Method for accelerating lattice-Boltzmann by utilizing graphic processing units (GPUs)
A lattice and lattice point technology, applied in the fields of computer high-performance computing and computational fluid dynamics, can solve the problems of low peak floating-point computing power of CPU, large network transmission overhead, large time, etc., to reduce construction costs and management, and improve processing. performance, the effect of reducing power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] With reference to the accompanying drawings of the description, the present invention is described in detail as follows:
[0044]In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
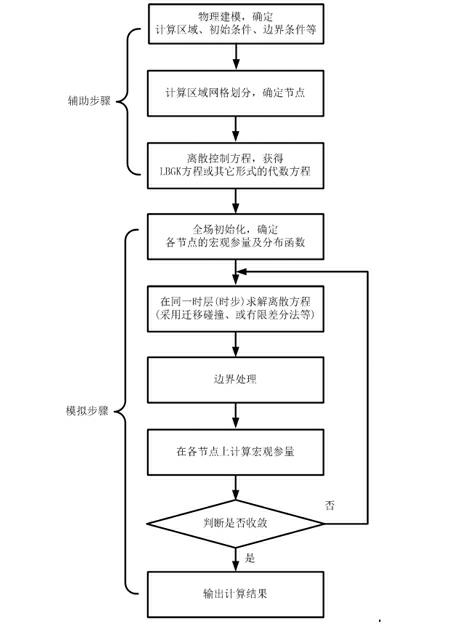
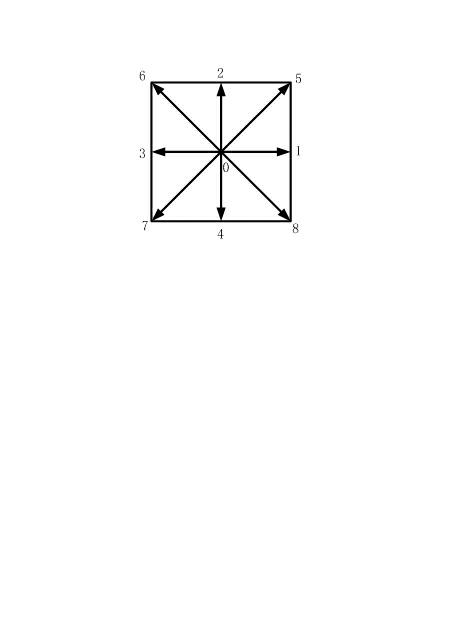
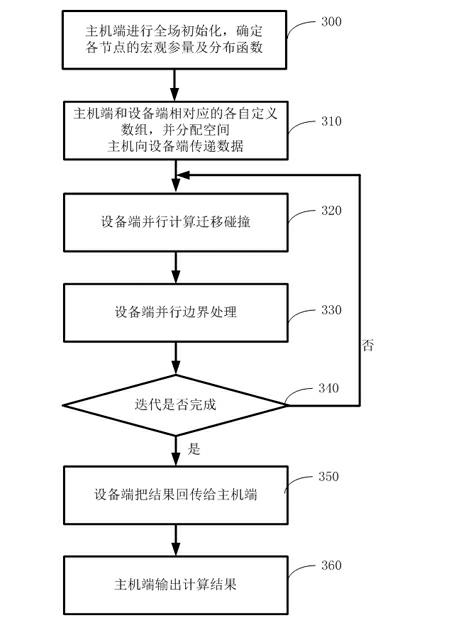
[0045] The purpose of the present invention is to accelerate the lattice Boltzmann method, improve its processing performance, and enable the CPU and GPU to perform collaborative calculations, thereby meeting the needs of fluid simulation, and reducing the construction cost and management, operation and maintenance costs of the computer room. In the present invention, it will be necessary to put the initialization calculation on the CPU side for execution, and use CUDA technology to carry out parallel transformation on the time-consuming and very good parallelism for solving discrete equations and boundary processing, so that it ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com