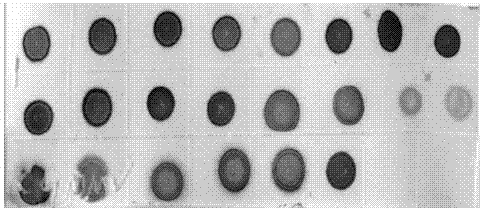
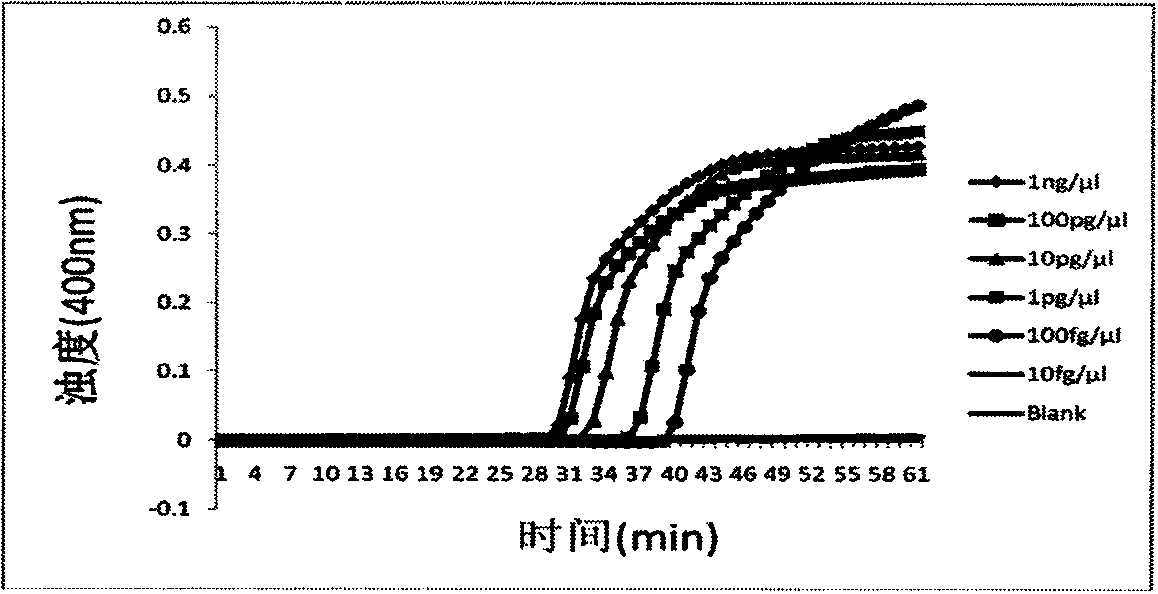
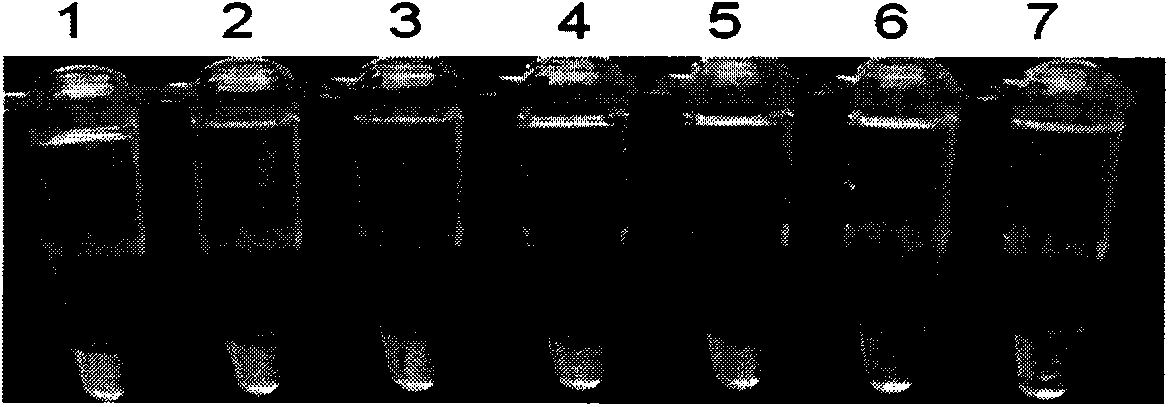
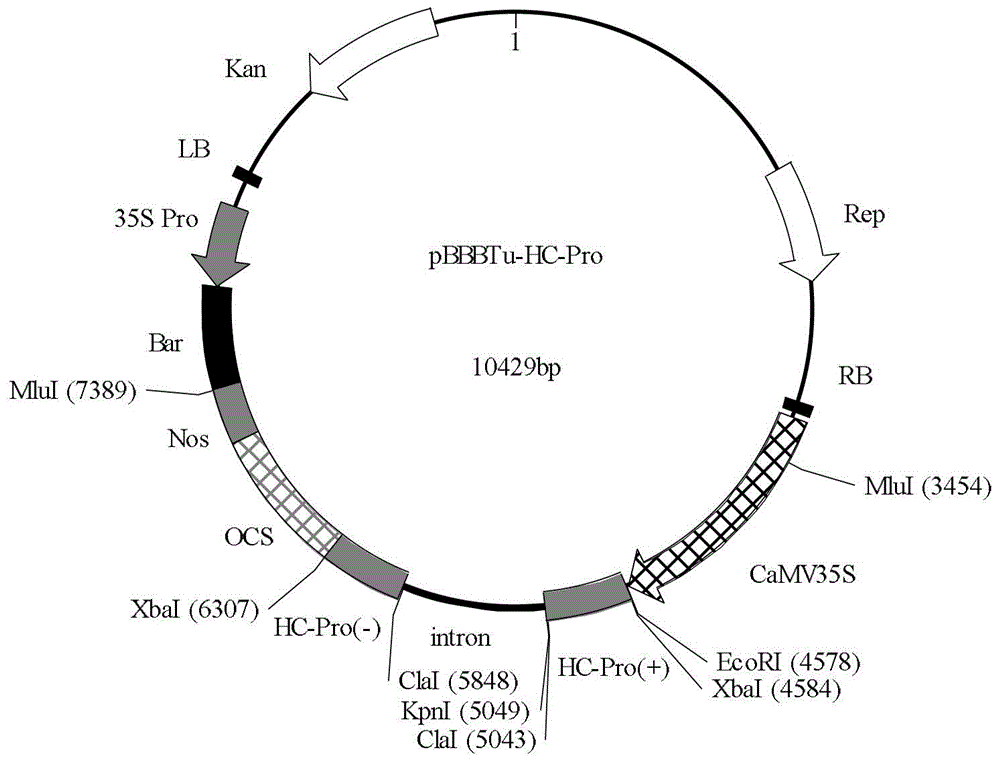
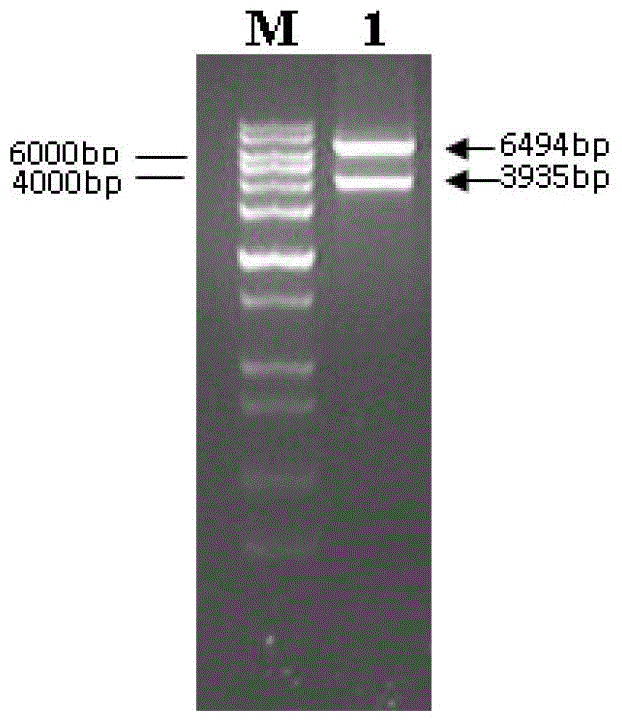
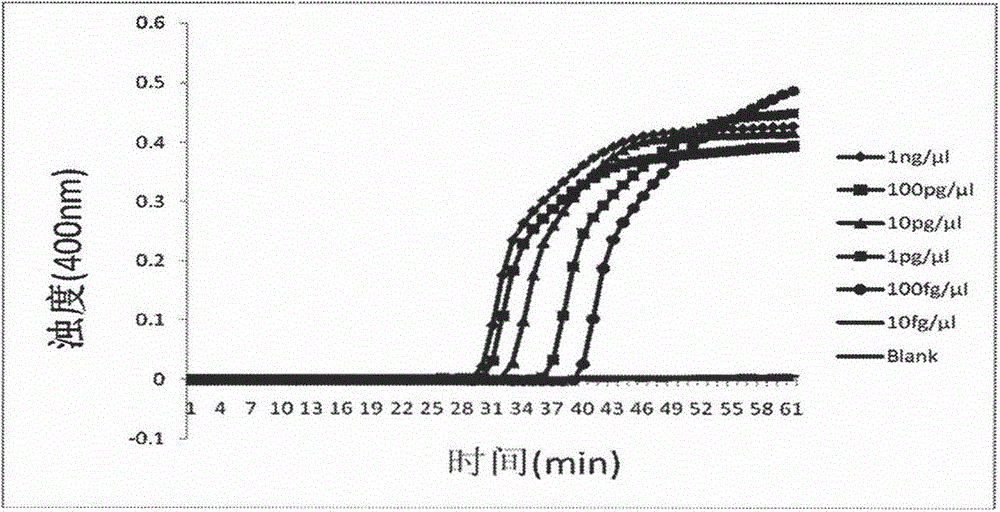
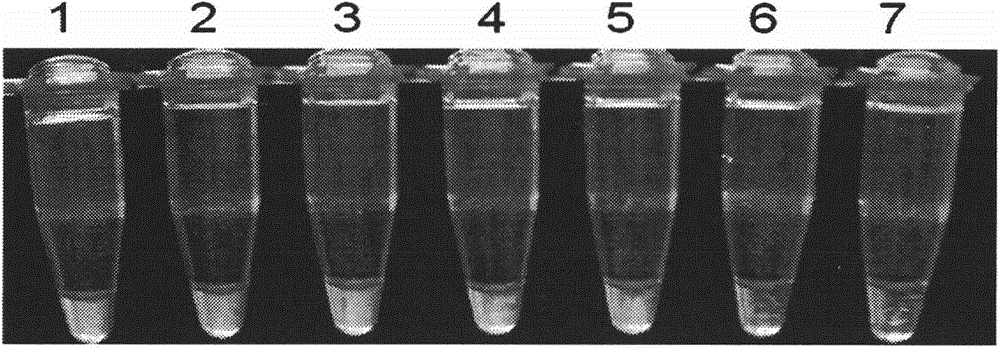
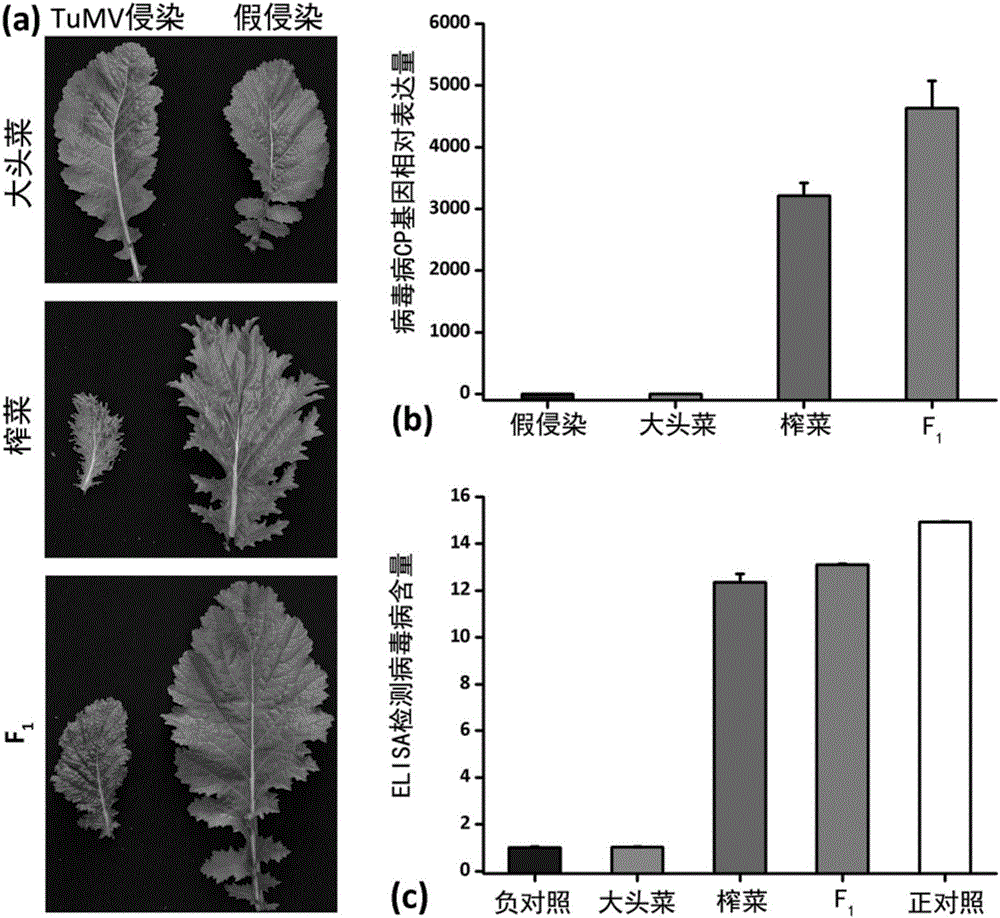
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Turnip mosaic virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) is a Potyvirus of the family Potyviridae that causes diseases in cruciferous plants, among others. The virus is usually spread by 40-50 species of aphids in a non-persistent manner. Infected plants, especially the natural hosts, show symptoms such as chlorotic local lesions, mosaic, mottling, puckering or rugosity. TuMV is a positive-sense single stranded RNA virus, consisting of a non-enveloped, helical capsid that is filamentous and flexuous, with an average length of 720 nm. The TuMV genome is linear and monopartite (single particle). The virus has a thermal inactivation point (TIP) of 62 °C, and longevity in vitro (LIV) of 3–4 days.
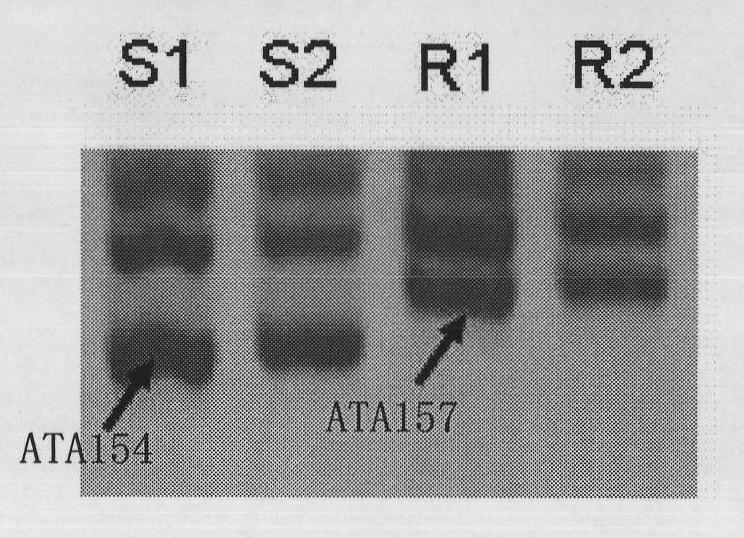
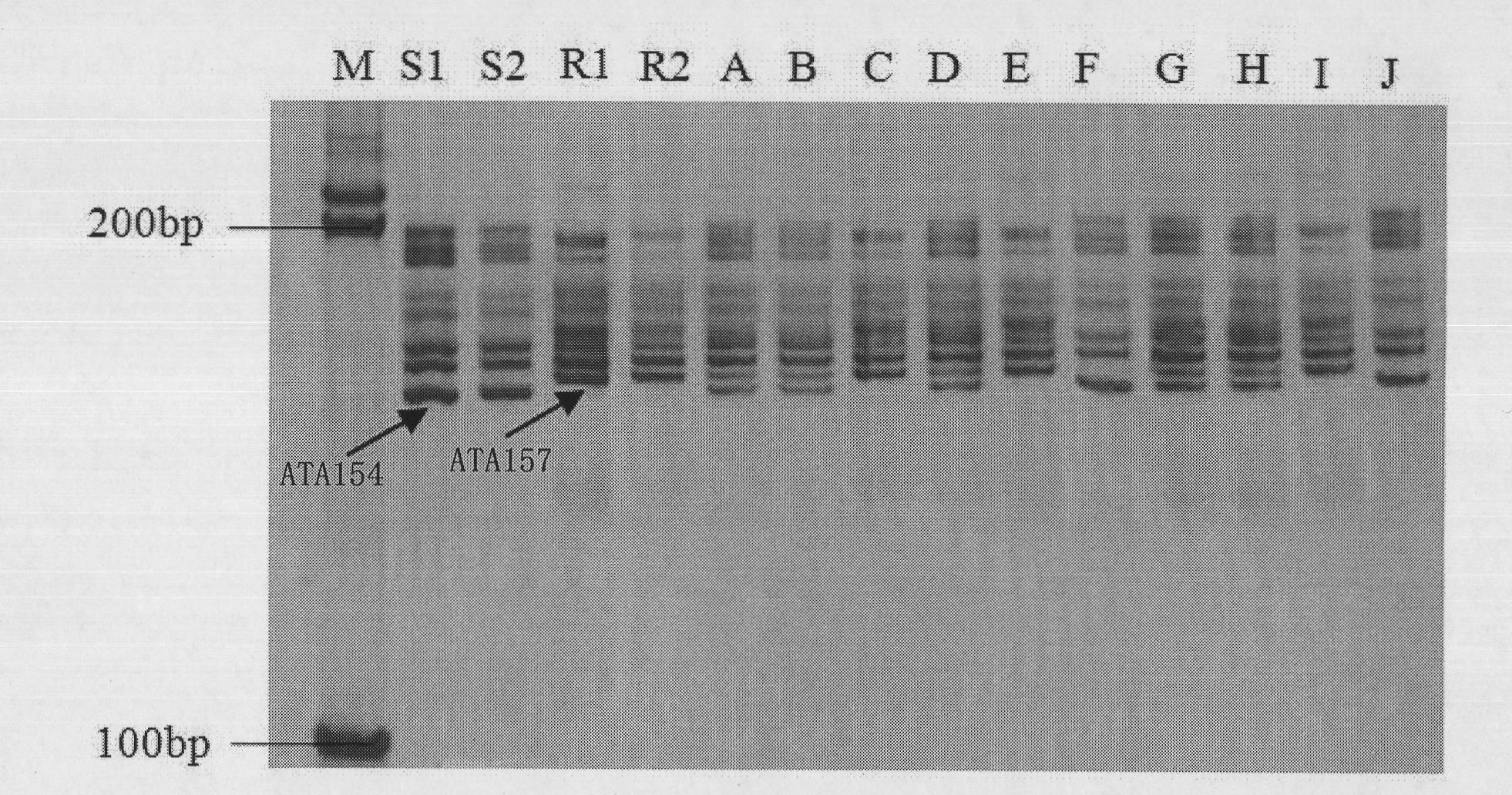
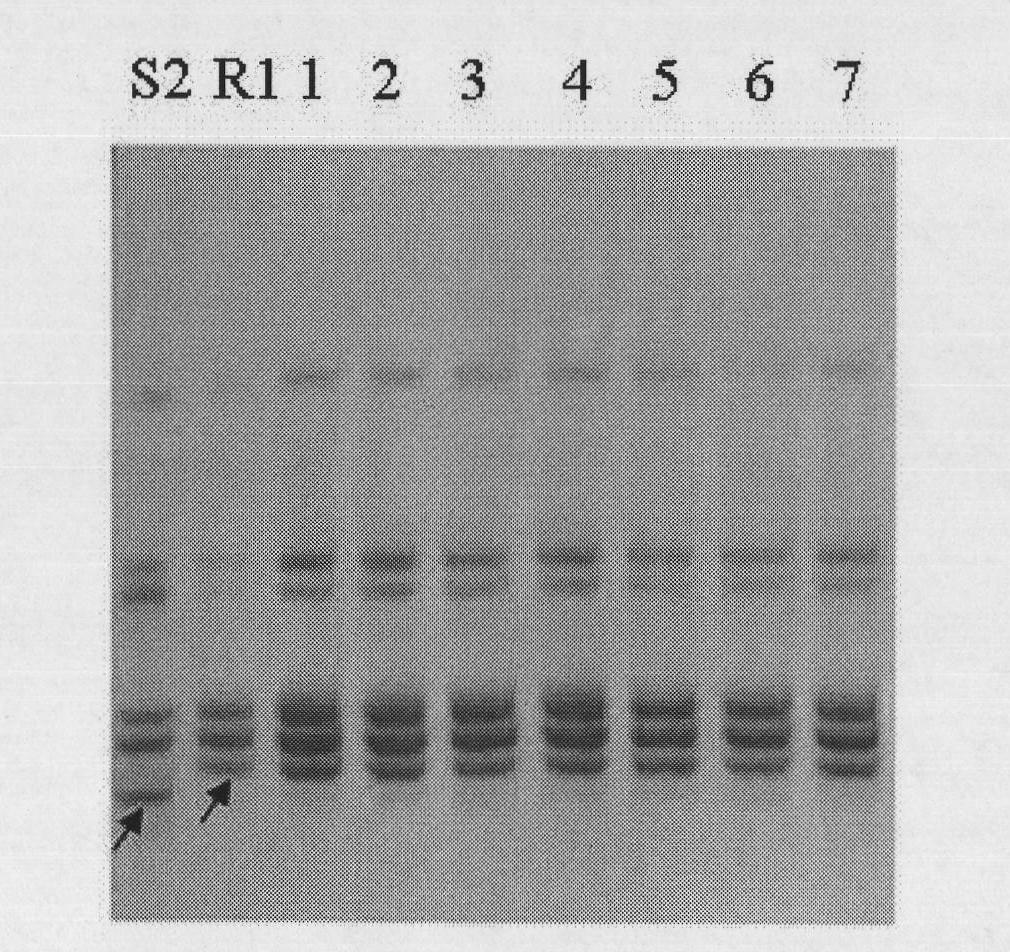
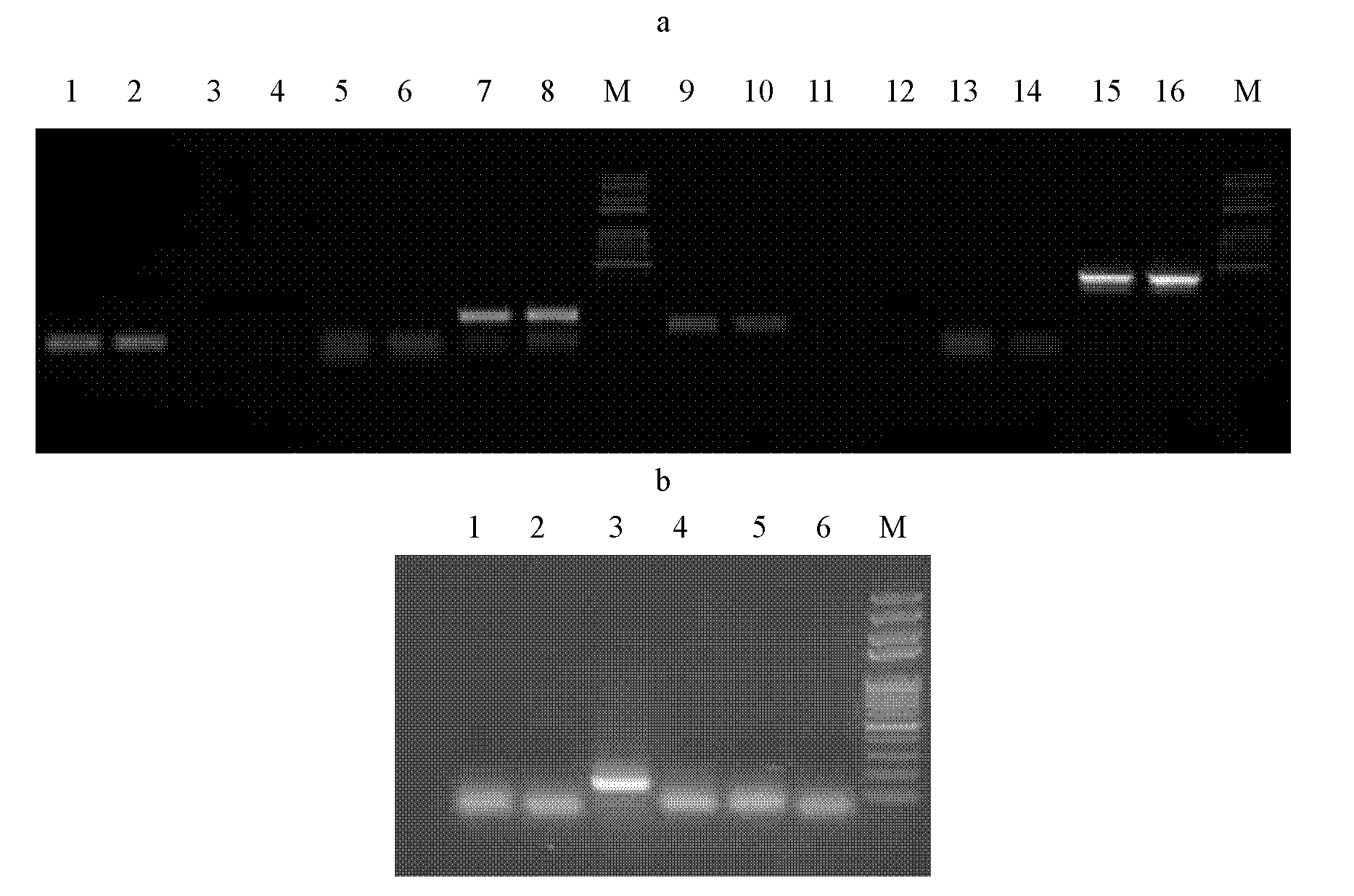
A pair of cabbage turnip mosaic virus EST-SSR markers and application thereof
InactiveCN101838645ASpeed up breedingImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDisease resistantSelection system
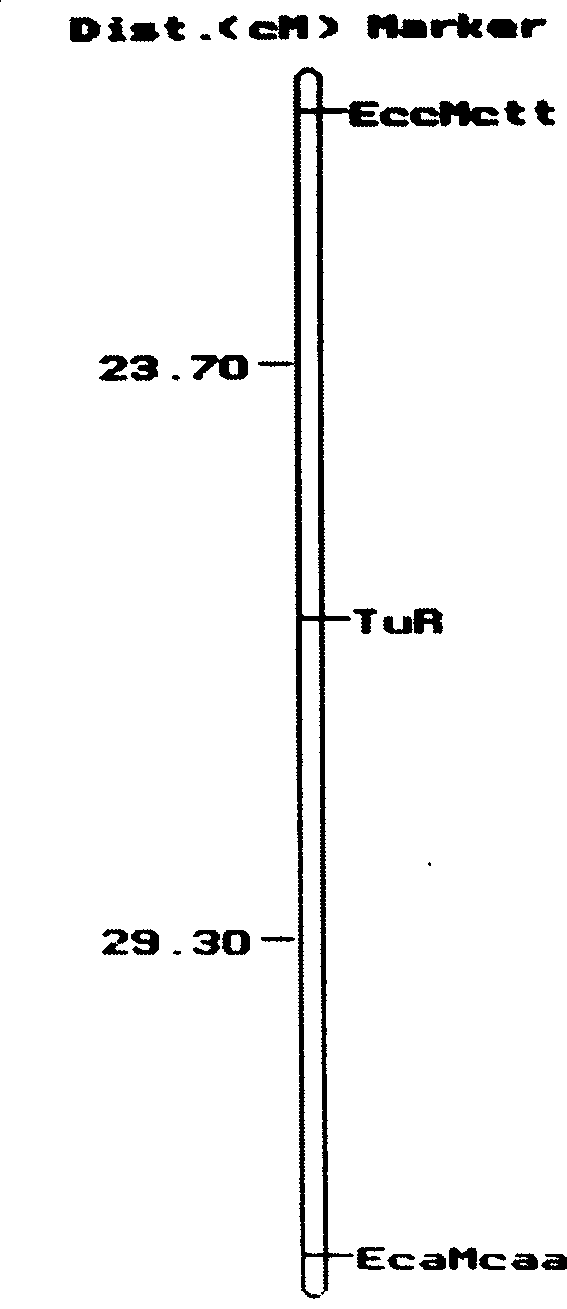
The invention discloses a pair of EST-SSR markers ATA157 and ATA154 which are closely interlocked with the disease resistant and susceptible genes of cabbage turnip mosaic virus, and belong to the technical field of biology. The markers are a pair of allelic markers, and the interlocking distance thereof with cabbage TuMV resistance locis is 3.8cM. Wherein the fragment length of the marker ATA157 is 157bp, and the fragment length of the marker ATA154 is 154bp. The invention also discloses a pair of EST-SSR labeled primers HCC259 which are provided with sequences in sequence tables SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No. 4. Through the primers, the genome DNA of a single plant to be tested is adopted as the template and the markers are amplified so as to realize the high-efficiency selection of cabbage TuMV resistance, speed up the breeding of novel TuMV resistant breed strains of cabbage, and establish a novel Chinese cabbage hybrid parent selection system.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Molecular marker method of turnip mosaic virus resistance gene in non-heading Chinese cabbage
InactiveCN101392293AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyVaccination
The invention relates to a molecular marker method of a non-heading Chinese cabbage turnip-mosaic-virus-resistance gene, including screening and cultivating of turnip-mosaic-virus-resistance non-heading Chinese cabbage parent materials, parent hybridization and F1 selfing, vaccination and testing of turnip mosaic viruses, DNA extraction of non-heading Chinese cabbage materials and the establishment of a resistance pool, the molecular marker screening of resistance genes, calculation of exchange rate and distance of resistance gene linked markers and establishment of a resistance gene linked marker map and the like; wherein, the molecular marker technology is applied to screen the parents of the turnip-mosaic-virus-resistance non-heading Chinese cabbage and the marking of the linked genes of the resistance genes; and different molecular markers have different reaction systems and amplification procedures. The method constructs the molecular marker procedures and systems of turnip-mosaic-virus-resistance genes with non-heading Chinese cabbage as material and provides bases for positioning the non-heading Chinese cabbage turnip-mosaic-virus-resistance gene on chromosome, resistance gene cloning and assisted breeding research of resistance molecules.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
SNP molecular marker A045736268C/T for identification of Chinese cabbage turnip mosaic virus resistance and application thereof
ActiveCN108103239AMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
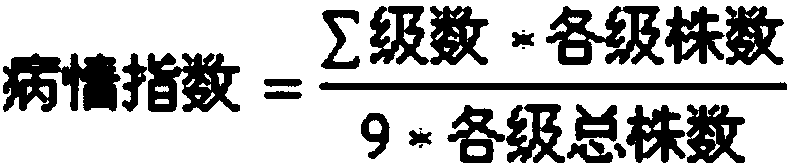
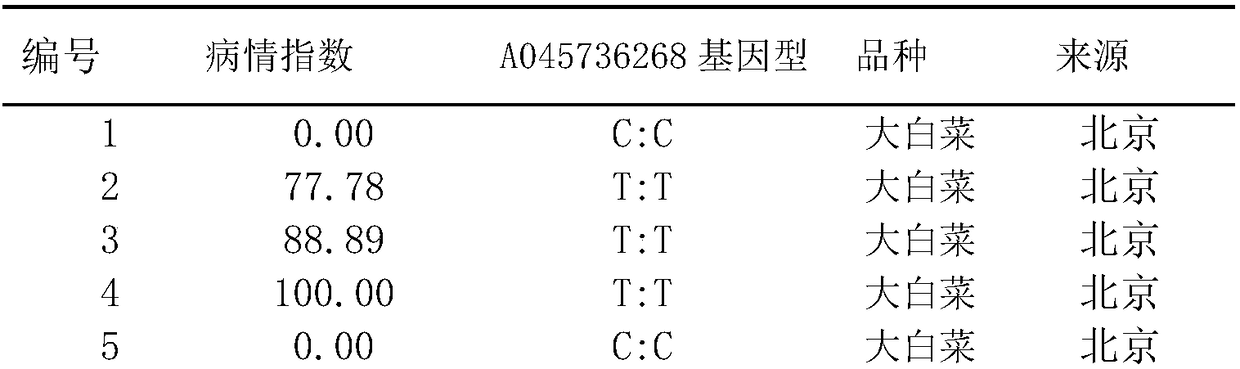
The invention discloses an SNP molecular marker A045736268C / T for identification of Chinese cabbage turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) resistance and application thereof. The invention provides application ofa polymorphic or genotype substance for detecting the A045736268C / T locus in a to-be-detected Chinese cabbage genome to identification or assistant identification of the turnip mosaic virus resistance of the to-be-detected Chinese cabbage. The experiment of the invention utilizes DH population, artificial mechanical inoculation of TuMV at seedling stage is carried out, existing Chinese cabbage genome information is utilized for resistant gene positioning and molecular marker development, preliminary research shows that the Chinese cabbage TuMV resistant gene is located on the A04 chromosome,the developed SNP marker closely linked to the resistant gene has a selection accuracy rate of 100% in both resistant and susceptible materials, and can be used for molecular marker assisted selectivebreeding. The study lays the foundation for further positional cloning and germplasm resource innovation of the Chinese cabbage TuMV resistant gene.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Bivalent carrier of against disease for coat protein gene of turnip mosaic virus and coat protein gene of cucumber mosaic virus
InactiveCN1687421AIncrease resistanceInhibition of replicationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseNucleotide
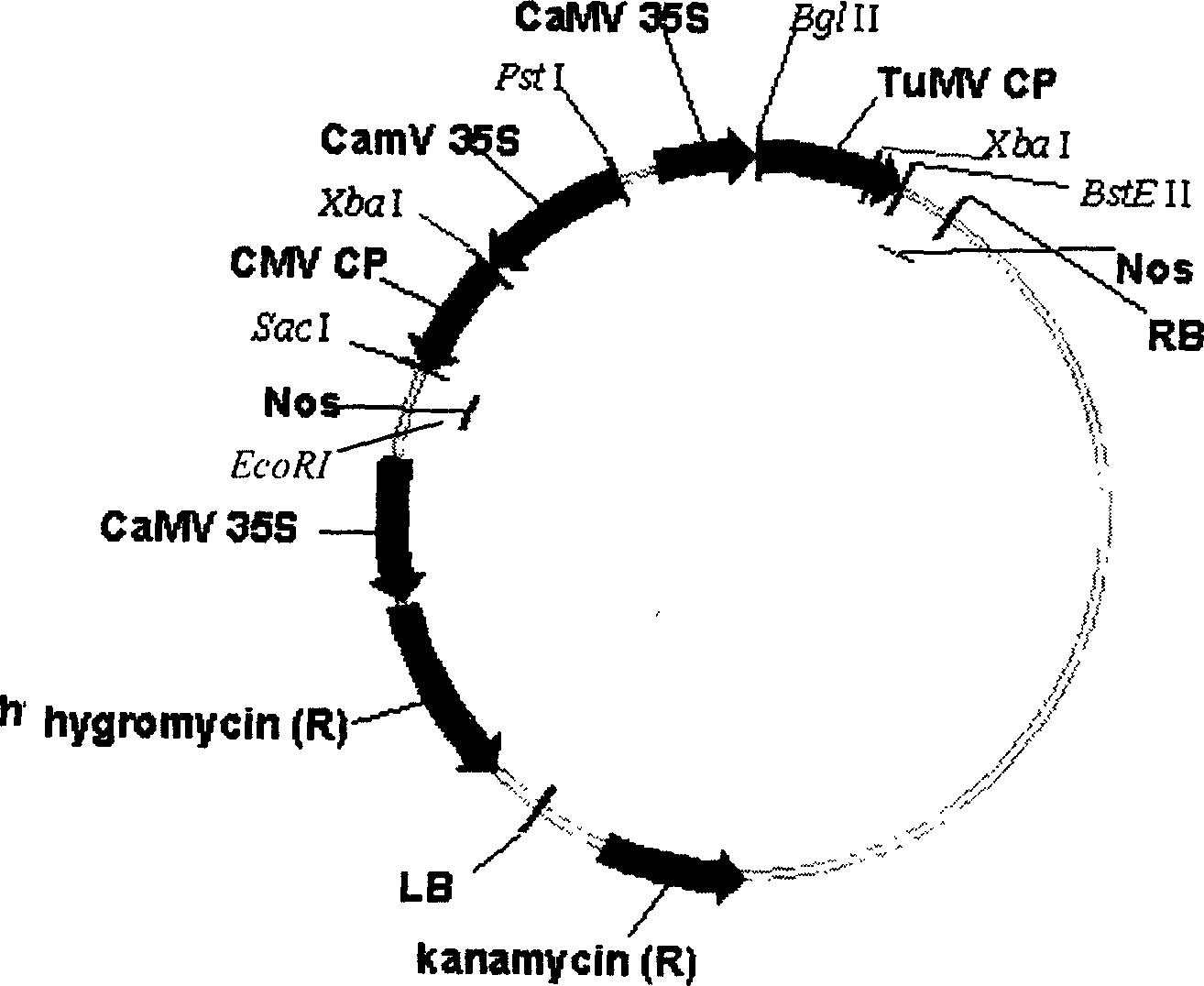
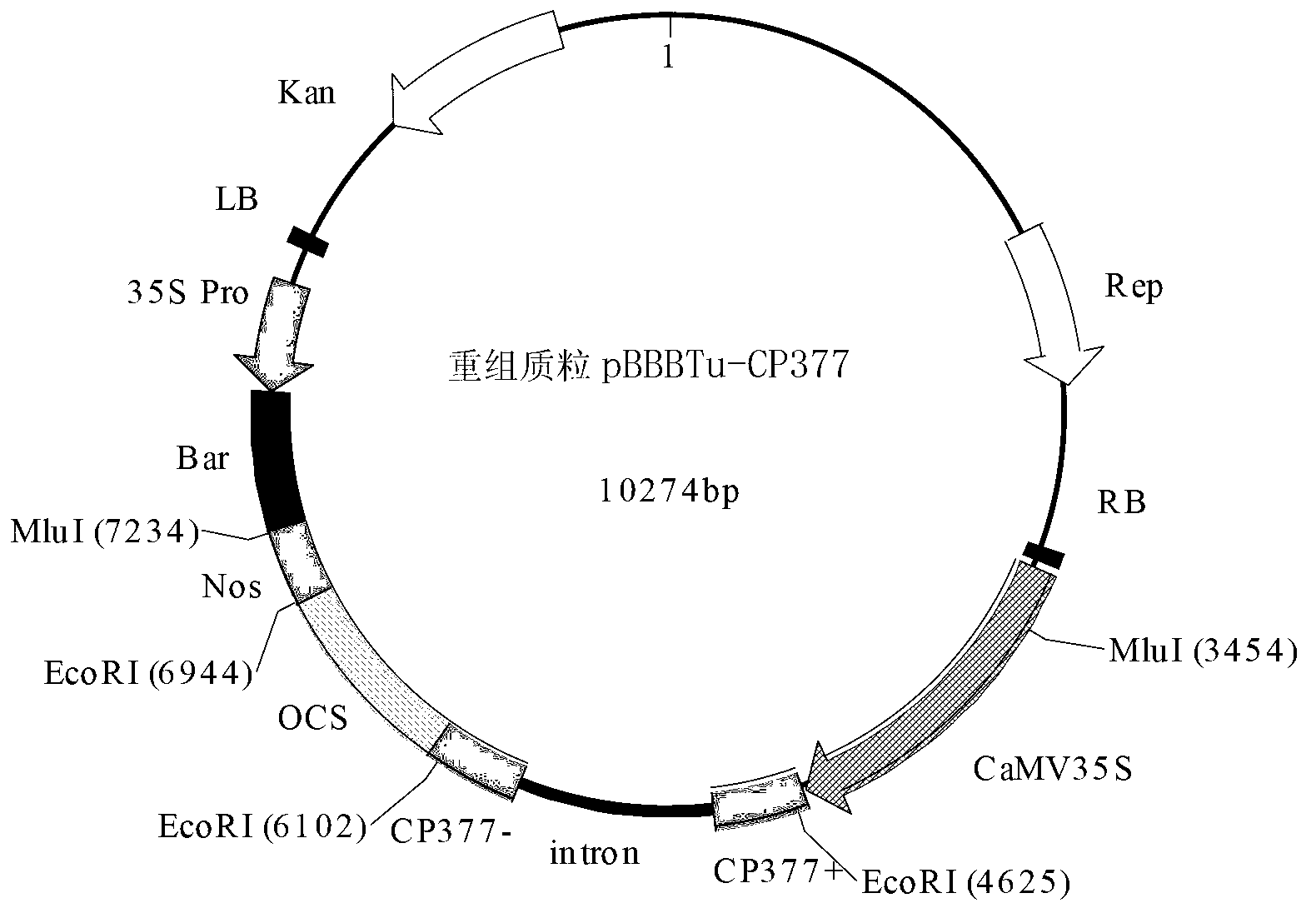
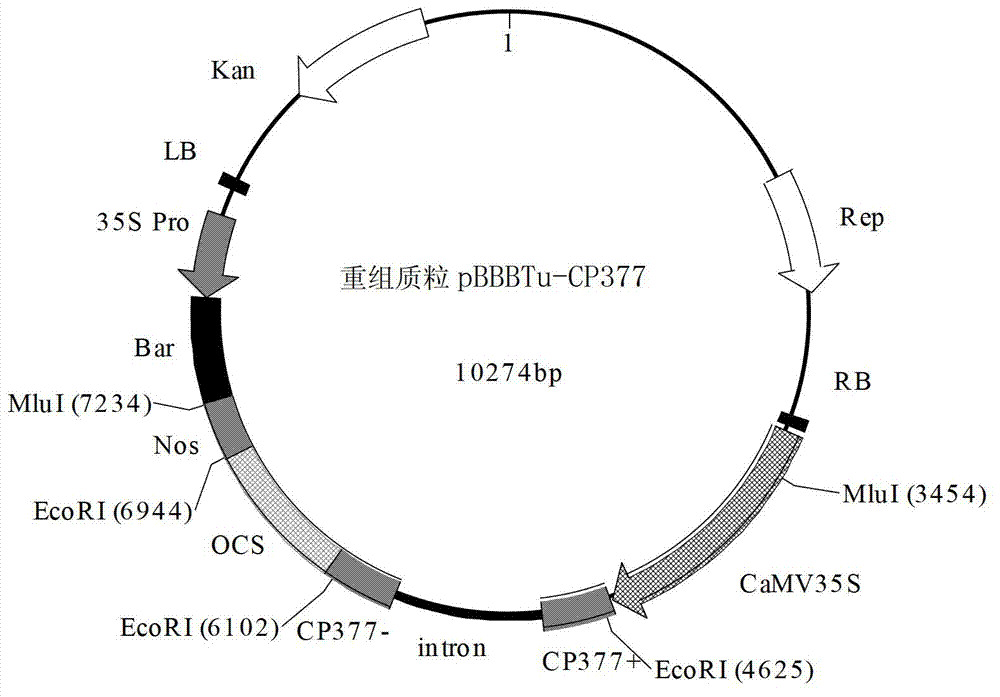
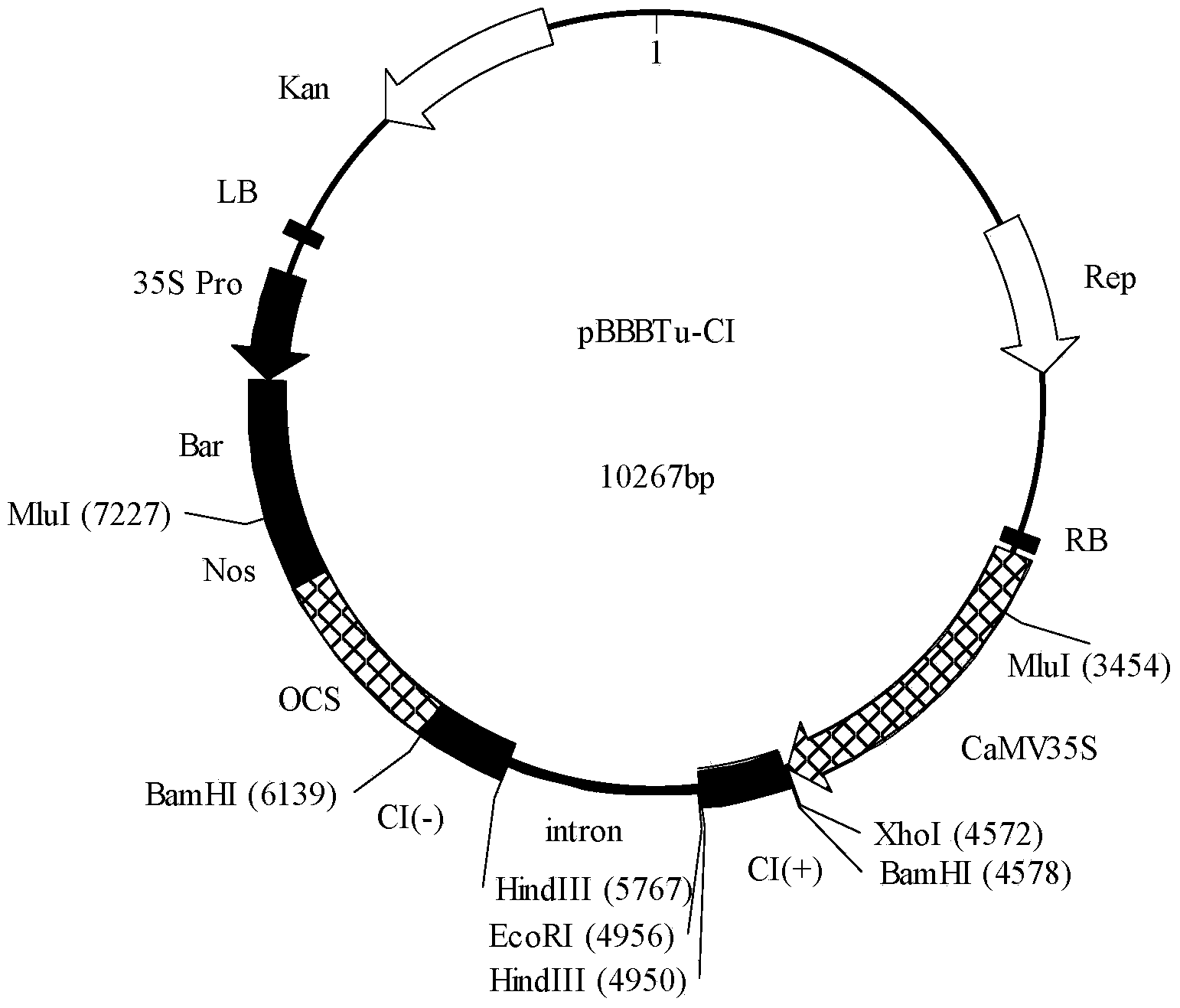
This invention provides a Bivalent carrier of against disease for coat protein gene of turnip mosaic virus and coat protein gene of cucumber mosaic virus. This carrier of pCam-TuMVCP-CMVCP consists of hygromycin, NoS terminator NoSter, Cucumber Mosaic virus Coat protein gene CMVCP, 35S promoter CaMV35Spro, Turnip Mosaic Virus Coat protein gene TuMVCP, and they connects each other one by one. TuMVCP and CMVCP is constructed on the same express carrier of plant. Because of CP has stopped uncoating process of the virus gene sequence. When the bare nucleotide of the inbreak virus enters into the cell, it is then re-covered by the free CP, and then the carrier stops the duplicate of the nucleotide; CP counterworks the virus particulate to expand and, then enhance the anti-disease ability of plants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
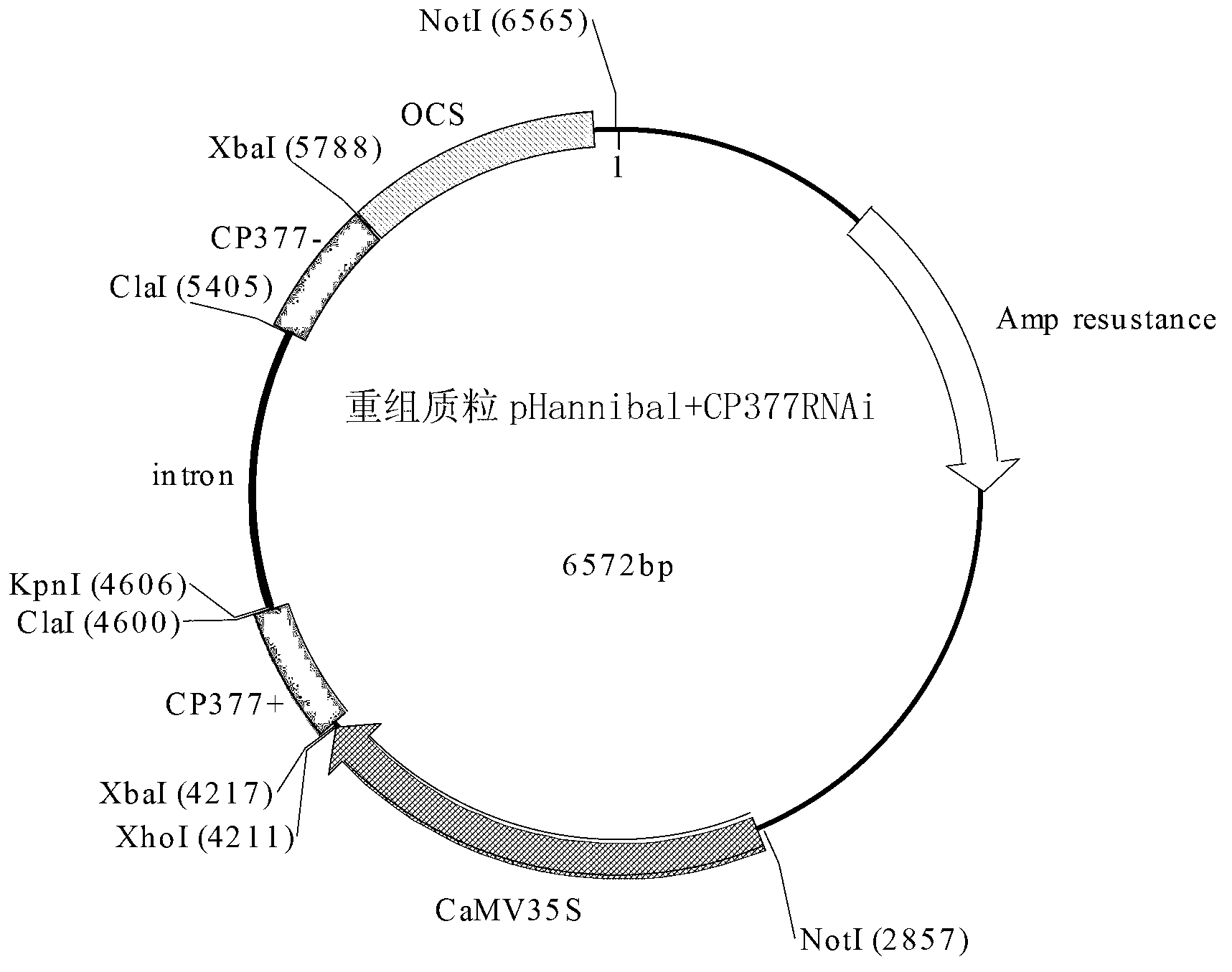
Application of TuMV-CP gene fragment-mediated RNAi carrier in cultivation of anti-TuMV transgenic plant
InactiveCN102796739ASame inhibitory effectBroad-spectrumBiocideDisinfectantsPlant cultivationGMO Plants
The invention discloses application of a TuMV-CP gene fragment-mediated RNAi carrier in cultivation of an anti-TuMV transgenic plant. The sequence 4 in a protection sequence table provided in the invention shows RNA fragments and its coding sequence. The RNA molecule can interfere with replication of TuMV RNA, thus inhibiting the TuMV. The invention also protects a transgenic plant cultivation method, which includes the following step of: expressing the RNA molecule in a starting plant so as to obtain a transgenic plant with higher TuMV resistance than that of the starting plant. The invention is of great value for cultivation of anti-TuMV plants (especially cruciferous plants).
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
One-step multiplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method for detecting turnip mosaic virus and special primers for method
InactiveCN102586478AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceInverse polymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses a one-step multiplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method for detecting turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) and special primers for the method. The invention provides a primer group for detecting the turnip mosaic virus. The primer group is a primer group C, a primer group A or a primer group B shown in the specifications, wherein the primer group C consists of the primer group A and the primer group B; the primer group A comprises a primer pair a; the primer group B comprises a primer pair b; the primer pair a consists of a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 3 in a sequence table and a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 4 in the sequence table; and the primer pair b consists of a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 5 in the sequence table and a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 6 in the sequence table. Experiments prove that: the TuMV is quickly and accurately detected by the one-step multiplex RT-PCR method.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Rapid test method for reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification of turnip mosaic viruses
ActiveCN103498011AQuick checkImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a rapid test method for reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification of turnip mosaic viruses. According to a turnip mosaic virus nucleotide sequence, a set of specific primers (F3, B3, FIP and BIP, shown in SEQIDNO.1-4) is designed, LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) reaction is performed after total RNA (ribonucleic acid) extraction, and a reaction product is subjected to turnip mosaic viruses test via a electrophoresis or fluorochrome method. The method is high in test specificity on the TuMV (turnip mosaic viruses), and has the advantages of rapidness, sensitivity, stability, efficiency, simple instrument requirements, convenience in operation, low cost and easiness in popularization and use at the grass roots.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
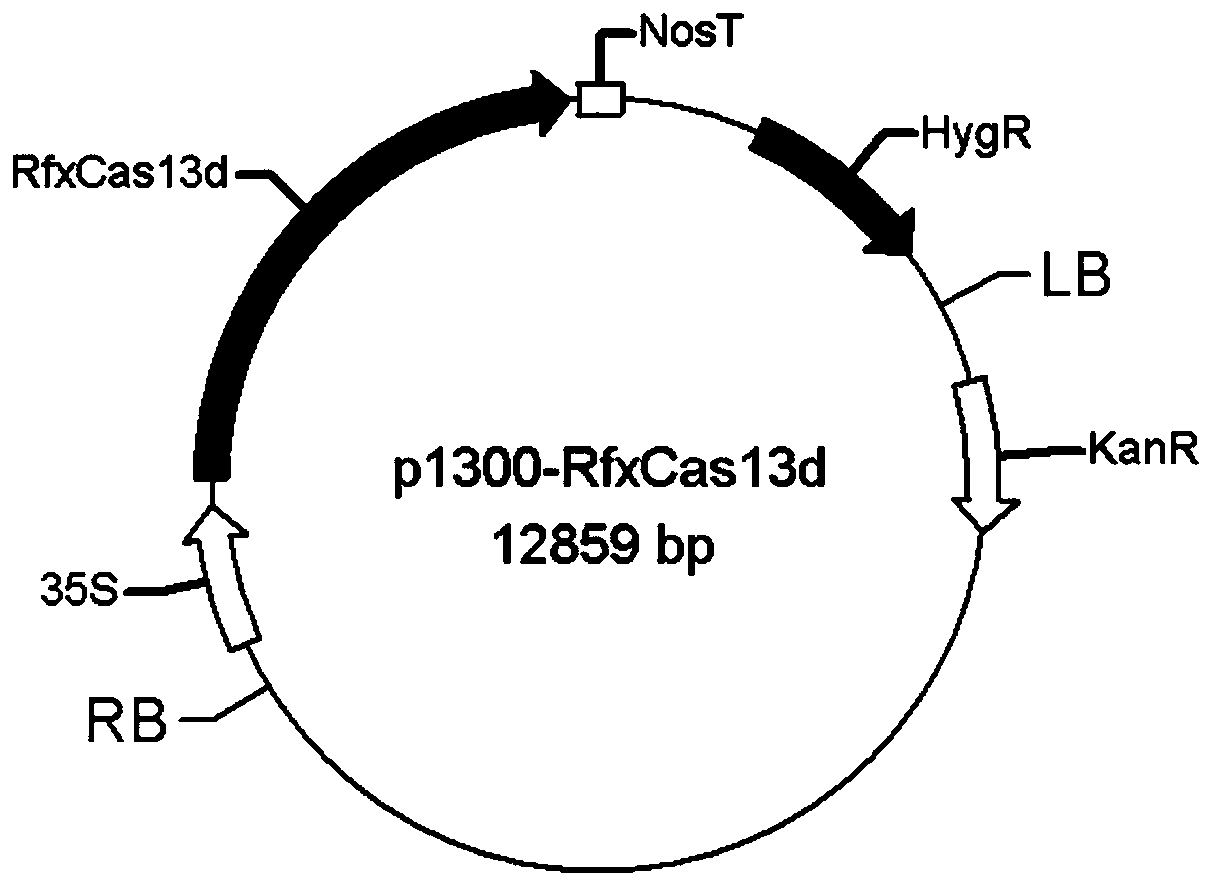
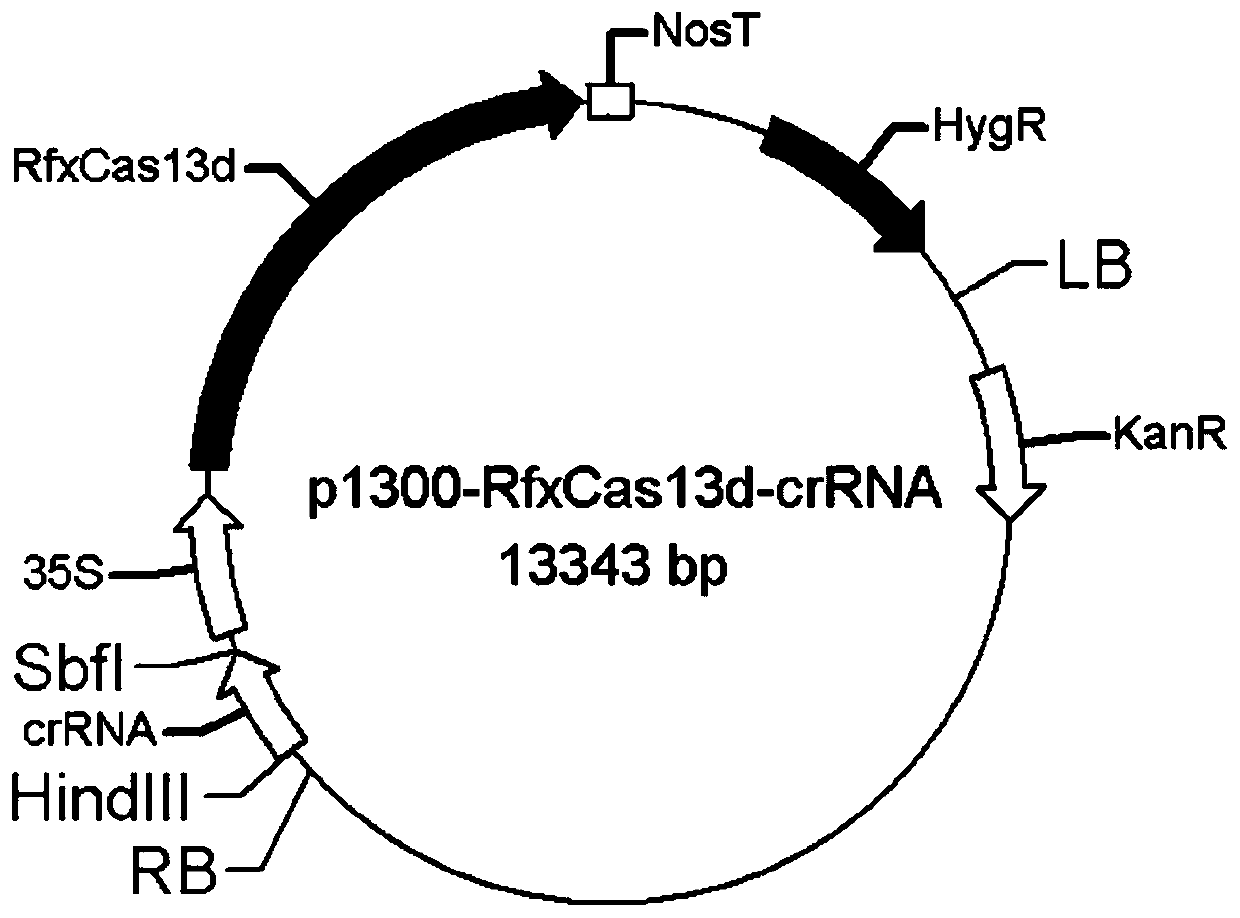
CRISPR/RfxCas13d anti-plant RNA virus vector and construction method and application of CRISPR/RfxCas13d anti-plant RNA virus vector
InactiveCN111549054AEfficient cuttingWide recognitionHydrolasesFermentationOrigin of replicationGene terminator
The invention discloses a CRISPR / RfxCas13d anti-plant RNA virus vector and a construction method and application thereof. The vector comprises a pCambia 1300-RfxCas13d recombinant vector, the recombinant vector is composed of a CaMV 35S promoter, a hygromycin gene, a CaMV poly(A) signal terminator, a pVS1 RepA, a pVS1 replication starting point, a CaMV 35S promoter, an RfxCas13d gene and an NOS terminator, the sequence of the RfxCas13d gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the sequence of the NOS terminator is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV-GFP) infectious clone with a GFPfluorescent label is used for indicating RNA viruses to naturally invade plants, and RNA can be directionally cut at a specific position through combination of RfxCas13d protein and sgRNA. The vectorconstructed by the invention can effectively inhibit infection of TuMV, provides a new strategy for prevention and control of plant virus diseases, and has important production significance.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecule labeling method of distinguishing mustard vegetables resisting turnip mosaic virus
The molecular marking process for identifying turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) resisting gene of mustard vegetables includes the following steps: extracting genome DNA's of different germplams of mustard vegetables, designing primer with the extracted genome DNA's as template according to the cloned TuMV resisting gene BjRT for PCR, agarose gel electrophoresis of the amplified product to detect the characteristic strip of TuMV resisting gene in mustard vegetables. The characteristic strip of TuMV resisting gene may be detected only in high TuMV resisting germplams. The present invention lays foundation for identifying TuMV resisting germplam resource of mustard vegetables.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
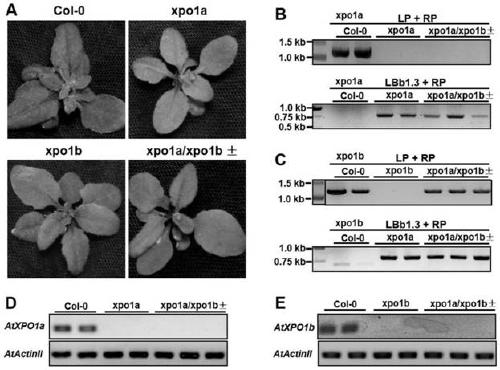
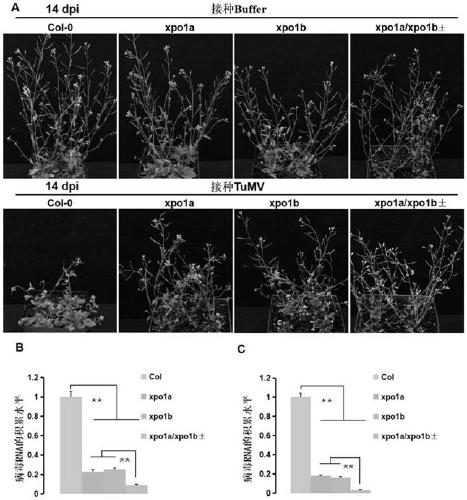
Cultivation and application methods of arabidopsis xpo1a/xpo1b+- double mutant
ActiveCN110150138AStable antiviral propertiesClear genetic backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceArabidopsis
The invention discloses cultivation and application methods of an arabidopsis xpo1a / xpo1b+- double mutant. The cultivation method comprises crossing an xpo1a mutant and an xpo1b mutant through genetichybridization and screening offspring to obtain the arabidopsis xpo1a / xpo1b+- double mutant. The obtained T3-generation arabidopsis xpo1a / xpo1b+- double mutant plant can significantly impede infection of turnip mosaic virus (TuMV).
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Hybridoma cell strain secreting monoclonal antibody against Iris yellow spot virus and application of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN104513812AAccurate detectionSensitive detectionImmunoglobulins against virusesMicroorganism based processesAntibody typesBALB/c
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain secreting monoclonal antibody against Iris yellow spot virus and application of the monoclonal antibody. Iris yellow spot virus particles purified by a differential centrifugation method are used as an antigen to immunize BALB / c mice; through cell fusion, screening and cloning, one strain of hybridoma cell strain 12C10 capable of stable passage and secreting anti-Iris yellow spot virus monoclonal antibodies is obtained; and the strain has a preservation number CGMCC No.9336. The monoclonal antibody secreted from the hybridoma cell strain has ascites indirect ELISA titer of 10 <-7>, and the antibody type and subtype are IgG1, kappa chain. The monoclonal antibody specifically and sensitively detect Iris yellow spot virus. The reaction with ZYMV. The monoclonal antibody secreted from 12C10 only has specific reaction with Iris yellow spot virus, but does not react with tomato spotted wilt virus, turnip mosaic virus and cucumber mosaic virus. The hybridoma cell strain 1C5 and monoclonal antibody secreted by the cell strain provide technical and material support for the diagnosis, inspection and quarantine, and scientific prevention and control of the virus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for detecting turnip mosaic virus by adopting reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology
InactiveCN103789449AImprove detection efficiencyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA extractionTotal rna
The invention relates to a method for detecting a turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) by adopting a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) technology. The method comprises the following steps: performing total RNA extraction, RT-LAMP reaction, real-time turbidity detection and electrophoresis detection on the TuMV, and determining whether the TuMV is existent in a sample. RT-LAMP primers are designed according to a conservation region of the TuMV gene, and the method for quickly, sensitively and highly specifically detecting the TuMV is created by adopting the one-step RT-LAMP technology. A novel means is provided for quickly detecting the TuMV.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
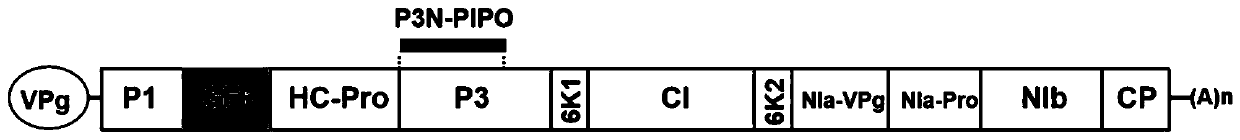
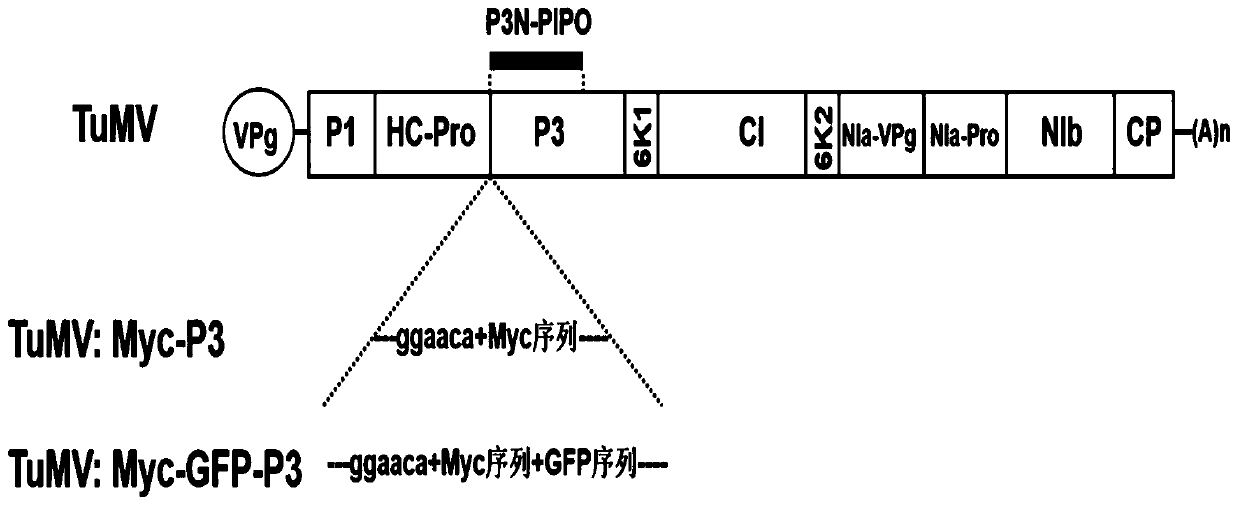
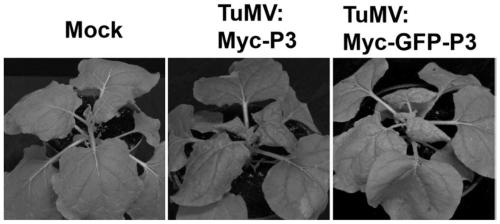
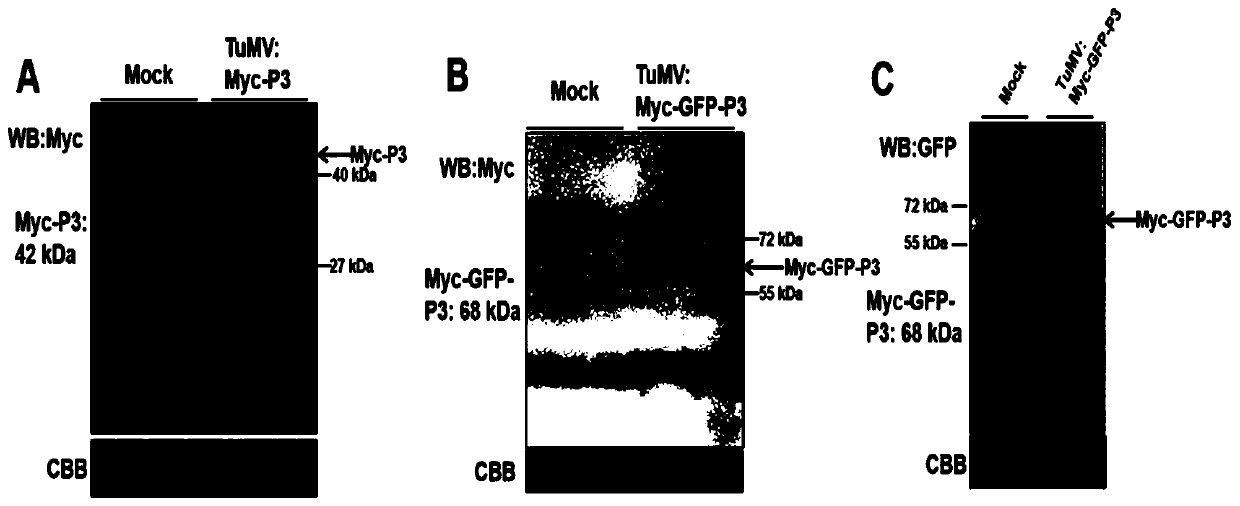
Method for inserting turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) P3 protein into labels and recombinant vector and application of (TuMV) P3 protein
ActiveCN110129362ASpecific tag fusion proteinObserve the real functionSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesFluorescenceTurnip yellow mosaic virus
The invention discloses a method for inserting turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) P3 protein into labels and a recombinant vector and application of the TuMV P3 protein. In the method, an Myc label and an Myc-GFP label are inserted into the N-terminal of P3 position in TuMV infected clone pCambia2300-TuMV, and Myc-P3 protein and Myc-GFP-P3 protein with the labels can be expressed; the constructed recombinant vectors pCambia2300-TuMV:Myc-P3 and pCambia2300-TuMV:Myc-GFP-P3 have the characteristics and advantages of infectivity, and the inserted labels do not affect the infectivity of the TuMV; the vectors can express specific label fusion protein and can be used for subsequent analyse of TuMV P3 protein; due to high expression of the fusion protein, P3 is proved to be the important functional gene of the TuMV, immunoprecipitation can be carried out by label antibody, and host proteins interacting with P3 are screened out; the P3 protein inserted into GFP fluorescence labels, and the real function of the TuMV P3 protein infected by virus can be observed.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
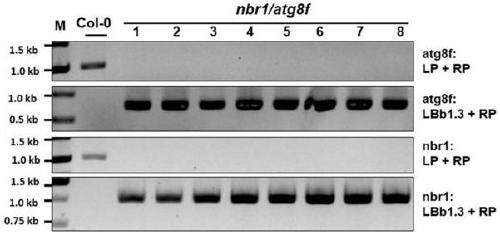
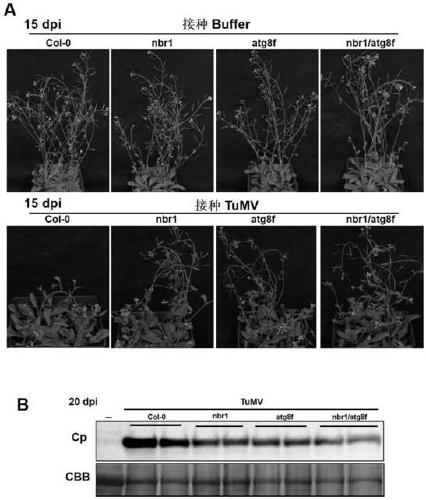
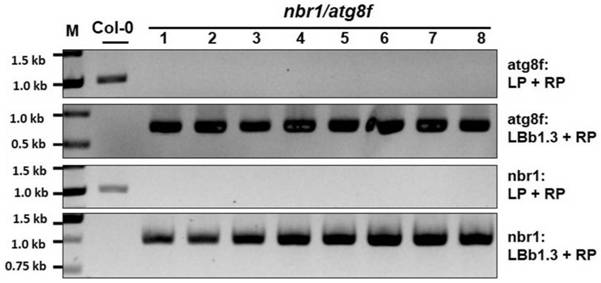
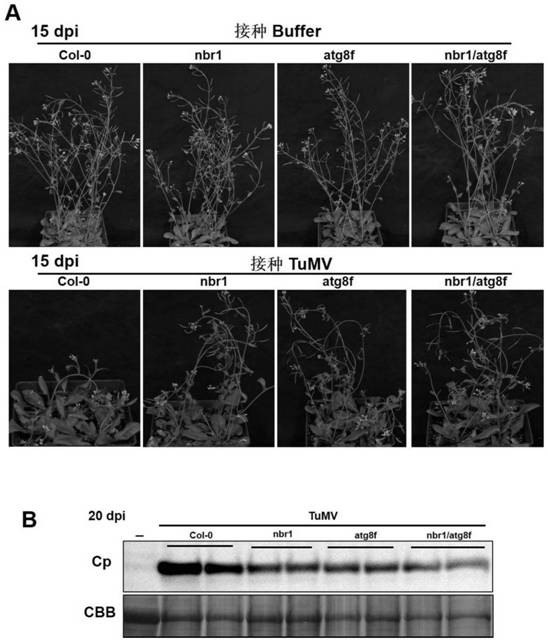
Cultivation and application methods of arabidopsis nbr1/atg8f double mutant
ActiveCN110150137AStable antiviral propertiesClear genetic backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationArabidopsisTurnip mosaic virus
The invention discloses cultivation and application methods of an arabidopsis nbr1 / atg8f double mutant. The cultivation method comprises determining that arabidopsis nbr1 and atg8f mutants can inhibitinfection turnip mosaic virus (TuMV), then crossing the arabidopsis nbr1 and atg8f mutants through genetic hybridization and screening offspring to obtain the arabidopsis nbr1 / atg8f double mutant. The obtained T3-generation arabidopsis nbr1 / atg8f double mutant plant can significantly inhibit infection of TuMV.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
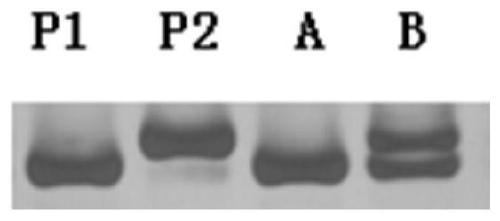
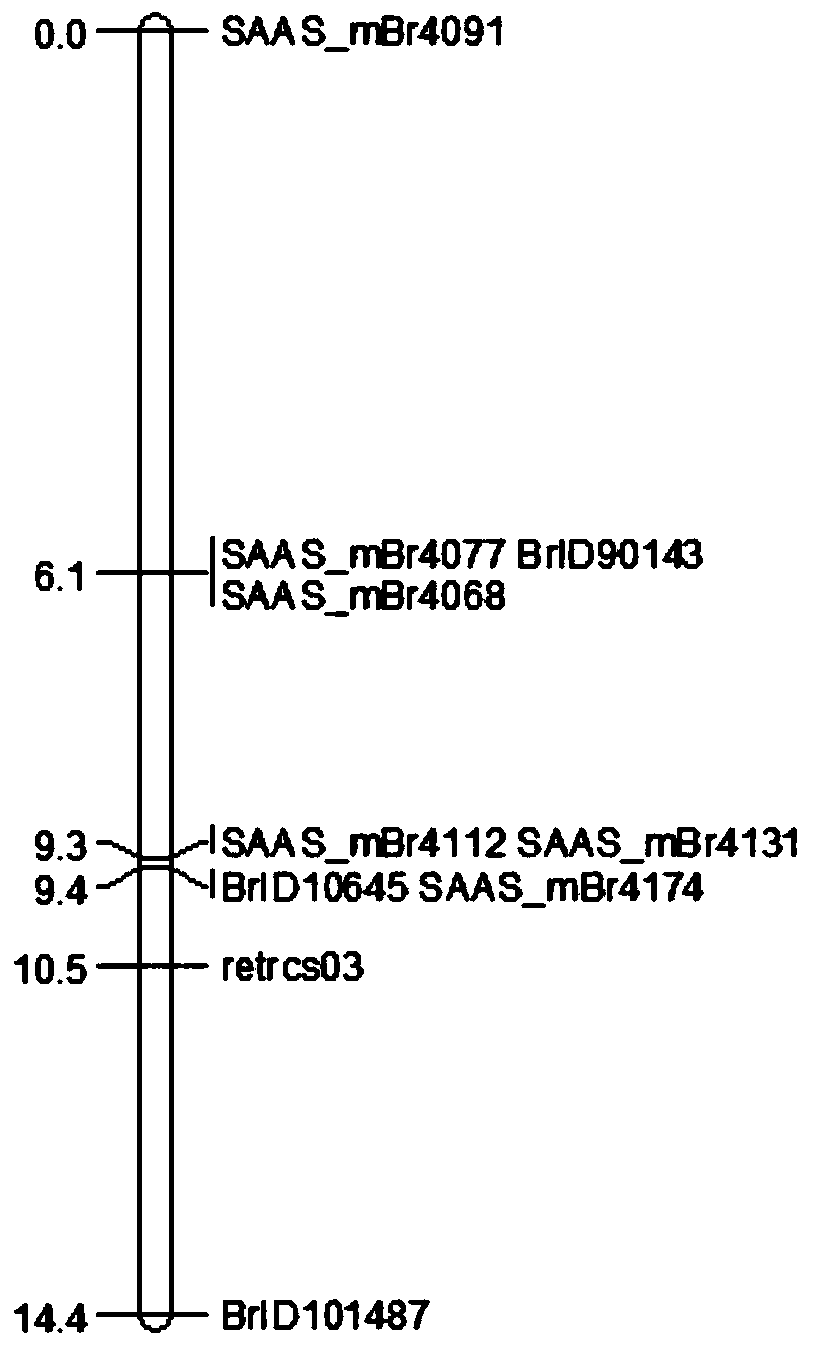
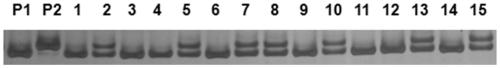
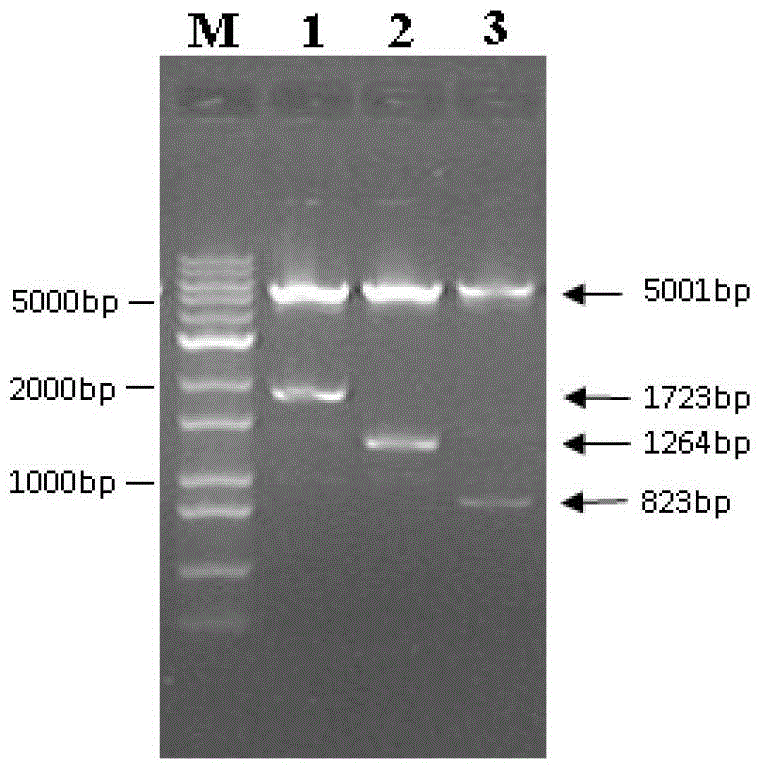
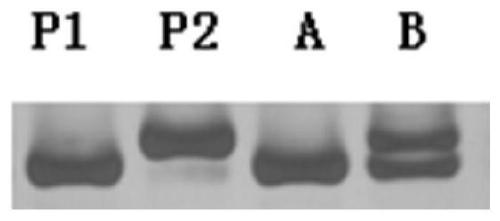
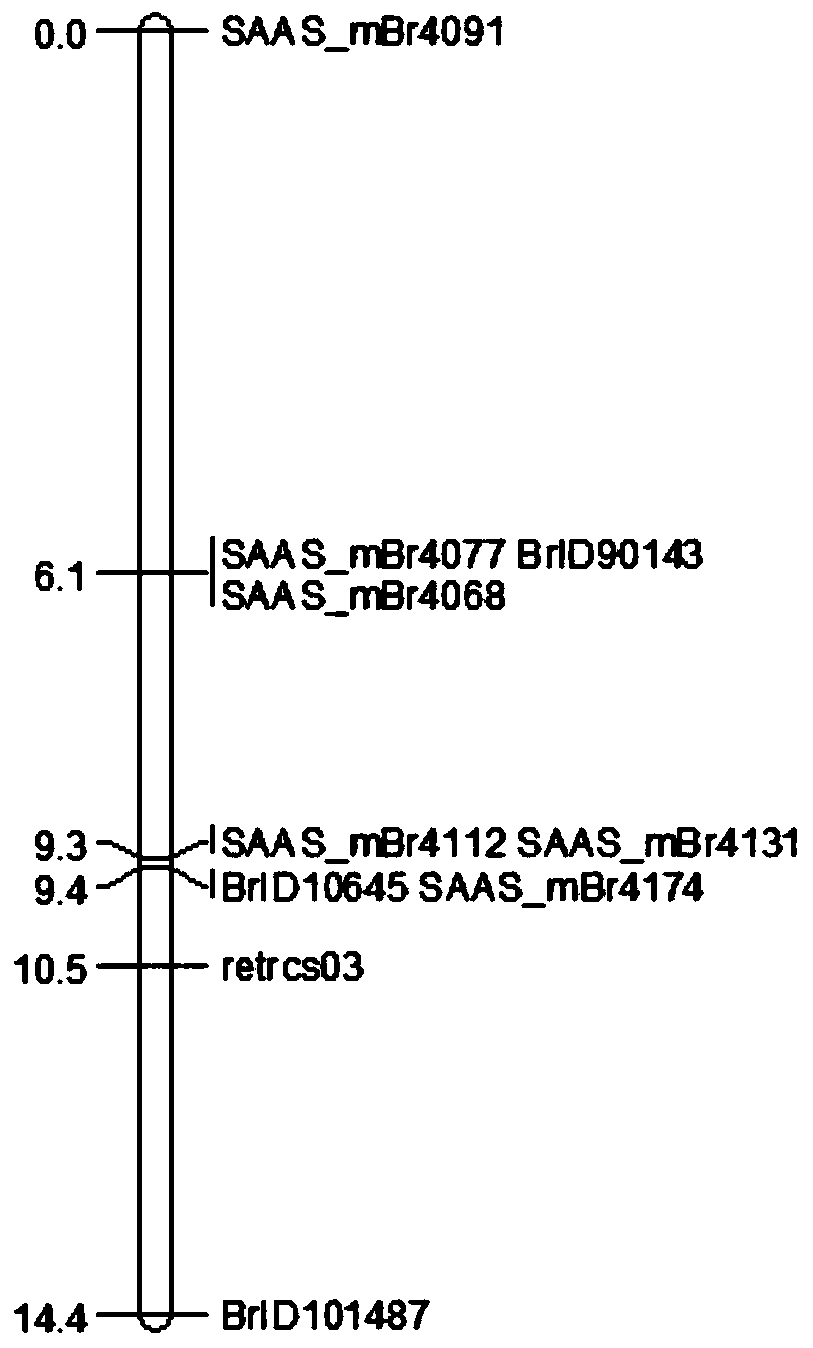
Molecular marker closely linked to Chinese cabbage turnip mosaic virus resistance gene retrcs03 and application thereof
ActiveCN110373494AEasy to breedStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionAgricultural science
The invention provides a molecular marker closely linked to a Chinese cabbage turnip mosaic virus resistance gene retrcs03 and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The molecular marker further locates a Chinese cabbage TuMV resistance gene retrcs03, contributes to better utilization in Chinese cabbage anti-TuMV molecular marker-assisted selection, meanwhile can locate the gene, and lays a foundation for the cloning, further utilization and research of the gene. At the same time, the application of the molecular marker in breeding work can greatly reduce the economicloss caused by TuMV epidemic to Chinese cabbage production, is beneficial to reducing production cost, and has great application potential and high economic value.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A highly resistant tumv rna and the rnai vector encoding the rna
The invention claims a TuMV (Turnip Mosaic Virus) high-resistance RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and an RNAi carrier for encoding the RNA. The TuMV high-resistance RNA consists of one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) nucleotide sequence indicated by SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table; 2) limited RNA sequence with more than 90% of homology and same functions, wherein concretely the homology is more than 95%, then concretely more than 96%, then concretely more than 97%, then concretely more than 98% and then concretely more than 99%. The RNA and the RNAi carrier for encoding the RNA are used for enhancing the resistance of the plant to TuMV or glufosinate-ammonium and meanwhile can be used for laying a foundation for cultivating the TuMV high-resistance transgenic plants.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Method for detection of turnip mosaic virus using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique
InactiveCN103789449BImprove detection efficiencyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA extractionTotal rna
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Hybridoma cell line secreting monoclonal antibody against tomato spotted wilt virus and its application
ActiveCN104450623BAccurate detectionSensitive detectionMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against virusesBALB/cAntibody types
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain capable of secreting a tomato spotted wilt virus resistant monoclonal antibody and application of the monoclonal antibody. The preparation method comprises the following steps: immunizing a BALB / c mouse by taking tomato spotted wilt virus particles purified by a differential centrifugation method to serve as an antigen, performing cell fusion, screening and cloning, thereby obtaining a hybridoma cell strain 1A5 capable of performing stable passage and secreting the tomato spotted wilt virus resistant monoclonal antibody, wherein the collection number of the strain is CGMCC No.9343. The monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cells has the ascitic fluid ELISA titer of 10<-8>, and the type and sub-type of the antibody are IgG1 and kappa chain. A specific reaction is carried out between the monoclonal antibody secreted by 1A5 and the tomato spotted wilt virus only, and the monoclonal antibody does not react with turnip mosaic virus, tomato mosaic virus, iris yellow spot virus and cucumber mosaic virus; and moreover, the monoclonal antibody can be used for specifically and sensitively detecting the tomato spotted wilt virus. The hybridoma cell strain and the secreted monoclonal antibody provide technology and material supports for diagnosis, detection and scientific prevention and control of the tomato virus diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
One-step multiplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method for detecting turnip mosaic virus and special primers for method
The invention discloses a one-step multiplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method for detecting turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) and special primers for the method. The invention provides a primer group for detecting the turnip mosaic virus. The primer group is a primer group C, a primer group A or a primer group B shown in the specifications, wherein the primer group C consists of the primer group A and the primer group B; the primer group A comprises a primer pair a; the primer group B comprises a primer pair b; the primer pair a consists of a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 3 in a sequence table and a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 4 in the sequence table; and the primer pair b consists of a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 5 in the sequence table and a DNA molecule shown as a sequence 6 in the sequence table. Experiments prove that: the TuMV is quickly and accurately detected by the one-step multiplex RT-PCR method.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Molecular markers closely linked to Chinese cabbage turnip mosaic virus resistance gene retrcs03 and its application
ActiveCN110373494BStrong specificityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention provides a molecular marker closely linked with Chinese cabbage turnip mosaic virus resistance gene retrcs03 and an application thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The molecular marker provided by the present invention further locates the Chinese cabbage TuMV resistance gene retrcs03, which helps to be better used in the Chinese cabbage resistance TuMV molecular marker-assisted selection, and at the same time, the gene can be located, and it can be used for the cloning and In-depth use and research to lay the foundation. At the same time, applying it to breeding work will greatly reduce the economic loss caused by the TuMV epidemic to Chinese cabbage production, which is beneficial to reduce production costs, and has great application potential and high economic value.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Molecular mark used for resistance identification of leaf mustard turnip mosaic virus disease and use of molecular mark
ActiveCN105755011AImprove anti-viral disease abilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesDiseaseMarker-assisted selection
The invention discloses a leaf mustard turnip mosaic virus disease resistant gene eIF2B beta. A nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1; and an amino acid sequence of a protein coded by the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention further discloses a molecular mark BjTur, used for resistance identification of leaf mustard turnip mosaic virus disease, developed based on the leaf mustard turnip mosaic virus disease resistant gene eIF2B beta. The leaf mustard turnip mosaic virus disease resistant gene has the function of resisting the leaf mustard turnip mosaic virus disease. The use of the molecular mark BjTuR is used for identifying a leaf mustard turnip mosaic virus disease resistant strain or offspring marker assisted selection thereof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant vector, preparation method thereof and method for improving turnip mosaic virus resistance and/or yield of vegetable crops
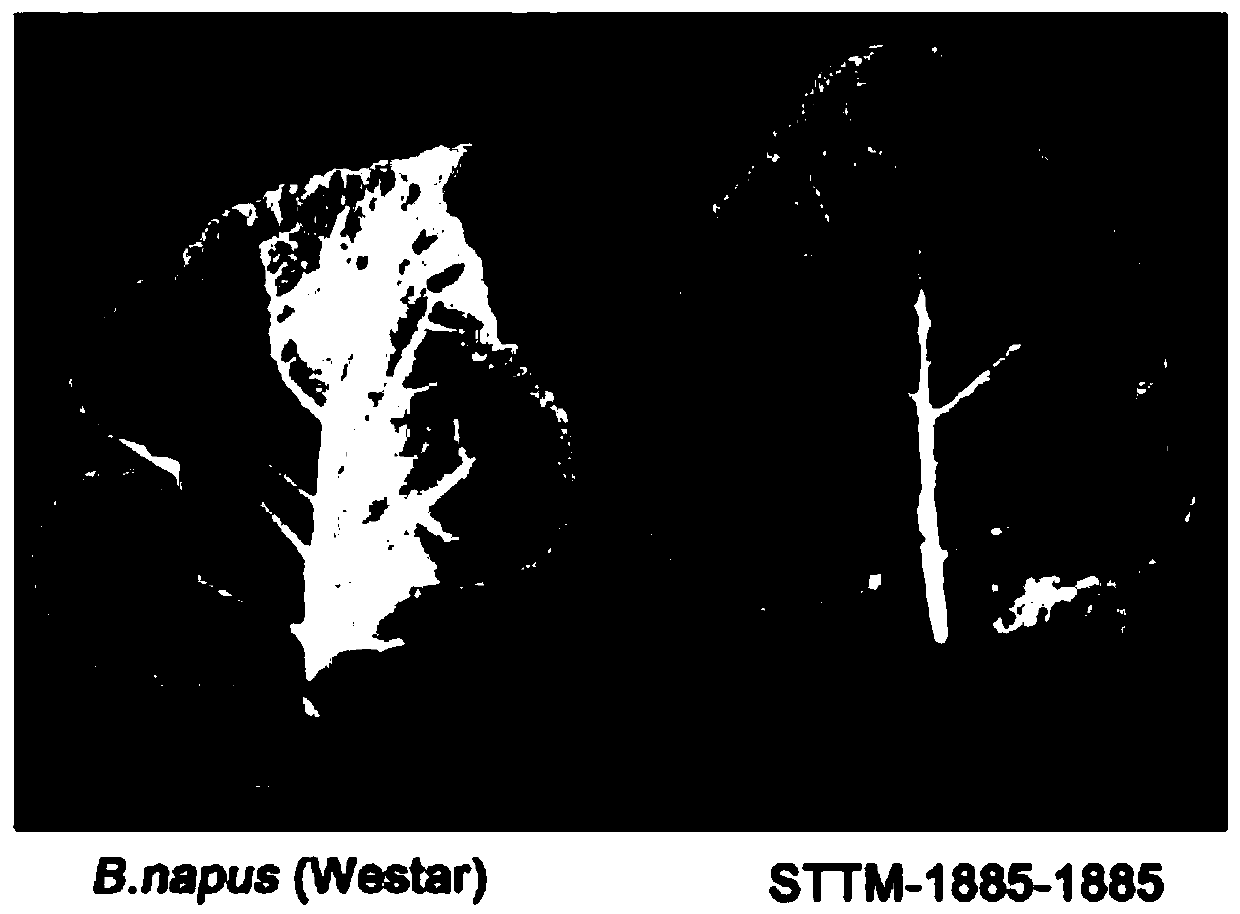
ActiveCN110885851ARegulate disease resistanceControl outputClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionBinding siteRNA Sequence
The invention relates to a recombinant vector and a preparation method thereof, and a method for improving the turnip mosaic virus resistance and / or yield of vegetable crops. The recombinant vector provided by the invention comprises a complementary binding site of an RNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.8. A transcribed RNA product of the recombinant vector mediates the degradation of miR1885a or inhibits the regulation and control of the miR1885a on a target by being combined with the miR1885a.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primer and method for quantitatively detecting turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) in limonium sinuatum
PendingCN113897462AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTotal rnaPlant disease
The invention discloses a primer and a method for quantitatively detecting turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) in limonium sinuatum, and belongs to the technical field of plant disease detection. The primer used in the invention is designed based on conserved regions of a TuMV CP gene sequence AB701704, KC119189 and AP017831; and the primer is as follows: an upstream primer TuMV-F:5'-CGACCATACATGCCACGACA-3', and a downstream primer TuMV-R:5'-TCCATCCAAGCCGAACGAA-3', and the primer can be used for both RT-PCR amplification and RT-qPCR amplification. The method for quantitatively detecting the TuMV in the limonium sinuatum comprises the following steps of: extracting total RNA of infected leaves of the limonium sinuatum; performing reverse transcription on the total RNA to form cDNA, and performing common PCR and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR by taking the cDNA as a template once. The primer designed by the invention is high in sensitivity, strong in specificity and good in repeatability; a set of method capable of rapidly and sensitively detecting the TuMV is established in the invention; and a technical support can be provided for early monitoring and early warning of the TuMV of the limonium sinuatum.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of TuMV-CP gene fragment-mediated RNAi carrier in cultivation of anti-TuMV transgenic plant
InactiveCN102796739BSame inhibitory effectBroad-spectrumBiocideDisinfectantsPlant cultivationGMO Plants
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) with high TuMV (Turnip Mosaic Virus) resistance and RNAi (RNA interfere) vector for coding same
The invention discloses an RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) with high TuMV (Turnip Mosaic Virus) resistance and an RNAi (RNA interfere) vector for coding the same. The RNA with high TuMV resistance has one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table; and 2) RNA sequences having more than 90% homology with the RNA sequence defined by the item 1), specifically more than 95% homology, more specifically more than 96% homology, further more specifically more than 97% homology, further more specifically more than 98% homology and the most specifically more than 99% homology, and having the same functions. The RNA and the RNAi vector for coding the RNA disclosed by the invention can be used for enhancing the resistance of plants to TuMV or glufosinate-ammonium herbicides, and simultaneously, also lay a foundation for breeding high-TuMV-resistance transgenic plants.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
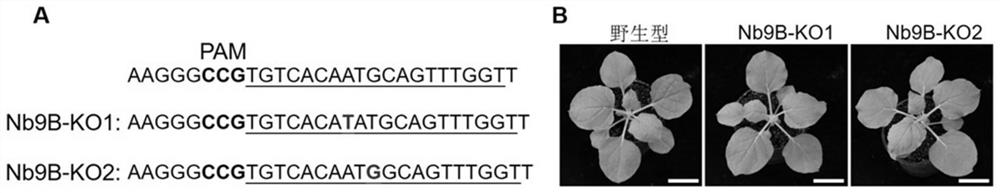
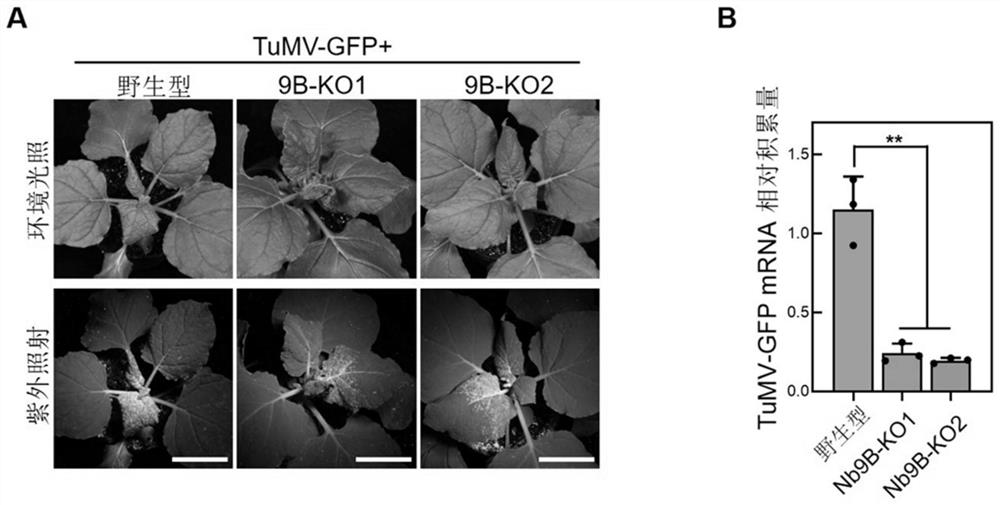
Application of nicotiana benthamiana ALKBH9B gene in regulation and control of plant virus resistance and transgenic plant cultivation method
The invention discloses an application of a nicotiana benthamiana ALKBH9B gene in regulation and control of plant virus resistance and a transgenic plant cultivation method, the virus is a potato Y virus virus turnip mosaic virus, and the transcript sequence of the ALKBH9B gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the invention, a gene knockout vector carrying a target gene target is introduced into a target plant through a tobacco leaf disc agrobacterium transformation method to obtain a nicotiana benthamiana ALKBH9B gene mutation homozygous plant, and the plant can significantly reduce the infection of turnip mosaic virus.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
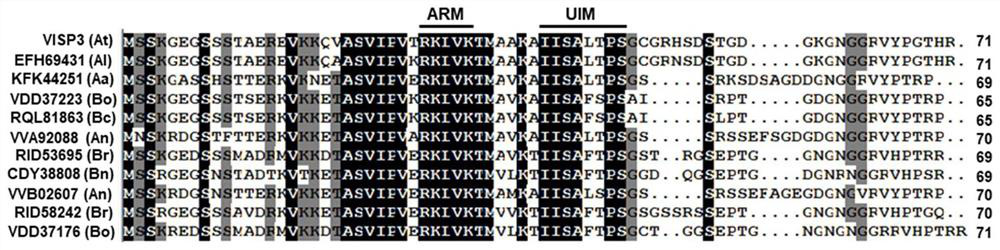
Plant selective autophagy receptor small peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN112830961AGood antiviral effectRegulation of antiviral abilityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyBrassicaceae
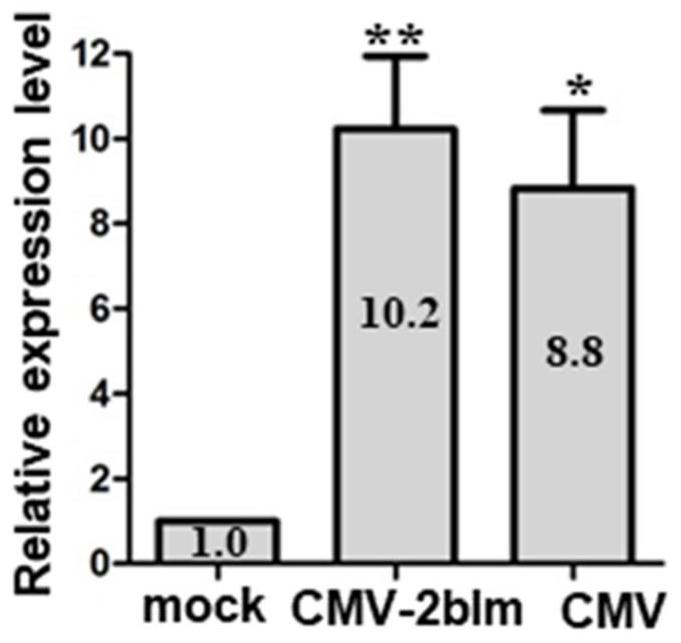
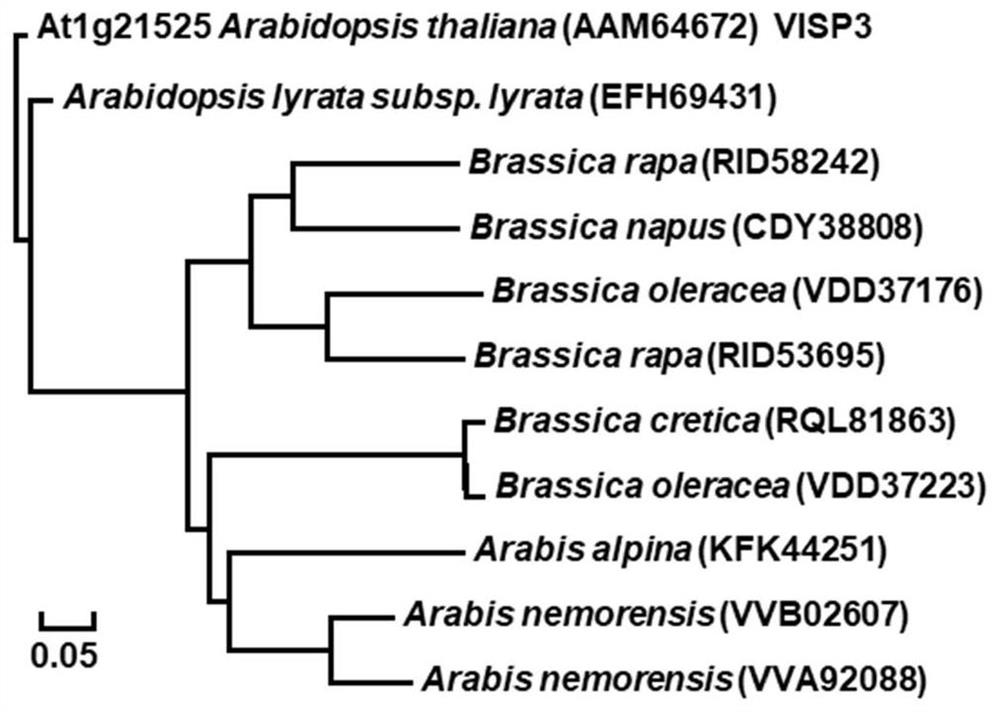
The invention relates to a plant selective autophagy receptor small peptide and application thereof. The invention provides a novel selective autophagy receptor VISP3, the VISP3 is a small peptide and is conservatively distributed in cruciferous plants, and the protein sequence of the VISP3 in arabidopsis thaliana is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The VISP3 degrades a key component SGS3 / RDR6 small body of an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) silencing pathway, interferes with synthesis of exogenous virus small interfering RNAs (vsiRNAs) and endogenous tasiRNAs, promotes virus infection and influences plant development. Infection of cucumber mosaic virus and turnip mosaic virus of plants can be promoted by increasing the expression quantity of the VISP3; by knocking out the VISP3, the antiviral capability of the plant can be enhanced. The knockout mutant can be used for preventing and treating plant diseases independently or in combination with other plant agents, and the yield and quality of plants are improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A kind of breeding method and application of Arabidopsis nbr1/atg8f double mutant
ActiveCN110150137BAvoid infectionInhibition of replicationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses cultivation and application methods of an arabidopsis nbr1 / atg8f double mutant. The cultivation method comprises determining that arabidopsis nbr1 and atg8f mutants can inhibitinfection turnip mosaic virus (TuMV), then crossing the arabidopsis nbr1 and atg8f mutants through genetic hybridization and screening offspring to obtain the arabidopsis nbr1 / atg8f double mutant. The obtained T3-generation arabidopsis nbr1 / atg8f double mutant plant can significantly inhibit infection of TuMV.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
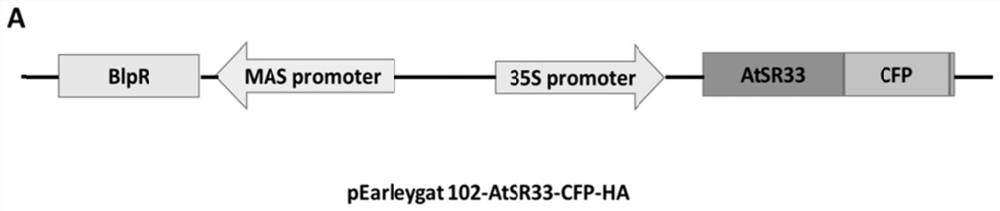
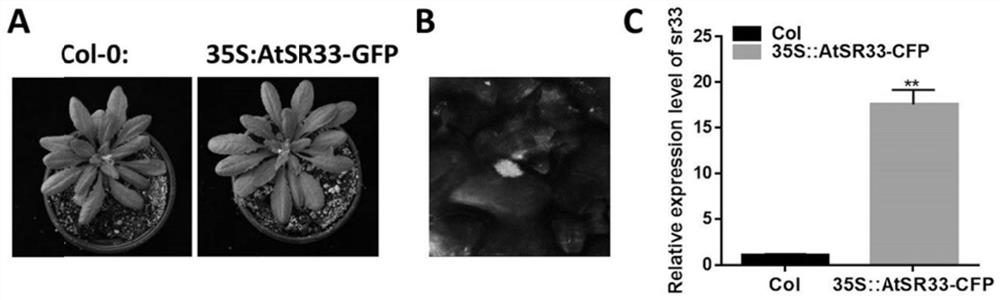
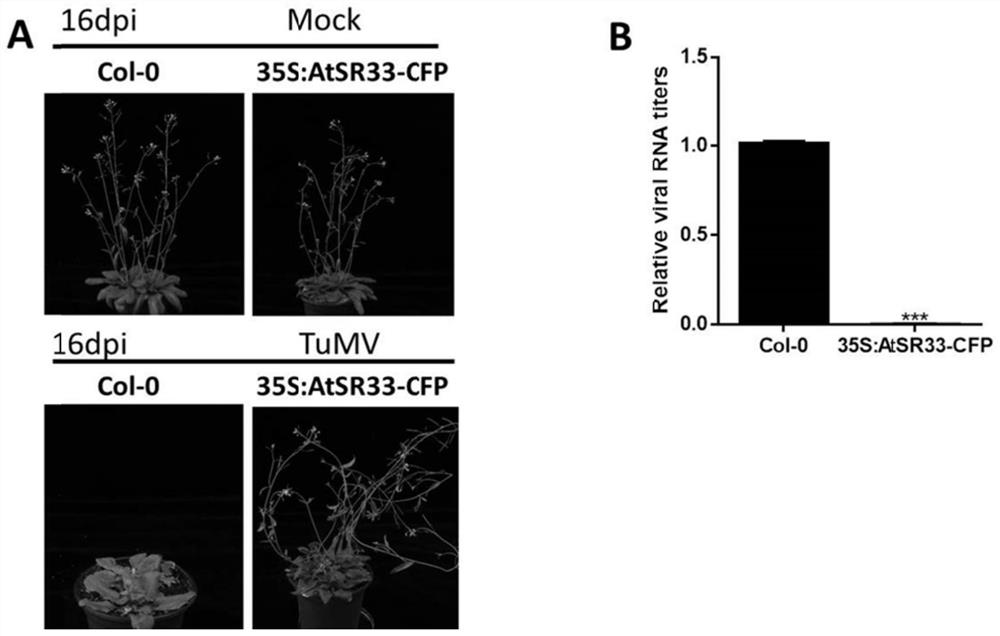
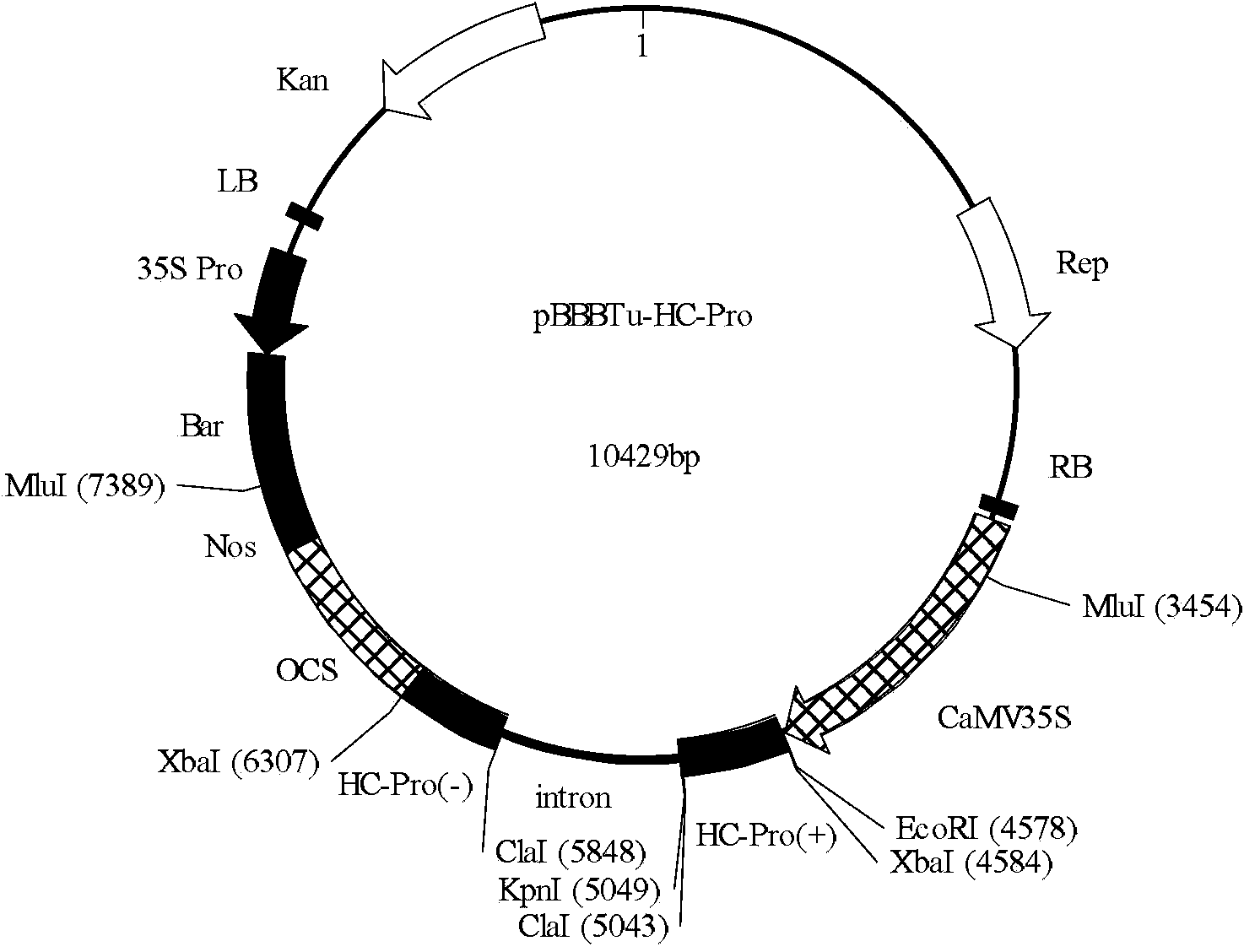
Application of arabidopsis thaliana AtSR33 gene in inhibition of turnip mosaic virus infection
ActiveCN113881700AImprove disease resistanceInfestation barrierPlant peptidesFermentationCloning vectorArabidopsis thaliana <plant>
The invention discloses an application of an arabidopsis thaliana AtSR33 gene in inhibition of turnip mosaic virus infection. A constructed infectious cloning vector pEarleygate 102-AtSR33-CFP-HA is used, and the construction method of the vector comprises the following steps: carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on an arabidopsis thaliana AtSR33 gene through a gateway system, connecting to a pDONR221 vector through a BP (Back Propagation) reaction, and connecting to a pEarleygate 102 vector through an LR (Local Regulation) reaction, so as to obtain the overexpression vector containing the AtSR33. The arabidopsis thaliana plant capable of stably expressing AtSR33 is obtained in a genetic transformation mode, and experiments show that the arabidopsis thaliana AtSR33 overexpression plant can remarkably inhibit infection of turnip mosaic viruses.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
TuMV (Turnip Mosaic Virus) high-resistance RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and an RNAi carrier for encoding RNA
The invention claims a TuMV (Turnip Mosaic Virus) high-resistance RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and an RNAi carrier for encoding the RNA. The TuMV high-resistance RNA consists of one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) nucleotide sequence indicated by SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table; 2) limited RNA sequence with more than 90% of homology and same functions, wherein concretely the homology is more than 95%, then concretely more than 96%, then concretely more than 97%, then concretely more than 98% and then concretely more than 99%. The RNA and the RNAi carrier for encoding the RNA are used for enhancing the resistance of the plant to TuMV or glufosinate-ammonium and meanwhile can be used for laying a foundation for cultivating the TuMV high-resistance transgenic plants.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com