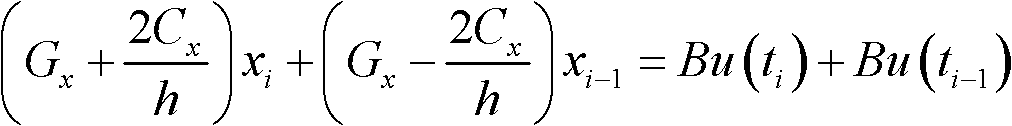Interconnection line model reduction method based on time-domain trapezoidal method difference
A technology of model reduction and interconnection, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of high complexity and difficulty in reducing the order of large-scale system models, and achieve high order reduction accuracy, Effect of eliminating errors and high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
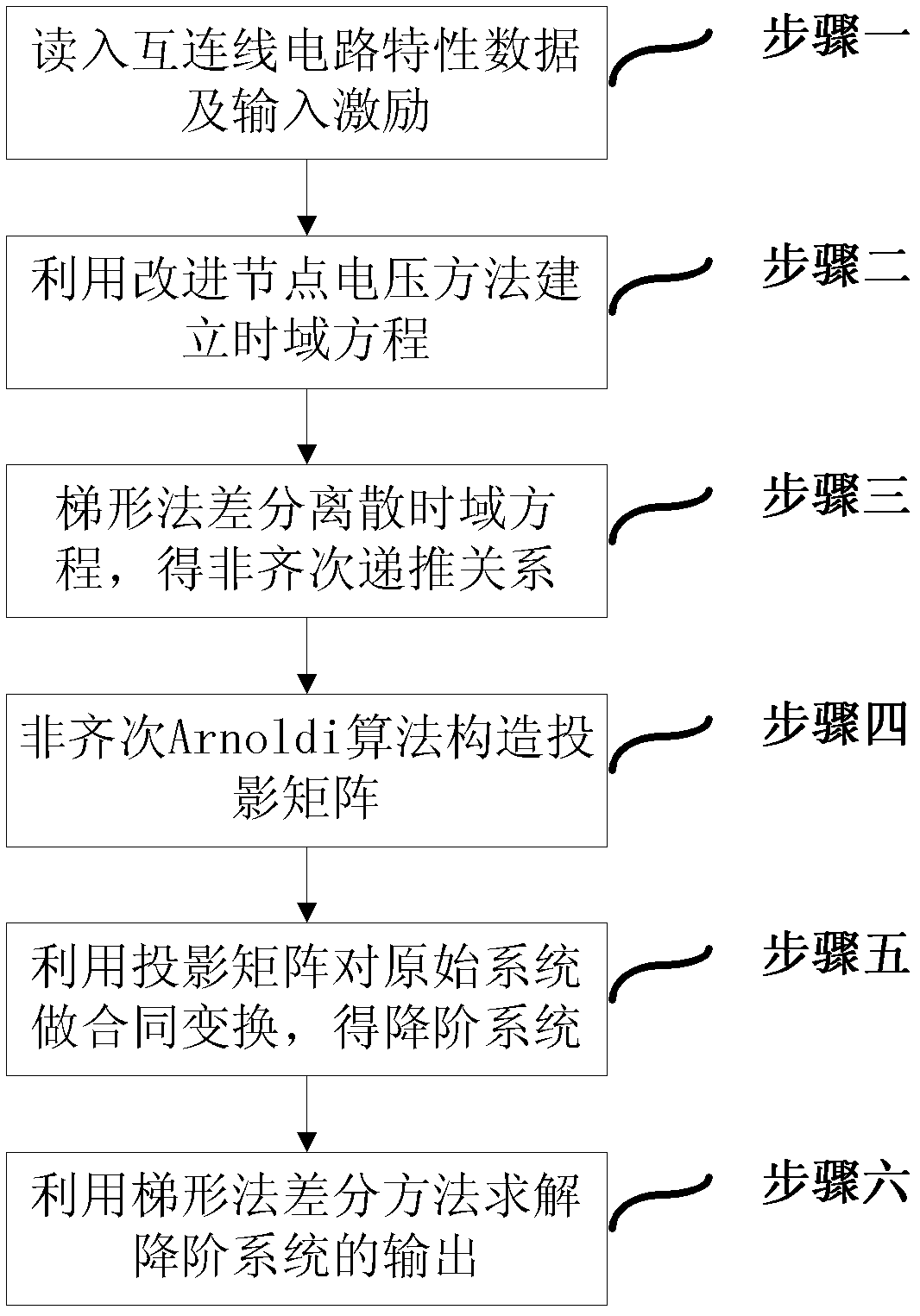
[0037] The implementation steps of the method for reducing the order of the interconnection line model based on the difference of the time-domain trapezoidal method in the present invention are as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0038] Step 1: Read the characteristic data and input excitation of the interconnection circuit, the characteristic data of the interconnection circuit includes the resistance, capacitance and inductance parasitic network netlist obtained by extracting the parasitic parameters of the interconnection;
[0039] Step 2: Use the improved node voltage method to establish the time domain equation (1) of the interconnect circuit:
[0040] (1)
[0041] y(t)=L T x(t)
[0042] where x∈i N×1 Represents the state variable composed of unknown node voltage and branch current, where N is the number of unknown variables in the equation, and represents the order of the original system; y represents the output voltage or current; C, G∈i N×N , where C represents the co...
Embodiment 2
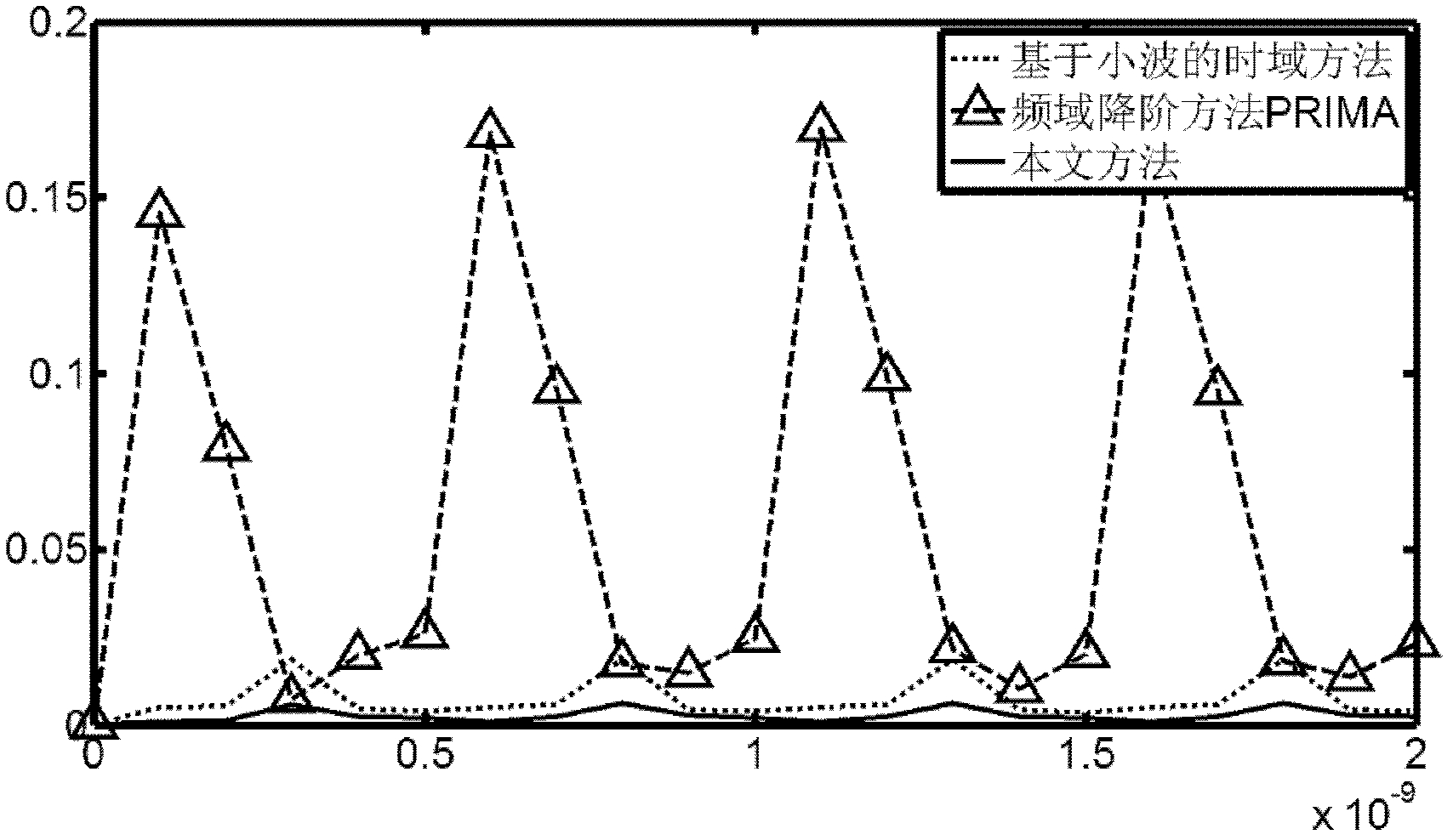
[0080] This embodiment adopts a bus circuit, the order of which is 12738, and the input is a pulse signal of 1 GHz. In this embodiment, the order of the circuit is reduced to 30, 50, and 70 respectively, and one of the output signals is observed in the time domain to measure the accuracy of different order reduction methods. The present invention takes the HSPICE simulation result as the accurate result of the original system output; the relative error rel_err is defined as follows:
[0081]
[0082] where y and denote the outputs of the original system and the reduced-order system, respectively.
[0083] mistake! Reference source not found. The reduction time and accuracy of different model reduction methods are shown. It can be seen from Table 1 that the order reduction time of the model reduction method based on the difference of the time-domain trapezoidal method proposed by the present invention is equivalent to that of the existing frequency-domain model reductio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com