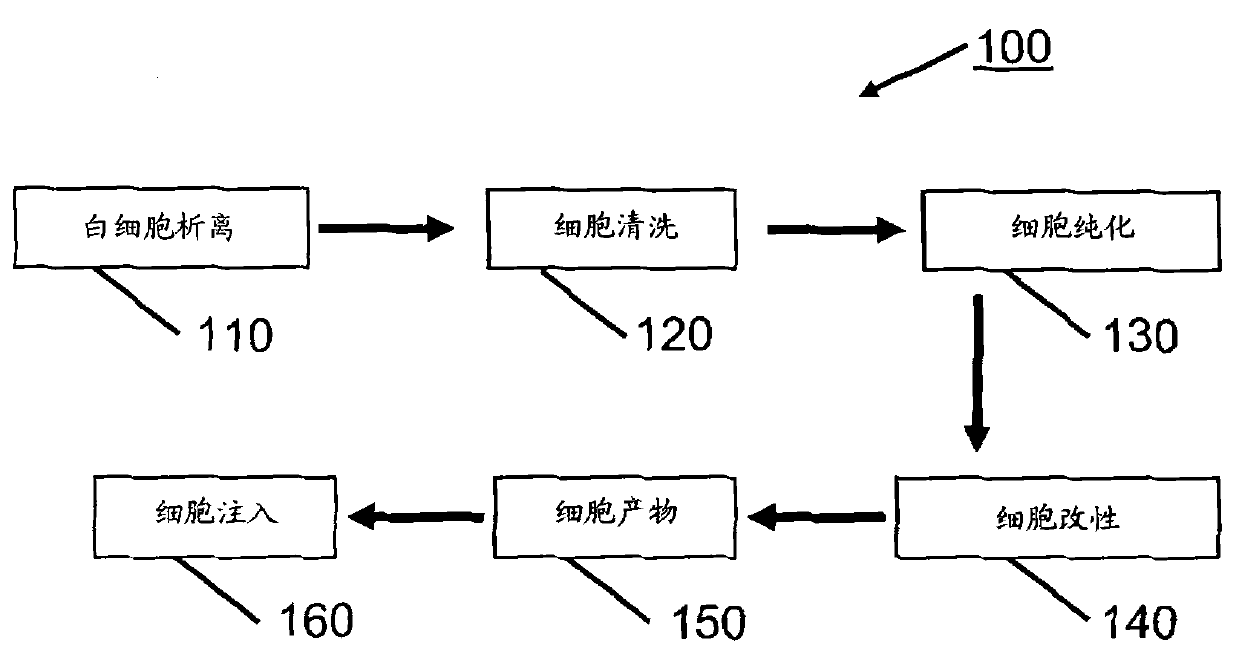
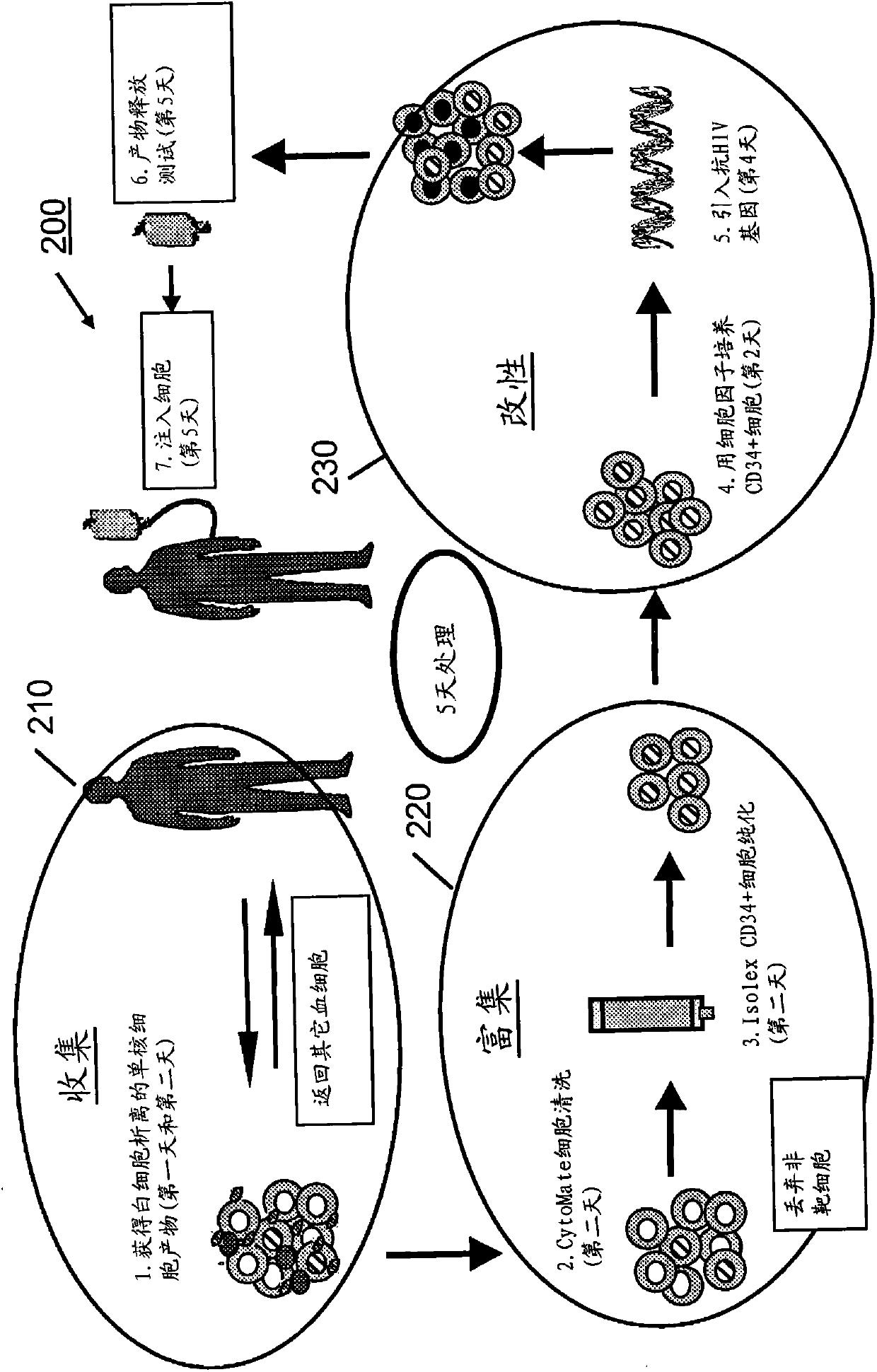
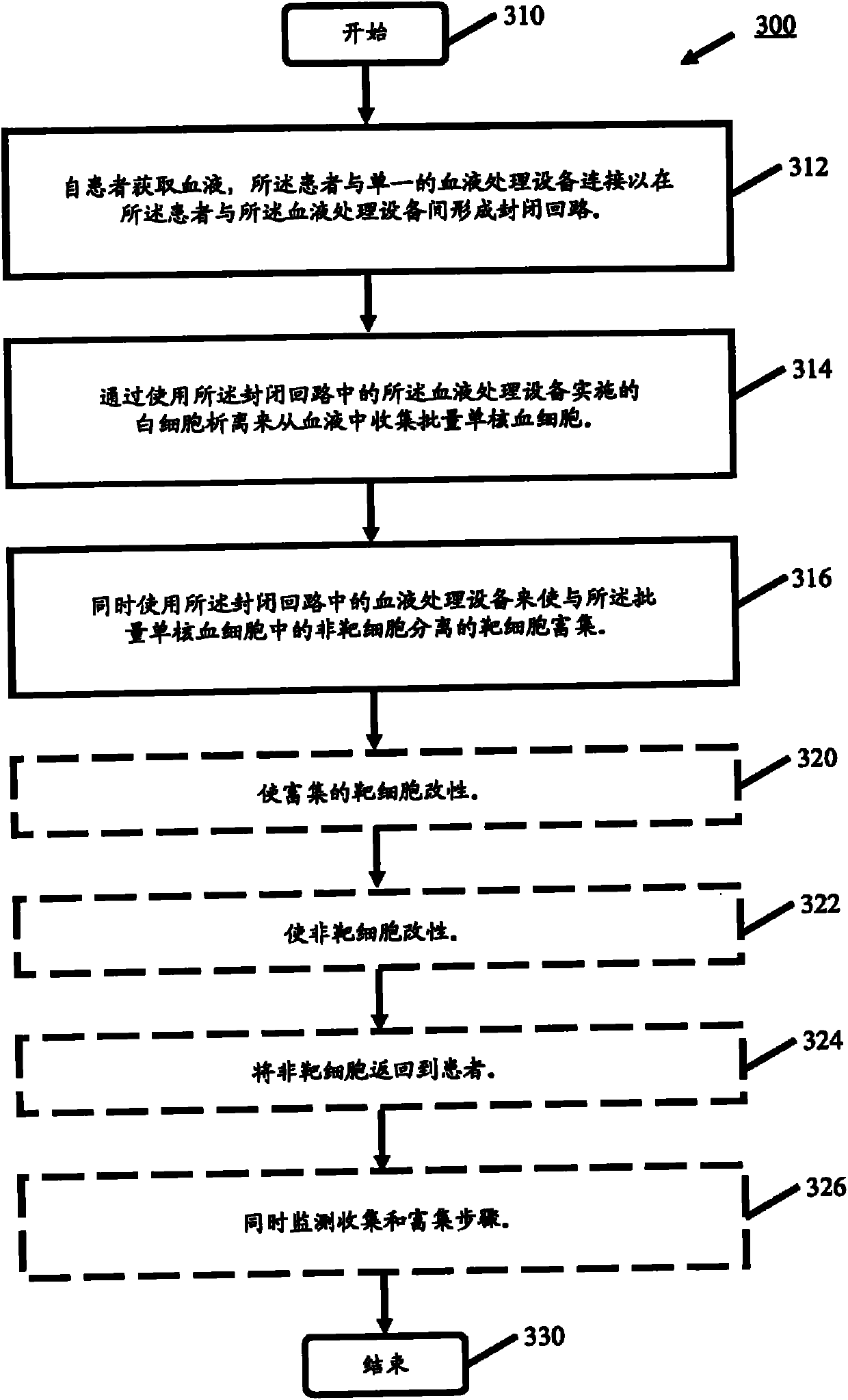
processing blood
A blood and blood processing technology, applied in the field of white blood cell separation, can solve the problems of lymphocyte loss, waste of materials, manpower and cost, and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0107] Example 1. Collection of monocytes and enrichment of CD4+ T lymphocytes from peripheral blood
[0108] Bags of peripheral blood were prepared to represent pseudo patients. Collect 4 units of ABO-matched whole blood from healthy donors into ACD-A anticoagulant 1-2 days before use. The blood of the plurality of units was leukocyte-depleted by filtration through a Sepacell leukocyte-reducing filter, and pooled into a 2L blood bag. A leukopak buffy coat was added to bring the white blood cell count to a physiological concentration, and the sham patient bag was kept on a rocking platform at room temperature to ensure a homogeneous cell suspension. A 10 mL sample was taken from the pseudo patient bag and the baseline cell composition was determined by electronic cell counting and automatic differentiation on a Beckman Coulter Act counter, and by using the included CD45-FITC, CD3-PECy7, CD4-APC, CD8-PECy5, CD14 - Flow cytometry of monoclonal antibody panels including PECy7...
example 2
[0127] Example 2. Collection of monocytes from peripheral blood and enrichment of CD8+ cells
[0128] overview
[0129] Figure 12 shown with Figure 7 System 700 is related to improvement of system 1200 . For the sake of brevity, Figure 7 and Figure 12 Like features in the system 1200 retain the same reference numerals (e.g., Figure 7 and Figure 12 Anticoagulant pump 712 in . In addition, unless expressly described below, Figure 12 These like-numbered features in the system 1200 also retain the same configuration. Figure 12 The system 1200 is a blood processing device that involves collection and enrichment (type 2) and contains 3 new bags, 6 new clamps and 2 magnets. Such as Figure 12 As shown, a modification of the standard CellEx process kit was made. A CLINIcell 25 bag 1278 was used instead of the photoactivation chamber. Patients 1200 in Figure 12 Denoted as patient bag #1 1206 in , the patient bag #1 is connected to the return node 756, and the ...
example 3
[0152] Example 3. Collection of monocytes from peripheral blood and enrichment of CD34+ cells
[0153] The collection and enrichment of CD34+ cells can be carried out as described in Examples 1 and 2 using substances that specifically bind to CD34.
[0154] Enrichment of CD34+ cells from collected monocytes
[0155] In one embodiment of the invention, the subject may be mobilized using granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF). Following completion of standard CellEx monocyte collection, washes were performed with cell enrichment buffer PBS / EDTA (Miltenyi) supplemented with HSA and CD34+ selection beads (Miltenyi) introduced via the needle-free access port of the "collection bag". The monocyte and bead mixture was incubated for 30 minutes while recirculating through the trapping module of the modified CellEx single-use kit and by transferring the cells via a peristaltic pump to a Miltenyi CliniMACS magnet at approximately the manufacturer's recommended flow rate. sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com