Semiconductor light-emitting element
A light-emitting element and semiconductor technology, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficulties, achieve good light extraction, improve light reflection, and reduce element resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
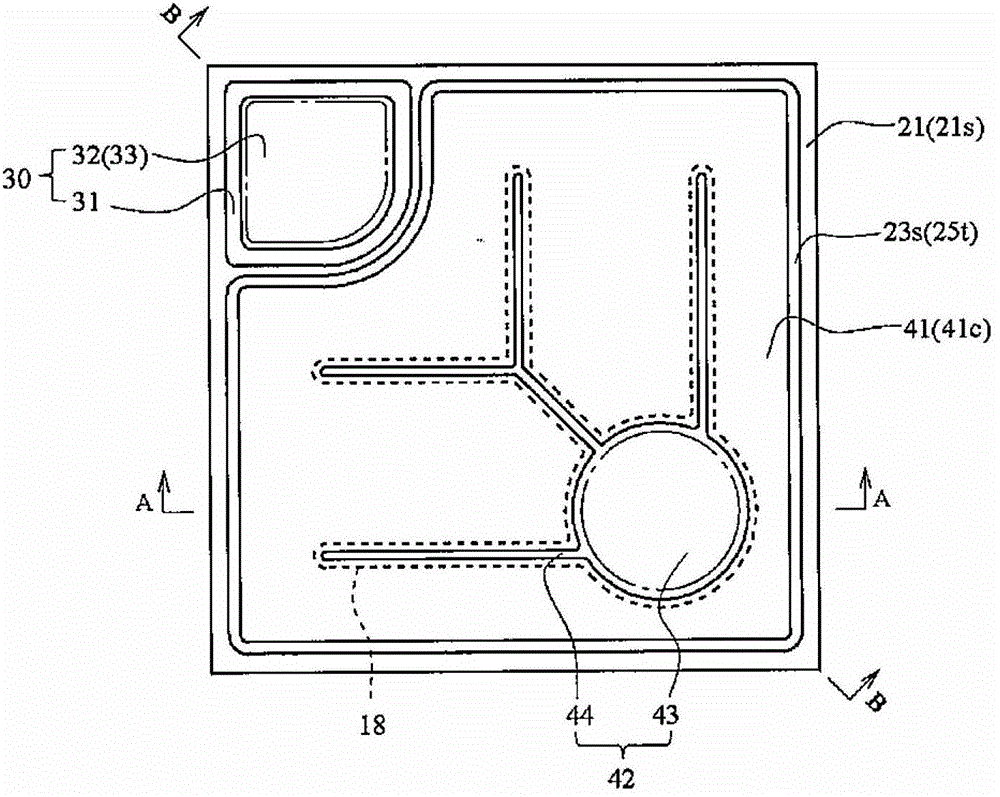
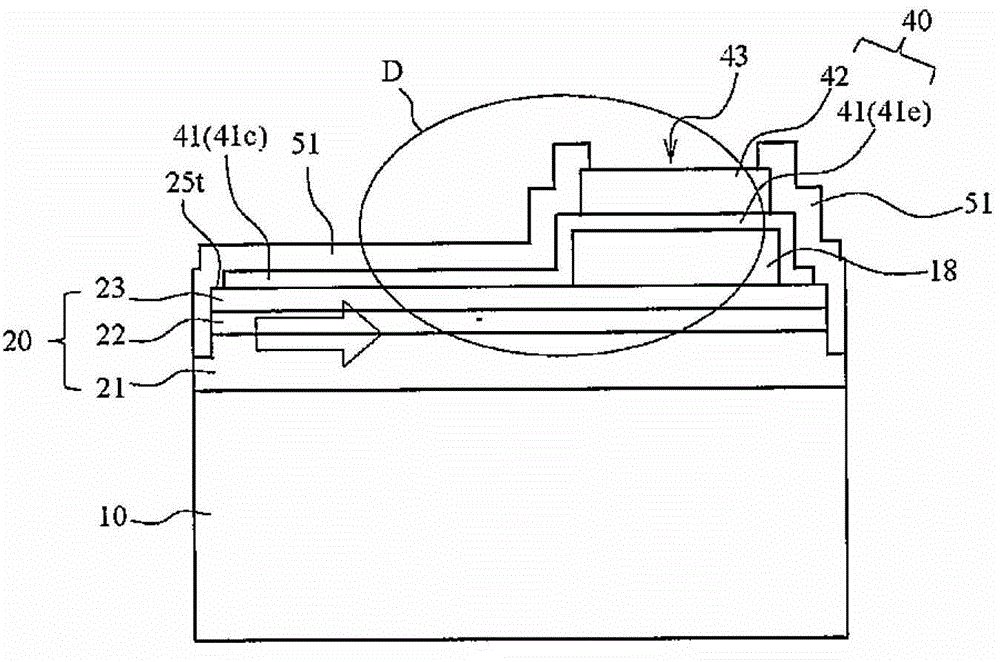
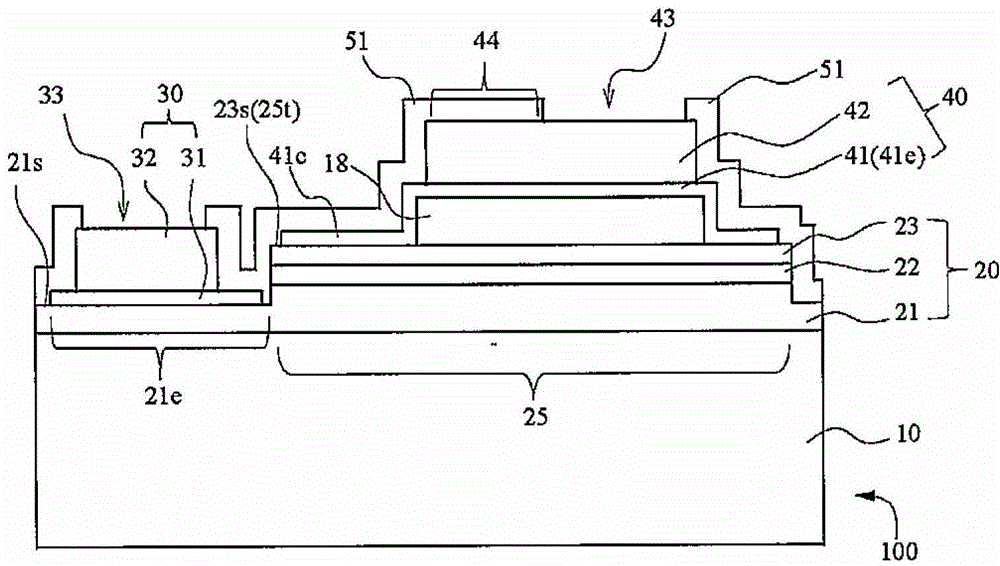
[0101] A specific example of LED100 of Embodiment 1 and its structure are demonstrated using FIG. 1. FIG. here, Figure 1A It is a schematic diagram illustrating a plane when viewing the LED according to Embodiment 1 from the electrode forming surface side, Figure 1B , Figure 1C is true Figure 1A A schematic diagram illustrating the cross-section on the A-A line and B-B line of Figure 1D , Figure 1E will be Figure 1C The schematic diagram after local enlargement, Figure 1E is description Figure 1D sketches of other forms.
[0102] The structure of the light-emitting element shown in FIG. 1 has a semiconductor structure 20 consisting of an n-type nitride semiconductor layer 21 in which a first conductivity type layer is laminated on a substrate 10 through a base layer (not shown) such as a buffer layer, The active layer 22 serving as the light emitting part and the p-type nitride semiconductor layer 23 of the second conductivity type layer are composed of a stacke...
Embodiment 1A
[0145] [Example 1A(1a)]2 2 2 2 <[embodiment 1C (1c)],
[0146] λ / 2n in Example 1B(1b) 2 Near, more specifically, at λ / 2n 2 ±λ / 4n 2 (λ / 4n 2 Above, 3λ / 4n 2 In the range below), better light output can be obtained. On the other hand, according to the comparison of Example 1A (1a) and Example 1C (1c), it can be seen that the thicker the insulating film, the higher the Vf tends to be. Vf becomes higher due to the first layer of the insulating film.
[0147] Next, in the above-mentioned Example 1 (research example, the structure of FIG. 1 ), the following study example, and Example 2 ( Figure 4 structure), Example 5 of Embodiment 7 ( image 3 structure) and the structures shown in the comparative examples of these examples, the film thickness of the first layer of ITO was changed between 20nm and 170nm to produce light-emitting elements respectively, and the following Figure 13 output characteristics shown. Here, in order to offset the difference in output due to the diff...
Embodiment approach 2
[0150] As Embodiment 2, in Example 1 of Embodiment 1, the shape of the extension portion 44 of the second electrode (p-electrode) is set to Figure 4 In the shape shown, the number of extensions is changed from 4 (Example 1) to 9, and a light-transmitting insulating film corresponding to the shape of the extensions (second layer) and electrodes is provided. , a substantially square (320 μm×320 μm) light-emitting element was produced with the same structure and dimensions as in Example 1.
[0151] In this light-emitting element, compared with Example 2, the number and area of electrode extensions are larger, so phenomena such as current diffusion are improved. decreased, and the output of the element tended to be slightly lower than in Example 2.
[0152]Concretely, for comparison, in the same manner as the study examples of Example 1 (Examples 1A to 1C, 1a to 1c), under the condition that the second layer of the second electrode and the light-transmitting insulating film ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com