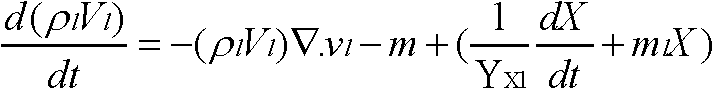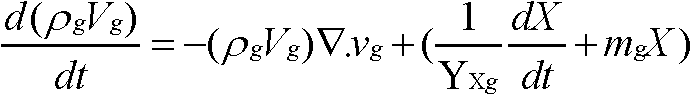Method for optimizing loading way of solid-state fermentation substrate
A solid-state fermentation and substrate technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measuring devices, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as ignoring interaction effects, ignoring coupling phenomena, and not being able to reflect the overall effect of fermentation substrate physical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
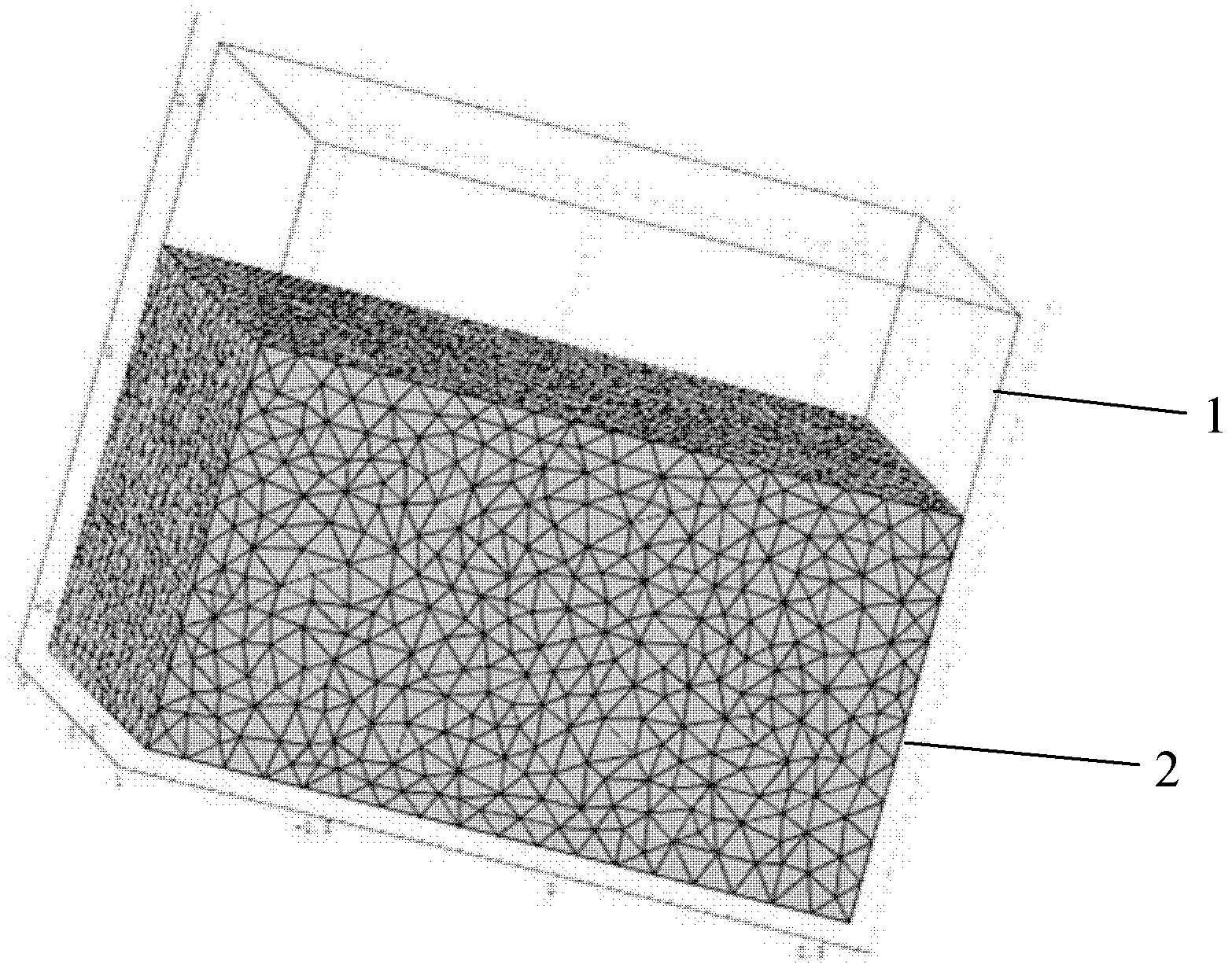
[0034] Example 1 Trichoderma viride uses steam-exploded rice straw as the fermentation substrate to determine the thickness range of the substrate layer for solid-state fermentation
[0035] Trichoderma viride is the main production strain of cellulase produced by solid-state fermentation, and the fermentation substrate is lignocellulosic material. In this example, the steam-exploded rice straw is used as the fermentation substrate, and the numerical analysis platform is used to calculate the thickness range of the substrate layer and the ratio range of the substrate layer and the headspace size of the solid-state fermentation in a static tray. The steps are as follows:
[0036] Step 1: Measure the physical property parameters of the steam-exploded rice straw matrix, and form a parameter table as follows:
[0037]
[0038] Step 2: Determination of growth kinetic parameters of microbial strains, mainly including growth kinetic equation, biomass, specific growth rate, and spe...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2 Aspergillus niger uses starch and bran as fermentation substrates to determine the thickness range of the substrate layer for solid-state fermentation
[0046] Aspergillus niger is the main production strain of α-acid amylase by solid-state fermentation. The fermentation substrate is 85% bran, 15% corn starch, and the ratio of material to water is 1:1. In this example, starch and bran are used as fermentation substrates, and a numerical analysis platform is used to calculate the thickness range of the matrix layer and the ratio range of the matrix layer to the headspace size. The steps are as follows:
[0047] Step 1: Measure the physical property parameters of the steam-exploded rice straw matrix, and form a parameter table as follows:
[0048]
[0049] Step 2: Determination of growth kinetic parameters of microbial strains, mainly including growth kinetic equation, biomass, specific growth rate, and specific growth amount;
[0050]
[0051]Step 3: Det...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com