Light-emitting element
A technology of light-emitting elements and light-emitting functional layers, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, semiconductor devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of uneven light emission, difficulty in luminous intensity, and difficulty in obtaining high luminous efficiency, and achieve high luminous efficiency and uniform luminous intensity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
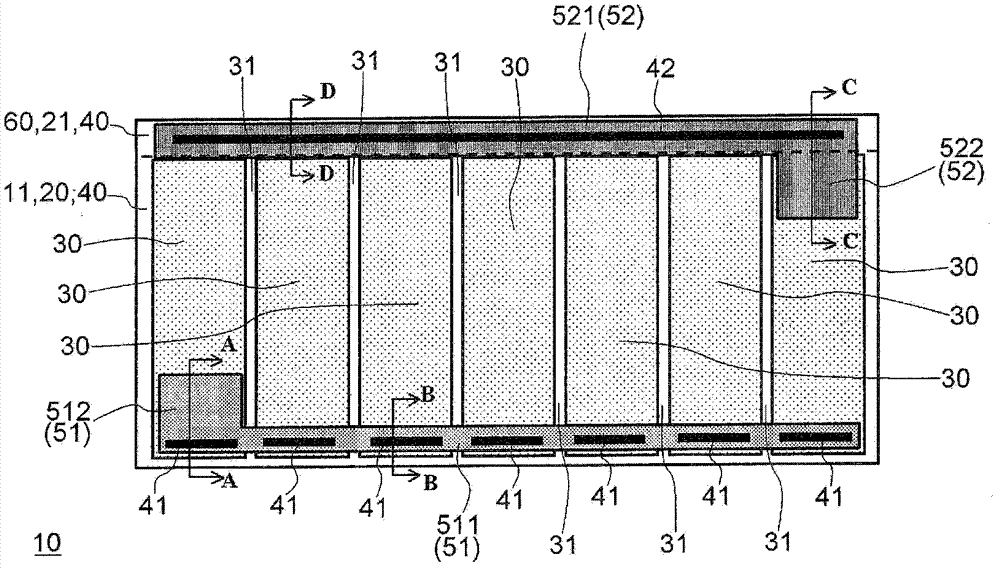
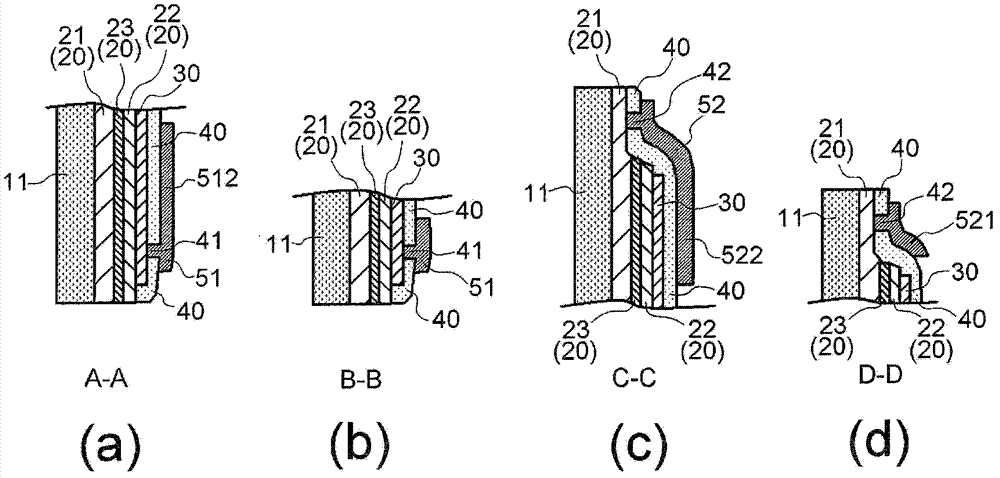
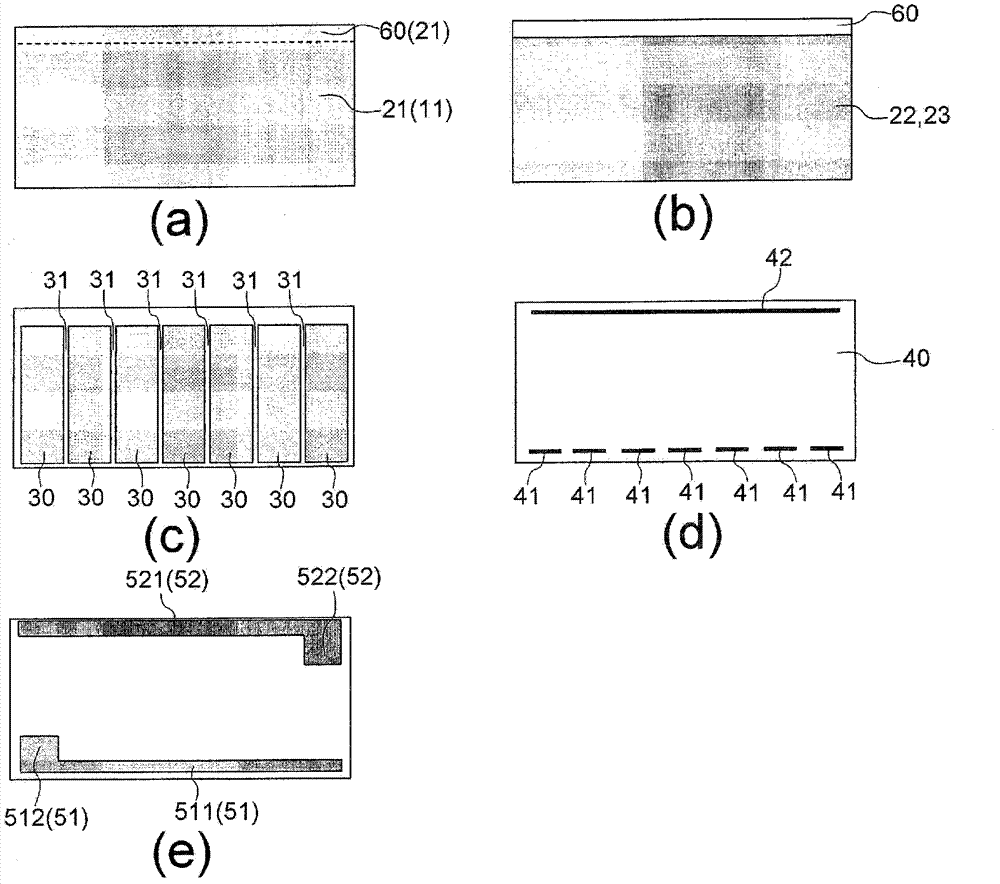
[0049] figure 1 It is a plan view seen from the upper surface side of the light emitting element 10 of the first embodiment. And, the sectional views of the A-A direction, B-B direction, C-C direction, and D-D direction in the plan view are respectively figure 2 (a) ~ (d). Furthermore, the n-type GaN layer (first semiconductor layer) 21, p-type GaN layer 22, transparent electrode 30, insulating layer 40, electrode The top view of (p-side electrode 51, n-side electrode 52) is image 3 (a) ~ (e). When looking down, the figure 1 Among them, the light-emitting element 10 has a rectangular shape long in the left-right direction.
[0050] The semiconductor light-emitting functional layer 20 that emits light in the light-emitting element 10 is formed on the substrate 11, and has an n-type GaN layer (the first semiconductor layer, hereinafter referred to as the n-type layer) 21, an MQW (Multi Quantum Well) layer 23 1. A stacked structure composed of a p-type GaN layer (second...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0075] Figure 7 It is a plan view seen from the upper surface side of the light emitting element 110 of the second embodiment. And, the sectional views of the E-E direction, the F-F direction, the G-G direction, the H-H direction, and the I-I direction in the plan view are respectively Figure 8 (a) ~ (e). Furthermore, the n-type layer 21, p-type layer 22, transparent electrode 30, insulating layer 40, electrodes (p-side electrode 51, n-side The top view of electrode 52) is Figure 9 (a) ~ (e). When viewed from above, the light emitting element 110 is Figure 7 A roughly square shape (1 side L) is shown.
[0076] The semiconductor light-emitting functional layer 20 that emits light in the light-emitting element 110 is formed on the substrate 11 as described above, and has a stacked structure composed of an n-type layer 21 , an MQW layer 23 , and a p-type layer 22 .
[0077] here, as Figure 9 As shown in (a), the n-type layer (first semiconductor layer) 21 on the subst...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0101] The light emitting element 210 of the third embodiment has a structure in which a light emitting diode having a structure similar to that of the light emitting element 10 of the first embodiment and a protective diode (diode) are monolithically connected on a substrate. Figure 11It is a circuit diagram of the light emitting element 210 of this structure. Here, the light emitting diode 220 and the protection diode 230 are reversely connected. In this case, when an excessive voltage is applied to the light emitting diode 220 , the protection diode 230 is turned on by the Zener effect to bypass the current, thereby protecting the light emitting diode 220 .
[0102] Figure 12 With figure 1 A plan view of the structure of the light emitting element 210 is similarly shown. and, Figure 13 (a) to (c) are cross-sectional views in the J-J direction, K-K direction, and L-L direction of the periphery of the protective diode portion in the light emitting element 210, respect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com