Manufacturing method of strain CMOS device
A manufacturing method and device technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of thickness consumption, damage to the first stress layer 101, and small spacing, so as to facilitate removal, solve over-etching, The effect of simple deposition process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] In order to make the above objects, features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, specific implementations of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0032] In the following description, many specific details are set forth in order to fully understand the present invention, but the present invention can also be implemented in other ways than those described here, so the present invention is not limited by the specific embodiments disclosed below.
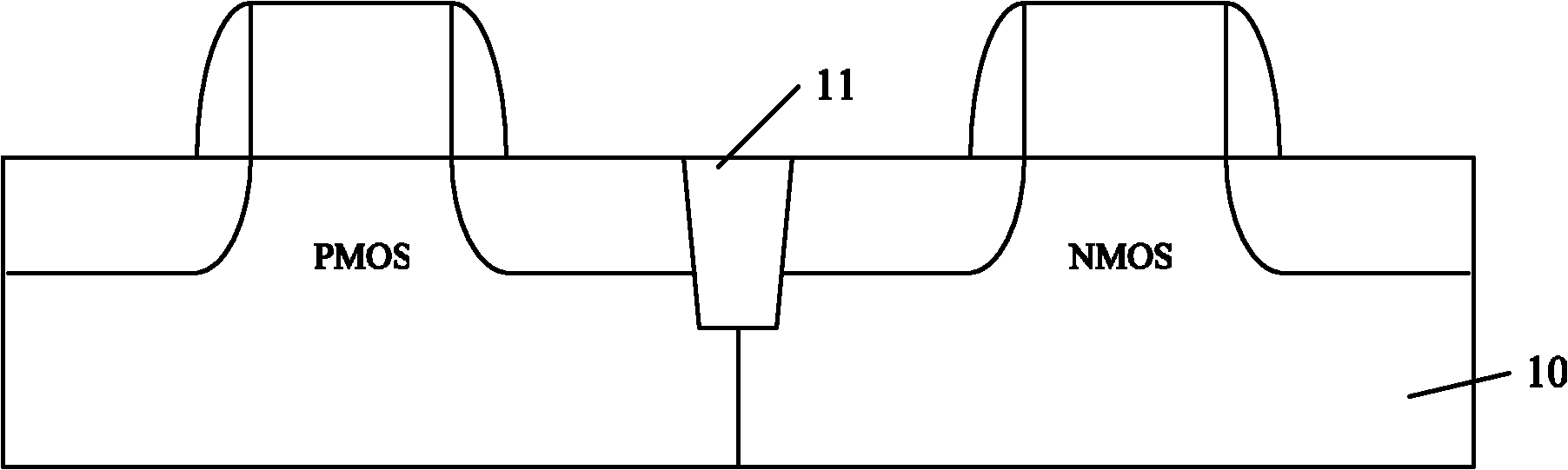
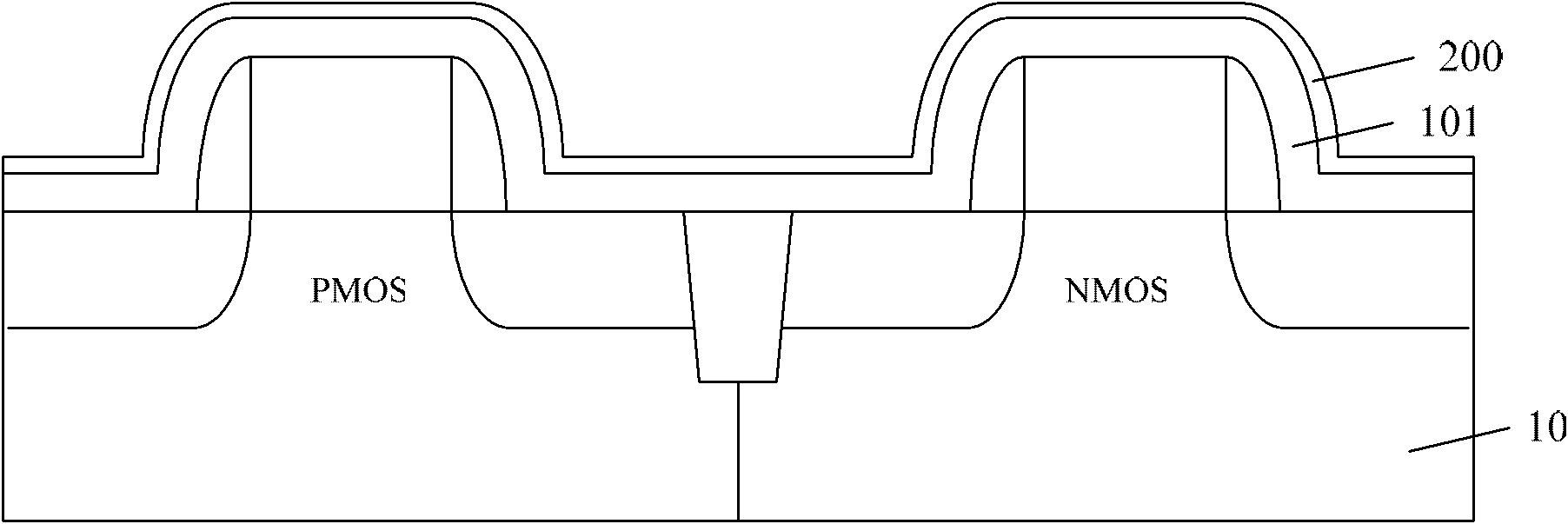
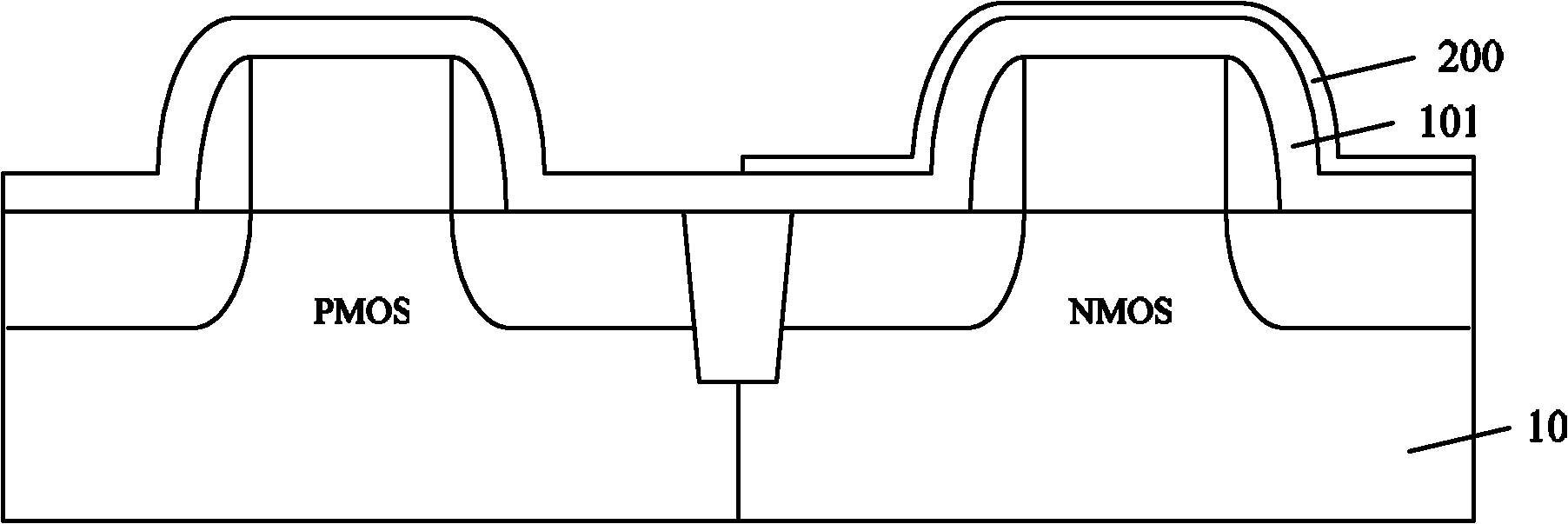
[0033] As mentioned in the background technology section, in the existing strained CMOS device manufacturing method, because the thin film oxide layer is too thin relative to the thickness, over-etching phenomenon is easy to occur during the etching process of the top strained layer, which penetrates and damages the bottom strained layer .
[0034] In view of the above problems, the inventors of the present invention provide a method for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com