Determination method of average radius of ripple serrated aperture for realizing Gaussian beam shaping
A technology of average radius and Gaussian beams, which is applied in optics, lasers, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of not having a clear range of the average radius of the aperture, and the study of the light intensity distribution of Gaussian beams, etc., so as to improve the utilization rate and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
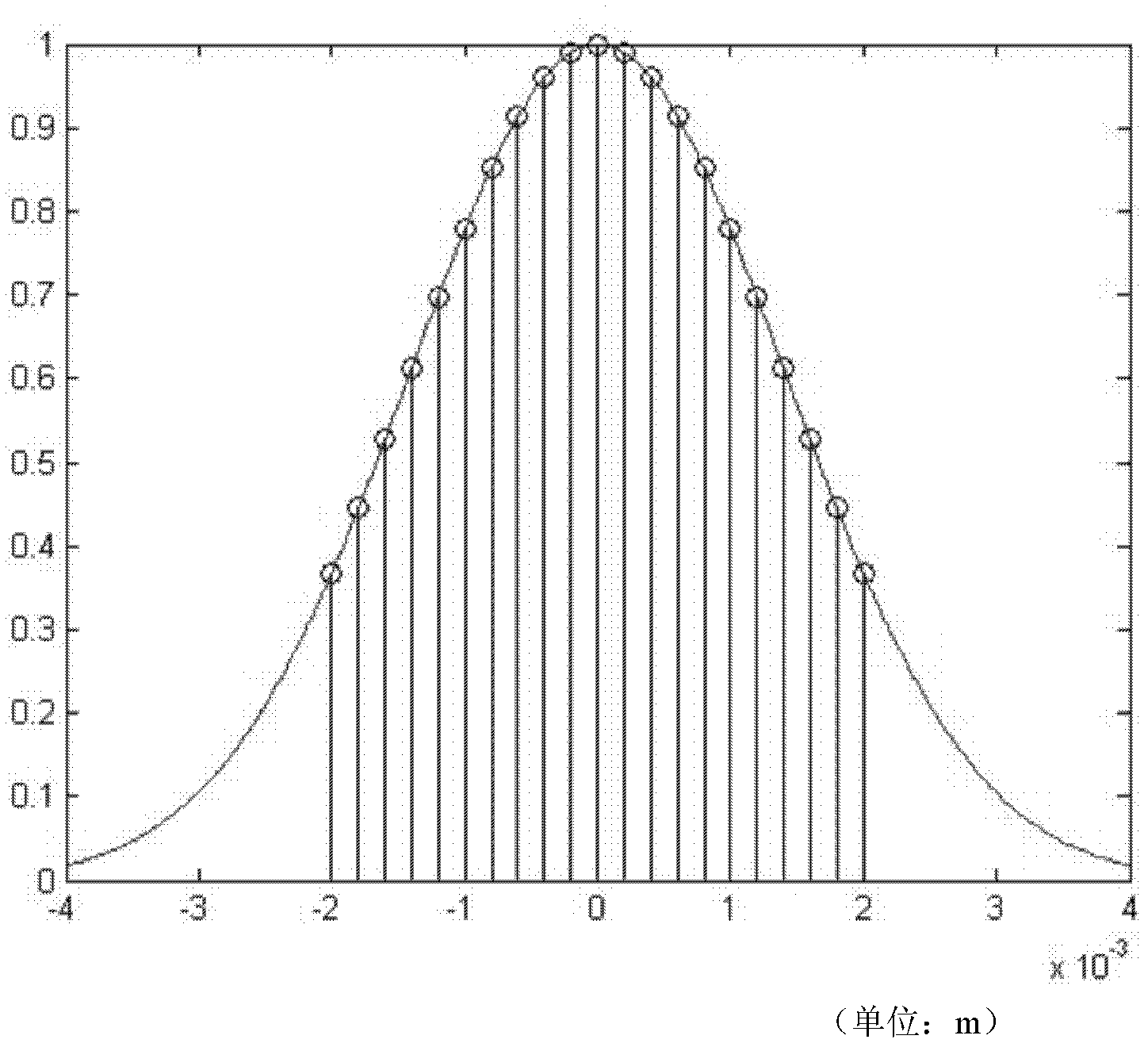
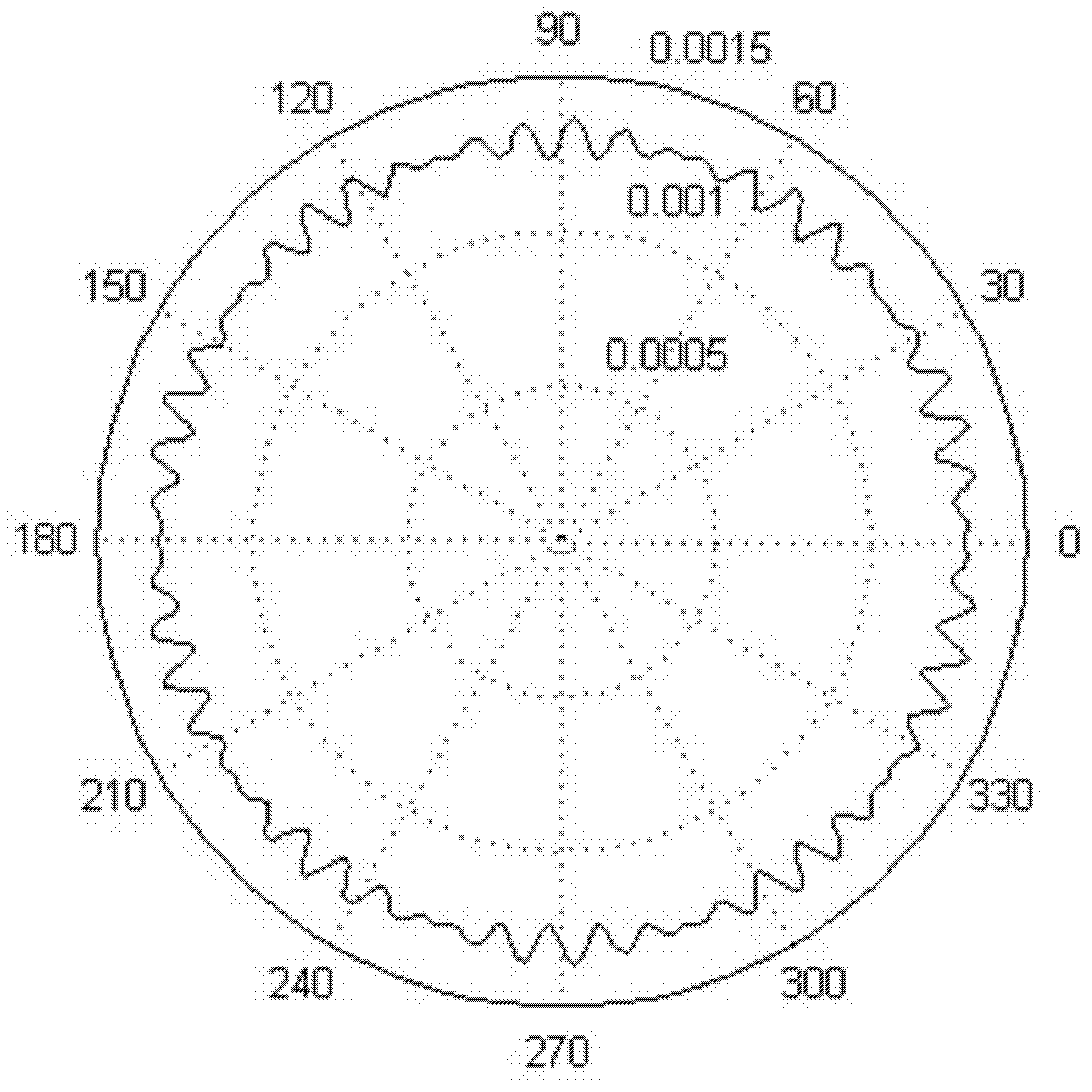
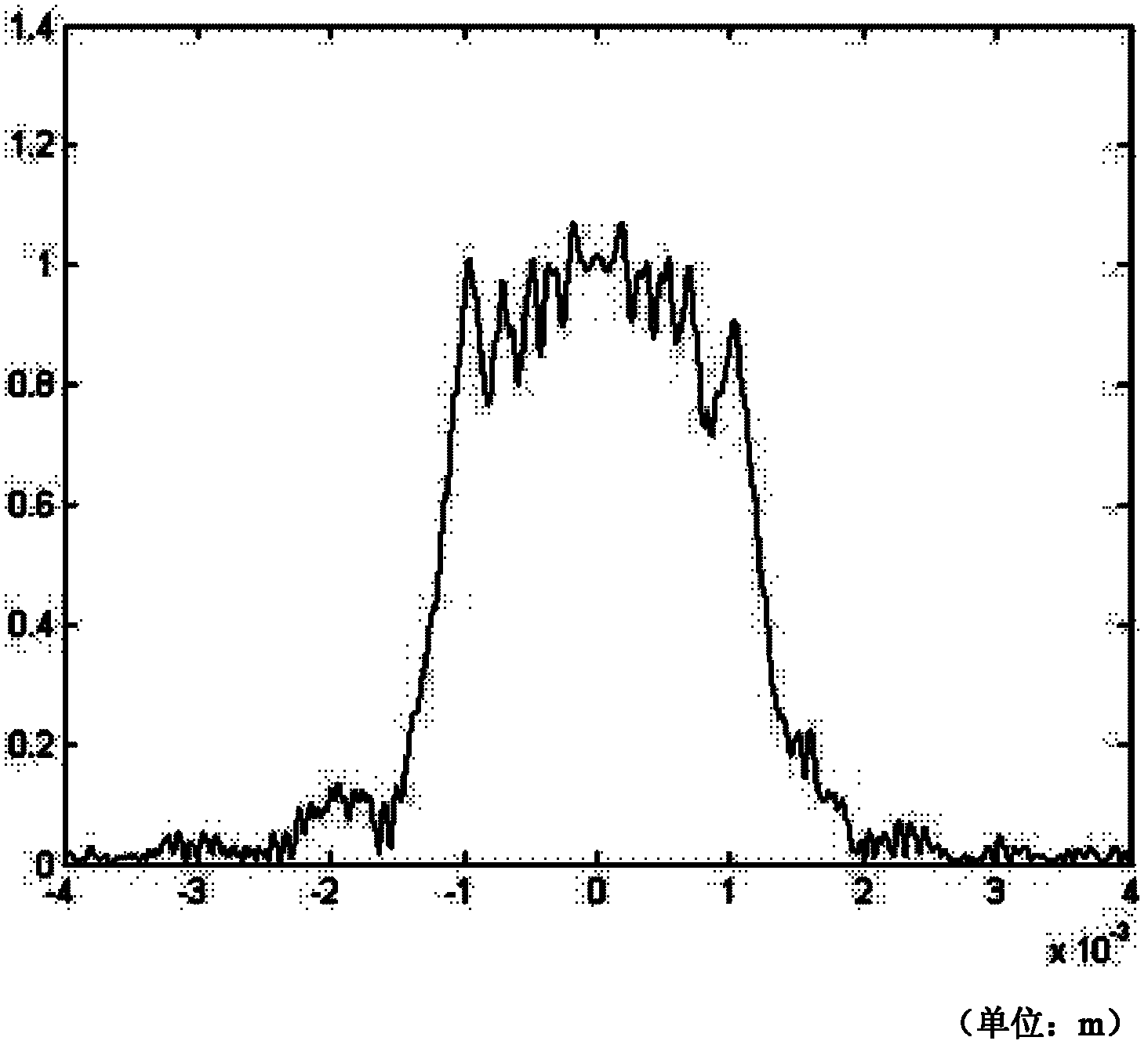
[0017] The present invention is a method of laser cutting on a stainless steel sheet, cutting out such as figure 2 The aperture of the shape shown is added to the laser light path of the Gaussian beam, and the light intensity distribution on the output optical axis and radial direction is measured. figure 1 is the incident light whose light intensity distribution is Gaussian distribution, and the area under the shade represents the Gaussian beam width. Then repeat the above operation with amplitude-modulated corrugated sawtooth apertures with different average radii, calculate and compare their characteristic parameters respectively, and find out the optimal average radius, which also determines the amplitude modulation to be used in the process of Gaussian beam shaping and uniformity. The ratio of the average radius of the corrugated sawtooth aperture to the beam width of the Gaussian beam. in Figure 4 The abscissa represents the average radius of the sawtooth aperture, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com