Standardization of tissue specimen preservation by ultrasound and temperature control
A technology of tissue samples and ultrasound, applied in the preservation of human or animal bodies, biochemical instruments, electric/wave energy processing enzymes, etc., can solve problems such as fixation, inconsistent test results, and cross-linking damage of biomolecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
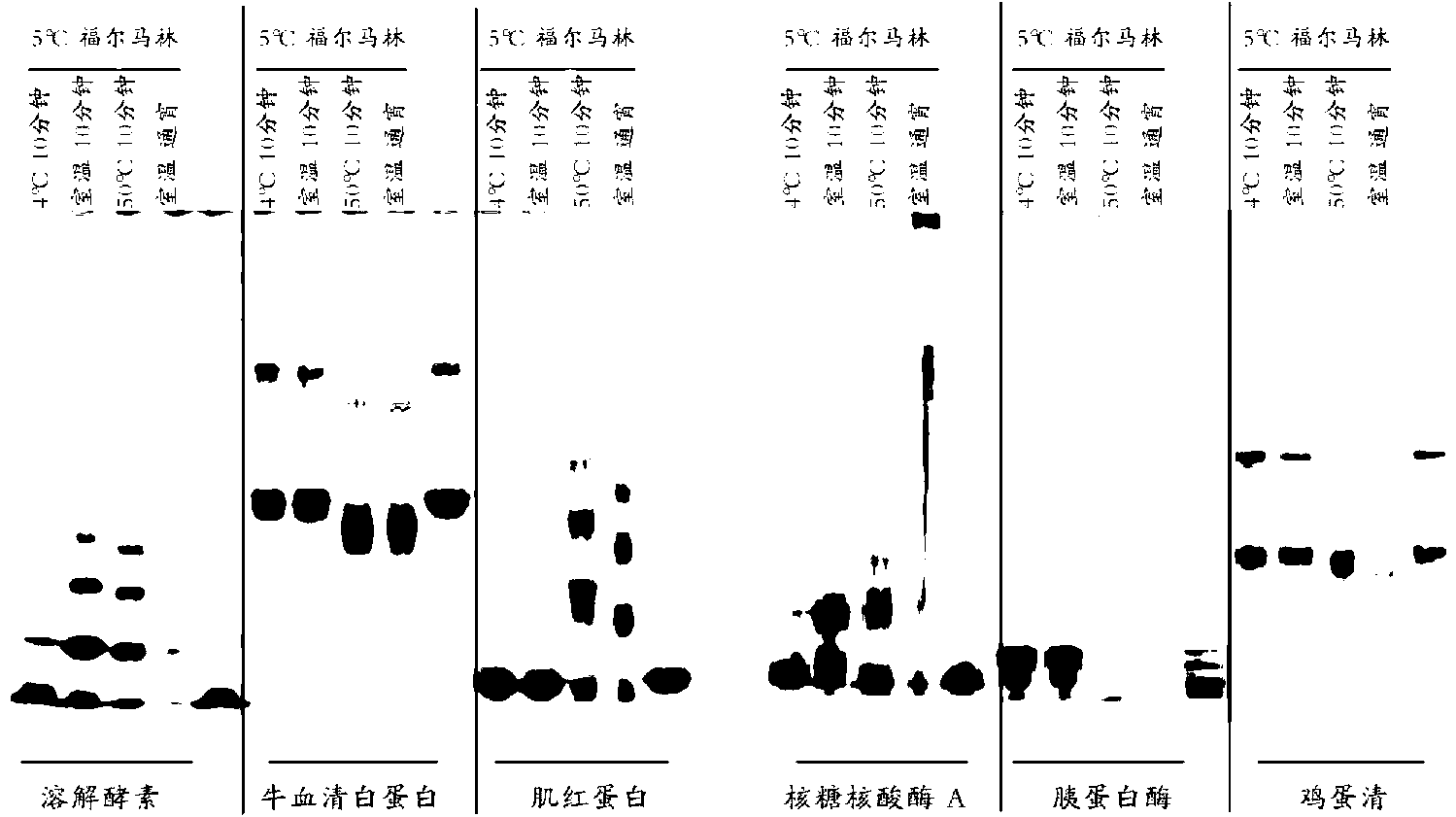
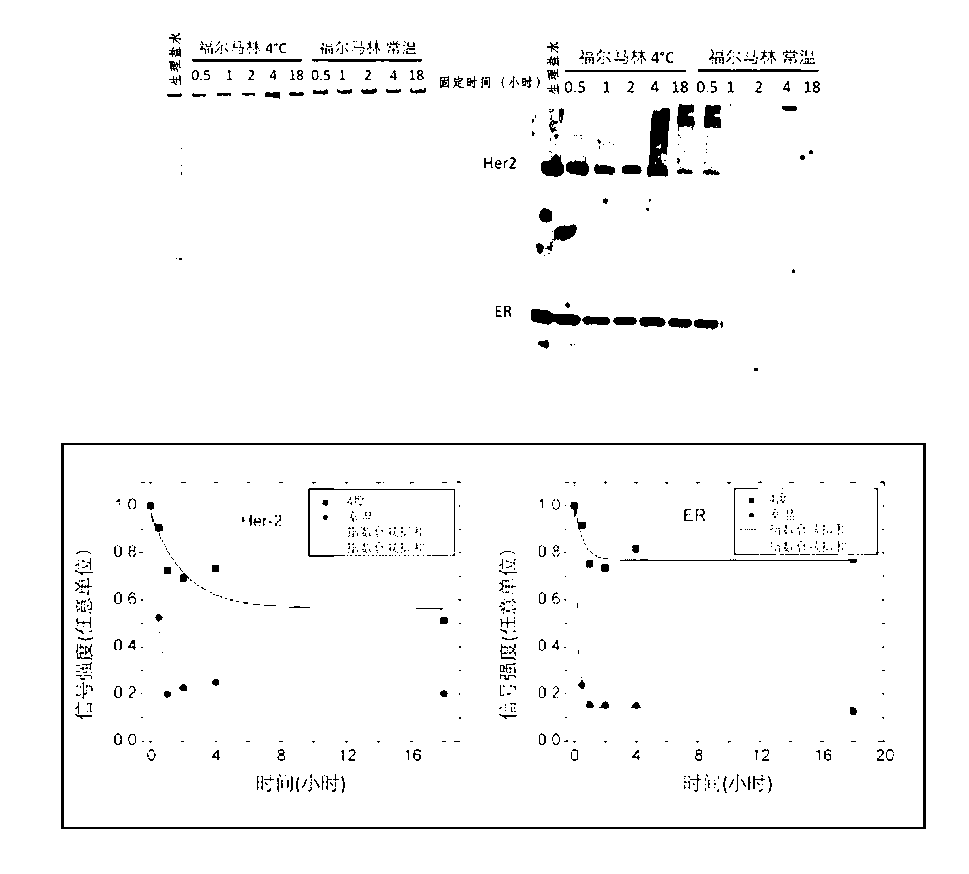
[0106] We treated lysozyme and BSA with NBF for 60 min at different temperatures, and immediately put the cross-linked product on an SDS gel for separation. The level of cross-linking for lysozyme and BSA gradually increased between 0-40 degrees Celsius. SDS electrophoresis showed that there was a significant increase in the size of oligomers (lysozyme) or in gelatinized fluidity (BSA) at 50 °C and reached a maximum around 60 °C. This finding predicts that when lysozyme is treated with NBF at temperatures above 60 °C, a large number of aggregates start to form. This aggregation is in highly intermolecularly cross-linked lysozyme molecules and may not be resolved by SDS electrophoresis. No aggregation was observed by BSA in NBF at high temperature, perhaps because the crosslinks in BSA are always intramolecular.
[0107] As for lysozyme, the speed of cross-linking increases gradually when the temperature is increased from 0-20°C to 20-40°C, and then suddenly increases when th...
example 2
[0109] Significant cross-linking occurs after 10 minutes of incubation at 50°C. In other experiments, we tested cross-link formers for various proteins, incubating in formalin at 4°C, at room temperature, and at 50°C for 10 minutes versus overnight in formalin at room temperature. Compare. As shown in Table 5, the speed of cross-linking at 4 °C was the slowest of all proteins tested. Then, there was a larger increase in cross-linking levels after 10 minutes of incubation at 50°C, almost comparable to overnight incubation at room temperature. For all proteins except BSA, protein precipitates formed after incubation for 10 min at 50 °C and overnight at room temperature. This experiment shows that, for most proteins, a 10-minute incubation in formalin at 50°C can form significant cross-linked morphology. Similar results were also obtained after 5 min incubation (material not shown).
example 3
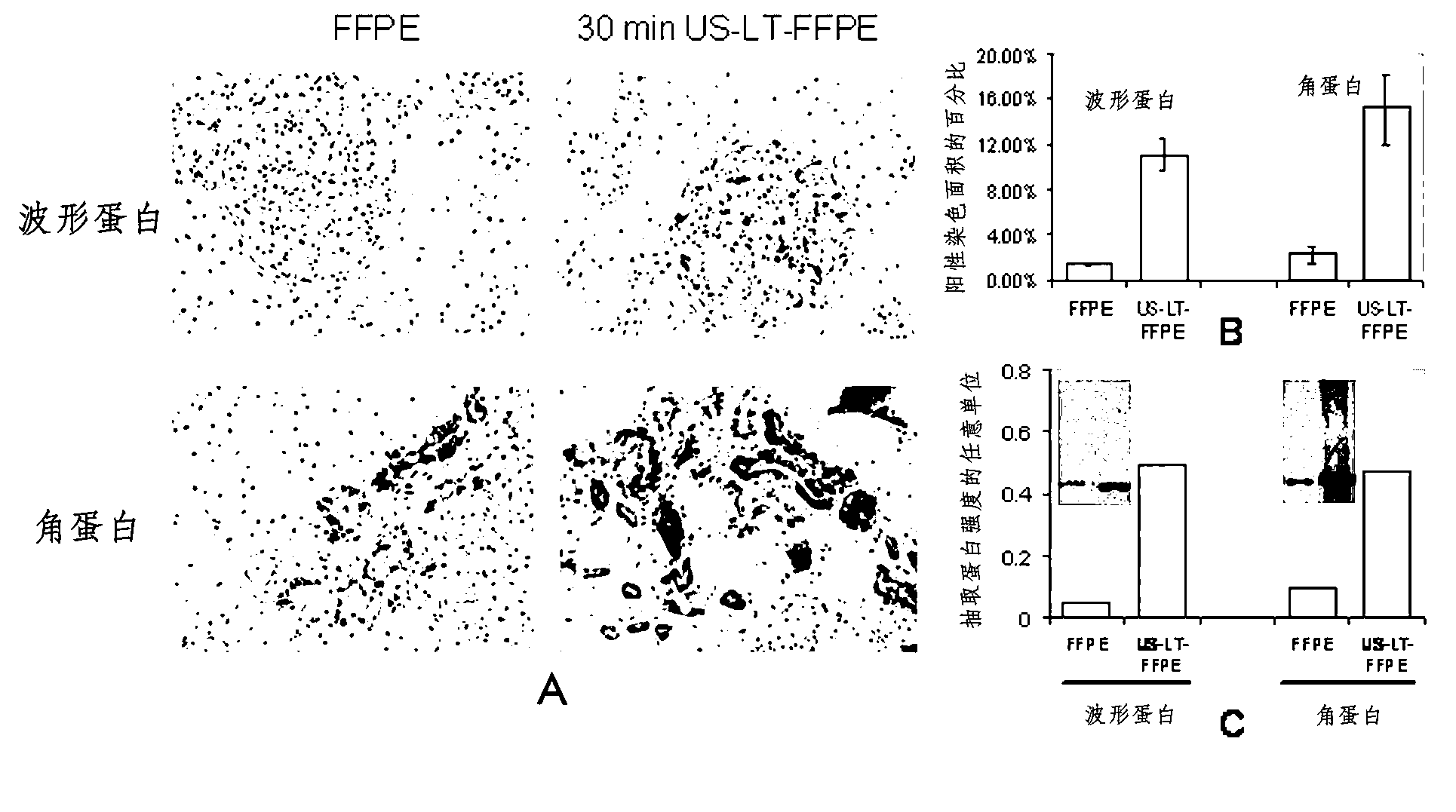
[0111] Tissue samples 1–4 mm thick are placed in tissue storage boxes and then submerged in a cross-linked fixative (eg, formalin, 4°C) until sonicated. Ultrasonic waves are applied to increase the temperature of the fixative alone or in combination with other heating devices to 50-80°C. This temperature needs to be maintained for 5-20 minutes.
[0112] This tissue sample is then placed in a dehydrating agent, eg, 100% ethanol. The temperature of the dehydrating agent needs to be raised to 50-75 degrees Celsius by ultrasonic alone or in combination with other heating devices. This temperature needs to be maintained by ultrasound alone or in combination with other heating devices for 5-30 minutes. This step is repeated at least once.
[0113] This tissue sample is then placed in a cleaning agent, eg, xylene or a xylene substitute. The temperature of the cleaning agent needs to be raised to 50-75 degrees Celsius by ultrasound alone or in combination with other heating device...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com