Methods of sequestering carbon dioxide
A carbon dioxide and liquid carbon dioxide technology, applied in carbon dioxide storage, storage devices, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of complex processing procedures, obvious greenhouse effect, high cost, and achieve the effect of wide application, reduced emissions and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
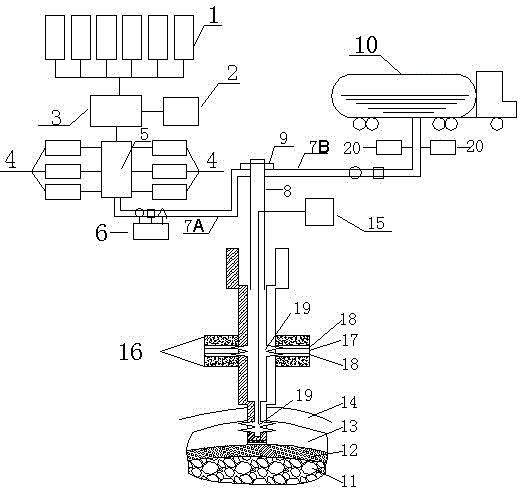
[0022] Such as figure 1 A method for sequestering carbon dioxide shown, comprises the steps:
[0023] (1) Selection of injection horizon: the injection horizon includes the goaf 11 and the unminable thin coal seam 17 above it, and the upper side of the unminable thin coal seam 17 of the selected injection horizon has a sandy mudstone layer with a thickness greater than 2m Or mudstone layer 16 exists.
[0024] Here, the injection site where the injection layer is located should be selected first: to make the injected CO 2 It can be better sealed. In order to prevent hidden dangers after injection, the injection site cannot be selected in the goaf 11 of the coal mine being mined, nor can it be selected in the goaf 11. The upper coal seam has been mined, and the lower part is not far away (generally not far away) Areas where coal seams over 200m) still need to be mined. Therefore, the injection site is selected to inject carbon dioxide sequestration construction in the abandon...
Embodiment 2
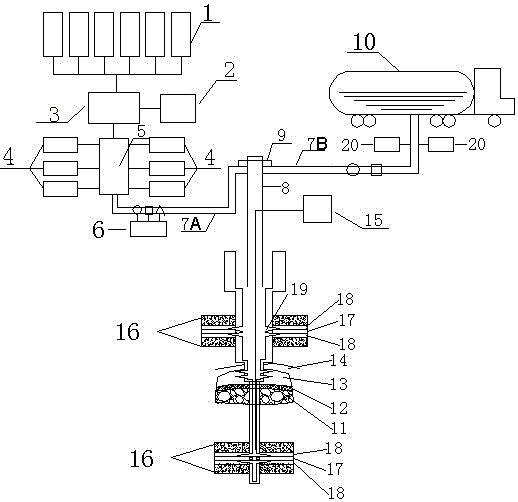
[0089] Depend on figure 2 The shown method for sequestering carbon dioxide differs from that of Example 1 in that: in step (1), the injection horizon includes the goaf 11 and the unminable thin coal seams located on the upper side and the lower side of the goaf 11 respectively 17. In this case, the upper and lower parts of the goaf 11 formed by the mineable coal seam have non-minable thin coal seams 17. For cost considerations, the upper and lower non-minable thin coal seams 17 are separated from the goaf 11 respectively. At this time, both the thin coal seams at the upper and lower parts of the goaf 11 will be injected, and the goaf 11 will be injected at the same time. The strata from top to bottom are: mudstone or sandy mudstone layer 16, sandstone layer 18, unminable thin coal seam 17, sandstone layer 18, mudstone or sandy mudstone layer 16, curved subsidence zone 14, fissure zone 13, caving Belt 12, goaf 11, mudstone or sandy mudstone layer 16, sandstone layer 18, unmin...
Embodiment 3
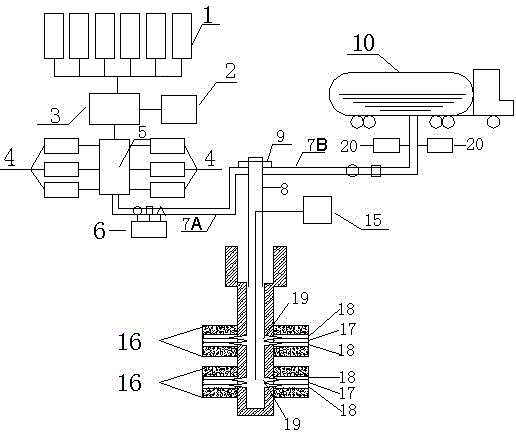
[0096] Depend on image 3 The difference between the shown method for sequestering carbon dioxide and that of Embodiment 1 is that in step (1), the injection layer only consists of several unminable thin coal seams 17 from top to bottom. However, due to cost considerations, the burial depth of these thin coal seams should not exceed 800m. The top and floor of each unminable thin coal seam 17 have a sandstone layer 18 and the upper side of the upper sandstone layer 18 and the lower side of the lower sandstone layer 18 all have mudstone or sandy mudstone layers 16 .
[0097] In step (2), the wellbore is drilled with a double-split wellbore structure: when carbon dioxide is injected only in several non-recoverable coal seams, the wellbore structure is similar to that of conventional CBM wells, that is, the double-split wellbore structure is adopted , while considering the drilling cost, the drill bit diameter is relatively small. The details are as follows: the first opening us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com