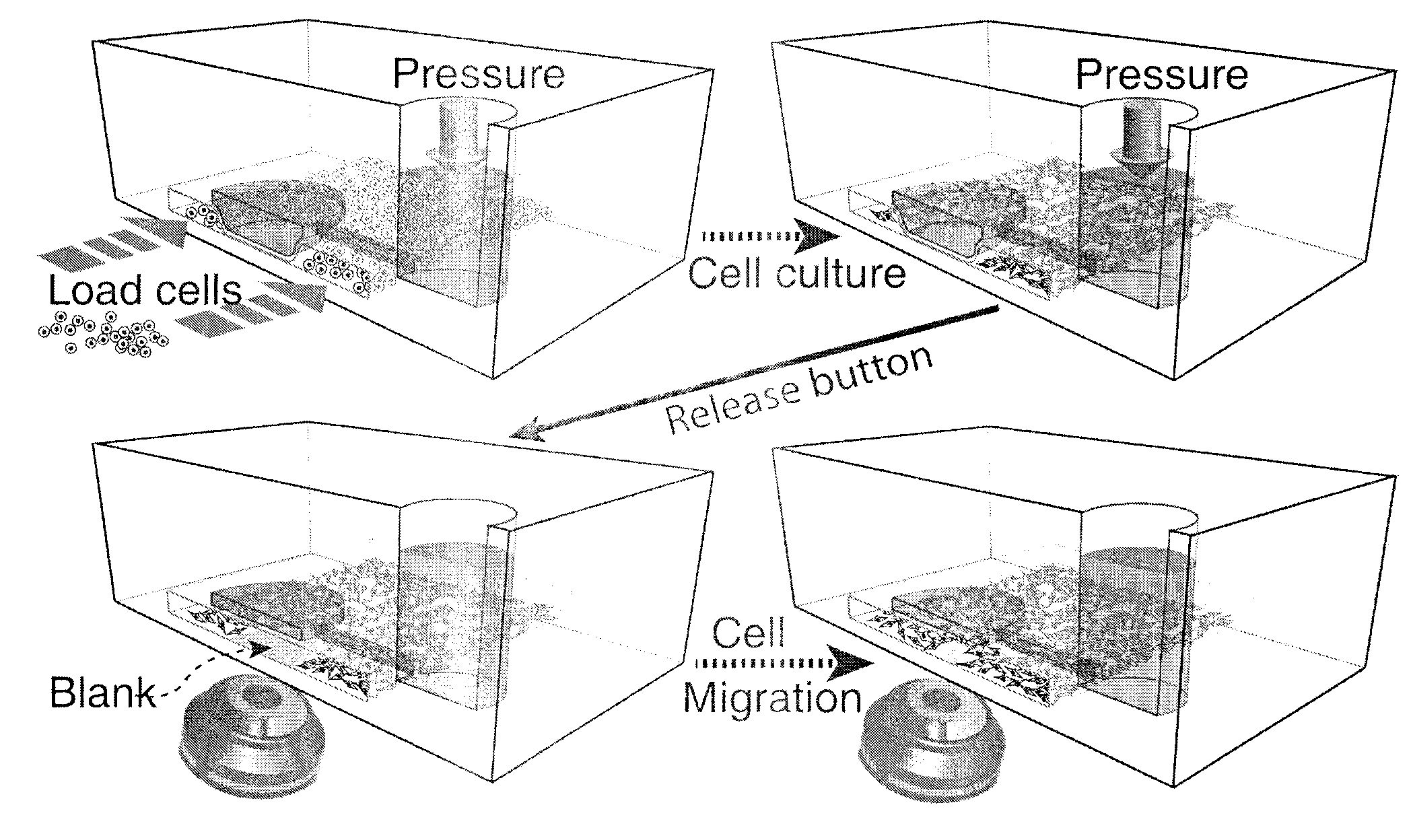
Microfluidic chip applicable to research on cell migration
A microfluidic chip and cell migration technology, which can be used in special-purpose bioreactors/fermenters, microbial measurement/inspection, enzymology/microbiology devices, etc., and can solve problems such as difficult automatic operation and cell damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] The following examples illustrate the preparation method of microfluidic chips. In the following examples, relatively simple photoresist SU-8, AZP 4620 and PDMS are used to prepare, but it does not mean that microfluidic chips can only be prepared by such methods. Those skilled in the art It can be understood that any existing technology in the art can be used to prepare the microfluidic chip with the structure of the present invention.
[0032] We first used photolithography to fabricate templates for the microfluidic channel and the control channel, respectively. The control channel was made with negative glue SU8-2010. Pour negative glue SU8-2010 onto a clean silicon wafer, rotate at 1000rpm for 1 minute, bake on a heating plate at 65°C for 5 minutes, bake on a heating plate at 95°C for 10 minutes, expose, repeat baking at 65°C for 5 minutes, Bake on a heating plate at 95°C for ten minutes, develop, and heat on a heating plate at 150°C for 3 hours to reinforce the g...
Embodiment 1
[0054] Structure of the microfluidic chip. This embodiment describes in detail a preferred structure of the microfluidic chip of the present invention, the structure is as figure 1 shown. The fluid delivery channel connected to the inlet is bifurcated to form 4 new fluid delivery channels, and each new fluid delivery channel is bifurcated to form 2 new fluid delivery channels, and the final 8 fluid delivery channels are widened to form cell growth microfluidic channel. The control layer includes a total of 2 control channels, of which the red control channel entrance is on the right, and the control channel directly connected to the entrance is bifurcated to form 4 new control channels, and each new control channel is formed above the cell growth microfluidic channel There are 8 cavities, so this control channel corresponds to controlling 4 cell growth microfluidic channels (corresponding to the 1st, 3rd, 5th, and 7th from bottom to top). Similarly, the green control channe...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Effect of different blank area areas on cell migration speed.
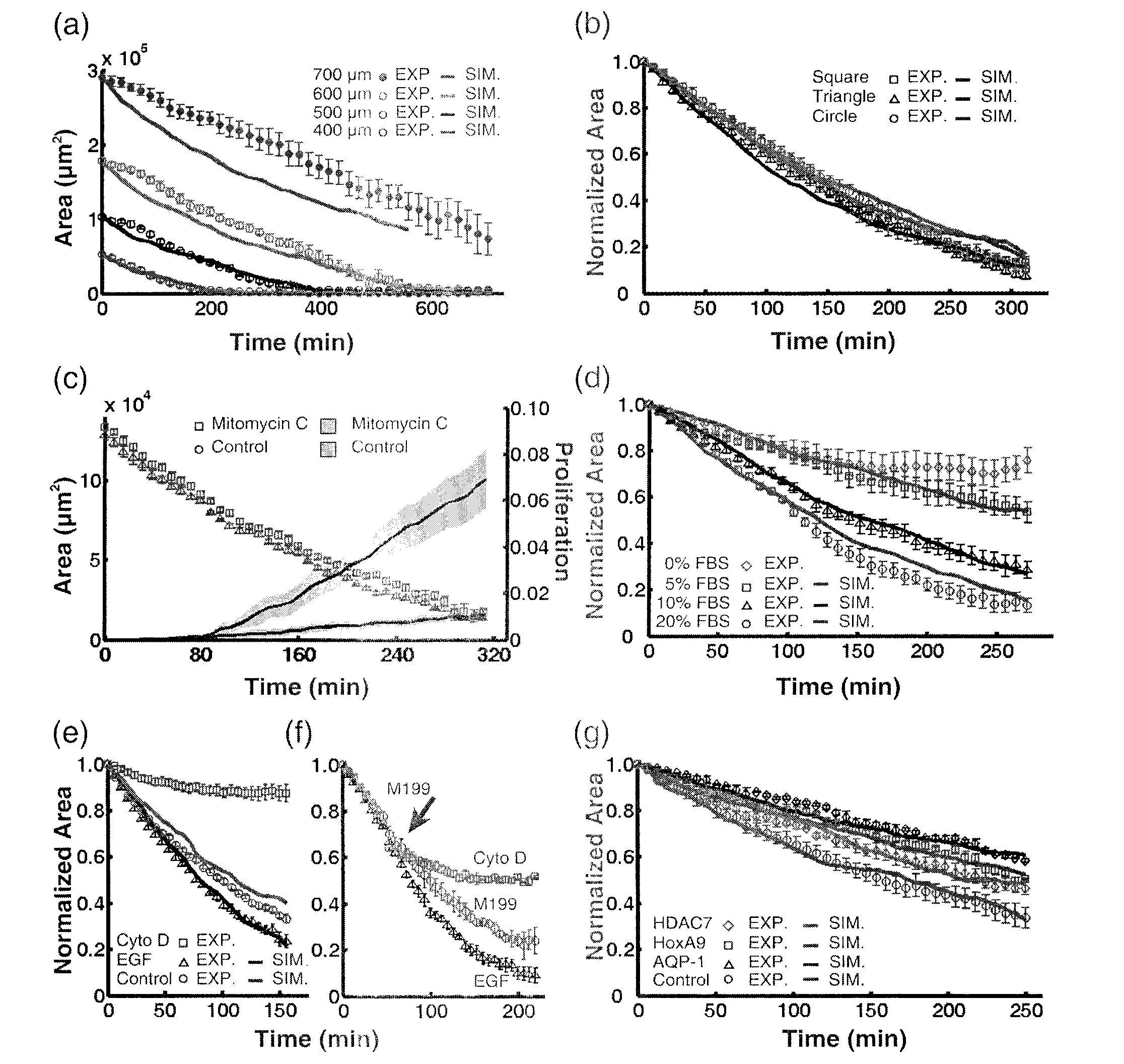
[0057] We designed the button valve (that is, the cavity and the connection layer at the cavity) into circles with diameters of 700 microns, 600 microns, 500 microns, and 400 microns in turn, which are used for microfluidic channels for culturing cells (that is, cell growth microfluidics). track) with a width of 1000 μm. The size of the blank "scar" area (that is, the area of the blank area) at each moment is obtained by image processing methods, and a graph of the number of pixels in the area and time is drawn. We find that the four curves corresponding to different diameters are almost parallel to each other, because the slope indicates that the cells The size of the migration speed, thus, we deduce that the cell migration speed has nothing to do with the initial "scar" area ( image 3 a).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com