RFID (Radio Frequency Identification )-based grid positioning system and method
A positioning method and grid technology, applied in the field of RFID-based grid positioning system, can solve the problems of not being widely used, limited, and unable to achieve positioning, and achieve the effects of convenient application, reduced impact, and strong anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
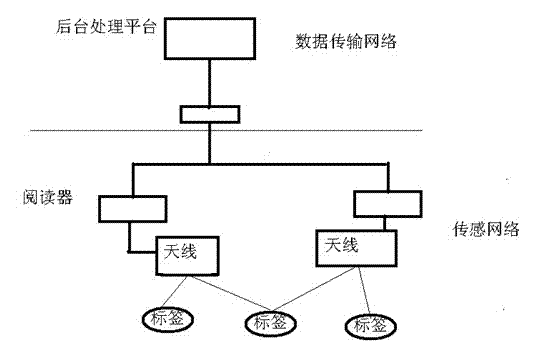
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, the RFID-based grid positioning system includes two networks, namely the sensor network and the data transmission network. The sensor network is generally composed of RFID readers and electronic tags, which can be regarded as a reader / electronic tag array set by the user. The target to be positioned carries a reader or tag, and the reader / electronic tag array receives instructions from the server, obtains the characteristic information (such as signal strength) of the target to be positioned according to the server's instructions, and stores it in the reader middle. The data transmission network includes a server and connections between the server and each reader. The server generates instruction signals according to the user's needs and transmits them to the sensor network. After the reader in the sensor network obtains the information related to the target to be located, it feeds back to the server through the data transmission network. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com