Heat-transfer fluid, preparation method for same and use thereof
A technology of heat transfer fluid and application, applied in the field of preparation of heat transfer fluid, can solve the problems of low solidification point of heat transfer fluid and high solidification point of heat transfer fluid, and achieve the effects of good thermal physical properties and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] The preparation method of this heat transfer fluid comprises the following steps:
[0052] a) Get the raw material according to the mass percent of the above-mentioned components and components, wherein Ca(NO 3 ) 2 The raw material is Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O(Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 The moisture contained in O is not included in the component mass);
[0053] b) Pour each component into a stainless steel container;
[0054] c) Heating to 200-220°C to make Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 The water in O is analyzed, thereby dissolving each component to obtain a dissolved salt mixture;
[0055] d) Expose the dissolved salt mixture to the air at 190-200°C for 1-2 hours, and after the water is completely evaporated, the heat transfer fluid is obtained.
[0056] Table 1 is the preferred components of the heat transfer fluid of the present invention and the content of the components.
[0057] Table 1
[0058]
[0059]
Embodiment 1
[0061] In the present embodiment, the components of the heat transfer fluid and the contents of the components are shown in Table 2:
[0062] Table 2
[0063]
[0064] 1. Description of the preparation process of heat transfer fluid
[0065] Take KNO 3 (purity>99%), LiNO 3 (purity>99%) to Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O (purity >99%). KNO 3 、LiNO 3 , Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O was ordered from Alpha-Aesar Co., UK. First, each nitrate is weighed separately, then poured into a stainless steel container, and heated in the atmosphere. The heating temperature was initially kept at about 200°C so that Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 The water in O is separated out, thereby dissolving the components. These molten salt mixtures are exposed to air for 1 hour in a high temperature environment (190-200° C.) to ensure that the water is completely evaporated to obtain molten salt mixtures, ie heat transfer fluids.
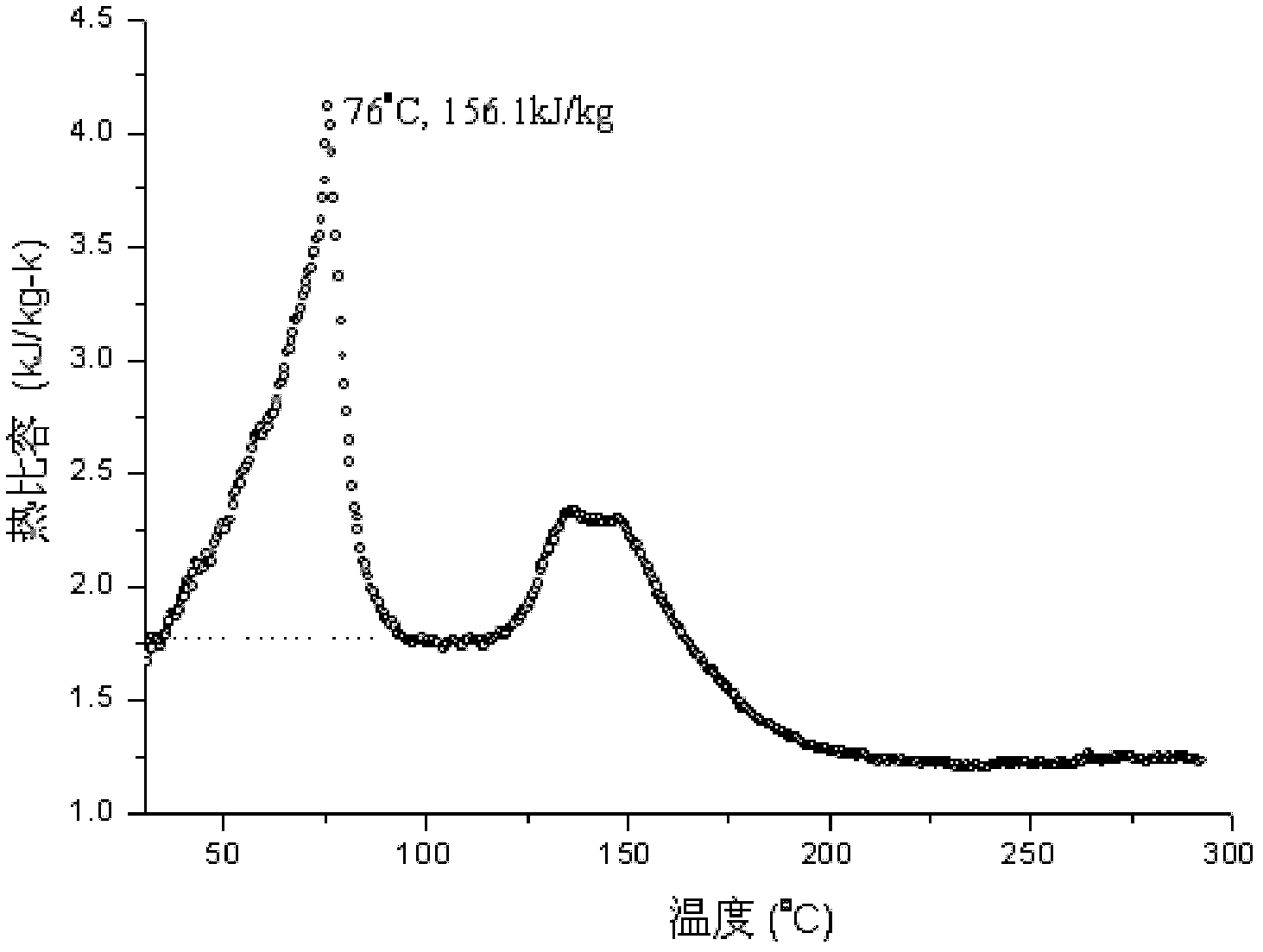
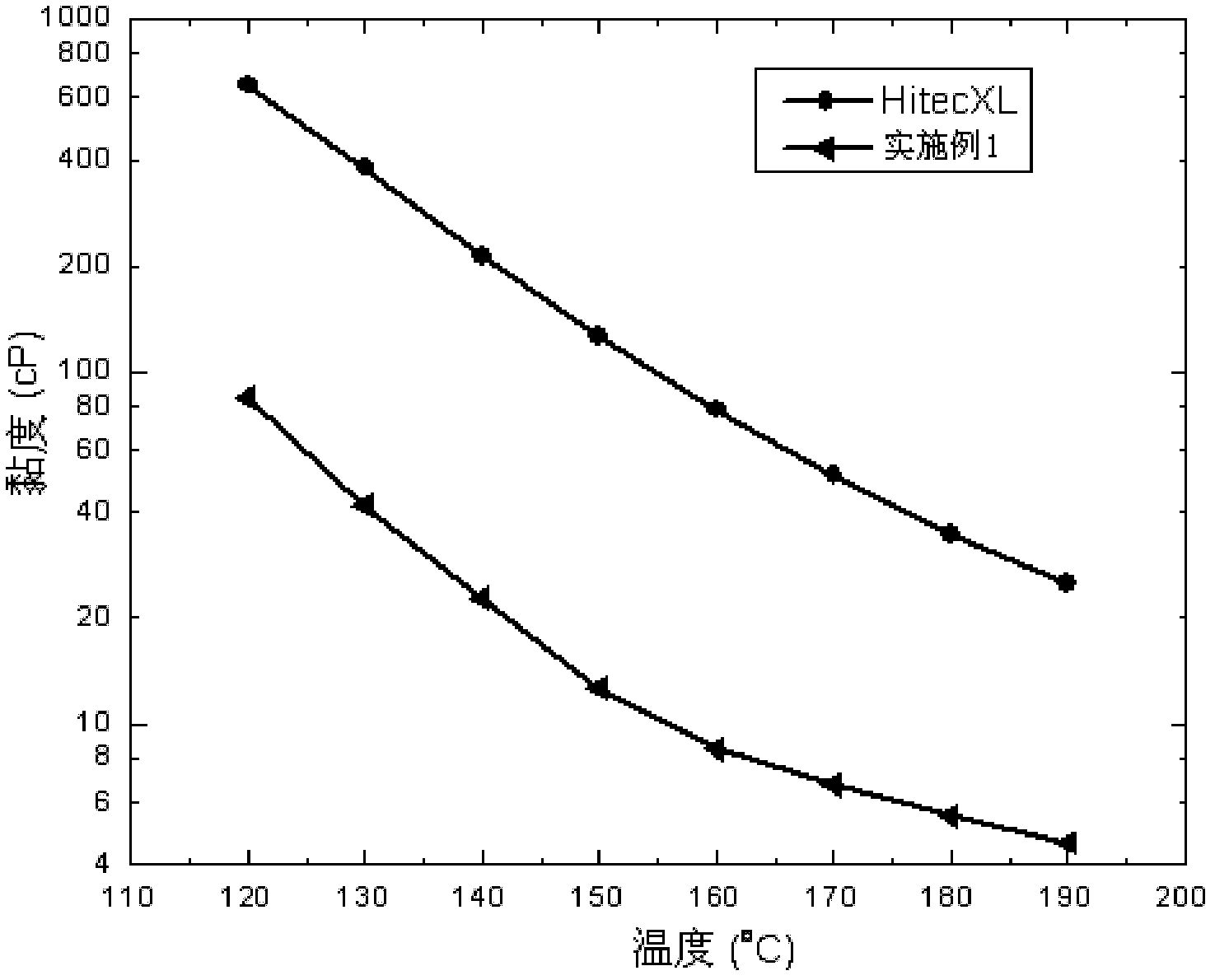
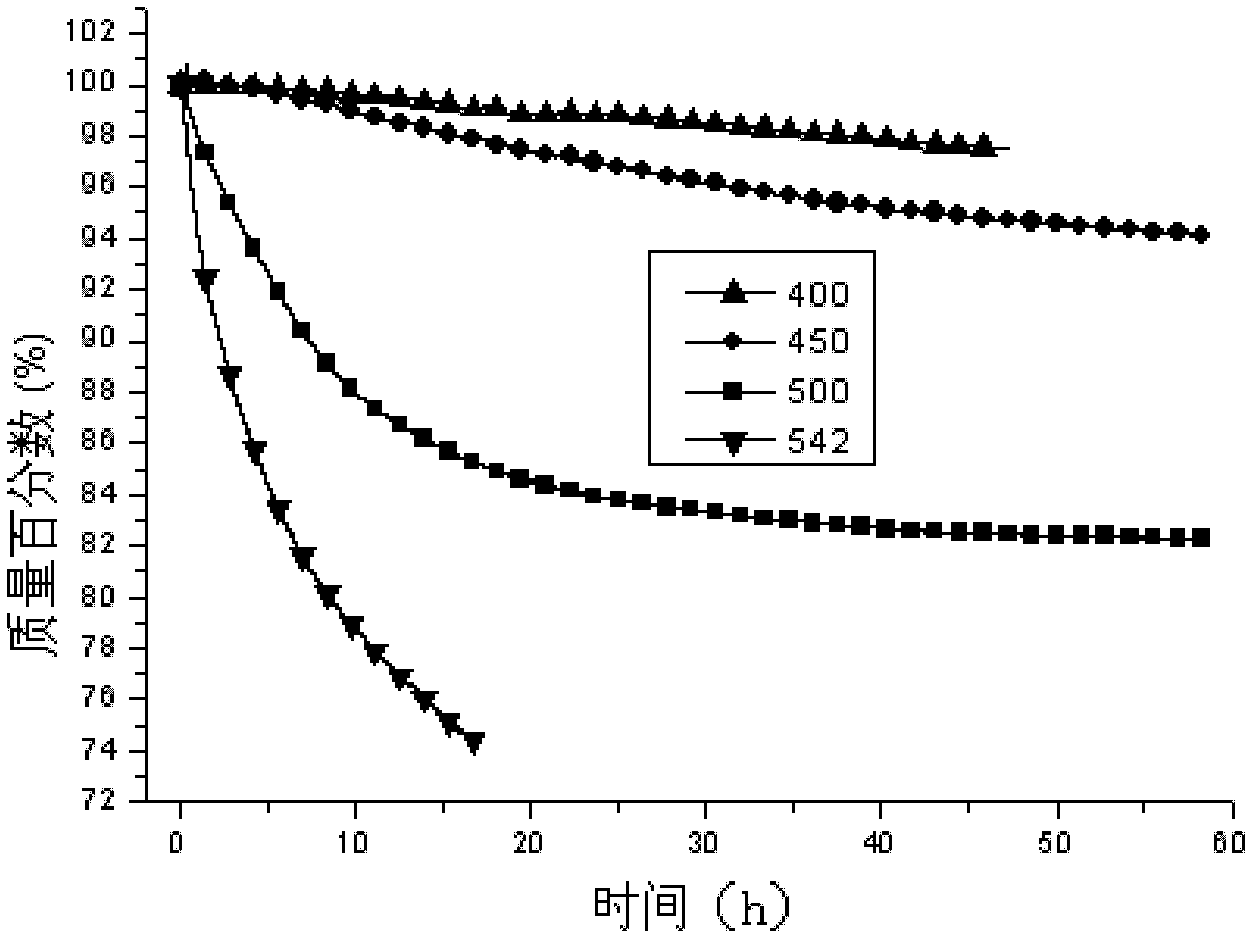
[0066] 2. The physical properties of the heat transfer fluid in the present embodiment
...
Embodiment 2
[0100] In this example, the components and contents of the heat transfer fluid are shown in Table 5, and the specific preparation method refers to Example 1.
[0101] table 5
[0102]
[0103] The physical properties of the heat transfer fluid in the present embodiment are as follows:
[0104] Melting point temperature: 78°C
[0105] Thermal conductivity: 0.42-0.44W / (m·k)
[0106] Cost: 0.81$ / kg
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com