Wireless energy transfer in lossy environments
A wireless power and transfer system technology, applied in antennas, power management, vehicle energy storage, etc., can solve problems such as small offset tolerance, and achieve the effect of low inherent loss rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
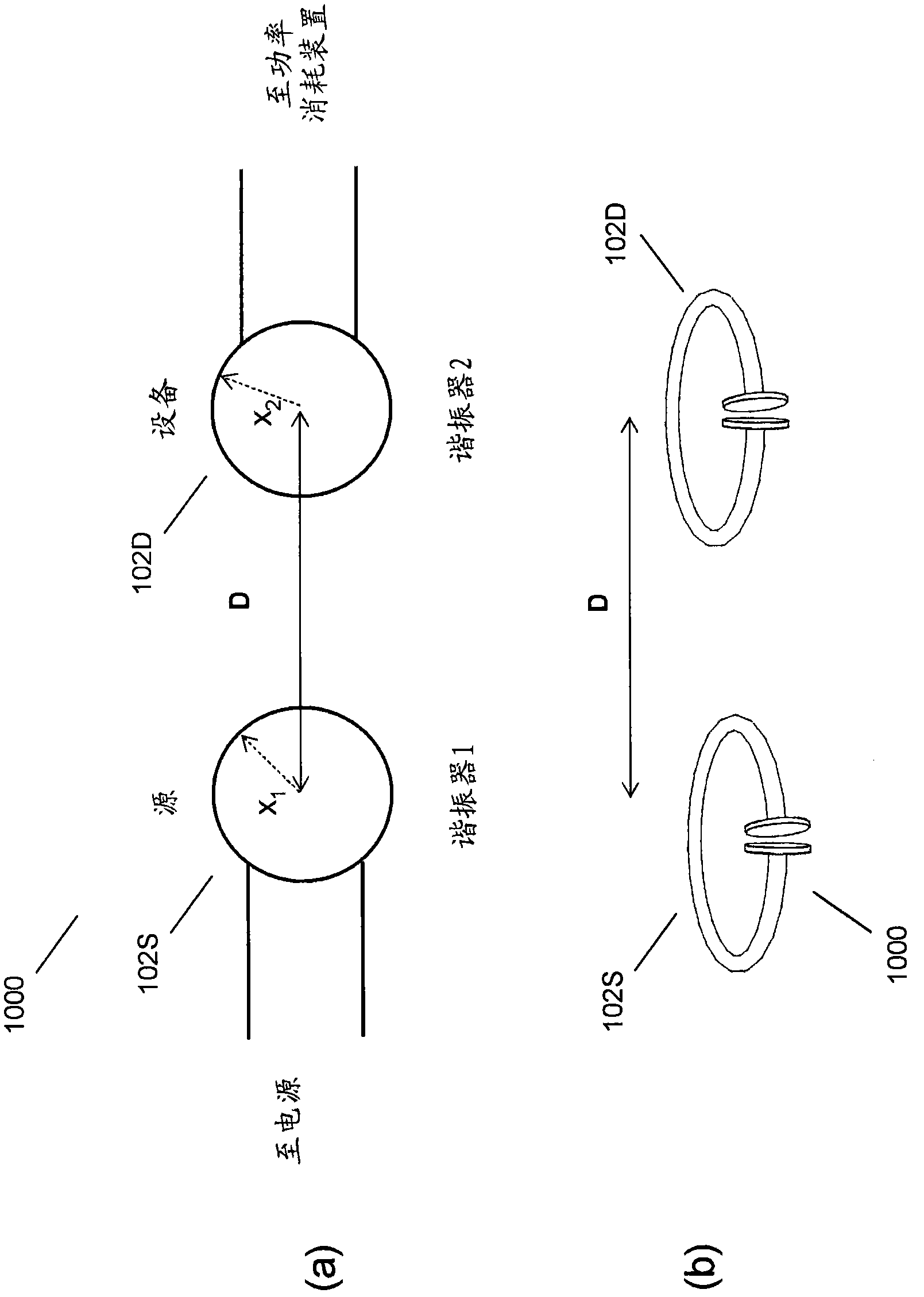
[0104] As noted above, the present disclosure relates to coupled electromagnetic resonators having long-lived oscillatory resonant modes that can wirelessly transfer power from a power source to a power sink. However, the present technique is not limited to electromagnetic resonators, but is general and can be applied to a variety of resonators and resonance objects. Therefore, we first describe the general technique and then disclose electromagnetic examples for wireless energy transfer.
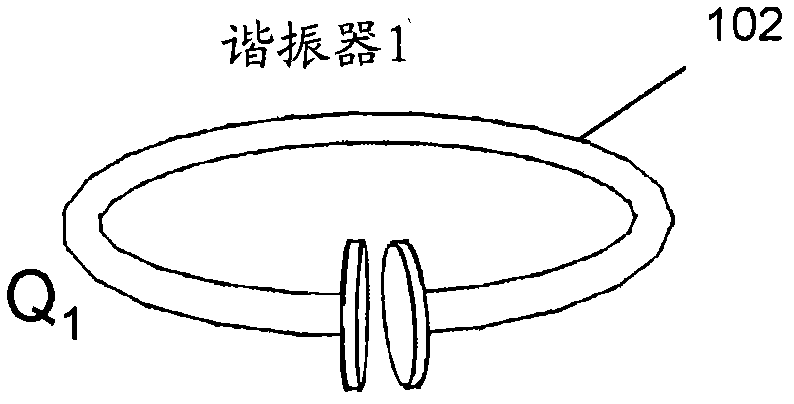
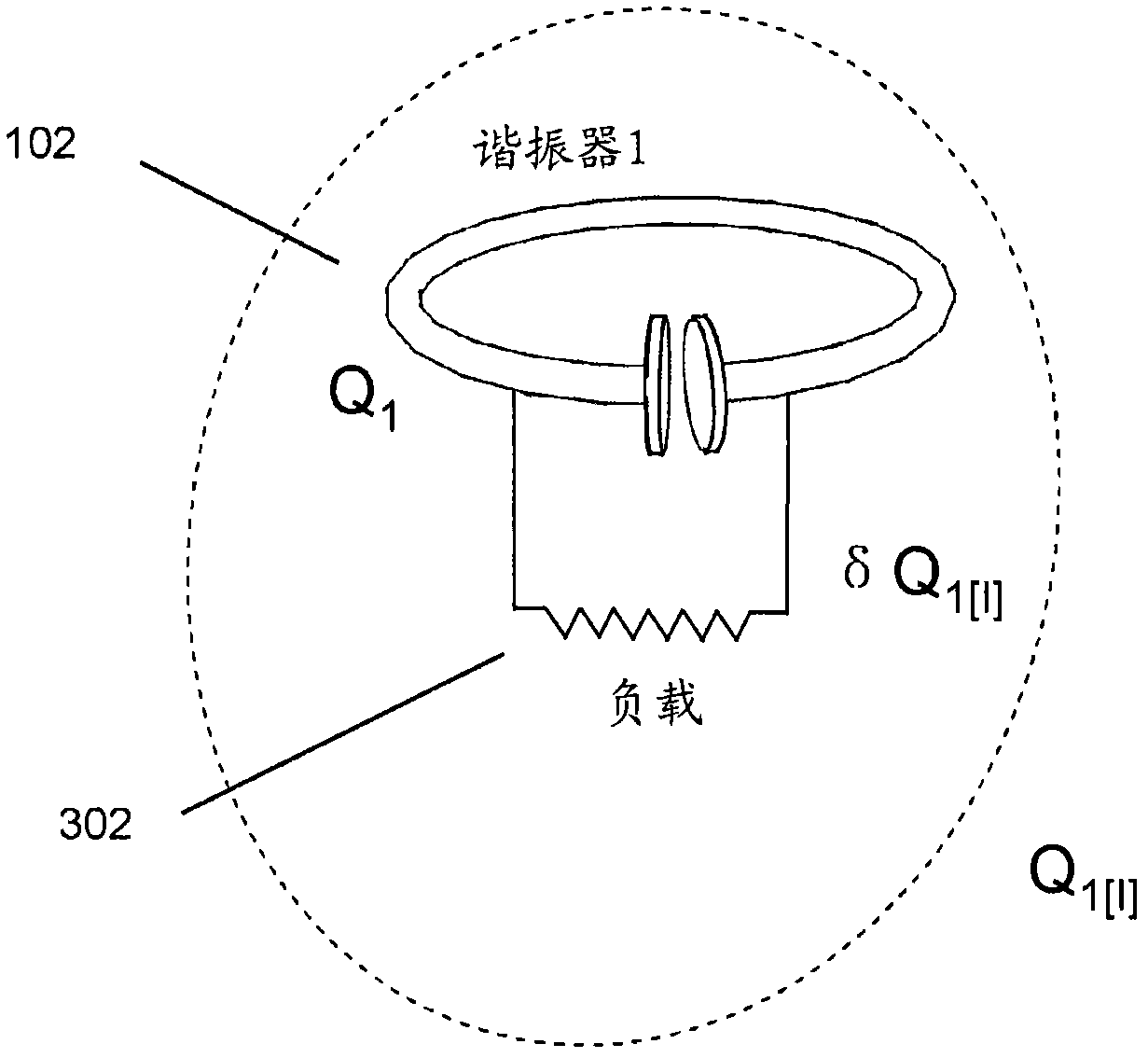
[0105] resonator
[0106] A resonator can be defined as a system capable of storing energy in at least two different forms, and in which the stored energy oscillates between the two forms. A resonance has a specific mode of oscillation with a resonant (modal) frequency f and a resonant (modal) field. The angular resonance frequency ω can be defined as ω=2πf, the resonance wavelength λ can be defined as λ=c / f, where c is the speed of light, and the resonance period T can be defined as T=1 / ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com