Application of TuMV-CP gene fragment-mediated RNAi carrier in cultivation of anti-TuMV transgenic plant
A technology of transgenic plants and fragments, applied in the field of RNAi vectors, can solve the problems of rapeseed yield loss, rapeseed quality reduction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1, have the discovery of the fragment that suppresses turnip mosaic virus function
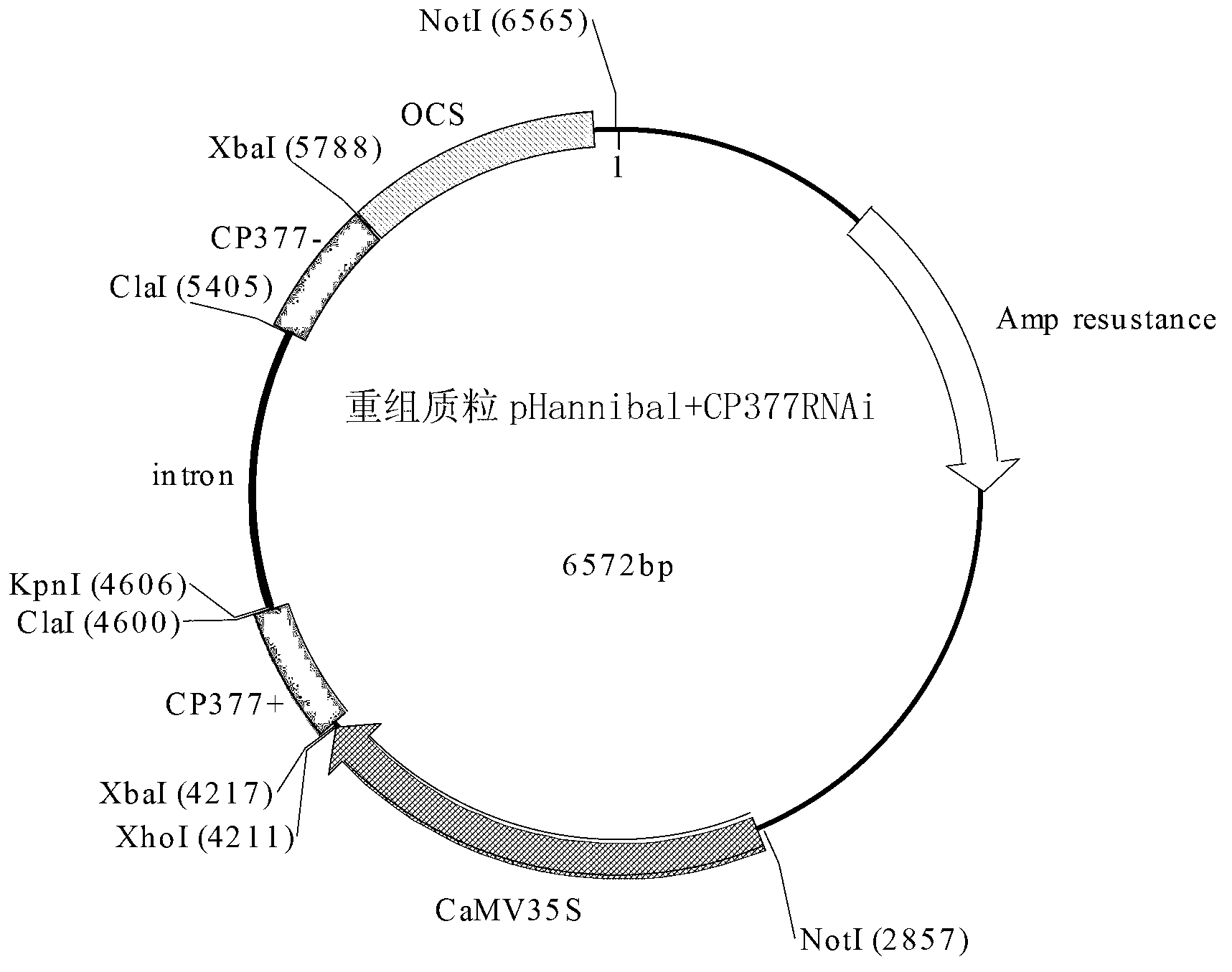
[0037] Sequence comparison of 122 TuMV strains registered in GenBank revealed that there is a conserved region in the CP gene of turnip mosaic virus (the CP gene is shown in sequence 2 in the sequence listing, encoding the coat protein shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing) , a fragment of 377bp was finally determined in this conserved region (named CP377 fragment, as shown in sequence 3 of the sequence listing, which is the 446-822 nucleotides from the 5' end of the CP gene shown in sequence 2 of the sequence listing ), the RNA encoded by this fragment is expected to inhibit the turnip mosaic virus. The RNA transcribed by the CP377 fragment is a single-stranded RNA shown in sequence 4 of the sequence listing.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2, the construction of RNAi expression vector
[0039] 1. Construction of plant expression vector pBBBasta
[0040] The construction method of the plant expression vector pBBBasta (referred to as pBBBasta vector) vector is as follows:
[0041] 1. Digest plasmid pDHB321.1 with restriction endonuclease SacI, and recover a fragment of about 2100 bp (the sequence between SacI digestion is shown in sequence 6 of the sequence table, including "LB-bar expression box-RB"). It is also possible to directly artificially synthesize the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 6 of the sequence table with SacI restriction sites at both ends, and then digest it with restriction endonuclease SacI to recover a fragment of about 2100bp (containing "LB-bar Expression box-RB", the sequence between the SacI restriction sites is shown in sequence 6 of the sequence table).
[0042] 2. Digest the plasmid pBBR1MCS-2 with restriction endonuclease SspI, and recover a fragment ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3, the acquisition and identification of transgenic plants
[0067] 1. Obtaining of transgenic plants
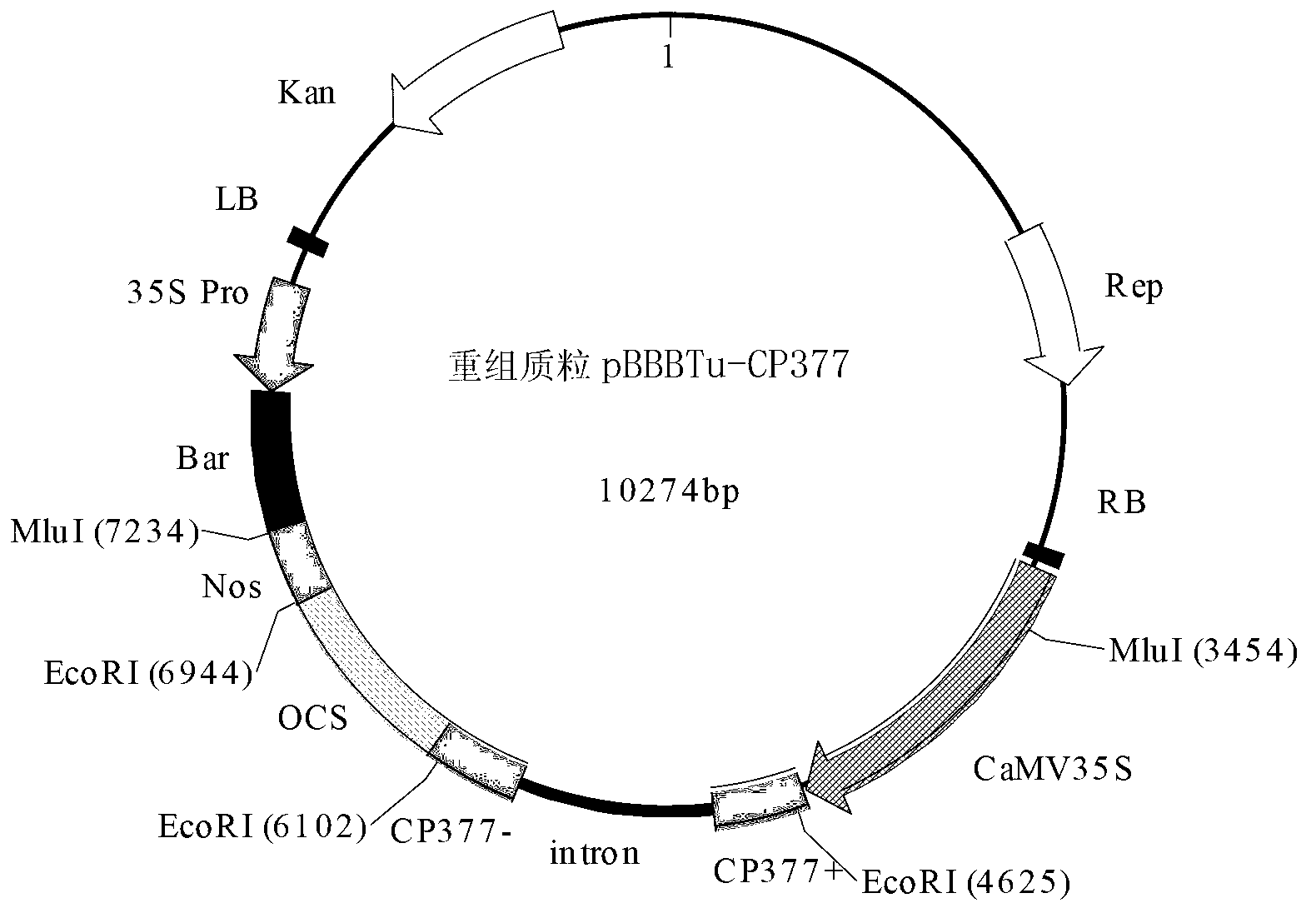
[0068] 1. Introduce recombinant plasmid pBBBTu-CP377 into Agrobacterium GV3101:pMP90 to obtain recombinant Agrobacterium.
[0069]2. Introduce recombinant Agrobacterium into Colombian ecotype Arabidopsis thaliana by inflorescence dipping method (Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: asimplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16, 735-743.) mustard, get T 0 generation seeds.
[0070] 3. Harvest T 0 Seeds obtained by selfing of generation plants, which grow T after sowing 1 For the first generation seedlings, spray Basta herbicide with a concentration of 1-2‰ (volume ratio) after the seedlings grow two cotyledons, and the plants that can survive and continue to grow are T 1 Positive plants. A total of 64 T 1 Positive plants.
[0071] 4. Take T 1 Cut the leaves of the positive plants for mol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com