Distributed stress/temperature sensing optical fiber coordinate locating method
A technology of distributed strain and sensing optical fiber, which is applied in the direction of physical/chemical change thermometers, thermometers, and measurement of the change force of optical properties of materials when they are stressed, which can solve the problems of measurement position deviation, elongation, Difficult to deal with and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving accuracy, reducing measurement error, and facilitating processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
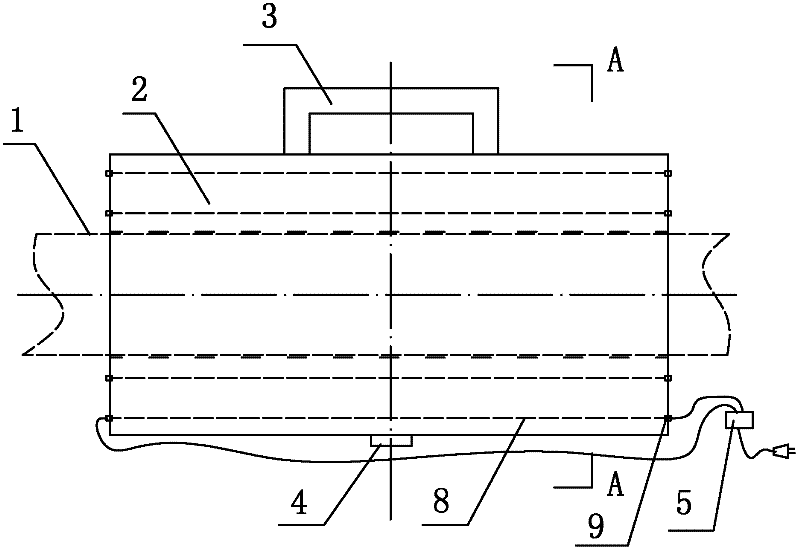
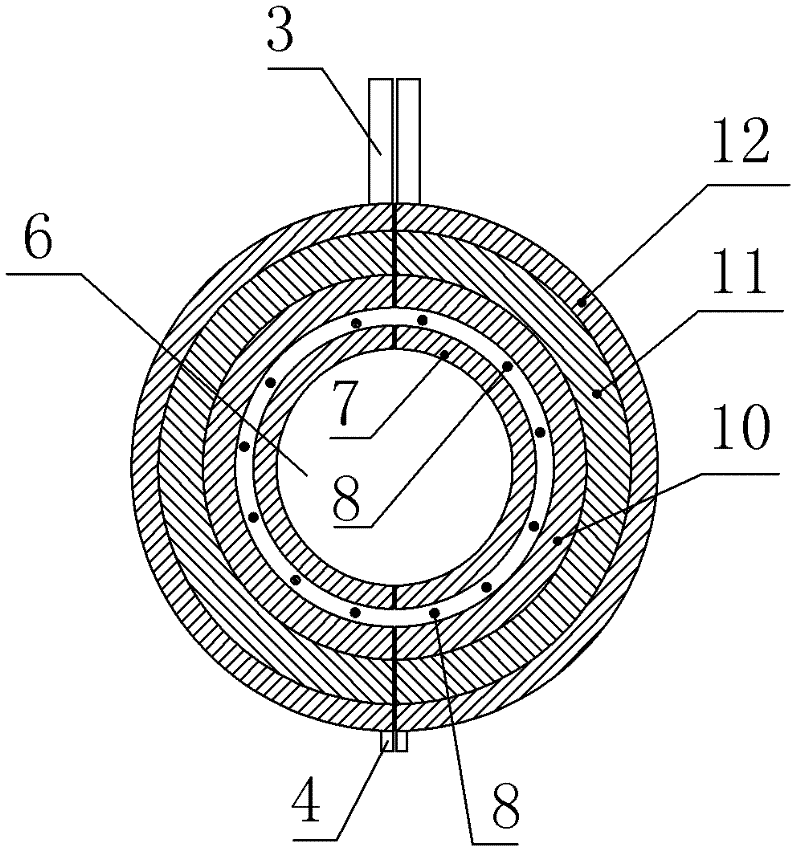
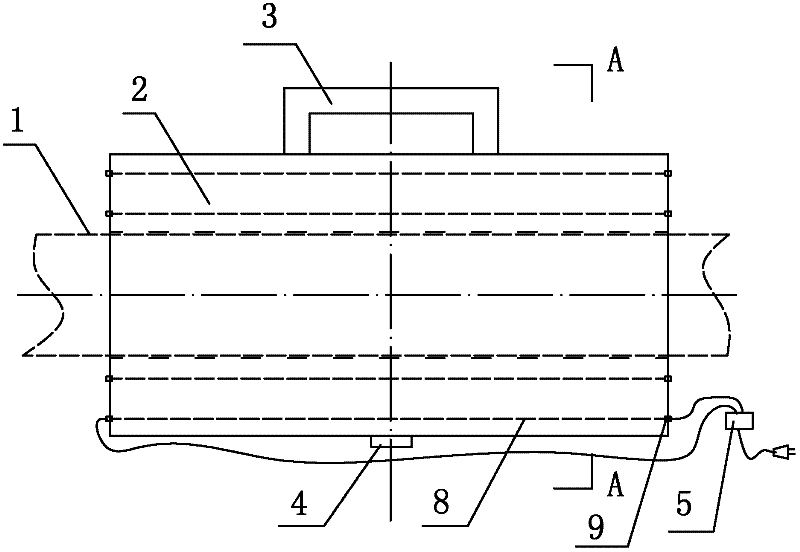
[0024] Distributed strain / temperature sensing optical fiber coordinate positioning method, it comprises the following steps:
[0025] 1) Arrange distributed strain / temperature sensing optical fiber on the measurement line required by the structure under test (that is, for distributed sensing optical fiber), and set a heating positioning device at the specific position required for measurement of the structure under test, distributed strain / The temperature sensing optical fiber passes through the heating positioning device;
[0026] 2) During measurement, the heating positioning device is energized, and the heating positioning device emits heat to the distributed strain / temperature sensing optical fiber. By changing the ambient temperature of the local optical fiber, the coordinates of the optical fiber measurement point at the specific position required for measurement of the measured structure are obtained. .
[0027] Experiments are carried out according to the above metho...
Embodiment 2
[0035] It is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that the length of the two semicircular ring members is 5 cm.
[0036] Experiments were carried out according to the method described in Example 1, and the results showed that the accuracy rate reached 100%.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Basically the same as embodiment 1, the difference is: the inner radius of the two semicircular ring members is 0.3cm, the radius of the semicircle ring iron sheet is 1cm, and the outer radius of the two semicircle ring members is 2cm.
[0039] Experiments were carried out according to the method described in Example 1, and the results showed that the accuracy rate reached 100%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com