Calcium-binding agents induce hair growth and/or nail growth
A technology of hair growth and calcium-binding peptides, applied in hair care, manicure, drug combination, etc., can solve problems such as great difference in results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0274] Calcium-binding peptides induce hair growth
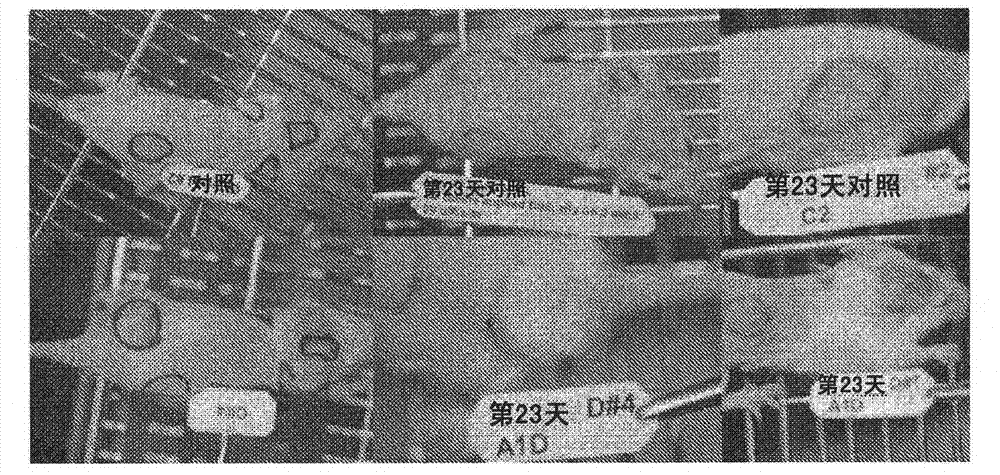
[0275] figure 1 DSS-treated (right) and mock-treated (left) mice are shown showing hair regrowth 13 days after scalp shaving. figure 2 The effect of calcium-binding compounds on hair growth in mice is shown. Leftmost panels in each group show day 0 mice after preparation and before treatment. The panel on the right shows mice on day 23 (endpoint date). The upper panel shows a negative control that received daily topical saline treatment. The lower panel shows daily treated mice with a topical formulation of DSS compound applied to the indicated area, showing significant hair growth compared to controls.
Embodiment 2
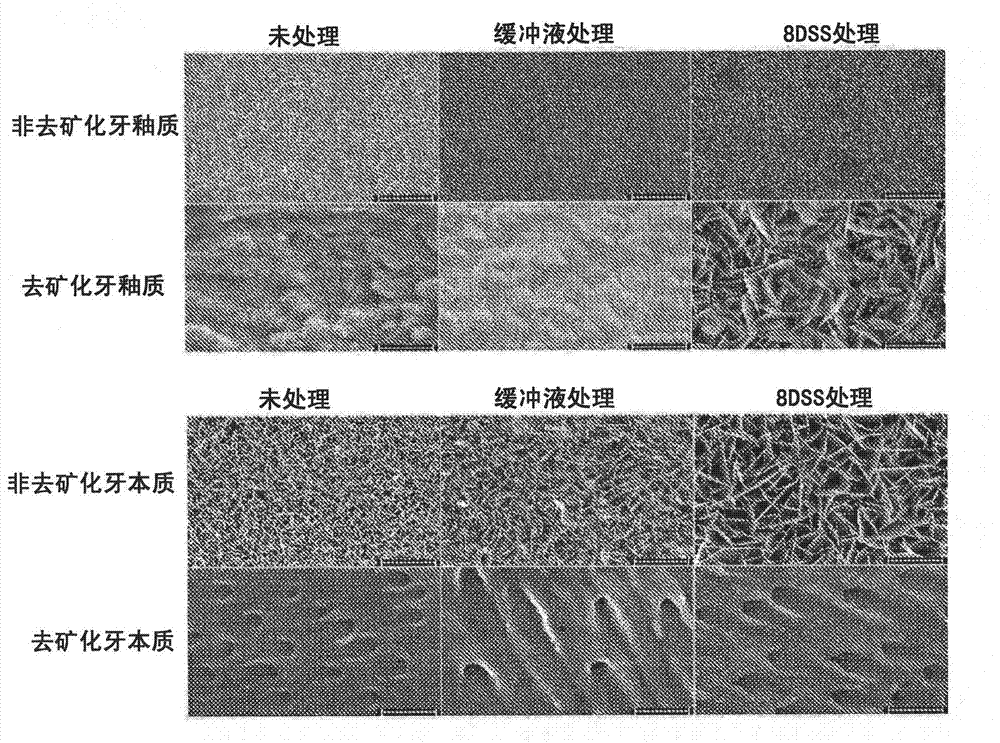
[0277] Nucleation of hydroxyapatite on enamel and dentin via DSS peptide
[0278] To determine whether application of DSS to various tissue preparations promotes HA nucleation that can ultimately lead to tissue remineralization, sagittal sections of adult teeth (obtained after extraction from normal clinical practice) were ground using a Streurs wheel, Preparations for nuclear experiments. Half of the sections were demineralized with 35% phosphoric acid for 15 min and then rinsed thoroughly with deionized water. The other half is left alone. All samples were then sonicated to remove excess debris left over from cutting and grinding and / or demineralization. Samples were treated with 12.5 [mu]M 8DSS dissolved in 50 mM HEPES buffer solution (pH 7.0), buffer solution alone, or left untreated. The samples were then immersed in stimulating body fluid (SBFn) for 4 hours, ie, to accelerate the nucleation of hydroxyapatite (HA) crystals. After the nucleation step, the samples wer...
Embodiment 3
[0285] Tissue-specific binding of DSS peptides in human teeth
[0286] To investigate the tissue specificity of DSS peptide binding to tooth tissue, human tooth sections were exposed to DSS peptides and variants and then imaged by CLSM. The peptides used in these experiments were 8DSS, 8ASS, 8DAA, 8NAA, 4DSS, 4ESS, 4NSS, 4DTT, 4ETT, 4NTT and 6DSS. Sagittal sections of human teeth extracted during normal clinical practice were ground and then incubated for 10 minutes in a solution of the appropriate 5(6) carboxyfluorescein-labeled peptide (12.5 pM) containing 10 mM NaCl and 50 mM HEPES at pH 7.0. A control sample without peptide was prepared. Samples were thoroughly washed after treatment and imaged by CLSM using blue laser irradiation (A=488 nm) and FITC emission filters, using the same camera and microscope settings for each sample. For each slide, multiple scans were collected and combined in automatic mode to generate an image representing a 13x13 mm area, which in most...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com