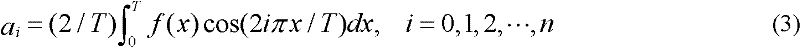A Calibration Method of Electronic Compass
An electronic compass and calibration method technology, applied in the field of directional navigation, can solve the problems of increased cost, large amount of data, and unsatisfactory compensation effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
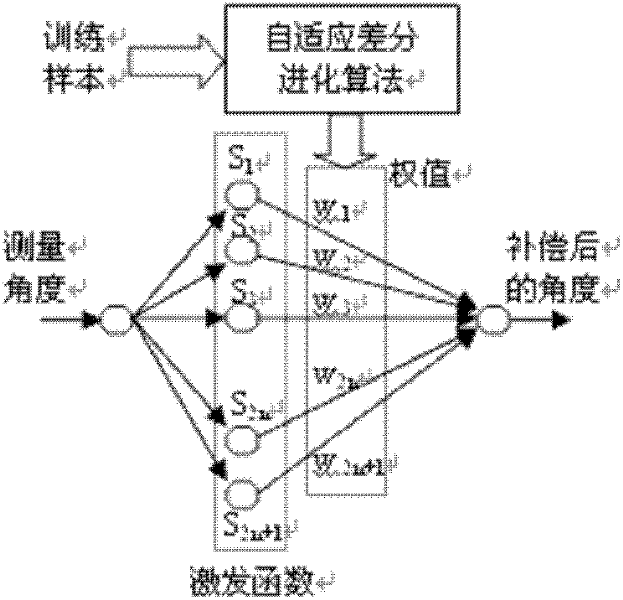
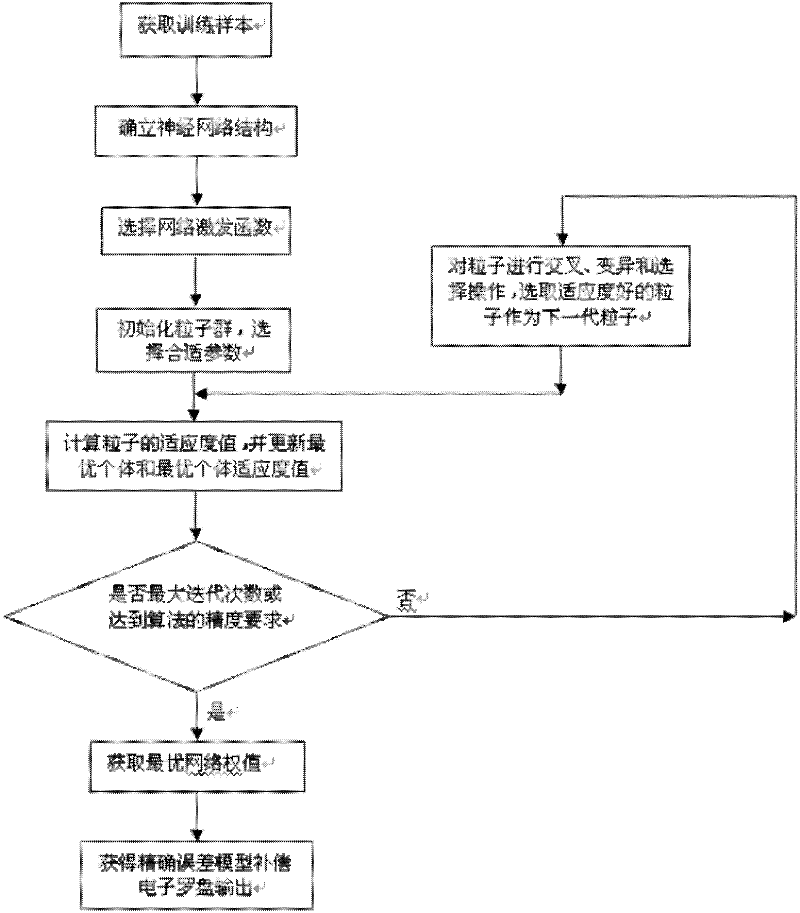
[0056] Attached below figure 1 The present invention is described further, the concrete realization steps of the present invention are:
[0057] Step 1: Obtain training samples: Rotate an ordinary two-dimensional solid-state magnetic resistance electronic compass with the manual turntable at a non-uniform speed in an indoor environment without any processing of the external magnetic field to obtain the measured value of the electronic compass and the corresponding The rotation angle of the turntable is used as a training sample, the measured value of the electronic compass is used as the value x to be compensated, and the rotation angle of the turntable is used as the ideal value Y.
[0058] The second step: determine the structure of the neural network: a single-input single-output Fourier neural network (SISO-FNN) is used to establish a model of the electronic compass direction angle error. The network is a three-layer forward network, and its three layers are input layer, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com