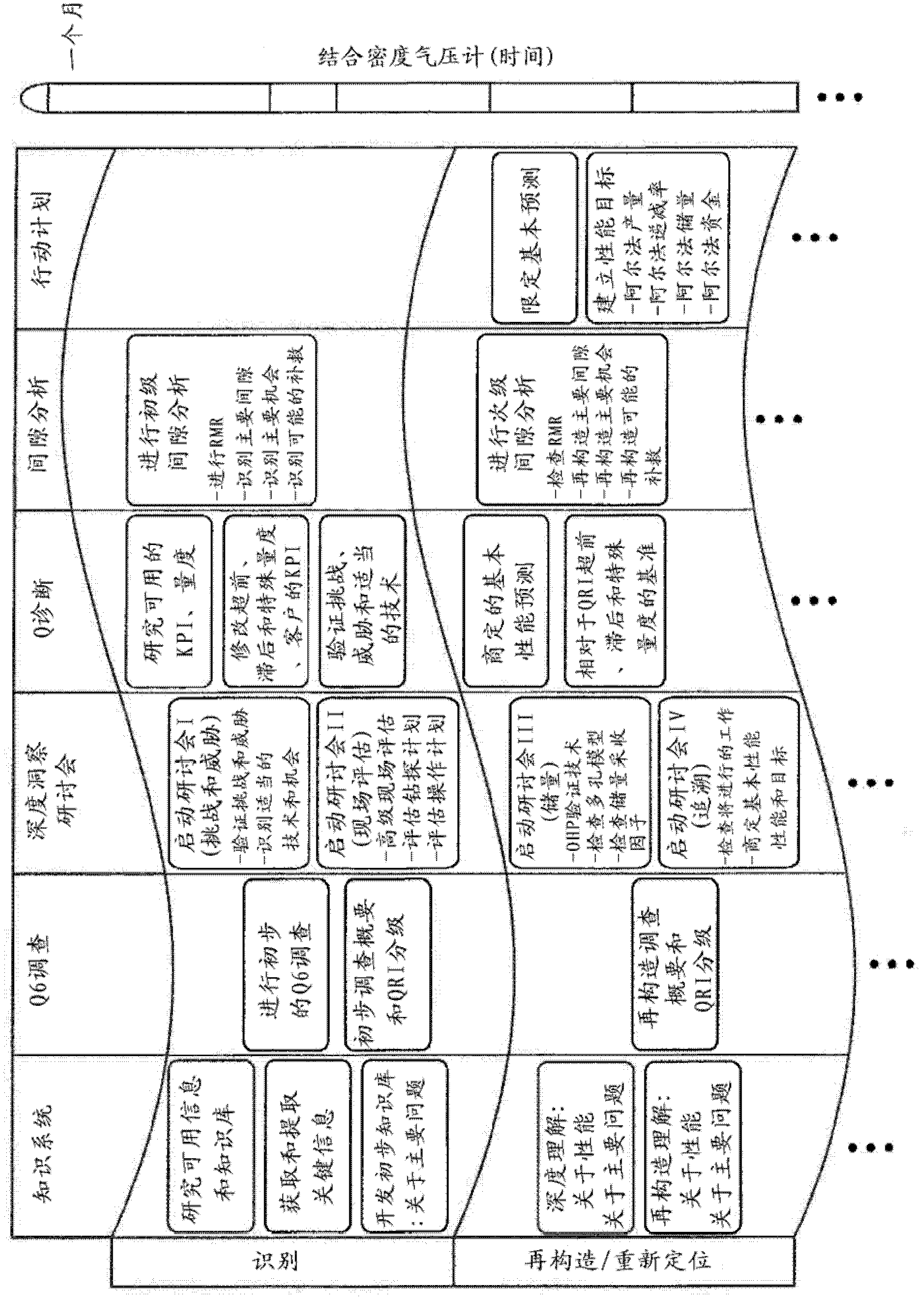
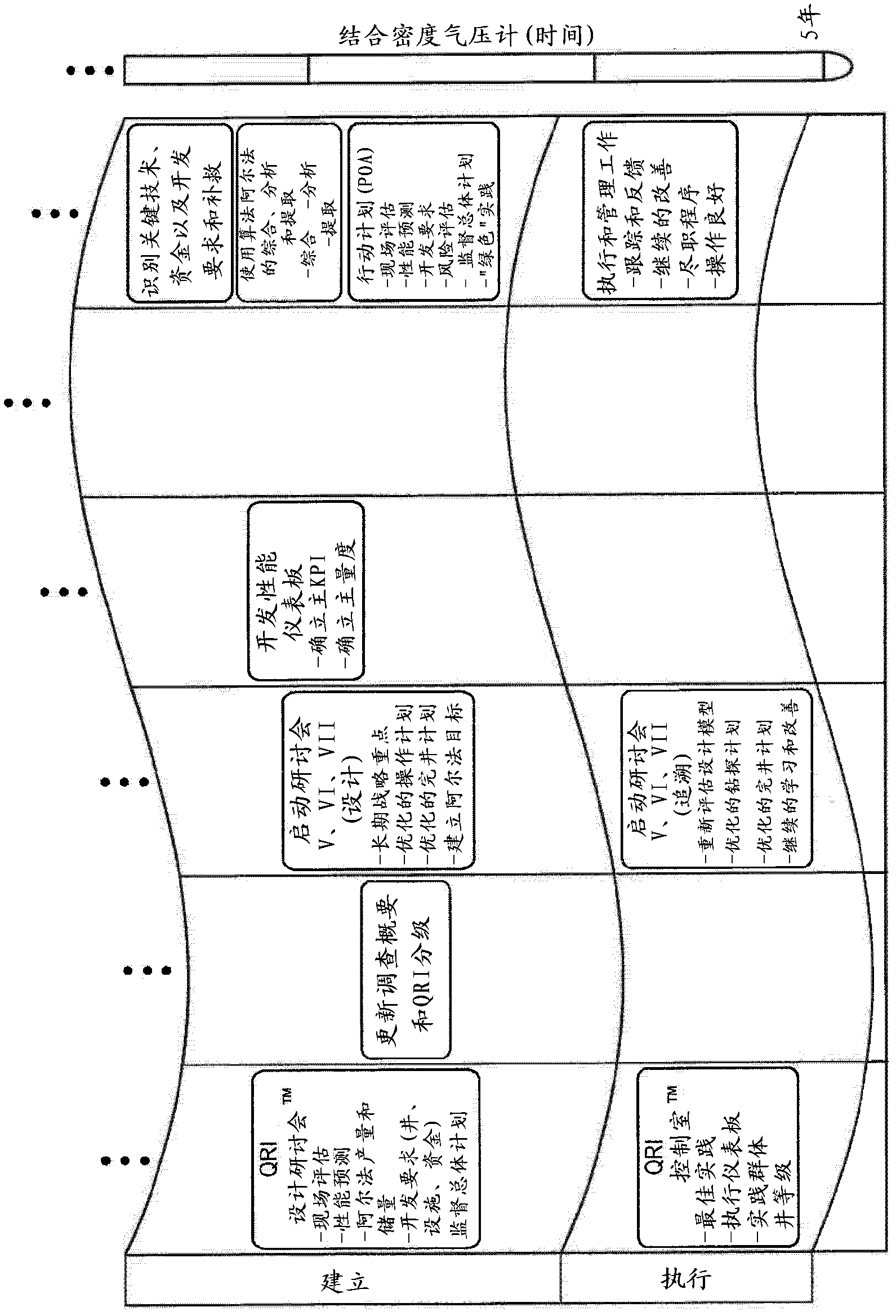
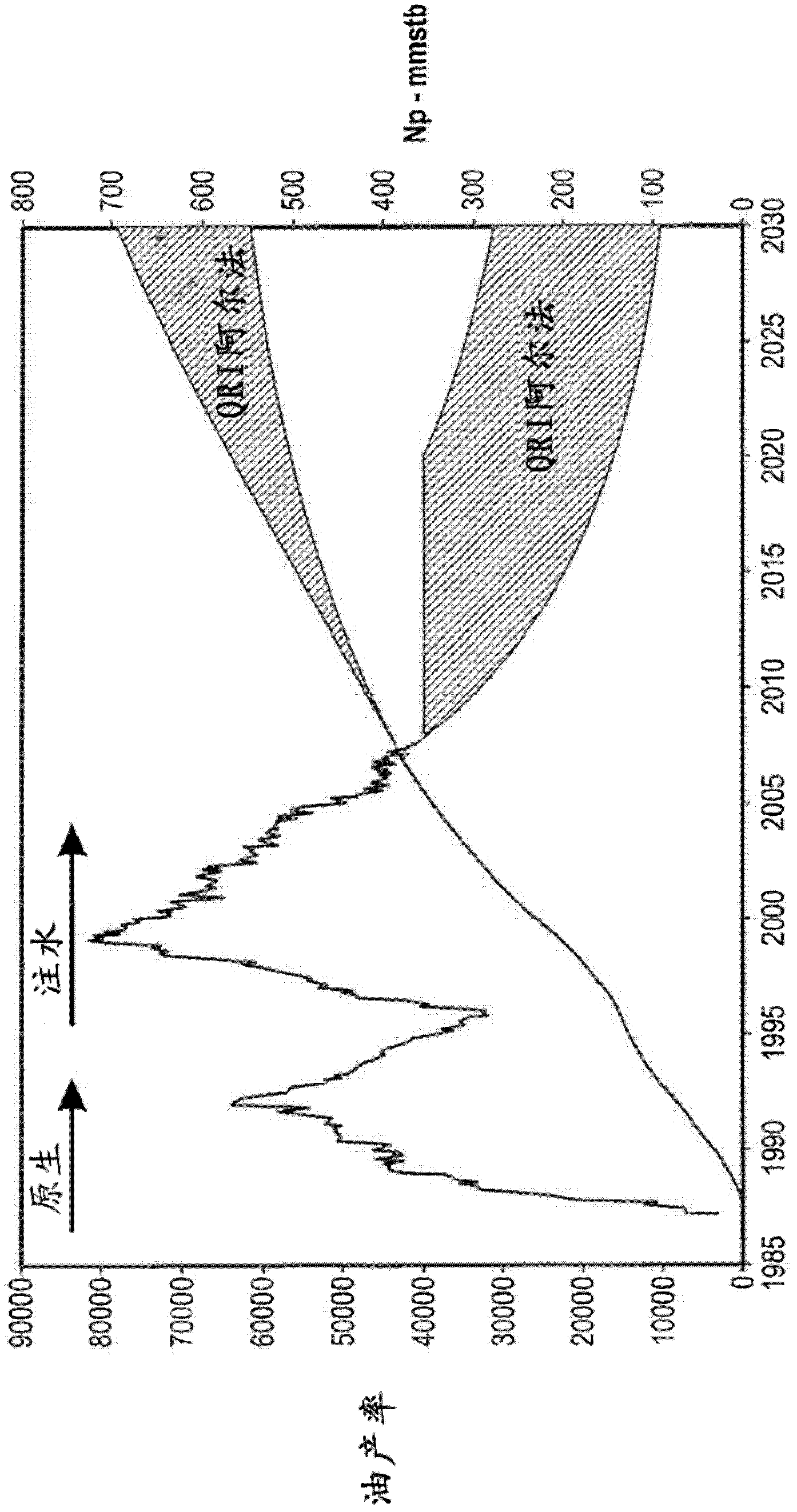
Method for dynamically assessing petroleum reservoir competency and increasing production and recovery through asymmetric analysis of performance metrics
A reservoir and recovery technology, applied in the direction of production fluid, earthwork drilling, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve problems such as low long-term recovery, difficult to plan action plans, low short-term productivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0789] Background Information
[0790] The field in this example is producing with peripheral water injection. It is in a mature consumption state having produced more than 70% of its reserves. Initiated redesign work to reduce field decline rate and water cut. A secondary purpose is to reduce ESP requirements and associated funding procedures.
[0791] geology
[0792] The field produces from a 60+ meter thick carbonate reservoir consisting of multiple upwardly shallowing periods. The reservoir has an average porosity of over 15% and a permeability of up to several Darcy. The upper half of the reservoir is usually very high reservoir quality; the lower half contains multiple interbeds of high and low reservoir quality. Enhance the quality of the lower half of the reservoir by increasing the fracture permeability, which significantly improves the reservoir conductivity, but also increases the risk of premature water breakthrough. The reservoir has a structural closure of...
example 2
[0797] Background Information
[0798] The field in this example was producing at a production rate of 300,000 barrels per day in 2006 and is the third increment of a three-increment field development plan. It's under the perimeter water injection. Due to concerns about premature water breakthrough, excessive development costs, and high well decline rates (all due to complex geology), redesign work was initiated to design new production increments. These considerations are based on experience gained through the development and performance of two adjacent oil-bearing increments.
[0799] geology
[0800] The field produces from a 60 meter thick carbonate reservoir consisting of multiple upwardly shallowing periods. The reservoir has an average porosity of about 15% and a permeability of up to 100 mD. The upper half of the reservoir is usually of medium reservoir quality; the lower half contains multiple interbeds of medium and low reservoir quality. Reservoir quality is en...
example 3
[0805] Background Information
[0806] The oil field in this example was producing at a production rate of 500,000 barrels per day in 1998. The field was developed with only one kilometer long horizontal wells. Current plans call for increasing production to 750,000 barrels per day by 2010. Initiate redesign efforts to reduce production decline, gas oil ratio (GOR), and associated field development capital and operating costs.
[0807] geology
[0808] The field is characterized by a gently folded northeast / southwest-trending anticline composed primarily of Cretaceous-era sandstones, shales and carbonates. The reservoir consists of thick crustal uplifts that change laterally into barriers and sill slopes. While matrix porosity is generally high (with an average value of 25%) and does not vary laterally, permeability is face-dependent and exhibits spatial variability. Typical permeability ranges from 5 to 10 mD in the southern portion dominated by low-energy lagoon accumul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com