Method for degrading phthalic acid esters in water by using ultramicro bacteria under oligotrophic conditions
A technology for hydrolyzing phthalates and oligotrophs, which is applied in the application field of microbial remediation of polluted water bodies, can solve problems such as limiting the practical application range of microbial remediation technology, and achieve low demand, wide application range, and good treatment effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
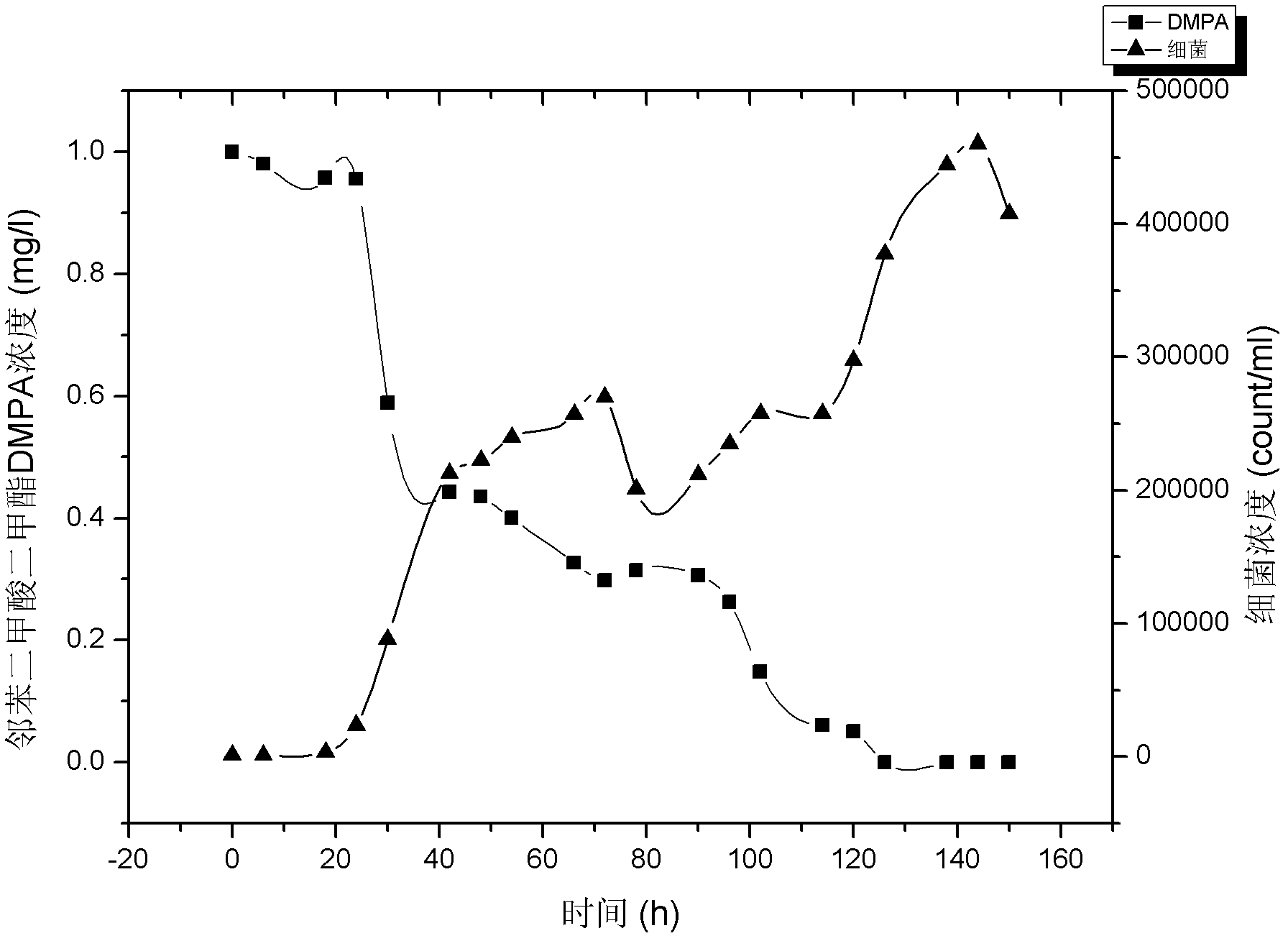
[0030] Use Evian water as the base water (pasteurized, pass through a 0.22μm filter membrane), add 1 mg / L of phthalate pollutants (dimethyl phthalate), and then inoculate with Rhodoferax ferrireducens PAE-UM strains, the inoculum concentration was 10 3 count / ml. Then subpackage into 100mL Erlenmeyer flasks, put into shaker and cultivate (30 ℃, rotating speed is 150r / min), utilize flow cytometry to detect bacterial growth and utilize high performance liquid chromatography to detect the degradation status of pollutants, such as attached figure 1 Shown is the degradation growth curve of dimethyl phthalate when the initial concentration is 1mg / L.
Embodiment 2
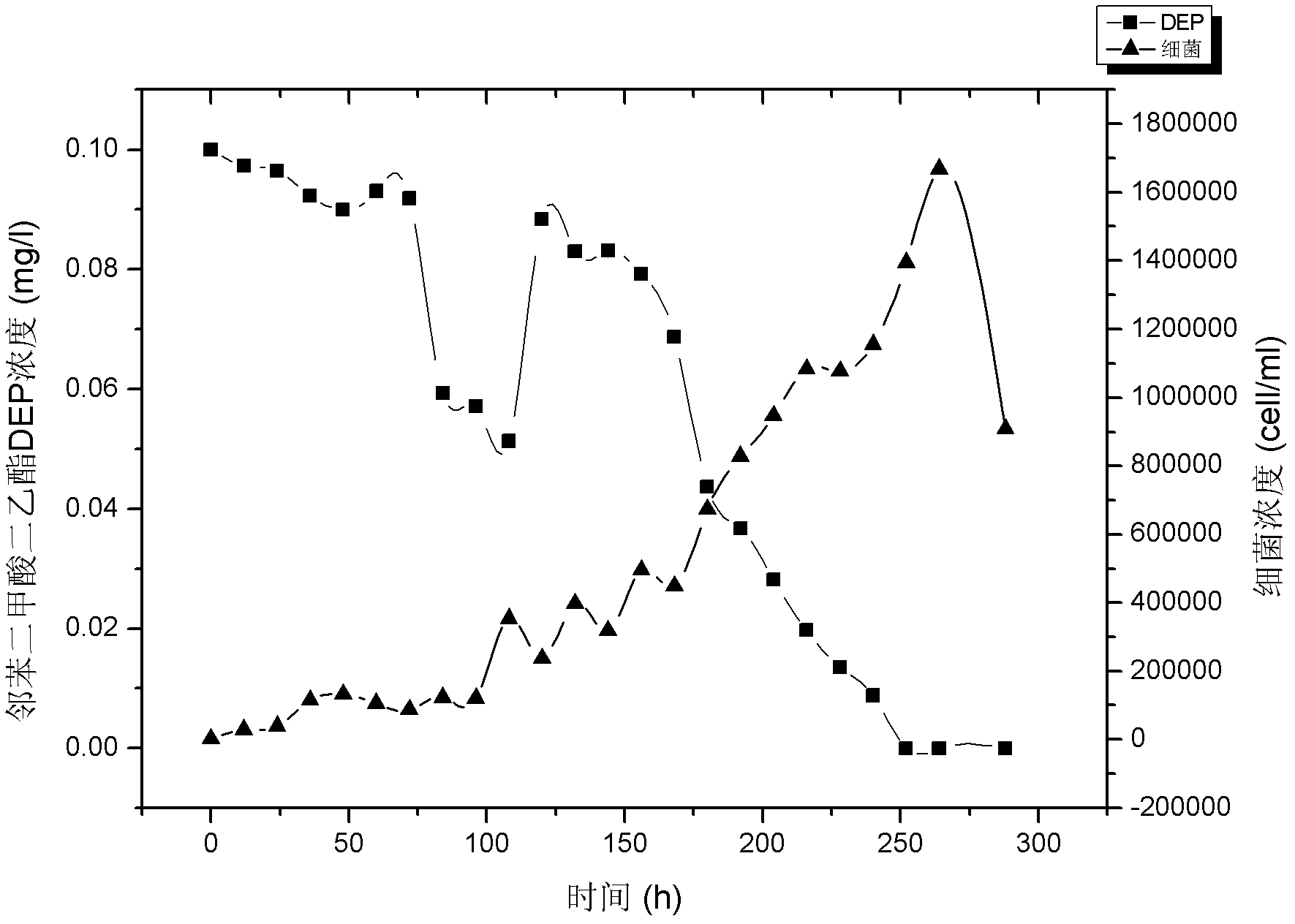
[0032] Use Evian water as the base water (pasteurized, pass through a 0.22μm filter membrane), add 0.1mg / L of phthalate pollutants (diethyl phthalate), and then inoculate Rhodoferax ferrireducens PAE- UM strains, inoculum concentration at 10 3 count / ml. Then subpackage into 100mL Erlenmeyer flasks, put into shaker and cultivate (30 ℃, rotating speed is 150r / min), utilize flow cytometry to detect bacterial growth and utilize high performance liquid chromatography to detect the degradation status of pollutants, such as attached figure 2 as shown, figure 2 It is the degradation growth curve of diethyl phthalate when the initial concentration is 0.1mg / L.
Embodiment 3
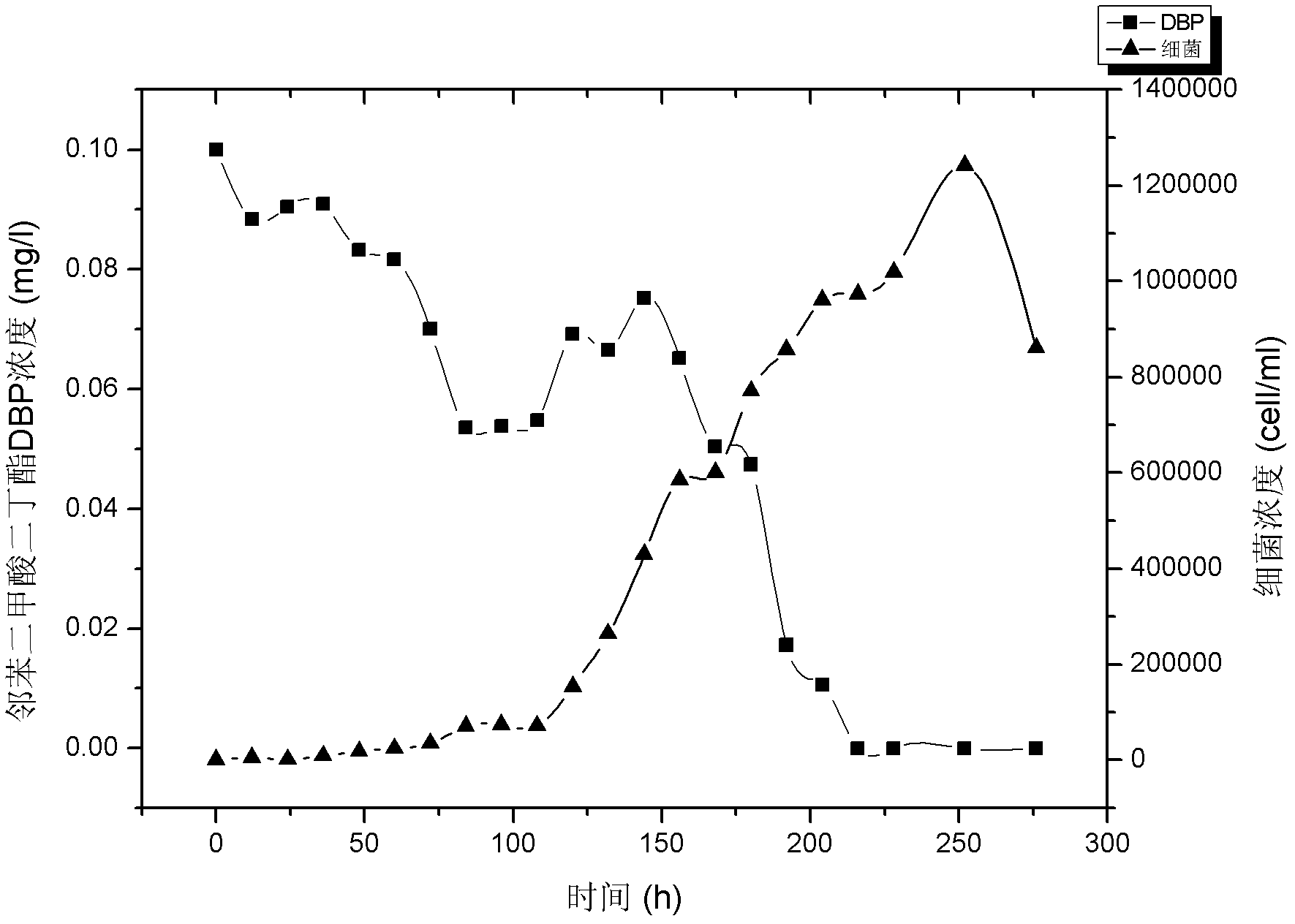
[0034] Use Evian water as the base water (pasteurized, pass through a 0.22μm filter membrane), add 0.1mg / L of phthalate pollutants (dibutyl phthalate), and then inoculate Rhodoferax ferrireducens PAE- UM strains, inoculum concentration at 10 3count / ml. Then subpackage into 100mL Erlenmeyer flasks, put into shaker and cultivate (30 ℃, rotating speed is 150r / min), utilize flow cytometry to detect bacterial growth and utilize high performance liquid chromatography to detect the degradation status of pollutants, such as attached image 3 as shown, image 3 It is the degradation growth curve of dibutyl phthalate when the initial concentration is 0.1mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com