Inhibition of inflammation using alpha 7 receptor-binding cholinergic agonists
A cholinergic and agonist technology, applied in the field of cholinergic agonists to reduce inflammation, can solve problems such as minor side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0348] Example 1. The α7 nicotinic receptor as a molecular substrate at the neuroimmune synapse
[0349] Example overview
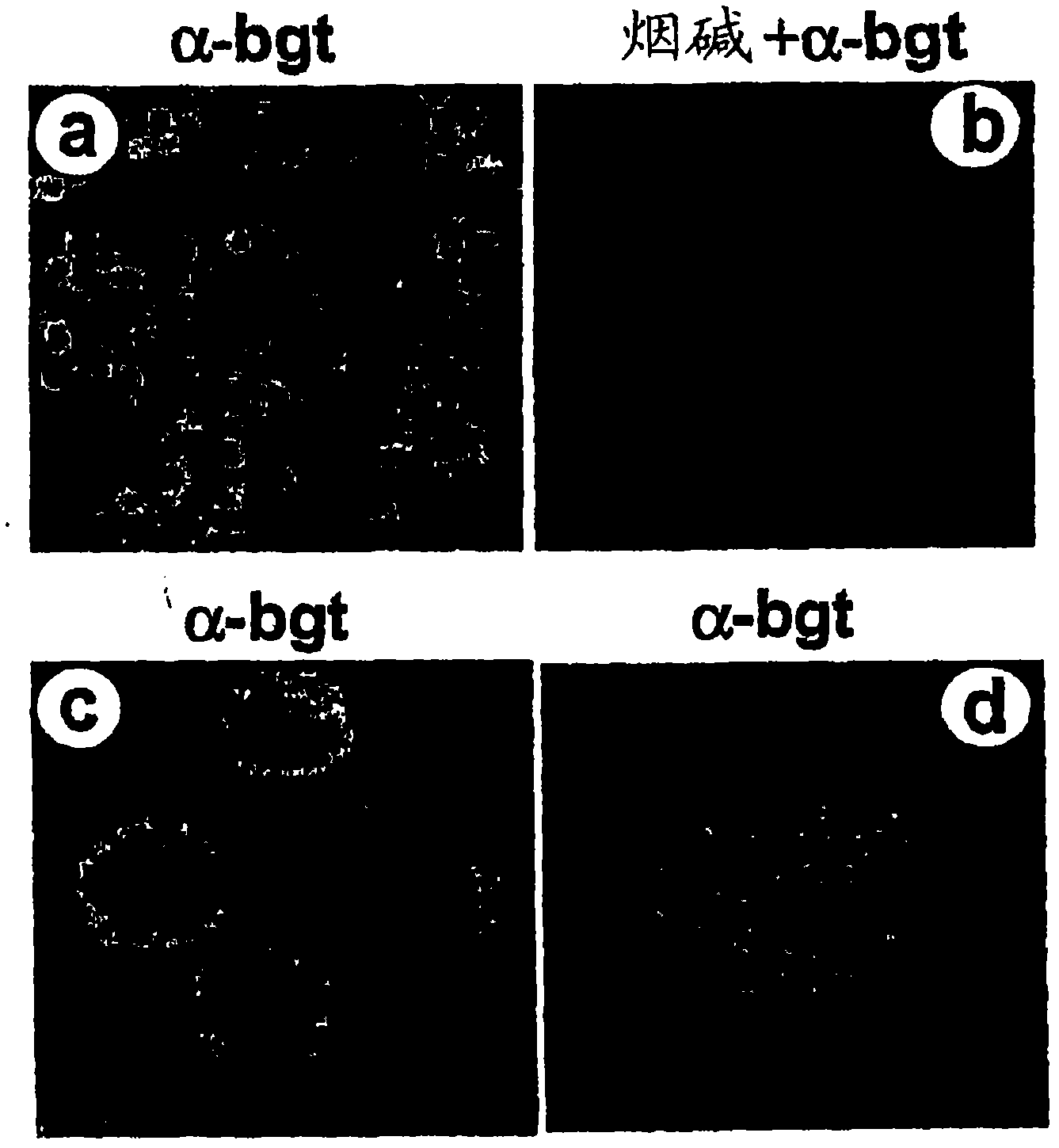
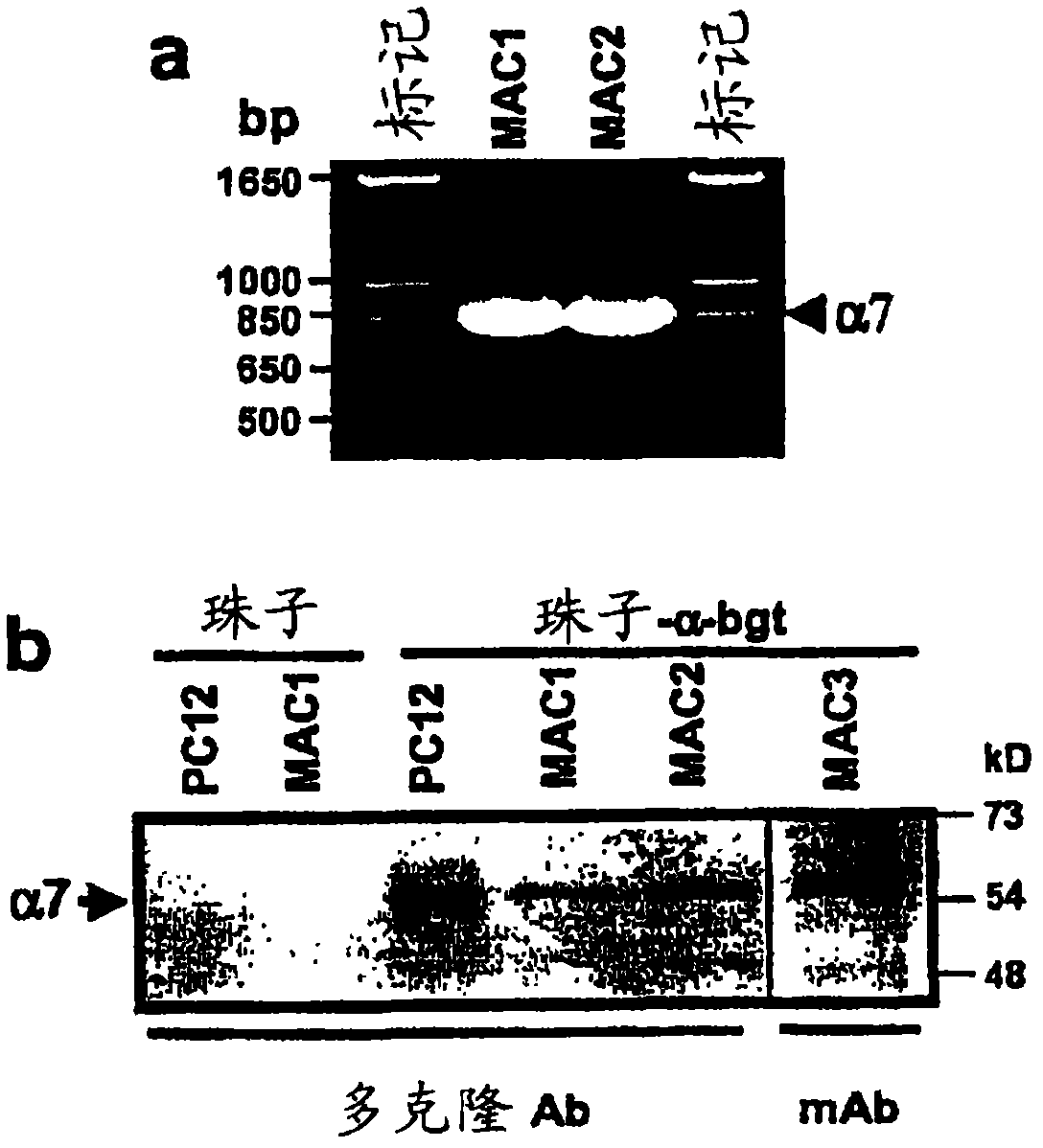
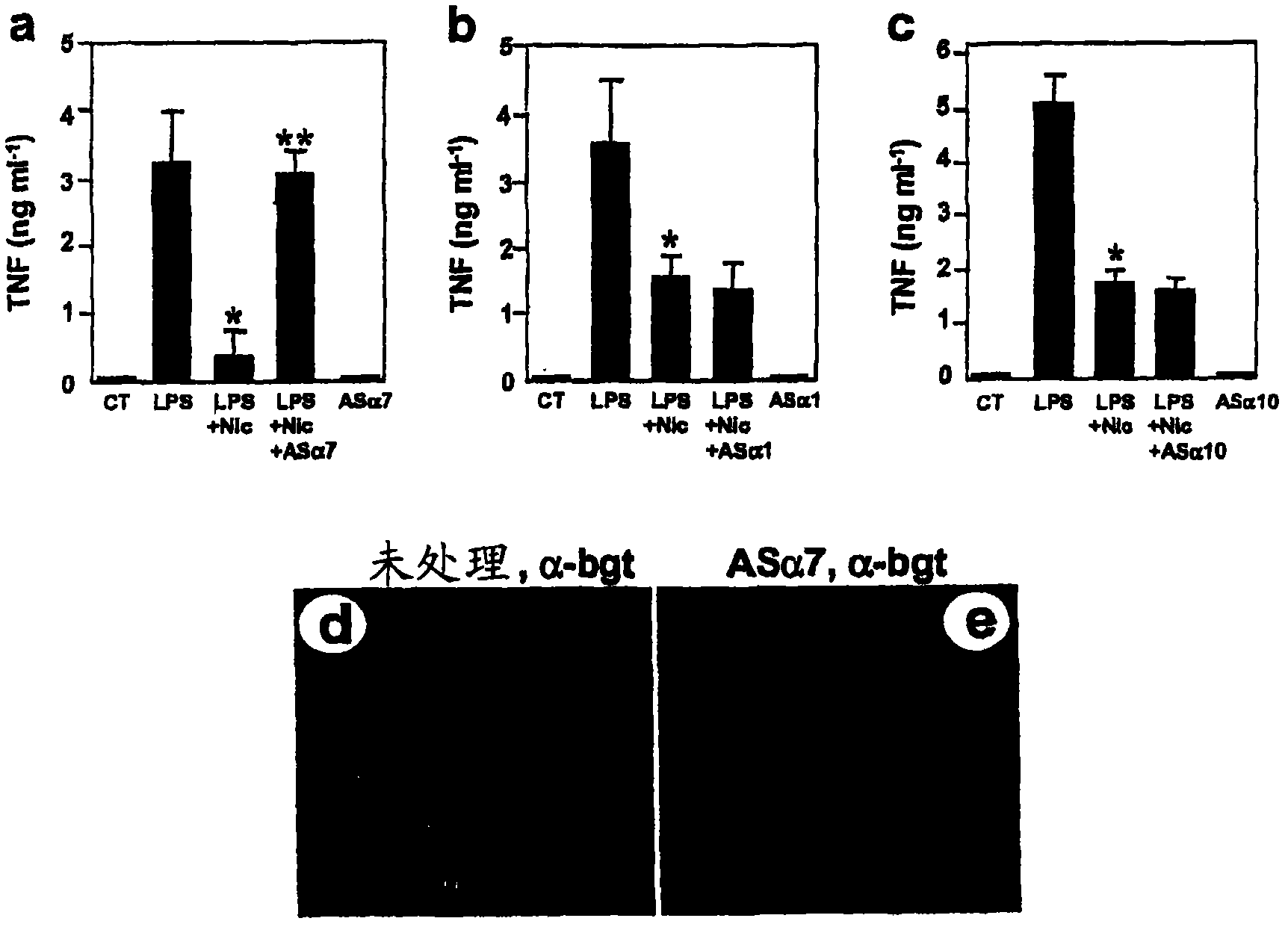
[0350] Here we show that inhibition of TNF release from macrophages by acetylcholine requires the α7 subunit of the nicotinic receptor. α-Bungarotoxin binds to a discrete cluster of receptors expressed on the surface of primary human macrophages. Immunoblotization with an α7-specific antibody demonstrated the identity of the α7 subunit in proteins isolated by adhesion of α-bungarotoxin-bound beads. Exposure of macrophages to α7 antisense oligonucleotides reduced α-bungarotoxin binding and restored TNF release in the presence of nicotine. Mice lacking the α7 subunit of the nicotinic receptor produced significantly more TNF, IL-1β, and IL-6 during endotoxemia than wild-type mice. Macrophages isolated from α7 knockout mice do not respond to cholinergic agonists and continue to produce TNF. As a result, electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve in a man...
Embodiment 2
[0372] Example 2: Compounds (V) and (VI) are protective in sepsis in cecal ligation and perforation mouse model
[0373] Compounds of formula (V) and (VI) are particularly effective in the treatment of sepsis in cecal ligation and perforation murine models.
[0374]
[0375] 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzylidene)anabaseine (V)
[0376]
[0377] 3-(4-Hydroxy-2-methoxy-benzylidene)anabaseine (VI)
[0378] Such as Fink and Heard, J.of Surg.Res.49:186-196 (1990), Wichman et al., Crit.Care Med.26:2078-2086 (1998) and Remick et al., Shock 4:89- 95 (1995) performed cecal ligation and perforation (CLP). Briefly, anesthesia was administered intramuscularly with 75 mg / kg ketamine (Fort Dodge, Fort Dodge, Iowa) and 20 mg / kg xylazine (Bohringer Ingelheim, St. Joseph, MO). A midline incision was made and the cecum was isolated. A 6-0 polypropylene textile fiber suture ligation was performed 5.0 mm from the end of the cecum distal to the ileocecal valve.
[0379]Make a single puncture of...
Embodiment 3
[0382] Example 3: Compound (V) and Nicotine Inhibit LPS-Induced TNF-α Release in Rat RAW 264.7 Macrophage-Like Cells
[0383] Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cells (American Type Tissue Culture Collection, Rockville, Md., USA) were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin and streptomycin. Cells were seeded at 90% confluence in Opti-MEM 1 medium in 24-well tissue culture plates. Cells were treated with 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 or 100 [mu]M of compound (V) or nicotine (Sigma). Five minutes after compound (V) or nicotine addition, cells were treated with LPS (500 ng / ml). After 4 hours, the supernatant was collected and TNF-α was detected by ELISA (mouse ELISA kit from R & D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, MN).
[0384] The result is as Figure 7 As shown, it was proved that compound (V) inhibited the TNF-α release of RAW 264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner like nicotine.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com