Axial-flow wind wheel
An axial flow wind and wind wheel technology, which is applied to the components of pumping devices for elastic fluids, non-variable-capacity pumps, pump components, etc. The work area of the wheel blade 12 is solved, so as to increase the work area, reduce the turbulence intensity and turbulent noise, and improve the work efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
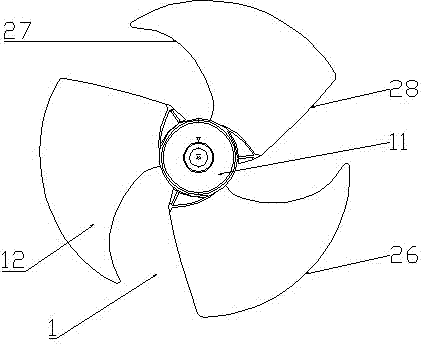
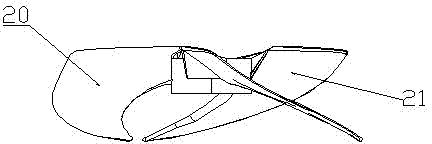
[0028] like Figure 4 and Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment includes a hub 101 and three wind rotor blades 102 arranged around the hub 101; the wind outlet surface of the wind rotor blade 102 is the pressure surface 120, and the wind suction surface of the wind rotor blade 102 is the suction surface 121; The outermost edge of the blade 102 along the radial direction is a blade tip 126 , and the blade tip 126 connects the leading edge 127 of the wind rotor blade 102 on the wind inlet side and the trailing edge 128 on the wind outlet side. A plurality of through holes 200 are provided in the region of the trailing edge 128 of the rotor. The shape of the through hole 200 is a circular or non-circular straight through hole or oblique through hole. The distribution positions of the through holes 200 are arranged vertically and horizontally according to regular rules; the aperture range of the through holes 200 is 0.1mm-300mm; all the through holes 200 are close to the area of ...
Embodiment 2
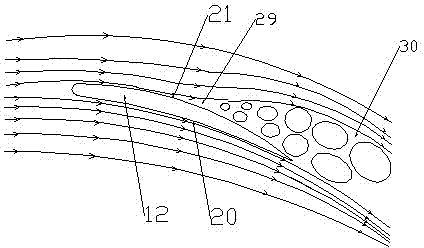
[0030] Embodiment 2: as Figure 6 As shown, several through holes 200 are designed in the trailing edge area of the wind rotor blade 102 . The circumferential dimension of the through hole 200 gradually increases from the center of the rotor to the outer edge of the rotor. Other structural features of the through hole 200 are the same as those in the first embodiment. The effect is that during the rotation of the wind rotor, the linear velocity of the fluid bypassing the circumferential section of the wind rotor gradually increases from the center of the wind rotor to the outer edge of the wind rotor, and the boundary layer separation zone at the trailing edge of the suction surface of the wind rotor also gradually increases. Therefore, the design of the through hole method in this embodiment is not only beneficial to the part of the fluid in the boundary layer of the pressure surface of the wind turbine to flow to the trailing edge area of the suction surface through the...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: as Figure 7 As shown, a through hole 200 is designed in the trailing edge region of the wind rotor blade 102 . The through hole 200 is located at the trailing edge of the rotor blade 102 near the outer edge of the rotor. Other structural features of the through hole 200 are the same as those in the first embodiment. The effect is that: during the rotation of the wind rotor, the linear velocity of the fluid passing around the circumferential section of the wind rotor is relatively large at the outer edge of the wind rotor, and the separation of the boundary layer at the trailing edge of the suction surface of the wind rotor is relatively slow near the outer edge of the wind rotor. Obviously, the design of the through hole method in this embodiment can not only effectively suppress the separation of the boundary layer at the trailing edge of the suction surface of the wind rotor, increase the actual work area of the wind rotor, and improve the working ef...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com