Method for distributed overcurrent protection and phase-to-phase fault isolation in distribution network
A phase-to-phase fault and overcurrent technology, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of inability to meet the requirements of the substation protection allowable range, long fault isolation time, and the impact of switch life, to avoid multiple switch splits. Combined operation, small power failure impact, reducing time-consuming and labor-intensive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
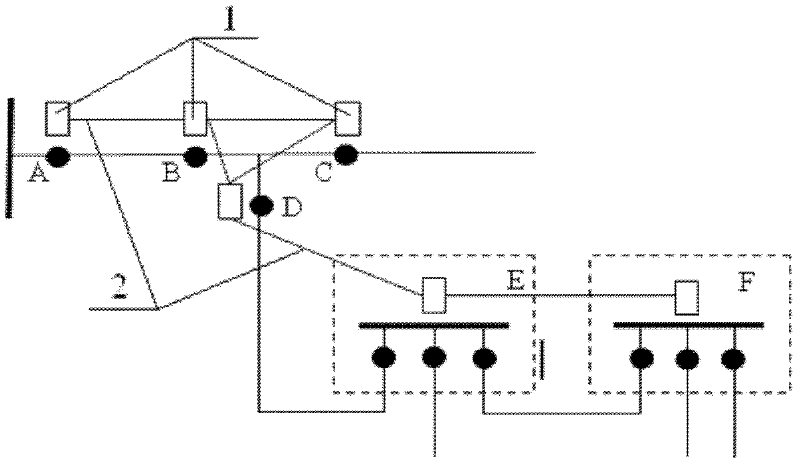
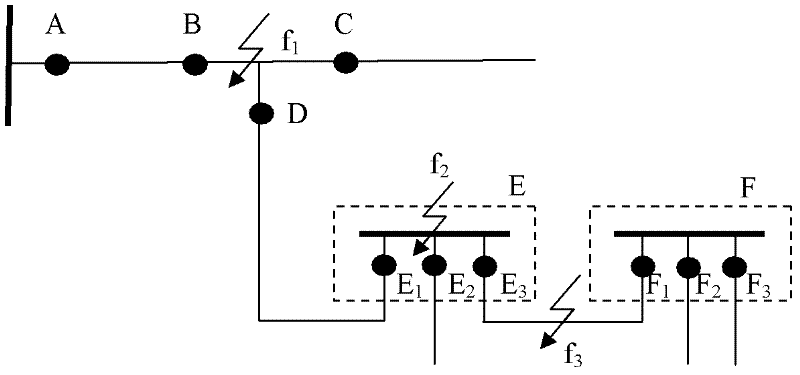
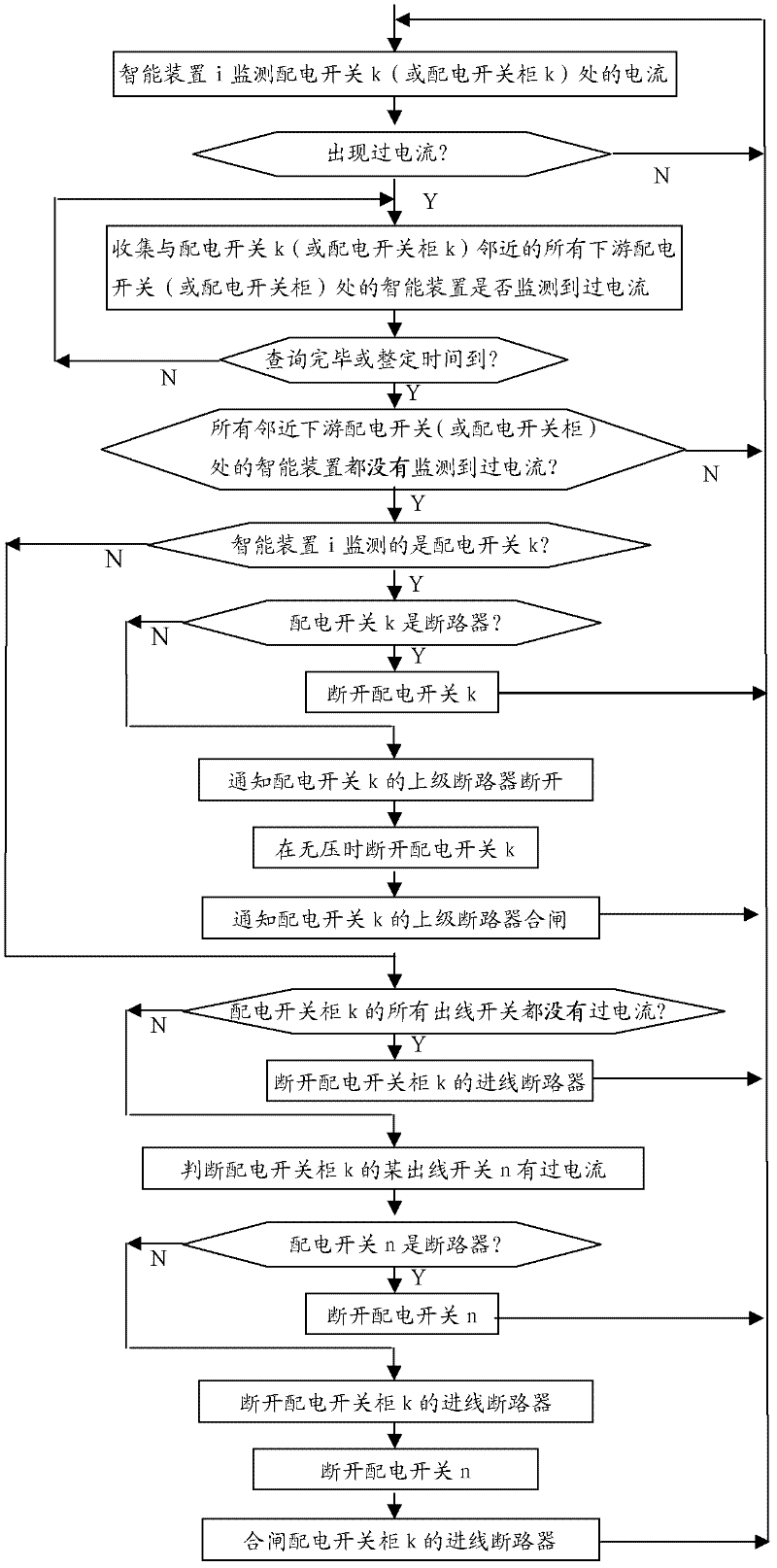
[0049] See attached Figure 4 As shown in the radial distribution network with branches, if a phase-to-phase short-circuit fault occurs on the CD line, the distribution switches A, B, and C all detect overcurrent, and the distribution switches D, E, and F do not detect the overcurrent. Switch A inquires that distribution switch B has detected overcurrent, so it is judged that the fault is not in the AB line; power distribution switch B inquires that distribution switch C has detected an overcurrent, so it judges that the fault is not in the BC line; power distribution switch C inquires about the power distribution Switch D does not detect overcurrent, so it is judged that the fault is on the CD line, and the power distribution switch C is disconnected to isolate the fault. If a phase-to-phase short-circuit fault occurs on the BC line, distribution switches A and B monitor overcurrent, and distribution switches C, D, E, and F do not detect overcurrent. Therefore, it is judged t...
Embodiment 2
[0051] See attached Figure 5 As shown, the present invention is applied to the hand-in-hand distribution network. If a phase-to-phase short-circuit fault occurs on the AB line, the distribution switch A detects an overcurrent, and the distribution switch A inquires that the distribution switch B has not detected an overcurrent, so it is judged that the fault occurred on the AB line, and the distribution switch A is disconnected to isolate the fault. . If a phase-to-phase short-circuit fault occurs on the BC line, the distribution switches A and B both monitor the overcurrent, and the distribution switch A inquires that the distribution switch B detects the overcurrent, so it is judged that the fault is not in the AB line; the distribution switch B inquires the power distribution Switch C does not detect overcurrent, so it is judged that the fault occurred on the BC line, and the power distribution switch B is disconnected to isolate the fault. If a phase-to-phase short-circ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] See attached Image 6 As shown, the present invention selects hand in hand multi-contact distribution network for use. If a phase-to-phase short circuit fault occurs on the HI line, the distribution switches I and J both monitor overcurrent, and the distribution switch J inquires that the distribution switch I monitors the overcurrent, so it is judged that the fault is not in the IJ line; the distribution switch I inquires about the power distribution Switches H and K have not detected overcurrent, so it is judged that the fault occurs in the HI line or KI line, the power distribution switch I is disconnected, and the power distribution switches H and K are notified to be disconnected to isolate the fault.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com