Dichlorodiketopyrrolopyrrole pigment, coloring material dispersion containing the pigment, and process for production of the coloring material dispersion
A technology of dichlorodiketopyrrole and coloring materials, applied in diketopyrrolopyrrole dyes, chemical instruments and methods, organic dyes, etc., can solve the problems of side reactions, low productivity, slowness, etc. The effect of cost burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
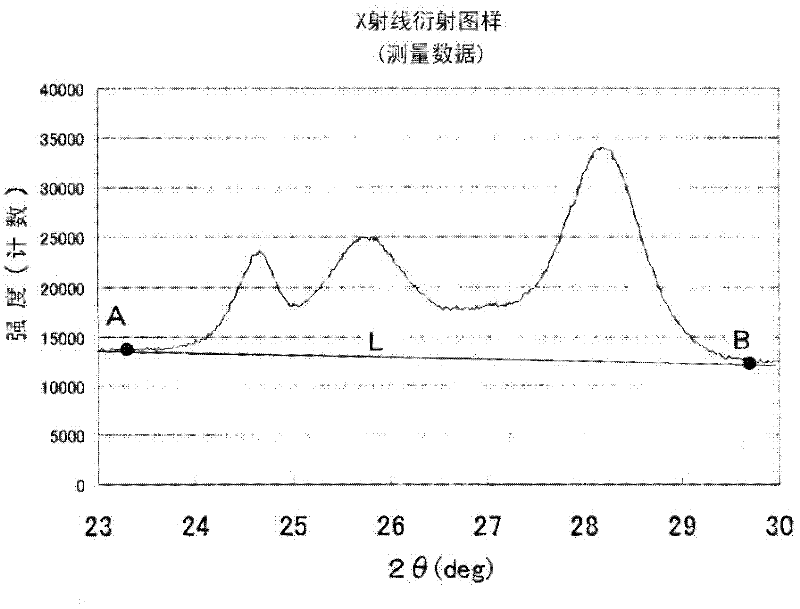
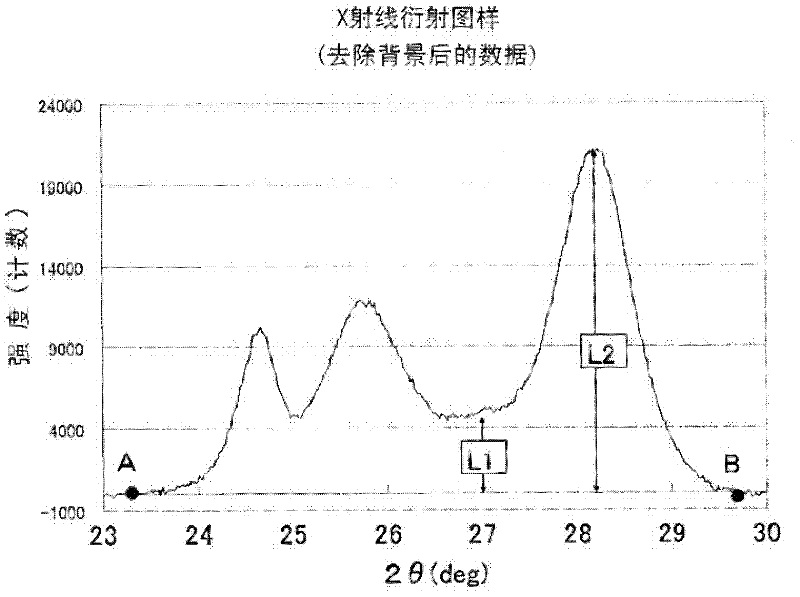
[0092] The coloring material dispersion of this embodiment is characterized in that it contains fine particles of a particle growth inhibitor and a dichlorodiketopyrrolopyrrole pigment having an α-type crystallinity of 0.65 to 0.90 in ( It has a grain size of 6.0 nm to 13.0 nm in the direction of the -151) crystal plane, and has a grain size of 5.0 nm to 23.0 nm in the direction of the (111) crystal plane.
[0093] [α-type crystallinity]
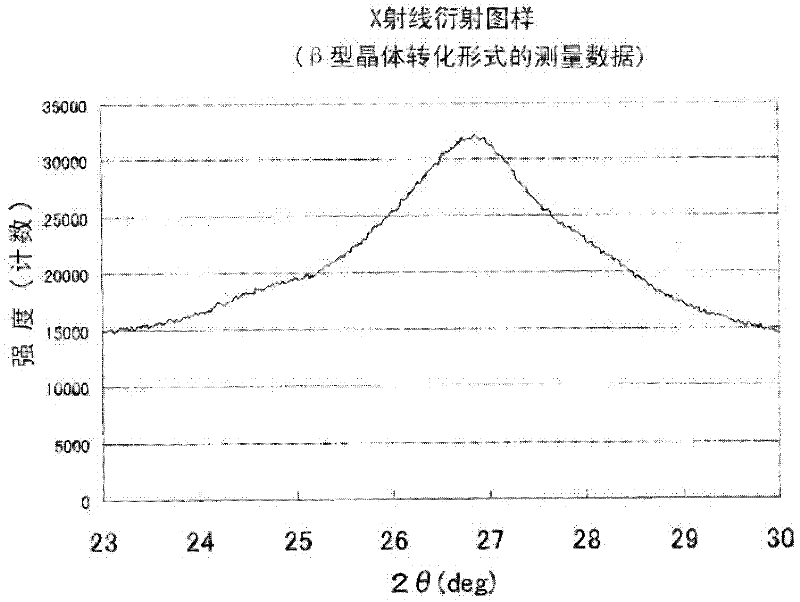
[0094] The use of dichlorodiketopyrrolopyrrole pigments in the α-type crystal conversion form for color filters is generally proposed (see Patent Document 3). When the α-type crystallinity is suppressed like the embodiment of the present invention, a color filter with high contrast can be obtained. On the other hand, there is concern that the viscosity of the dispersion as a raw material increases to impair the stability of the dispersion. The present inventors found that by setting the grain size of the dichlorodiketopyrrole pigment withi...
no. 2 approach
[0337] Another preferred embodiment (ie the second embodiment) of the present invention is described hereinafter. However, the invention is not limited to the embodiments described. Points common to the first embodiment may not be described, but some of them may be explained again.
[0338] In this embodiment, the crystallite size of the p-dichlorodiketopyrrolopyrrole pigment (see formula (I) below) as determined in the direction perpendicular to the (-151) crystal plane from the X-ray diffraction pattern 9nm or less, preferably 6nm or more, more preferably 7nm to 8.5nm. In the present embodiment, the method of obtaining the grain size as determined in the direction perpendicular to the (-151) crystal plane from the X-ray diffraction pattern was carried out according to the conditions and sequences described in the following examples, unless otherwise specified. By having a crystal grain size equal to or smaller than the above upper limit, particles having a small primary pa...
Embodiment
[0564] The present invention is described in more detail based on the examples given below, but the present invention is not limited to the examples. Unless otherwise specified, "parts" in the examples means "parts by mass", and "%" means "% by mass".
[0565] [Examples and comparative examples corresponding to the first embodiment]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com