membrane device under the operating pressure of 150kPa, obtains emulsion, emulsion The membrane passing time is less than 10s, and then the emulsion is stirred at room temperature for 24 hours to remove the organic solvent chloroform, and then centrifuged and washed to obtain the drug-loaded microspheres. The obtained microspheres were vacuum-dried for 48 h to obtain finished microspheres. The dried microspheres were redispersed in water, and the su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com