SNP molecular marker A045736268C/T for identification of Chinese cabbage turnip mosaic virus resistance and application thereof
A technology of turnip mosaic virus and DNA molecules, applied in the biological field, can solve the problem of virus disease without specific chemical control and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of SNP molecular marker
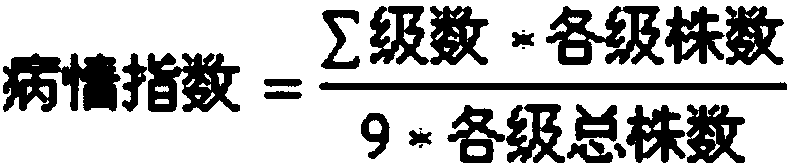
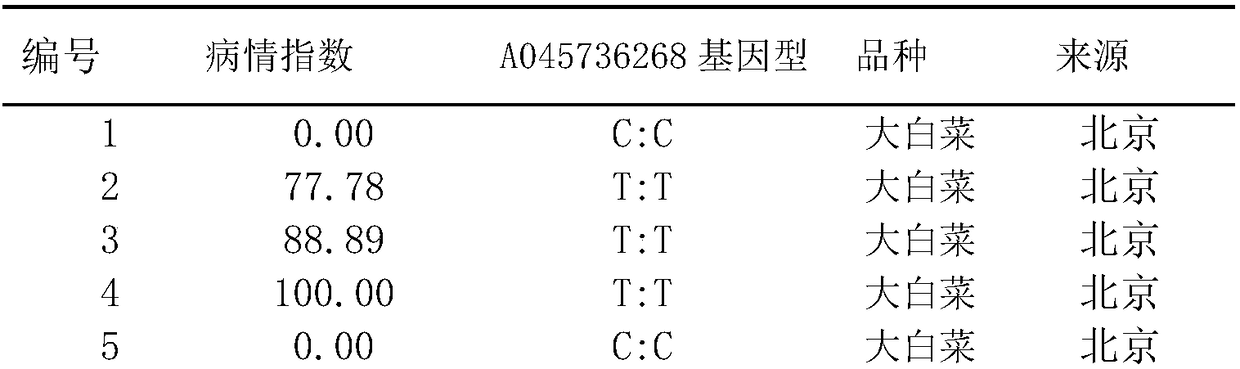
[0063] Through genome resequencing data analysis of the highly susceptible turnip mosaic virus strain T12-19 and the highly resistant turnip mosaic virus strain 91-112, it was found that (the male parent 91-112 in the embodiment was continuously selfed for 9 generations The advanced inbred line of Chinese cabbage is highly resistant to TuMV-C4; the female parent T12-19 is a double haploid line and highly susceptible to TuMV-C4. Both the male parent 91-112 and the female parent T12-19 are listed in the literature "Genetic mapping and localization of a major QTL for seedling resistance todowny mildew in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis, Mol Breeding (2009) 23: 573–590", publicly available from Vegetable Research Center, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences.), There is a C / T mutation SNP site at base 5736268 of chromosome A04. This SNP site is named A045736268C / T site, which can be used a...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2, Application of Molecular Marker A045736268C / T Site in Identifying Susceptibility to Turnip Mosaic Virus and Resistance to Turnip Mosaic Virus
[0076] 1. Molecular marker identification of materials susceptible to turnip mosaic virus disease and materials resistant to turnip mosaic virus disease
[0077] 1) DNA extraction
[0078] The male parent 91-112 in the examples is a Chinese cabbage high-generation inbred line that has been self-bred for 9 generations and is highly resistant to TuMV-C4; the female parent T12-19 is a double haploid line and is highly susceptible to TuMV-C4. Both the male parent 91-112 and the female parent T12-19 were disclosed in the literature "Geneticmapping and localization of a major QTL for seedling resistance to downymildew in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis, Mol Breeding (2009) 23:573-590" However, the public can obtain it from the Vegetable Research Center of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com