Assay For Phytol-free Chlorophyll Derivatives
A technology of chlorophyll and phytol, which is applied in the fields of biomaterial analysis, microbial measurement/inspection, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as low activity of nitrophenyl esters, false negatives, and unreliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0086] In these examples, assays were developed to measure chlorophyllase, pheophytinase and pyropheophytinase activities. In the first step of the assay, a substrate consisting of chlorophyll, pheophytin or pyropheophytin in buffer is prepared. This substrate was added to the enzyme solution and reacted at 40°C for 10 minutes. After a reaction time of 10 min, an aliquot of the sample was transferred to the assay buffer. The measurement of enzyme activity relies on the principle that chlorophyll, pheophytin or pyropheophytin form dimers in the assay buffer (see figure 1 ). Dimer formation will quench the fluorescence signal of chlorophyll, pheophytin or pyropheophytin. The detection buffer is formulated such that the produced phytochlorophyll, pheophorbide or pyropheophorbide does not form dimers and is thus detectable by fluorescence spectroscopy.
example 1
[0087] Example 1 - Development of an Assay for Pyropheophytinase Activity
[0088] A 100 mM pH 7 phosphate buffer was prepared as a reaction buffer containing 50 mM KCl, 0.2% Triton X-100 and 5.17% acetone. Prepare the following solutions containing pyropheophytin, pyropheophytin, or mixtures thereof, and add them to the reaction buffer:
[0089] 1) Pyropheophytin solution: 500 μl reaction buffer + 50 μl water + 30 μl pyropheophytin (1mg / ml acetone solution)
[0090] 2) Pyropheophorbide solution: 500 μl reaction buffer + 50 μl water + 15 μl pyropheophorbide (2 mg / ml acetone solution) + 15 μl acetone.
[0091] 3) Pyropheophytin: 1:1 solution of pyropheophytin: 500 μl reaction buffer + 50 μl water + 15 μl pyropheophytin (1 mg / ml acetone solution) + 7.5 μl pyropheophytin ( 2 mg / ml acetone solution) + 7.5 μl acetone.
[0092] Various detection solutions (A-G) were prepared containing different concentrations of Triton X-100 (surfactant) and ethanol or isopropanol (solvent), a...
example 2
[0105] Example 2 - Development of an Assay for Pheophytinase Activity
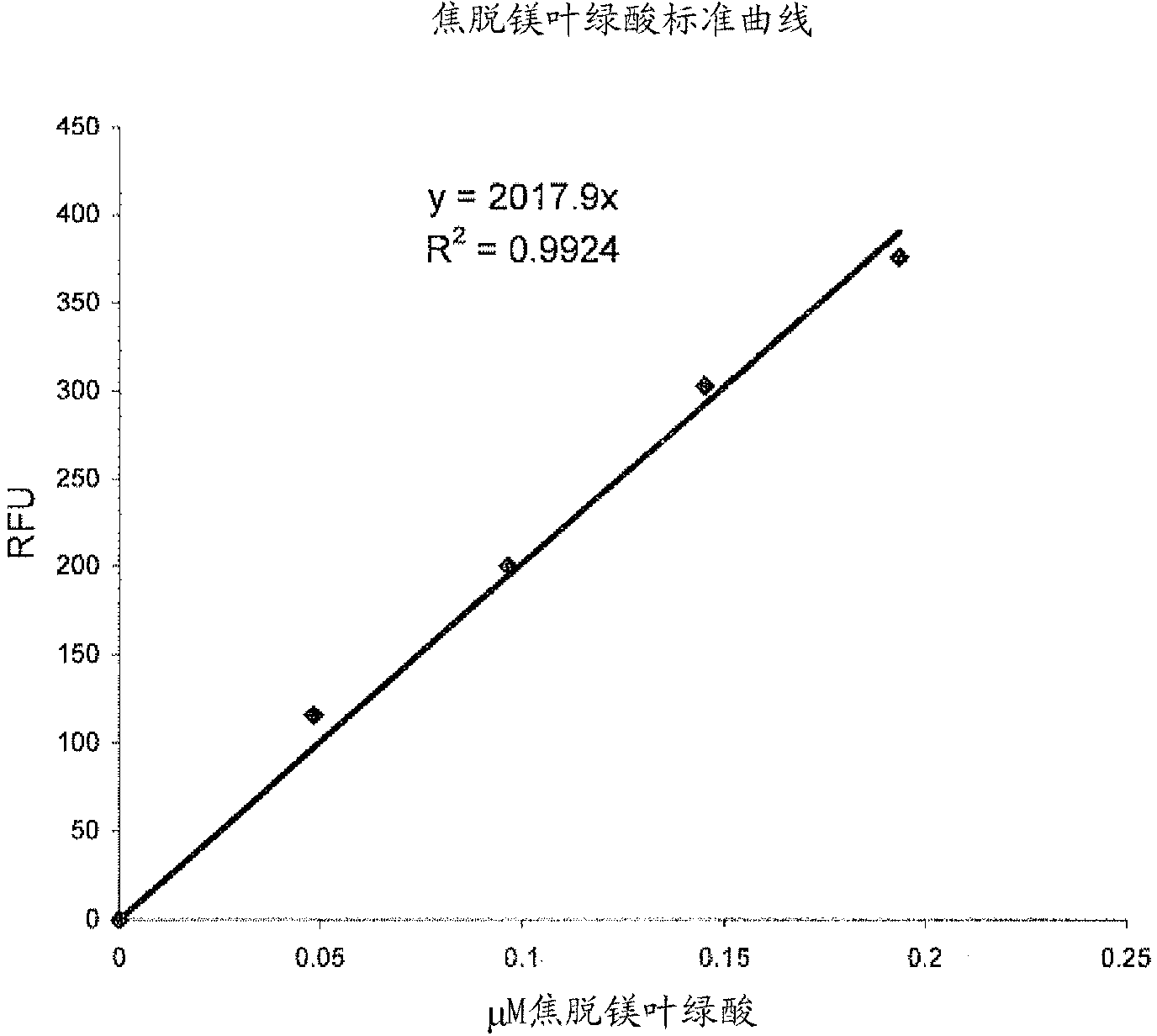
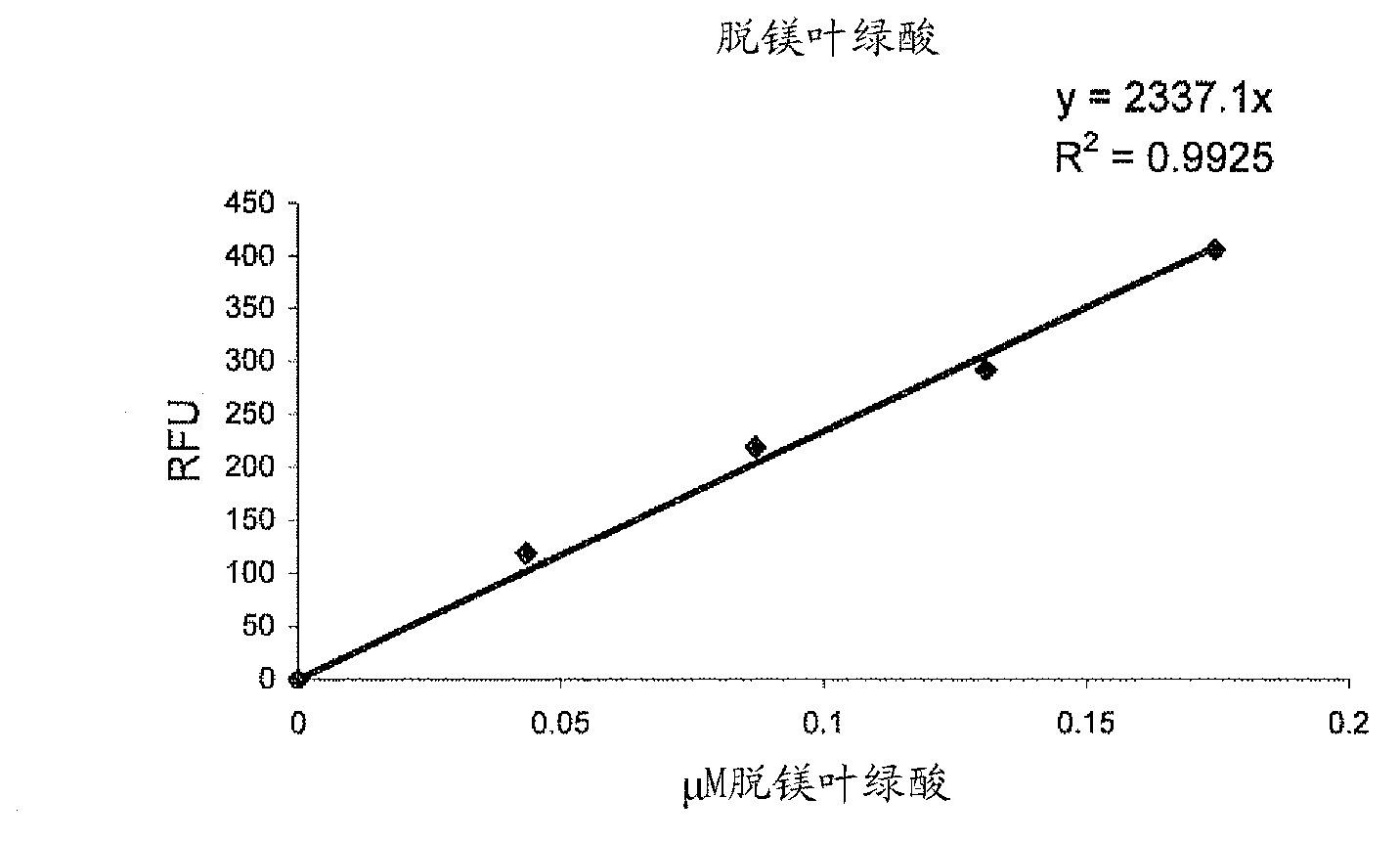
[0106] Based on the results of Example 1, an assay for the detection of pheophytinase activity was developed. When added to detection solution E (0.015% Triton X-100; 15% IPA; 0.05M NaOH), the fluorescence emitted by pheophytin was largely quenched (in terms of pyropheophytin) at room temperature, but Pheophorbide produced a strong fluorescent signal. Therefore, a calibration curve for pheophorbide was constructed (see image 3 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com