Application of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in screening drugs for resisting cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure or cardiac fibrosis
A technology for cardiac fibrosis and cardiac hypertrophy, applied in the field of application of bone morphogenic protein-4 in the screening of anti-cardiac hypertrophy, anti-heart failure or anti-cardiac fibrosis drugs, can solve the problem of inability to completely cure arrhythmia, inability to inhibit cardiac decay process etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
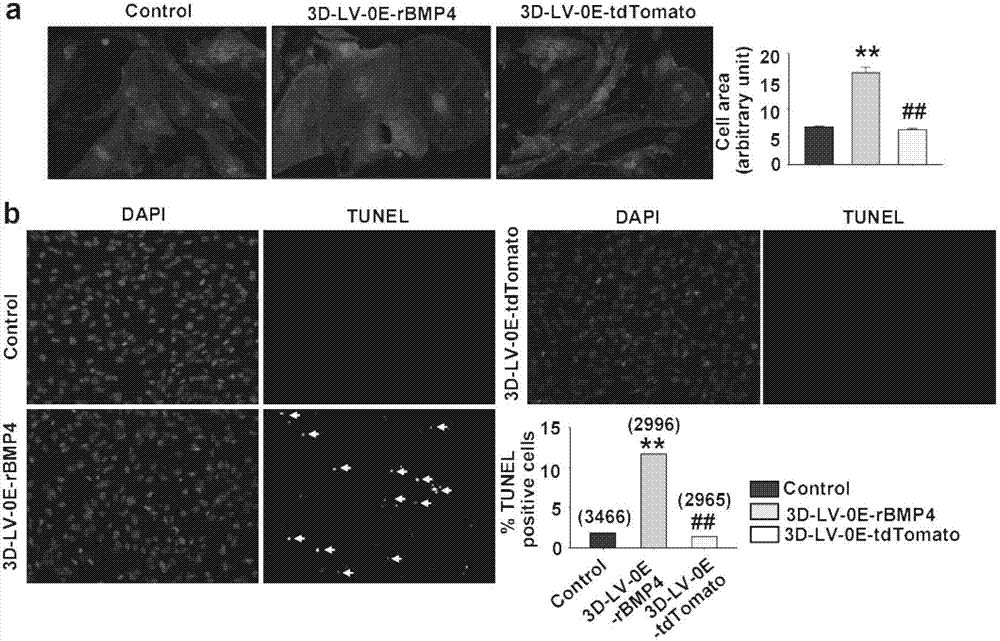
[0043] The relationship between embodiment 1 BMP4 and myocardial hypertrophy, heart failure and cardiac fibrosis
[0044] 1. Establishment of pressure load-induced cardiac hypertrophy model
[0045] Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium 65 mg / kg, placed supine on a mouse board, and under sterile conditions, tracheal intubation was performed and a ventilator was connected. A median chest incision (1-2 cm) was made to expose and separate the aortic arch. A 26-gauge needle was placed close to the thoracic aorta in parallel, the two were ligated with a 7.0-gauge thread, and the needle was withdrawn after ligation. The chest incision was sutured layer by layer and the chest was closed. Postoperative penicillin sodium intramuscular injection 3d anti-infection. Four weeks later, the mice were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital, and the mice were sacrificed after weighing their body weight (BW). Heart weight (HW) and left ventricle weight ...
Embodiment 2
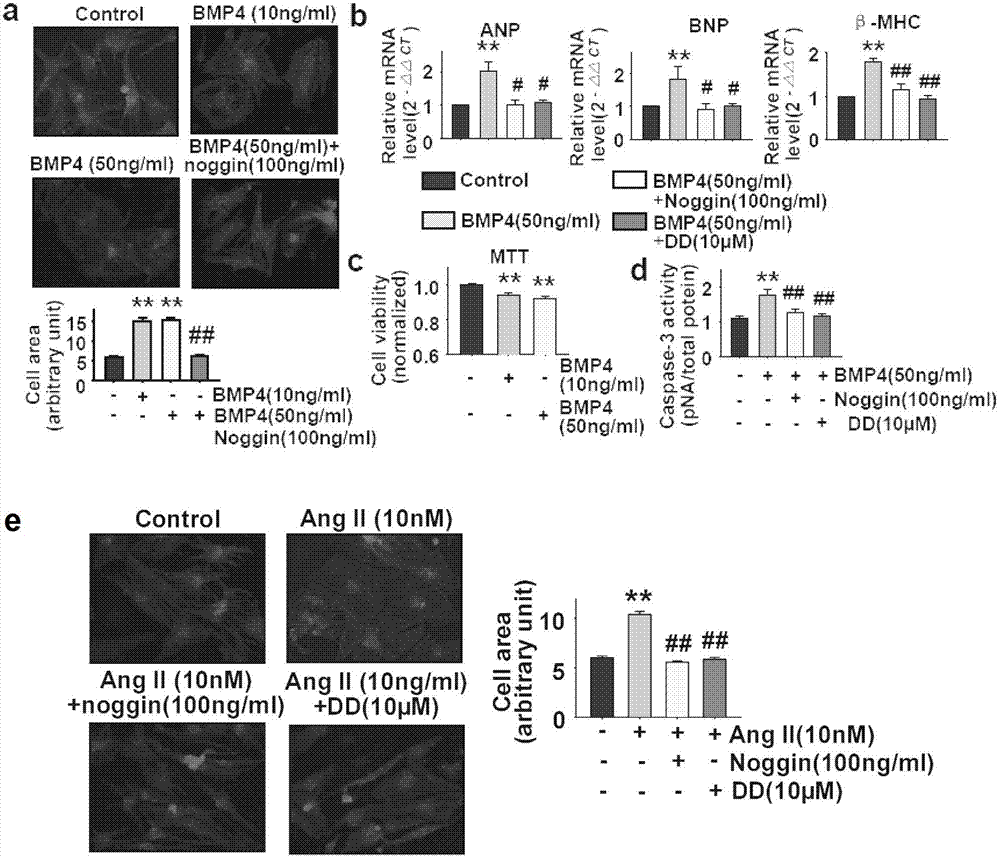
[0058] Example 2 The effect of Noggin protein on anti-cardiac hypertrophy, anti-cardiac apoptosis, and anti-cardiac fibrosis
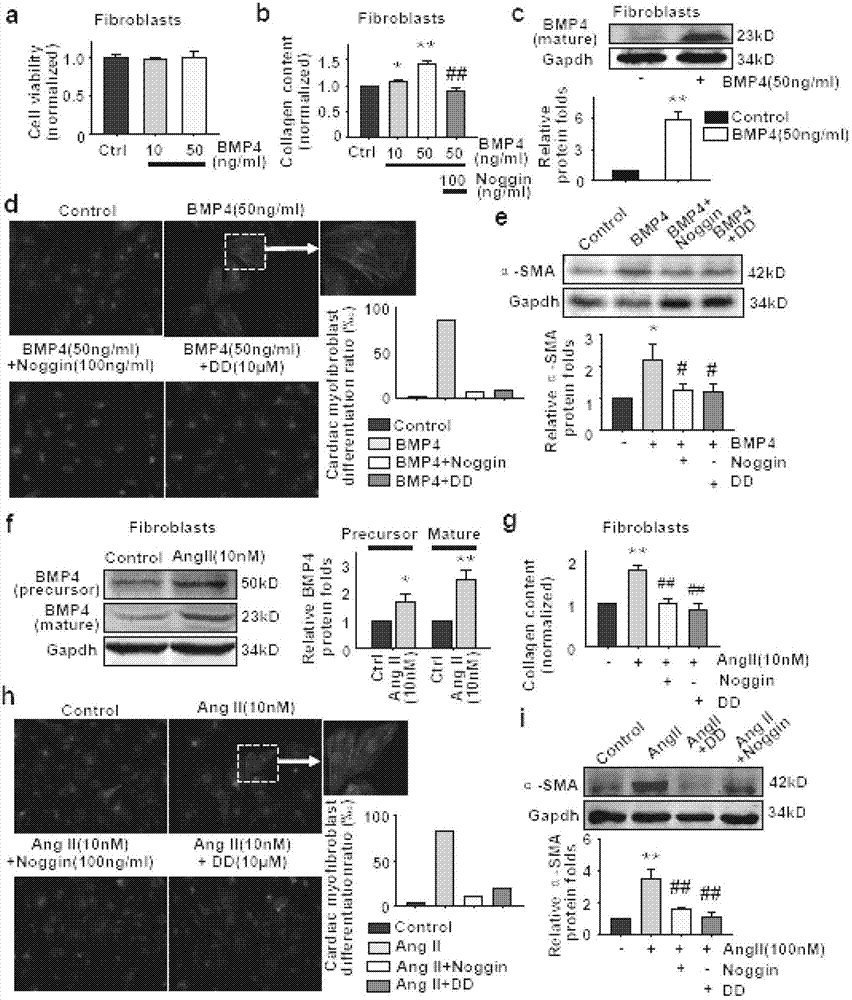
[0059] Such as figure 2 As shown in e, angiotensin II was used to induce cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in vitro, and administration of Noggin protein could significantly inhibit angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Such as figure 2 As shown in d, in cultured cardiomyocytes, BMP4 induced the increase of Caspase-3 activity, and the administration of Noggin protein could significantly inhibit the increase of BMP4-induced cardiomyocyte Caspase-3 activity, indicating that Noggin protein can inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Such as image 3 As shown in h, i, in the cultured cardiac fibroblasts, angiotensin II was used to induce fibroblast transformation, and the administration of Noggin protein could significantly inhibit the fibroblast transformation induced by angiotensin II, indicating that Noggin protein has anti-cardiac fibroblast transform...
Embodiment 34
[0061] Example 34-[6-(4-isopropoxy)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]quinoline (DD, the structure is shown in formula I) in anti-cardiac hypertrophy, anti-cardiac Apoptosis, anti-cardiac fibrosis
[0062] Such as figure 2 As shown in e, using angiotensin II to induce hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes in vitro, giving 4-[6-(4-isopropoxy)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]quinoline can Significantly inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Such as figure 2 As shown in d, in cultured cardiomyocytes, BMP4 induces an increase in Caspase-3 activity, giving 4-[6-(4-isopropoxy)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl] Quinoline can significantly inhibit the increase of cardiomyocyte Caspase-3 activity induced by BMP4, indicating that the compound can inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Such as image 3 As shown in h, i, in cultured cardiac fibroblasts, angiotensin II was used to induce fibroblast transformation, and administration of this compound could significantly inhibit angiotensin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com