Plant selective autophagy receptor small peptide and application thereof
A plant and autophagy technology, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve the problems of unreported virus infection and achieve the effect of improving anti-virus ability and broad-spectrum disease resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1 Obtaining of AtVISP3 gene and construction of expression vector
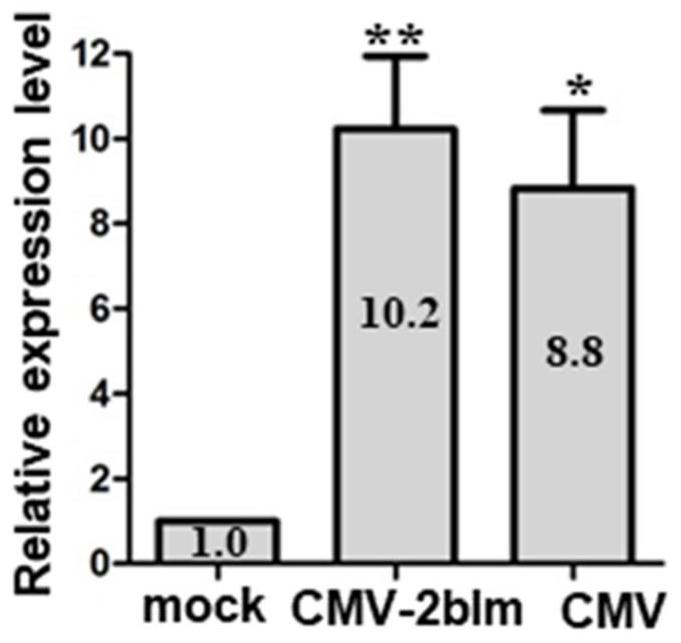
[0058] In this example, transcriptome sequencing was performed on Arabidopsis plants inoculated with cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) for one week. The sequencing results showed that, compared with the control (mock), the transcription level of the gene AT1G21525 was up-regulated by more than four times after inoculation with CMV, and the results were verified using realtime (such as figure 1 shown). figure 1 The results show that inoculation of wild-type CMV or attenuated mutant virus CMV-2blm can significantly induce the expression of gene AT1G21525, and this gene is named AtVISP3 gene. The full-length amino acid sequence of VISP3 protein in Arabidopsis is as SEQ ID NO.1 As shown, the nucleotide sequence of the coding frame is shown in SEQ ID NO.12. Amplification primers were designed according to the cDNA nucleotide sequence.
[0059] The amino acid sequence and nucleotide sequence of VISP3 wer...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Overexpression of VISP3 gene and construction of knockout mutant plants
[0061] 1. Construction of overexpression plants of VISP3 gene
[0062] (1) Extraction of plant tissue total RNA
[0063] Total RNA was extracted from plant tissues by the Trizol method. The specific method was as follows: collect plant tissues, grind with liquid nitrogen, add 1ml Trizol (Invirtogen) to 0.1g tissue leaves, and then add 200 μL chloroform, let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 5 minutes. Take the upper aqueous phase into a centrifuge tube, add 200 μL chloroform to extract again, and repeat the previous step. Take 500 μL of the upper aqueous phase into a centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of isopropanol, mix thoroughly, place at room temperature for 20 min, and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 20 min. Discard the supernatant, add 500 μL of 70-80% ethanol (prepared with DEPC water), centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3 Analysis of autophagy level and SGS3 accumulation level in VISP3 overexpression and knockout plants
[0076] 1. Analysis of autophagy in VISP3 overexpression plants and knockout plants
[0077] Analysis of the autophagy situation analysis of the overexpressed plants and knockout mutant plants of the VISP3 gene constructed in Example 2, the specific methods are as follows:
[0078] (1) The wild-type Col-0, VISP3 overexpression plants and visp3 mutant plants were further transformed into YFP-ATG8e indicator gene, and the positive plants were grown in 1 / 2MS medium for 5 days, and Col-0 / 35S:YFP-ATG8e They were transferred to nitrogen-deficient or non-nitrogen-deficient medium, respectively, and VISP3 / 35S:YFP-ATG8e and visp3 / 35S:YFP-ATG8e were transferred to non-nitrogen-deficient medium for 4 days, and the whole plant was taken for Western blotting experiment. The last Col-0 is a non-transgenic negative control.
[0079] (2) Western blotting detection. Sampling...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com