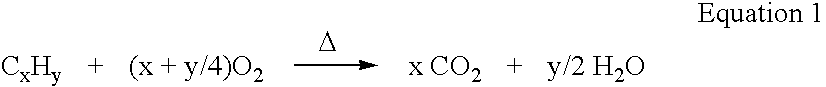Patents
Literature
62 results about "Negative carbon dioxide emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A negative carbon dioxide emission or negative emission or a process that is carbon negative gives a permanent removal of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide from Earth's atmosphere. It is considered the direct opposite of carbon dioxide emission, hence its name. It is the result of carbon dioxide removal technologies, such as bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, biochar, direct air capture or enhanced weathering. Negative emissions is different from reducing emissions, as the former produces an outlet of carbon dioxide from Earth's atmosphere, whereas the latter decreases the inlet of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Both have the same momentary net effect, but for achieving carbon dioxide concentration levels below present levels, such as 350 ppm, negative emissions are critical. Also for meeting higher concentration levels, negative emissions are increasingly considered to be crucial as they provide the only possibility to fill the gap between needed reductions to meet mitigation targets and global emission trends.
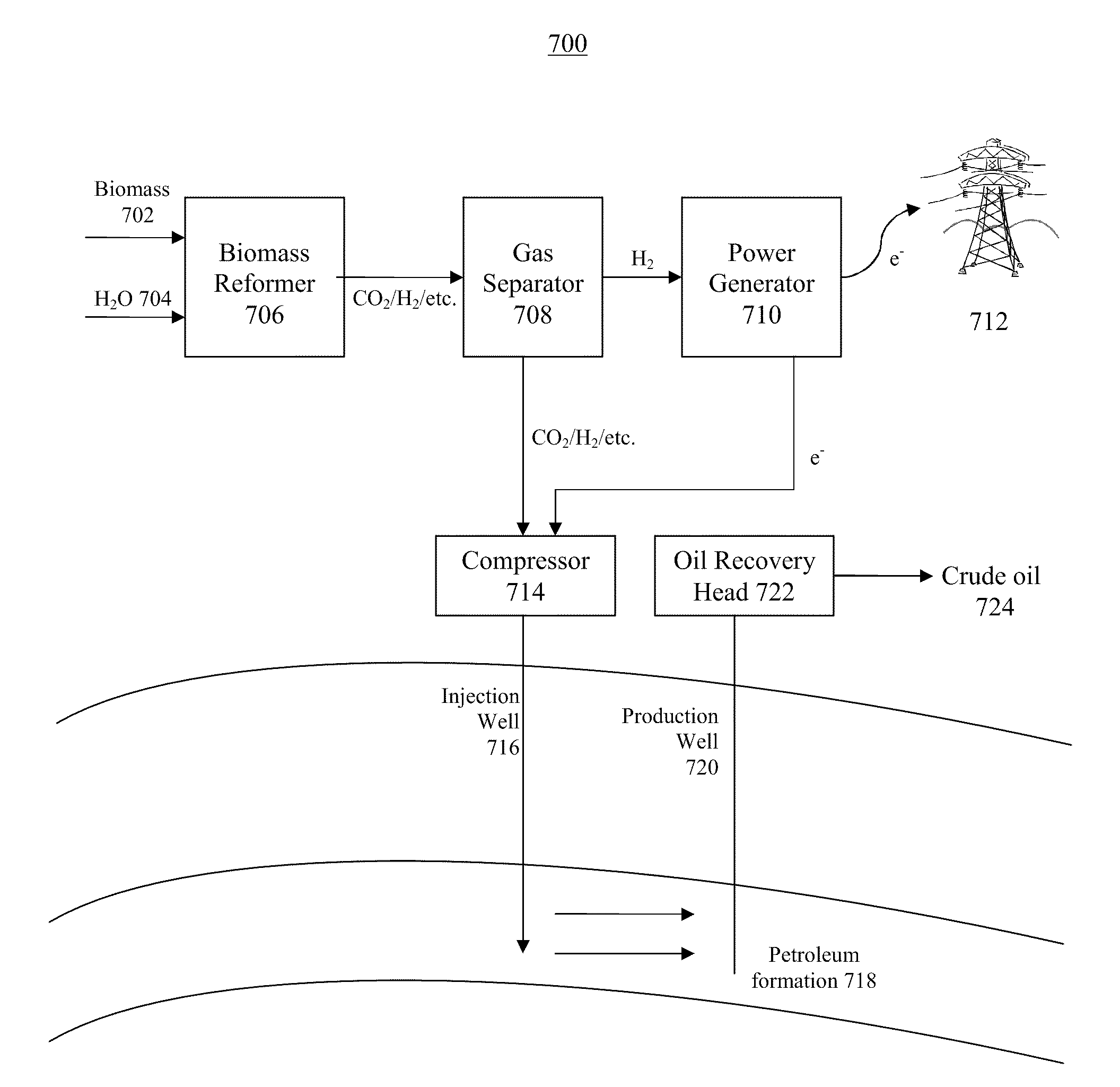
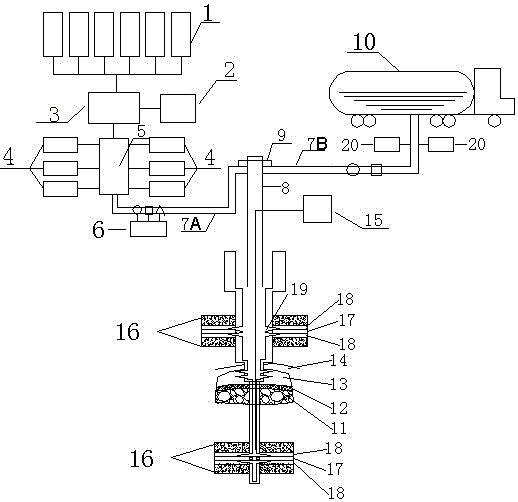
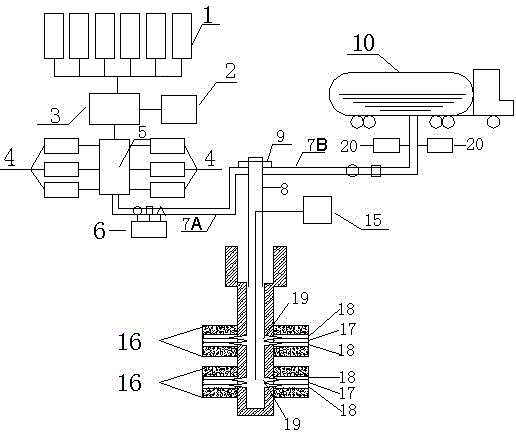
Portable renewable energy system for enhanced oil recovery (preseor) using biomass having net negative co2 emissions and for generating electricity having zero co2 emissions
InactiveUS20100038082A1Increase blockingPromote recoveryBiofuelsWaste based fuelPetroleumElectric power
The Portable Renewable Energy System for Enhanced Oil Recovery (“PRESEOR”) is a truck mobile system that reforms biomass into CO2 and hydrogen, following which the gases are separated, with the CO2 sequestered underground for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and the hydrogen used to generate several megawatts of carbon-free electricity. In contrast to large central power plants that are generally not well-located to support EOR, the small PRESEOR can go directly to the oilfields where it is needed, and do so in a timely manner. The PRESEOR sequesters more biomass-derived carbon than is released by the burning of the oil it yields, thereby producing not only carbon-free electricity but carbon-free oil. Using PRESEOR, over 80 billion barrels of U.S. oil would be made recoverable, without the need to drill new wells in pristine areas.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
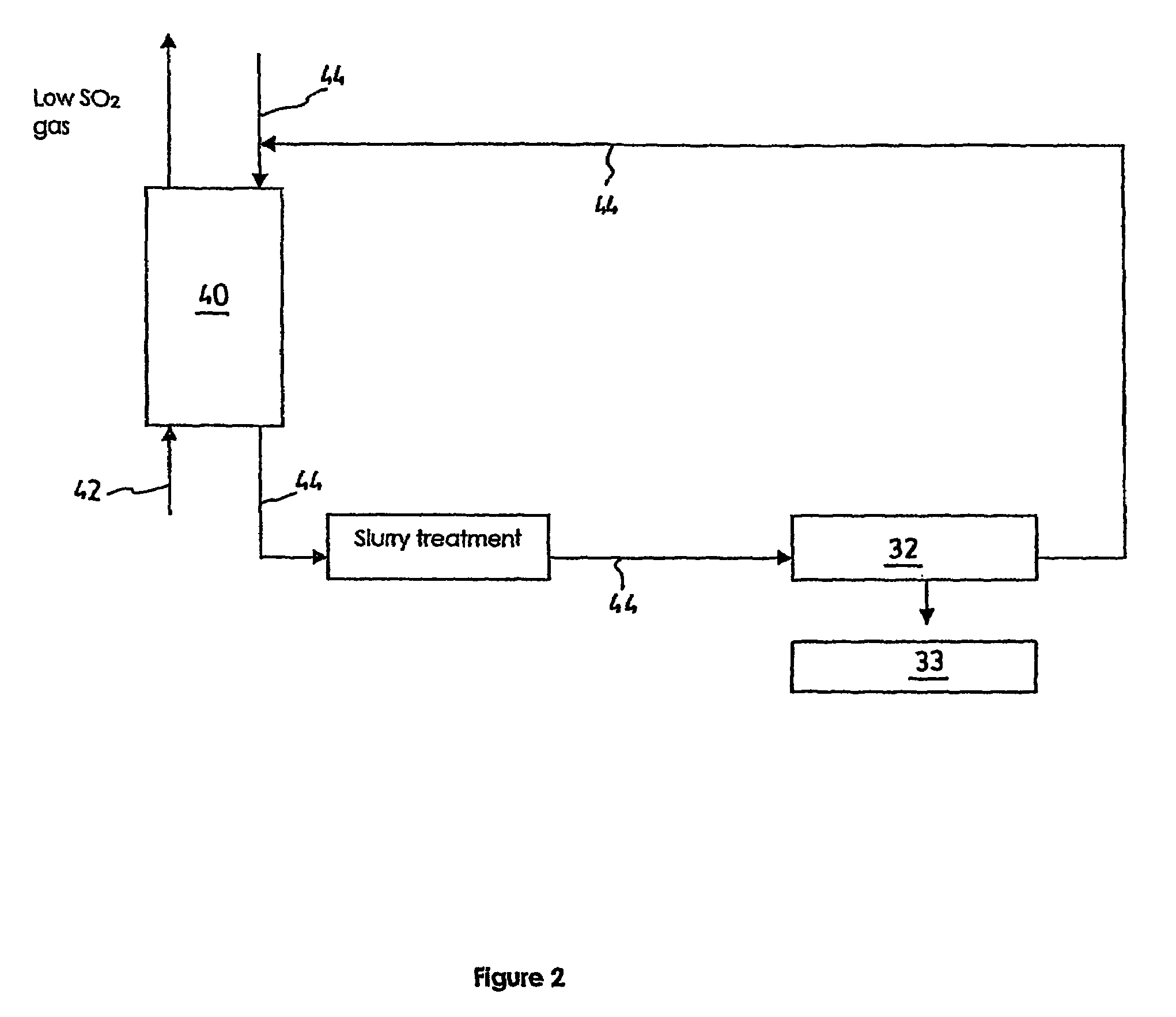
Process and a plant for recycling carbon dioxide emissions from power plants into useful carbonated species
ActiveUS7596952B2Useful carbonated speciesEnvironment safetyCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesGas turbine plantsAtmospheric airNegative carbon dioxide emission
A process is disclosed for recycling carbon dioxide emissions from a fossil-fuel power plant into useful carbonated species The process primarily comprises the steps of: a) burning the fossil fuel, thereby generating heat and a hot exhaust gas containing CO2; and b) converting the heat into energy. The process is characterized in that it further comprises the steps of: c) cooling the exhaust gas; and d) biologically transforming the CO2 contained in the cooled exhaust gas into carbonated species, thereby obtaining a low CO2 exhaust gas and producing useful carbonated species. The low CO2 exhaust gas obtained in step d) can be released in the atmosphere without increasing the problem of greenhouse effect.
Owner:SAIPEM SPA
Solar aided carbon dioxide trapping integrated system
ActiveCN103752142ATake full advantage of high heat collection efficiencyReduced capture efficiencyCarbon compoundsSolar heat devicesReboilerTrapping
The invention discloses a solar aided carbon dioxide trapping integrated system, which mainly comprises three parts, i.e. a power generation subsystem, a carbon dioxide trapping subsystem and a solar heat collection subsystem, wherein the subsystems are connected mainly through a boiler feed water heater, a reboiler and a flue gas pretreatment device to form the whole integrated system. According to the system, the high and low energy requirements of related parts among the solar heat collection subsystem, the power generation subsystem and the carbon dioxide trapping subsystem are reasonably allocated and integrated in different connecting ways at the heat output end of the solar heat collection subsystem to realize the gradient utilization of energy, so that the energy consumption of extraction of vapor from a steam turbine of a power plant can be greatly reduced, the stability of the power plant can be maintained, the dual effects of utilizing renewable energy resources and reducing the carbon dioxide emission of the power plant are achieved, and the large-scale application of solar energy and an integrated flue gas trapping technology in China are forcefully promoted.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
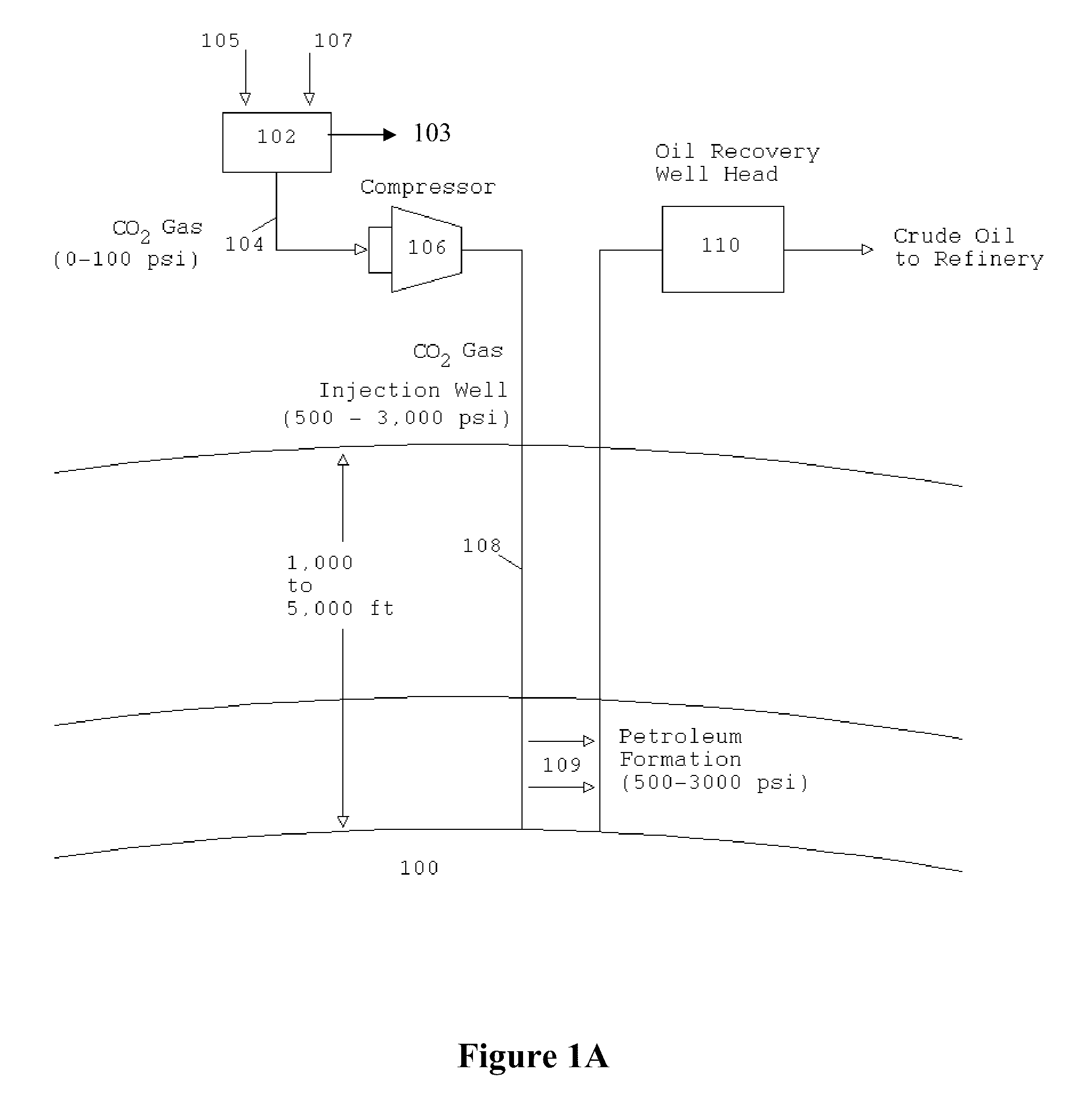
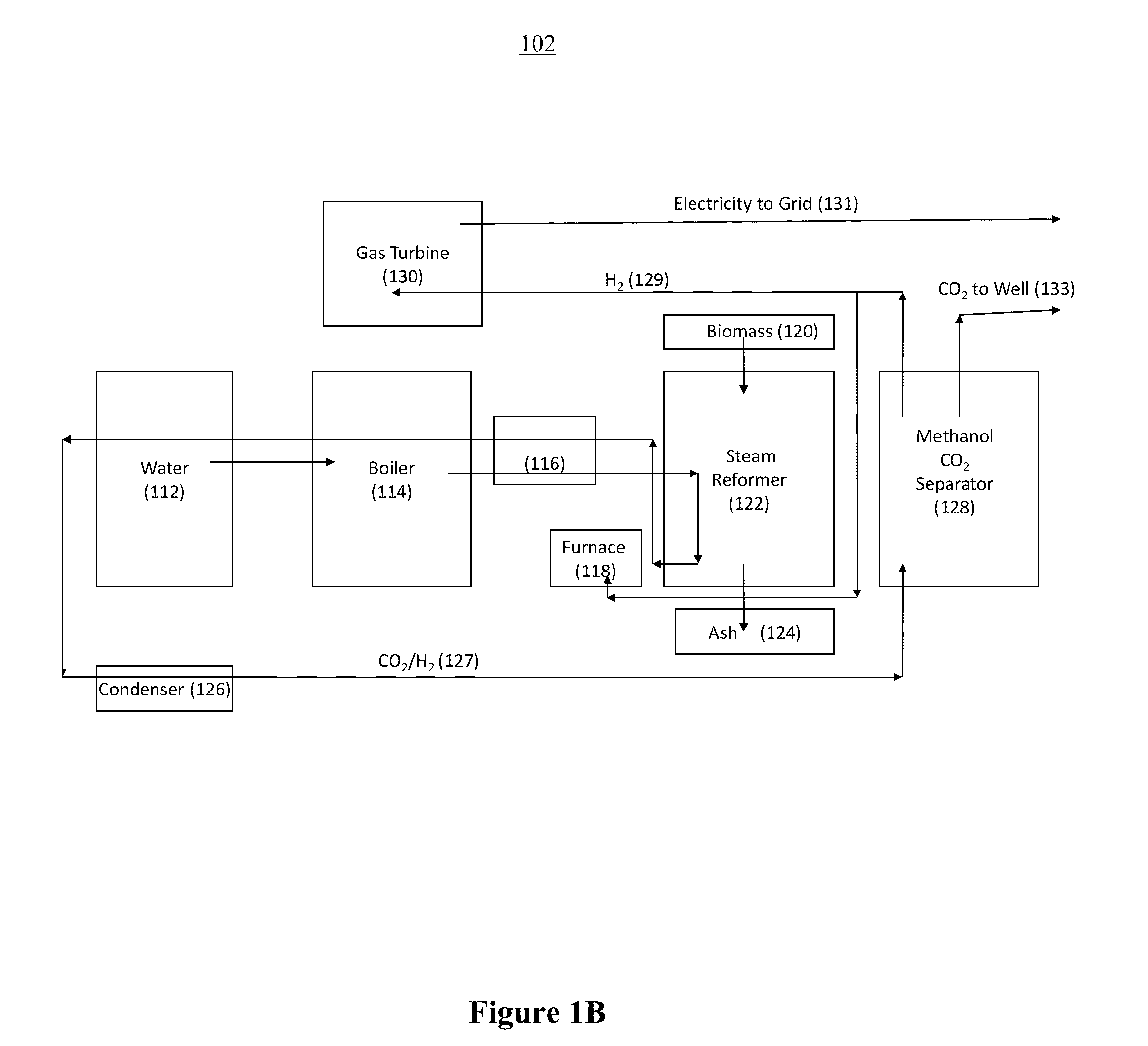
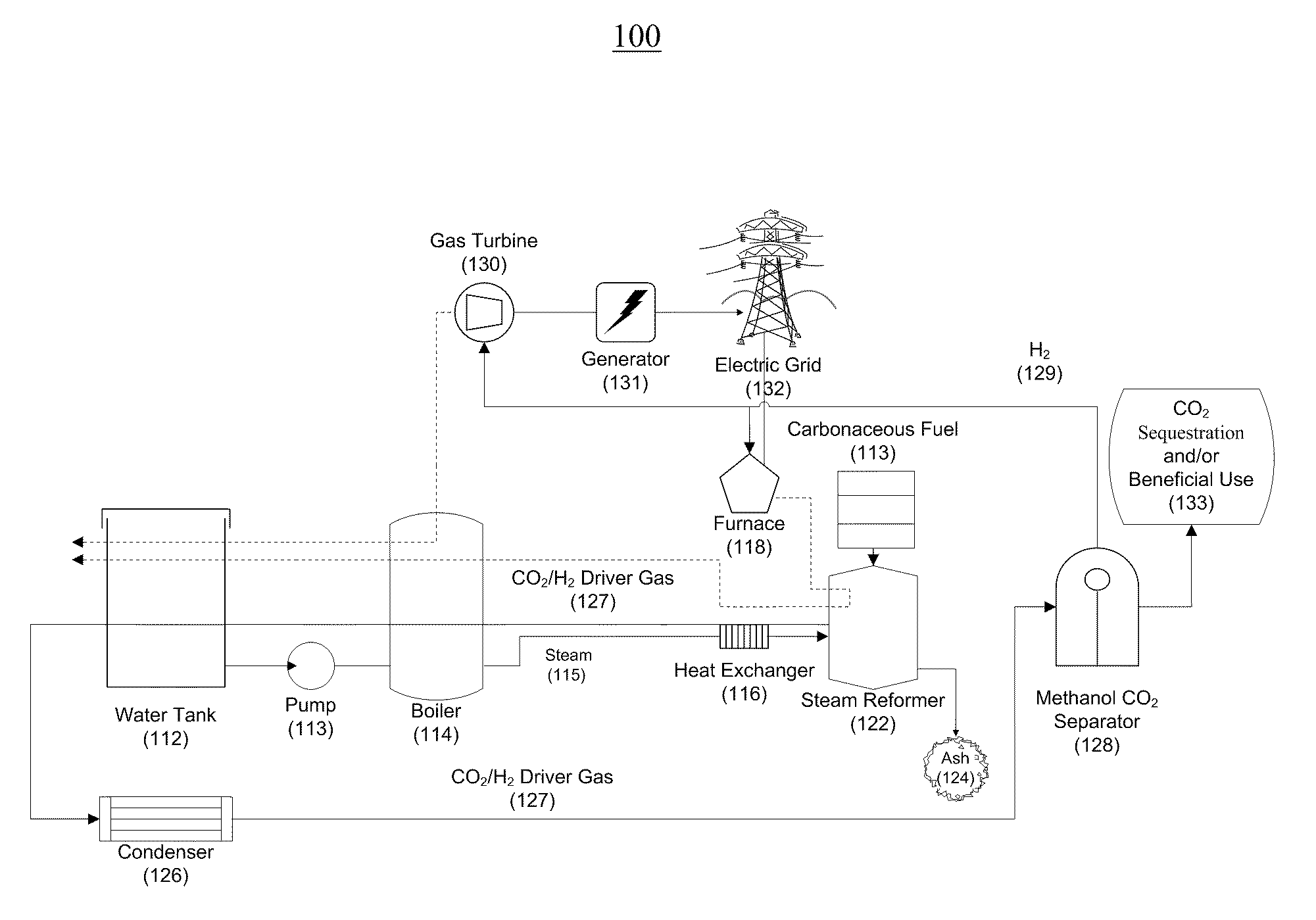
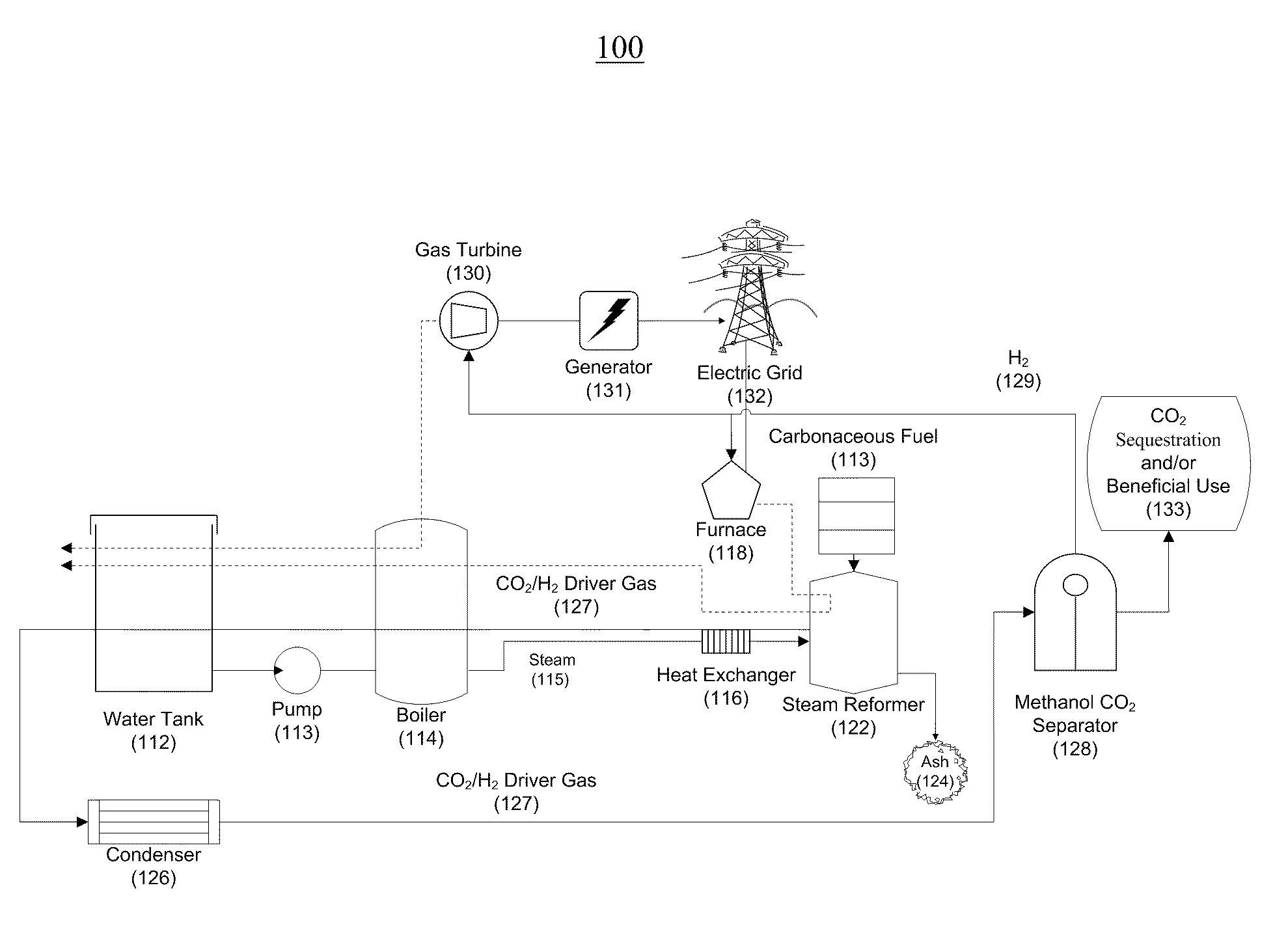
Systems and methods for generating electricity from carbonaceous material with substantially no carbon dioxide emissions
InactiveUS20110067410A1Little and no carbon dioxide emissionReduce carbon emissionsBiofuelsCombustion enginesCarbon dioxide corrosionMechanical energy
A reformation power plant generates clean electricity from carbonaceous material and high pressure CO2 which can be easily sequestered or utilized for a beneficial purpose, such as fuel production. The reformation power plant design utilizes a reformation process that reforms carbonaceous fuel with super-heated steam into a high-pressure gaseous mixture that is rich in carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas. This high-pressure gas exchanges excess heat with the incoming steam from a boiler and continues onward to a condenser. Once cooled, the high-pressure gas goes through a methanol separator, after which the CO2-rich gas is sequestered underground or beneficially re-used. The remaining hydrogen-rich gas is combusted through a gas turbine. The gas turbine provides power to a generator and also regenerative heat for the boiler. Finally, the generator converts mechanical energy into electricity, which is transferred to the electric grid. Therefore, carbon-free electricity is generated from coal, biomass, or other carbon-based feedstock.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
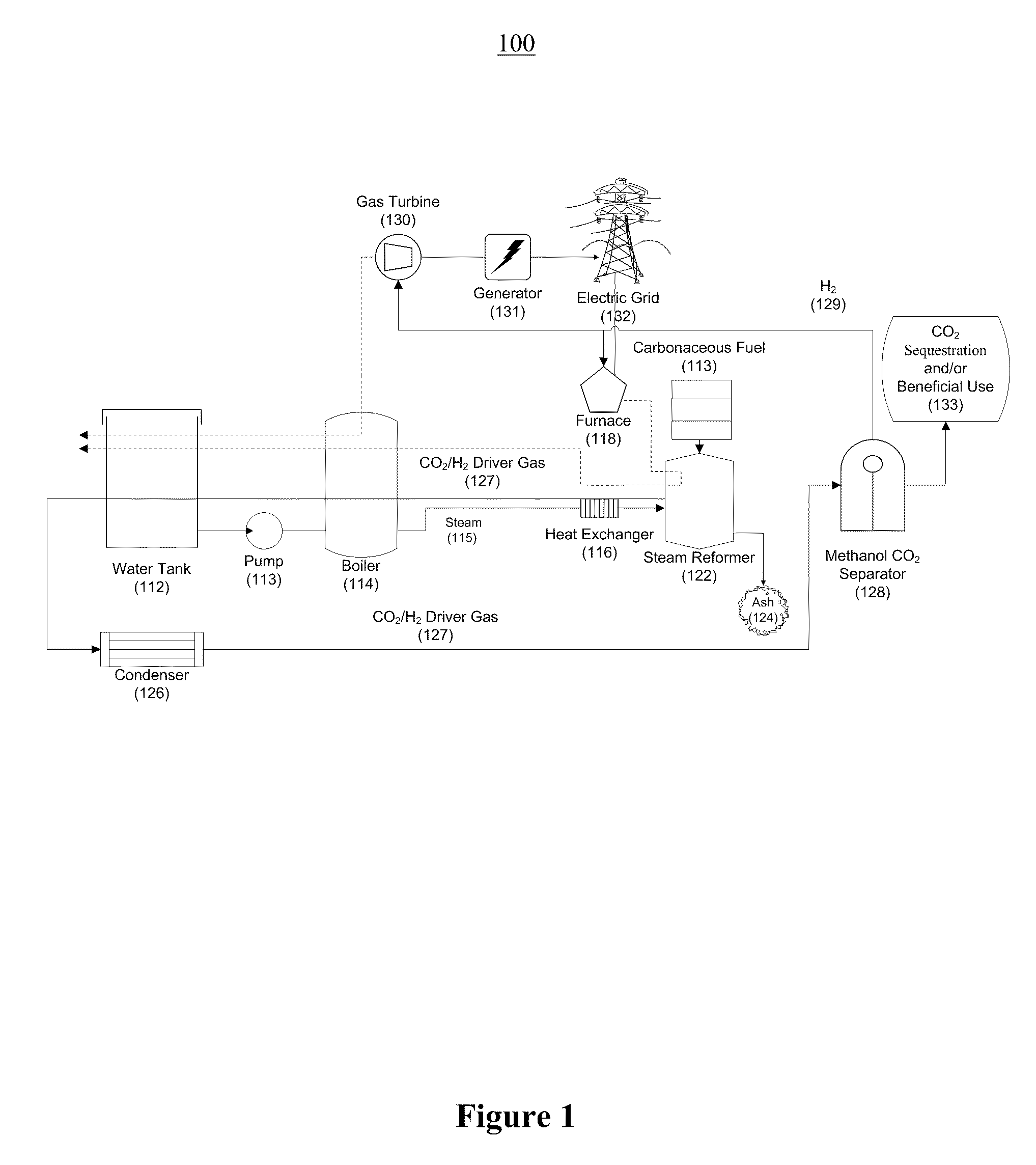
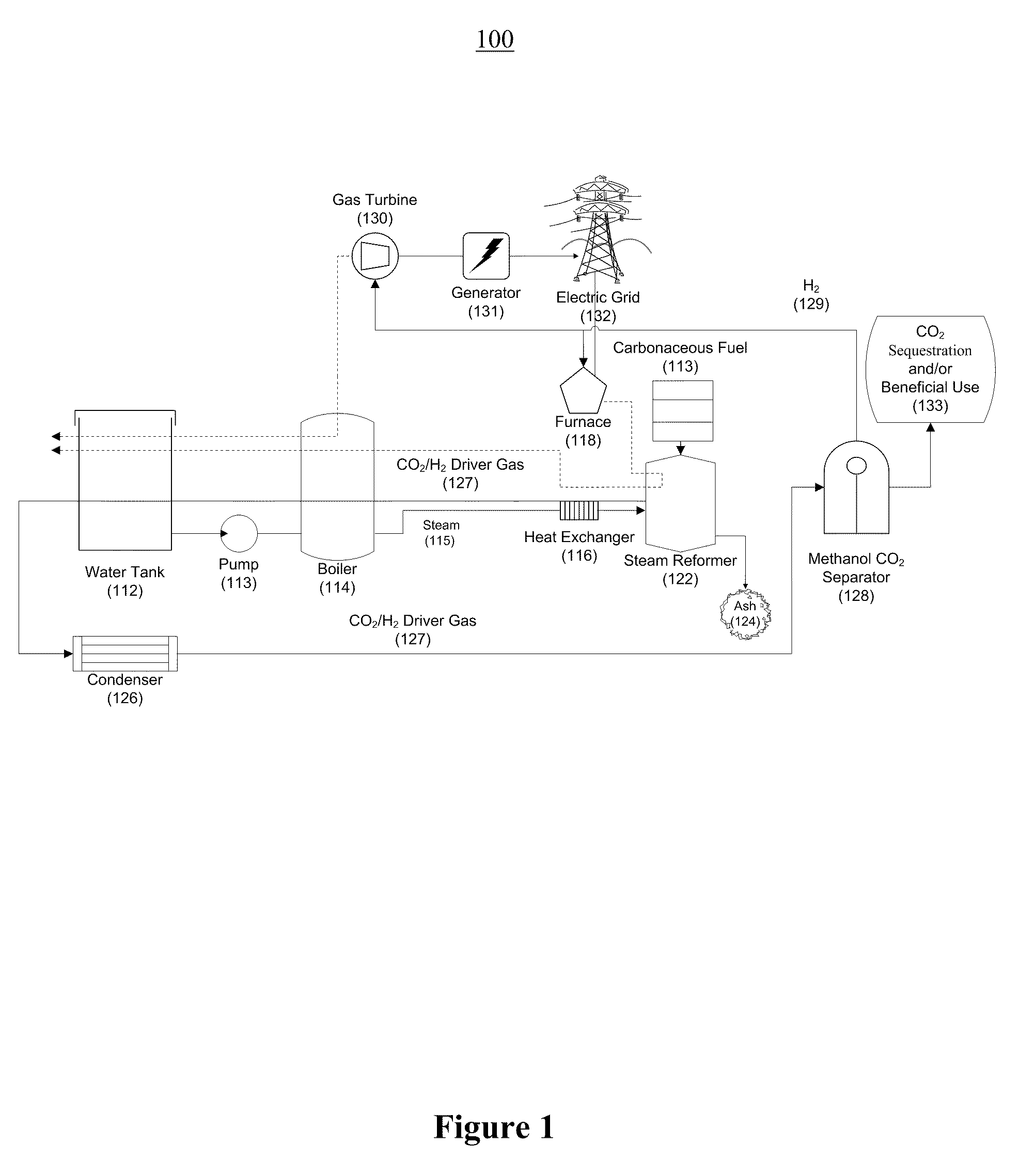
Systems and methods for generating electricity from carbonaceous material with substantially no carbon dioxide emissions
A reformation power plant generates clean electricity from carbonaceous material and high pressure CO2 which can be easily sequestered or utilized for a beneficial purpose, such as fuel production. The reformation power plant design utilizes a reformation process that reforms carbonaceous fuel with super-heated steam into a high-pressure gaseous mixture that is rich in carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas. This high-pressure gas exchanges excess heat with the incoming steam from a boiler and continues onward to a condenser. Once cooled, the high-pressure gas goes through a methanol separator, after which the CO2-rich gas is sequestered underground or beneficially re-used. The remaining hydrogen-rich gas is combusted through a gas turbine. The gas turbine provides power to a generator and also regenerative heat for the boiler. Finally, the generator converts mechanical energy into electricity, which is transferred to the electric grid. Therefore, carbon-free electricity is generated from coal, biomass, or other carbon-based feedstock.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
Carbon dioxide emission reduction method
InactiveUS20100158776A1Increase productionLess carbonSolidificationLiquefactionMethane reformerMethane
Carbon dioxide emissions within a refinery are reduced by reforming a hydrocarbon containing feed at low pressure to enhance the conversion of methane to hydrogen and carbon monoxide and thereby reduce methane slip. The hydrocarbon containing feed is composed entirely or at least in part of a refinery off gas. The resulting reformed stream is then subjected to water-gas shift conversion to form a shifted stream from which carbon dioxide is separated. As a result of the separation and the low pressure reforming, hydrogen containing fuel gas streams, that are thereby necessary lean in carbon dioxide and methane, are used in firing the steam methane reformer and other fuel uses within the refinery to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. The carbon dioxide that is separated can be sequestered or used in other processes such as enhanced oil recovery.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
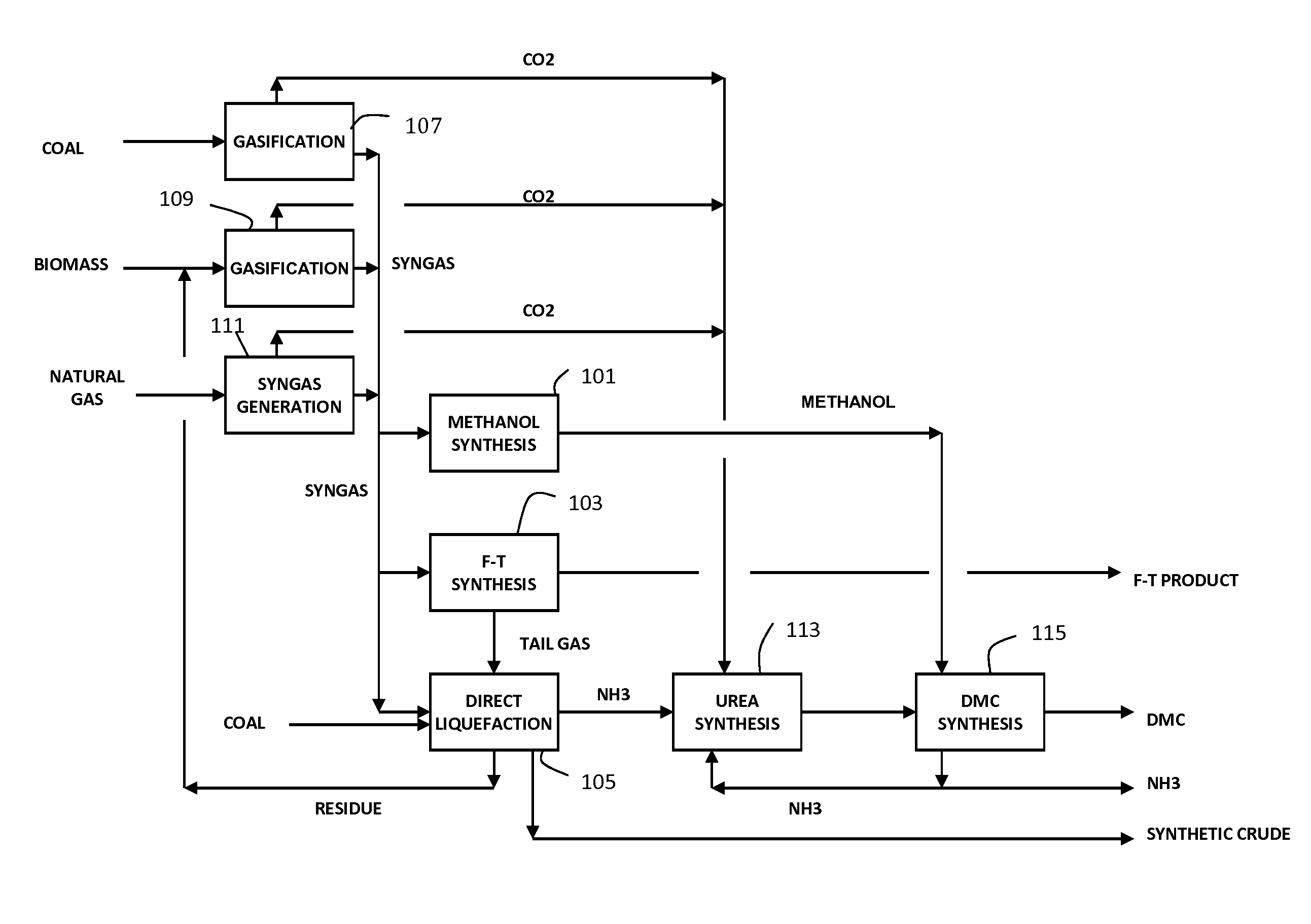
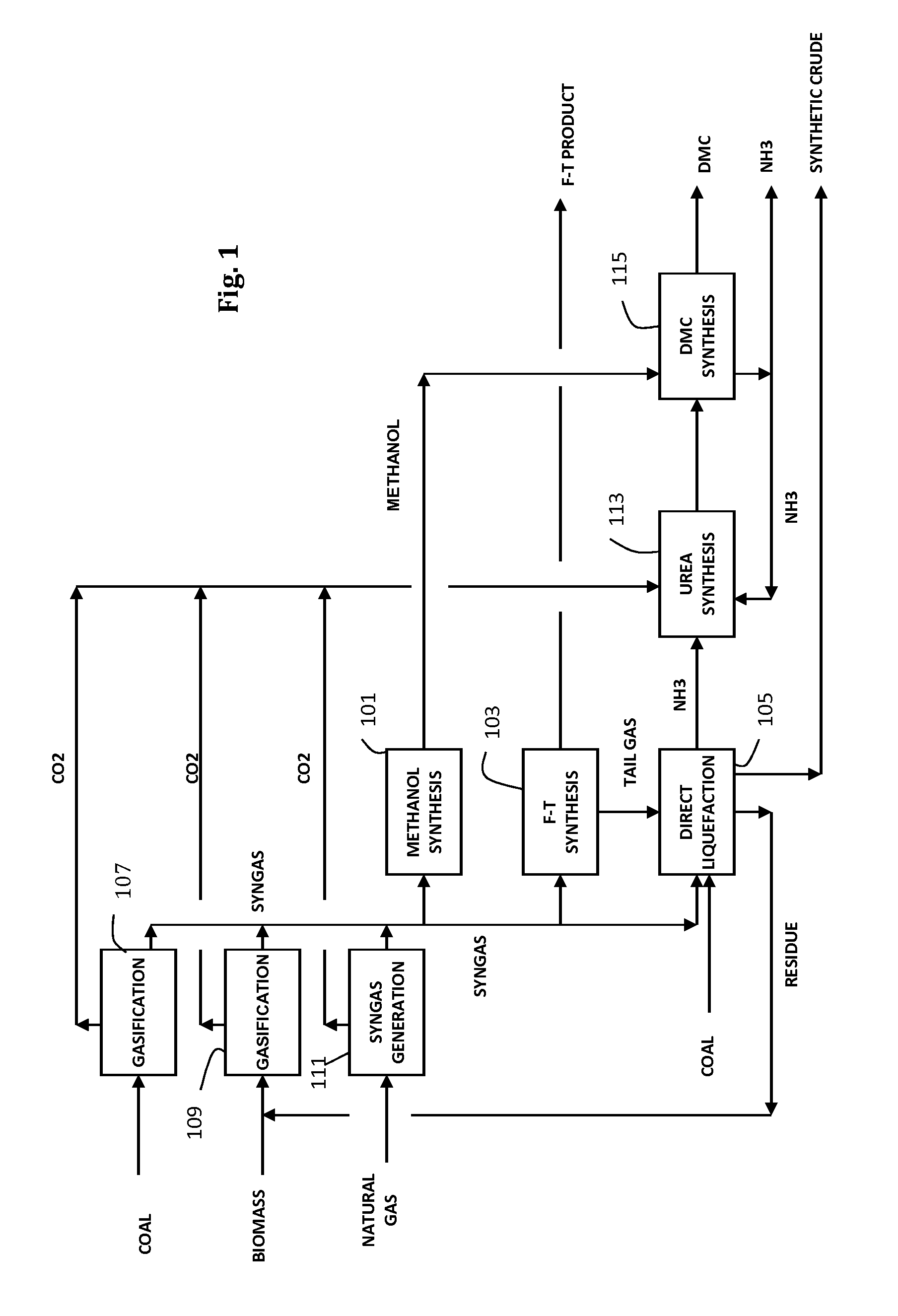
Integrated coal to liquids process and system
InactiveUS20090286889A1Efficient use ofMinimize carbon dioxide emissionUrea derivatives preparationProductsNegative carbon dioxide emissionCarbonylation
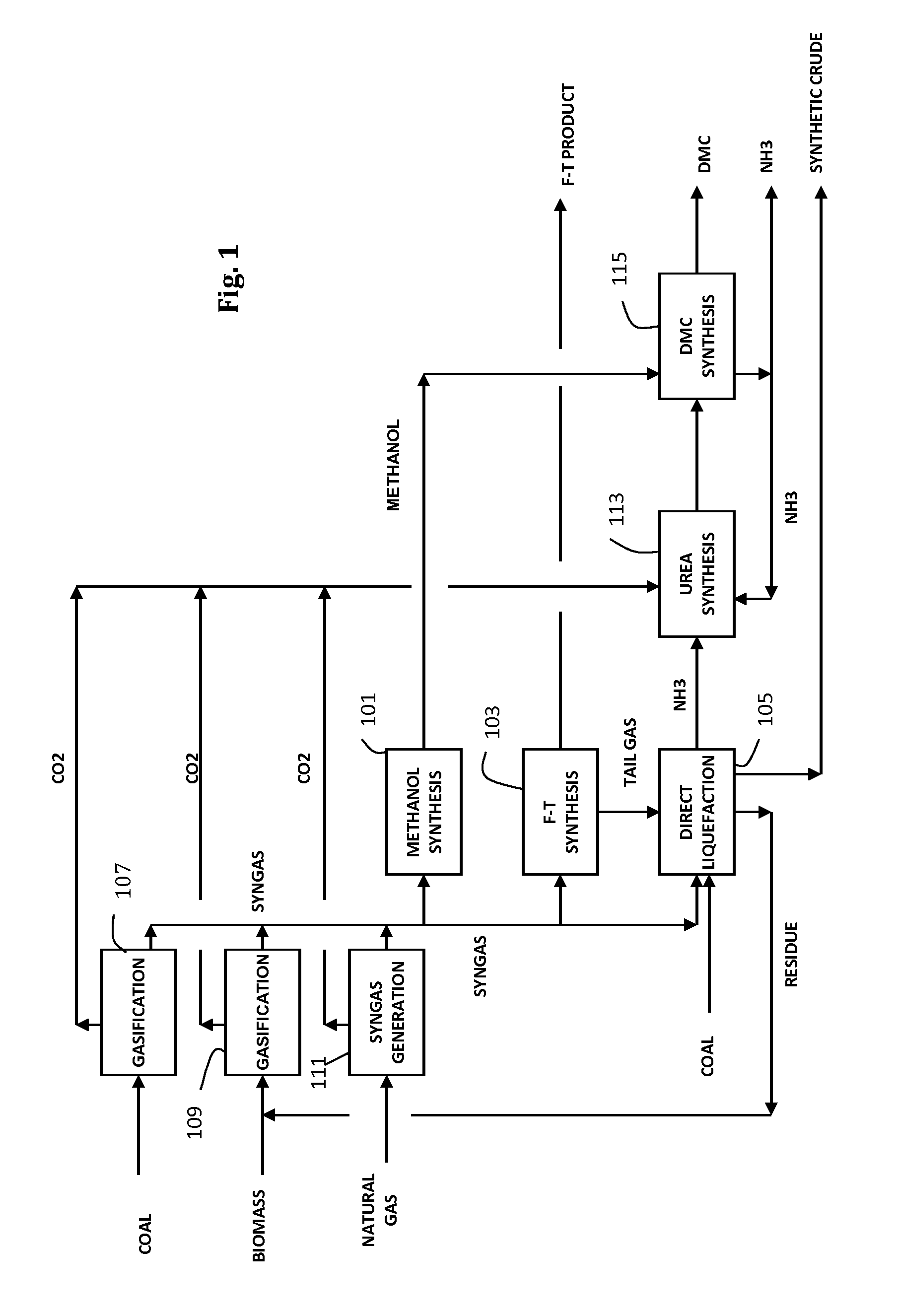
An integrated coal-to-liquids process is provided to minimize carbon dioxide emissions and efficiently make use of carbon resources, by recovering carbon dioxide emissions from Coal-to-Liquids (CTL) facilities, using the recovered carbon dioxide in at least one carbonylation reaction step for converting ammonia to urea and then converting urea into dimethyl carbonate.
Owner:ACCELERGY CORP
Method for reducing carbon dioxide emissions and water contamination potential while increasing product yields from carbon gasification and energy production processes
InactiveUS20090145843A1Water/sewage treatment by substance additionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionCarbon dioxide corrosionOxygen
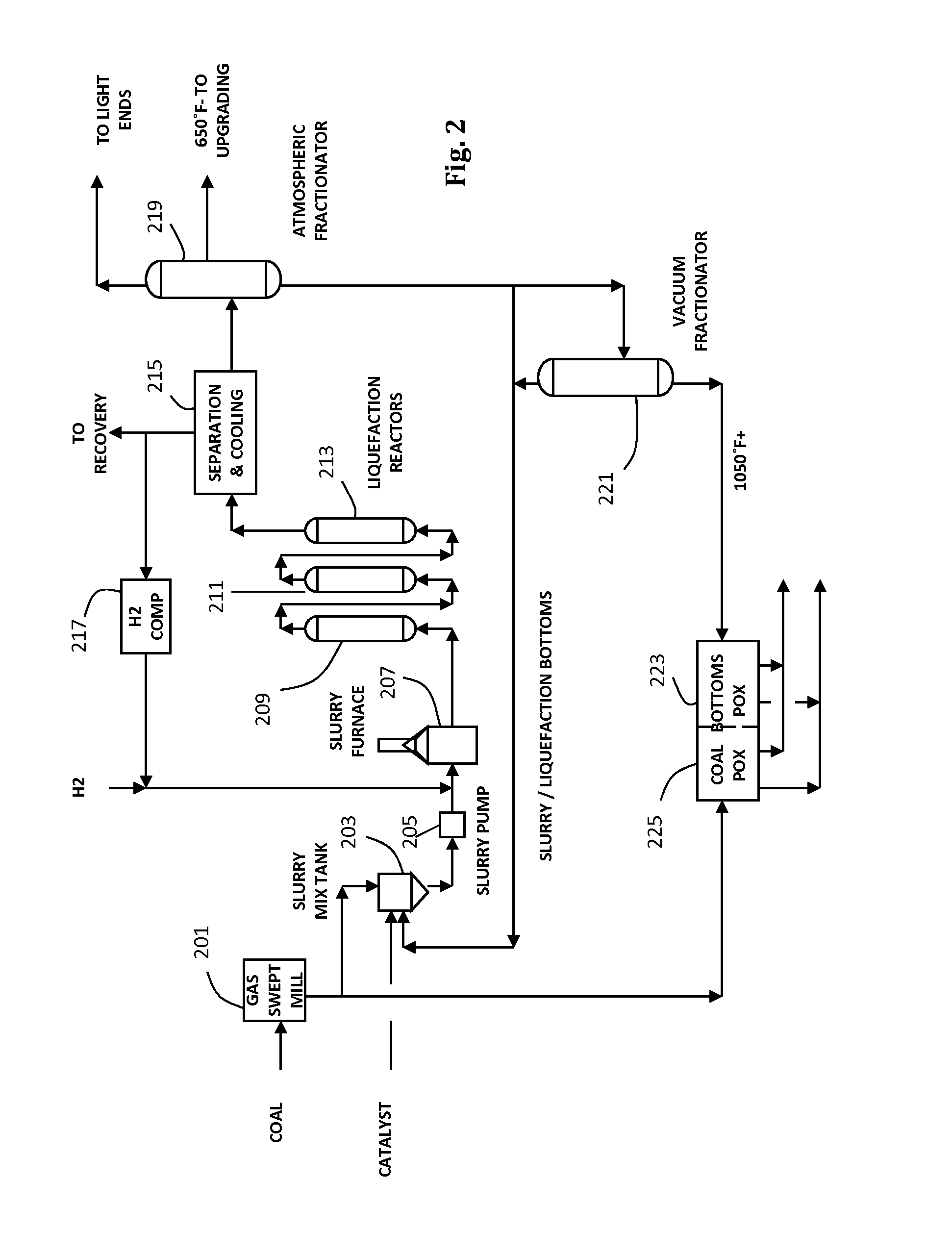
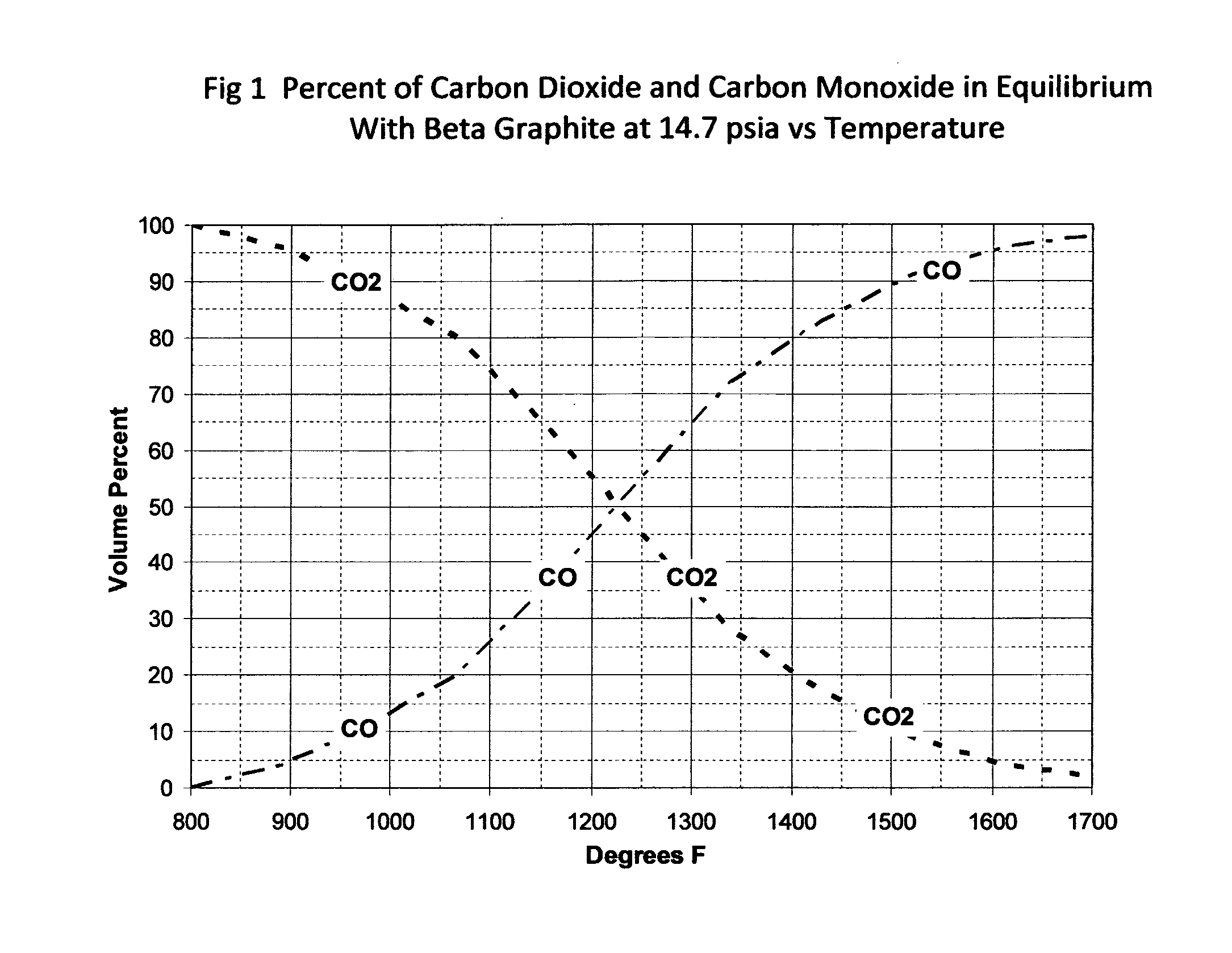
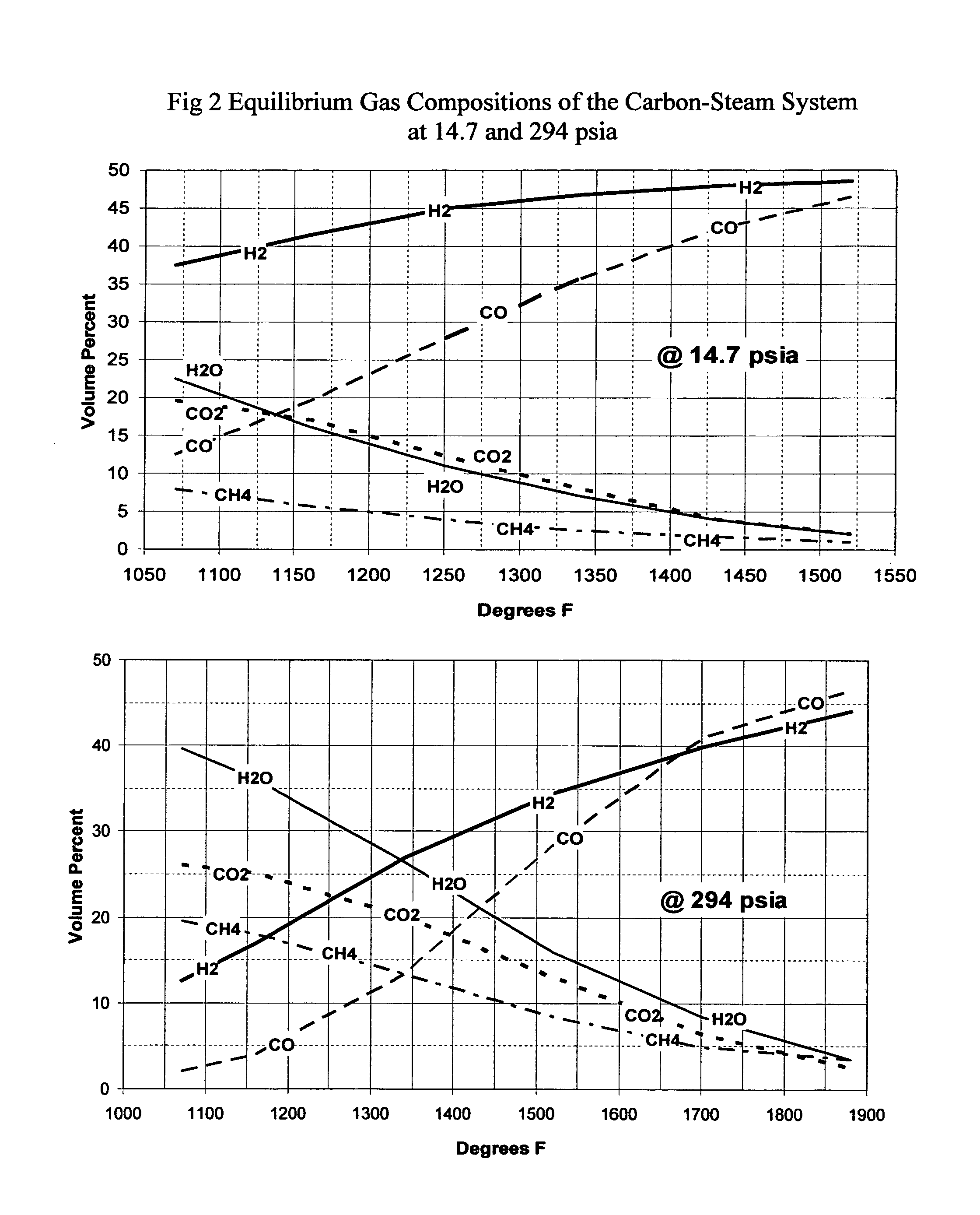
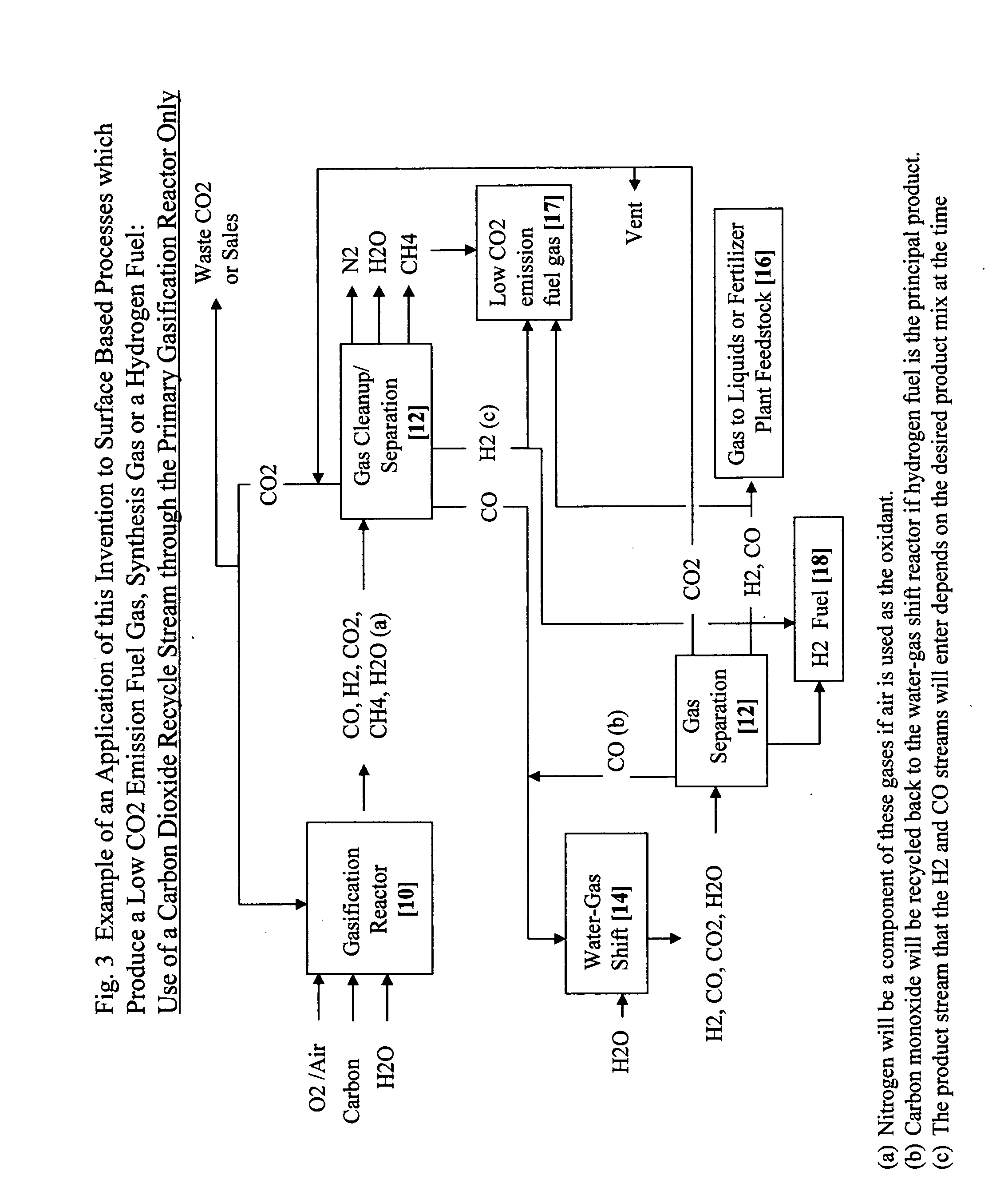
Carbon dioxide from a process which oxidizes a carbon containing feed is separated and reduced to carbon monoxide using a carbon dioxide reduction reactor [22, 26] coupled to a water gas shift reactor [14], to simultaneously reduce carbon dioxide emissions and increase the product yield of clean fuels. In the preferred underground carbon gasification application, these reduction and shift reactions are substantially promoted by utilizing temporary [24] and permanent storage [28] of the carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide coupled with cyclic operational procedures. Additional advantages include carbon dioxide sequestration, removal of contaminants from the groundwater affected by the process and the ability to influence groundwater flow patterns to improve gasification efficiency and reduce potential environmental effects.
Owner:AHNER PAUL F
Carbon dioxide emission reduction method
InactiveUS8007761B2Less carbonLess carbon dioxide contentSolidificationLiquefactionMethane reformerMethane
Carbon dioxide emissions within a refinery are reduced by reforming a hydrocarbon containing feed at low pressure to enhance the conversion of methane to hydrogen and carbon monoxide and thereby reduce methane slip. The hydrocarbon containing feed is composed entirely or at least in part of a refinery off gas. The resulting reformed stream is then subjected to water-gas shift conversion to form a shifted stream from which carbon dioxide is separated. As a result of the separation and the low pressure reforming, hydrogen containing fuel gas streams, that are thereby necessary lean in carbon dioxide and methane, are used in firing the steam methane reformer and other fuel uses within the refinery to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. The carbon dioxide that is separated can be sequestered or used in other processes such as enhanced oil recovery.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
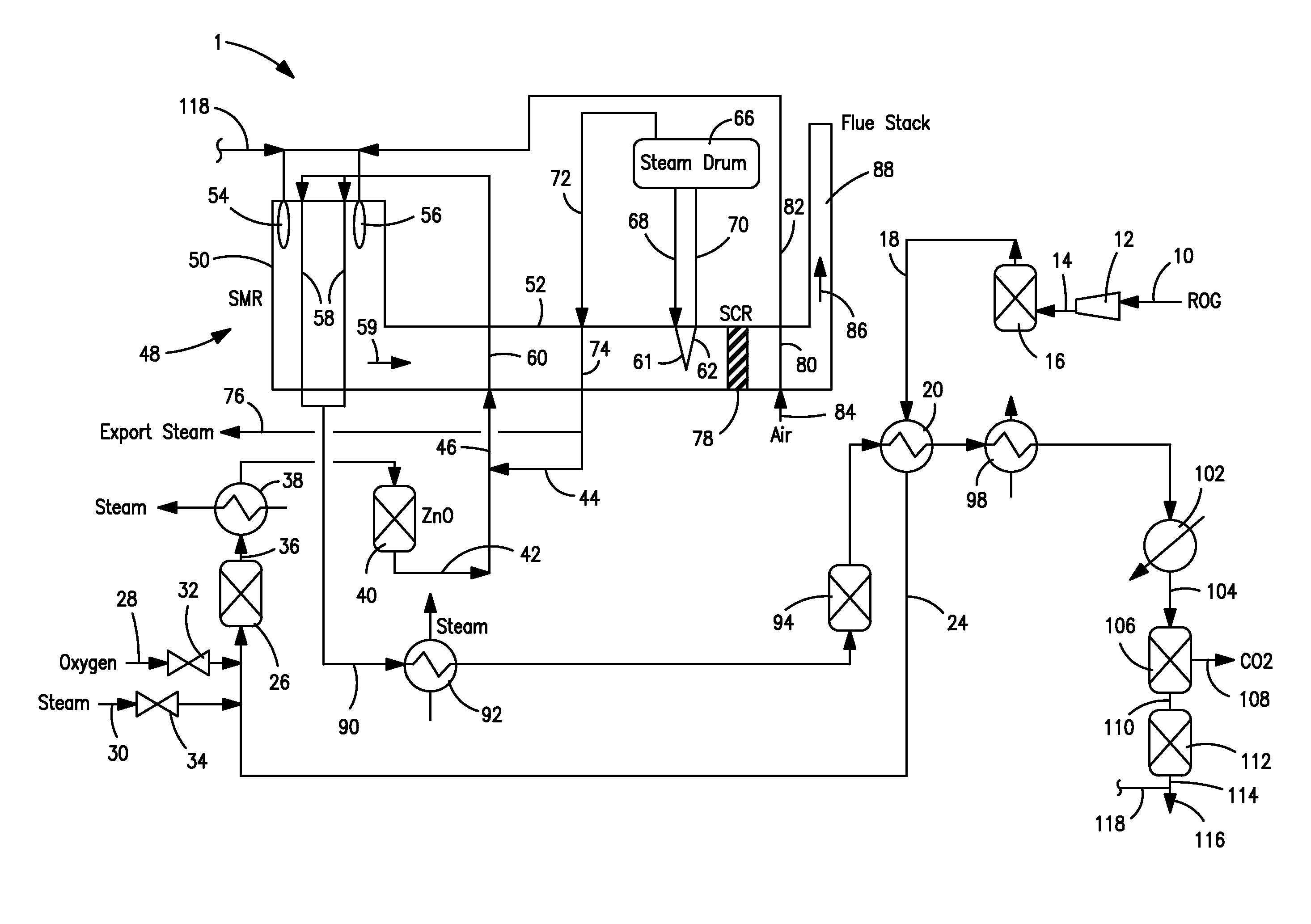
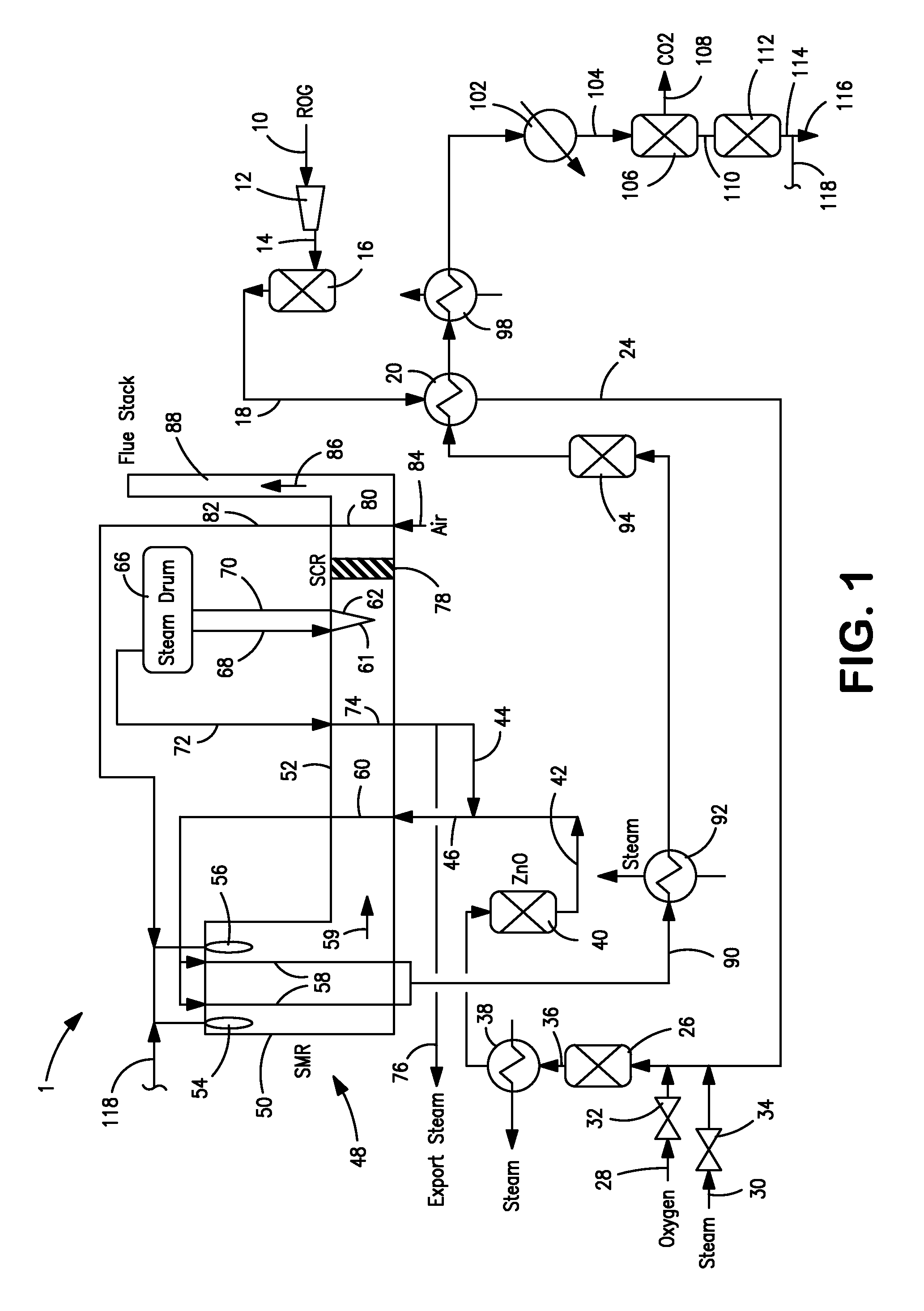
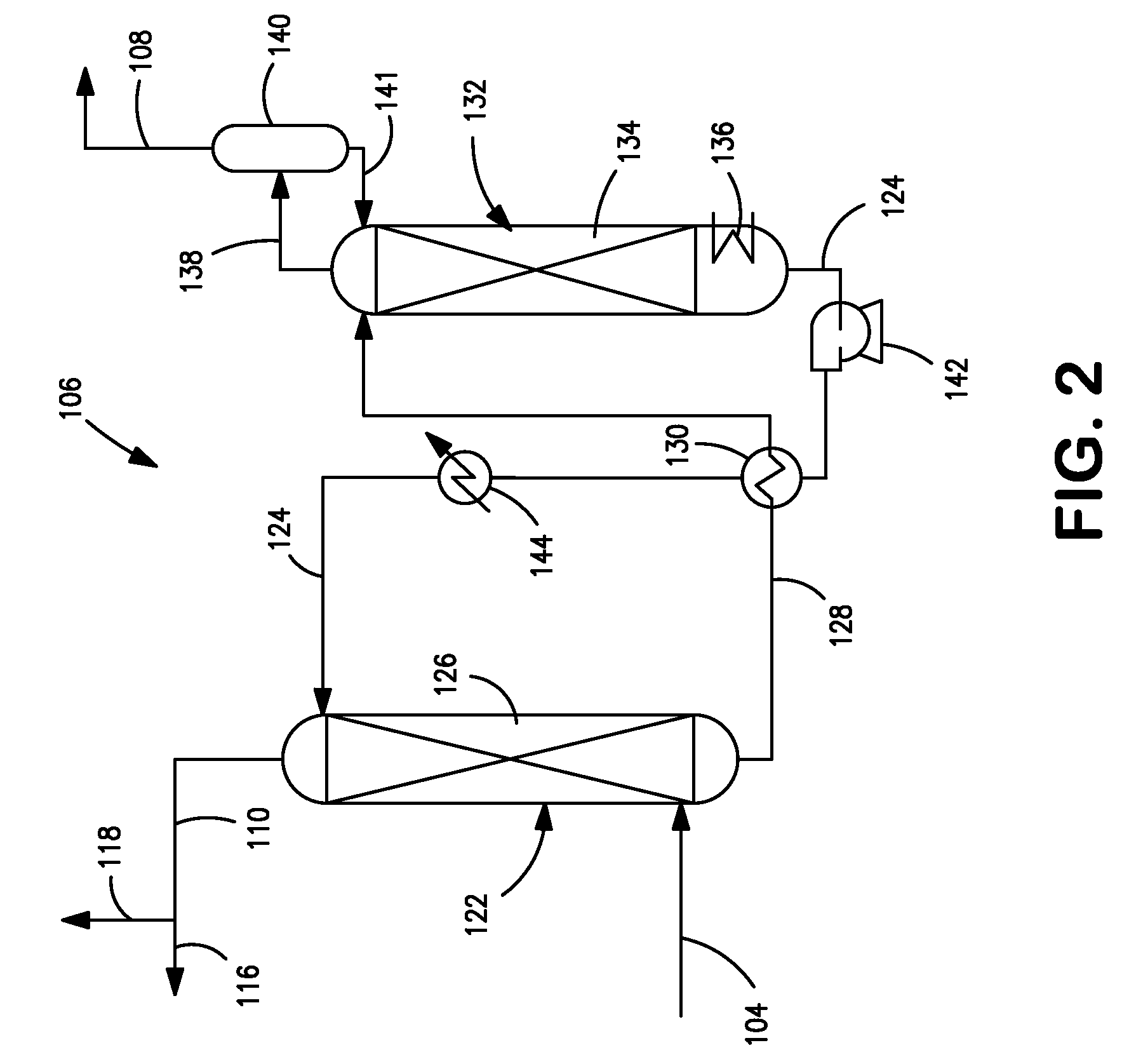
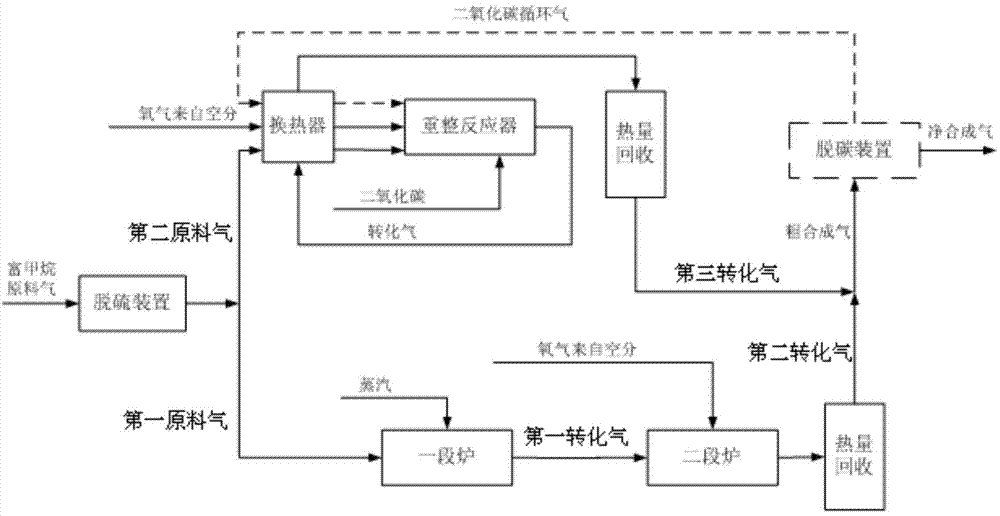
Process method for preparing synthesis gas by using zero carbon or negative carbon emission system
ActiveCN104709876AEmission reductionAchieve recyclingHydrogenChemical industrySyngasNegative carbon dioxide emission
The present invention discloses a process method for preparing synthesis gas by using a zero carbon or negative carbon emission system. The process method comprises that: 1) first raw material gas is subjected to desulfurization, steam is matched, pressurization and heating are performed, a reaction is performed to obtain first conversion gas, the first conversion gas is output, the output first conversion gas and pure oxygen are mixed and then enter a two-stage furnace to react so as to obtain second conversion gas, and the second conversion gas is output from the two-stage furnace; 2) second raw material gas is subjected to desulfurization, pressurization and heating and then is mixed with pure oxygen and carbon dioxide, then a reforming reaction is performed to obtain third conversion gas, and the third conversion gas is output from the reforming reactor; and 3) the second conversion gas is subjected to heat recovery and then is mixed with the third conversion gas to form crude synthesis gas, wherein the crude synthesis gas is adopted as the subsequent synthesis gas with or without a decarbonization device. According to the present invention, the greenhouse gas emission is reduced, the carbon efficiency is improved, the recycling of the carbon resources of the energy source chemicals is achieved, the hydrogen-carbon ratio of the synthesis gas achieves the ideal ratio of the downstream process requirement, and the zero carbon or negative carbon emission of the whole system is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
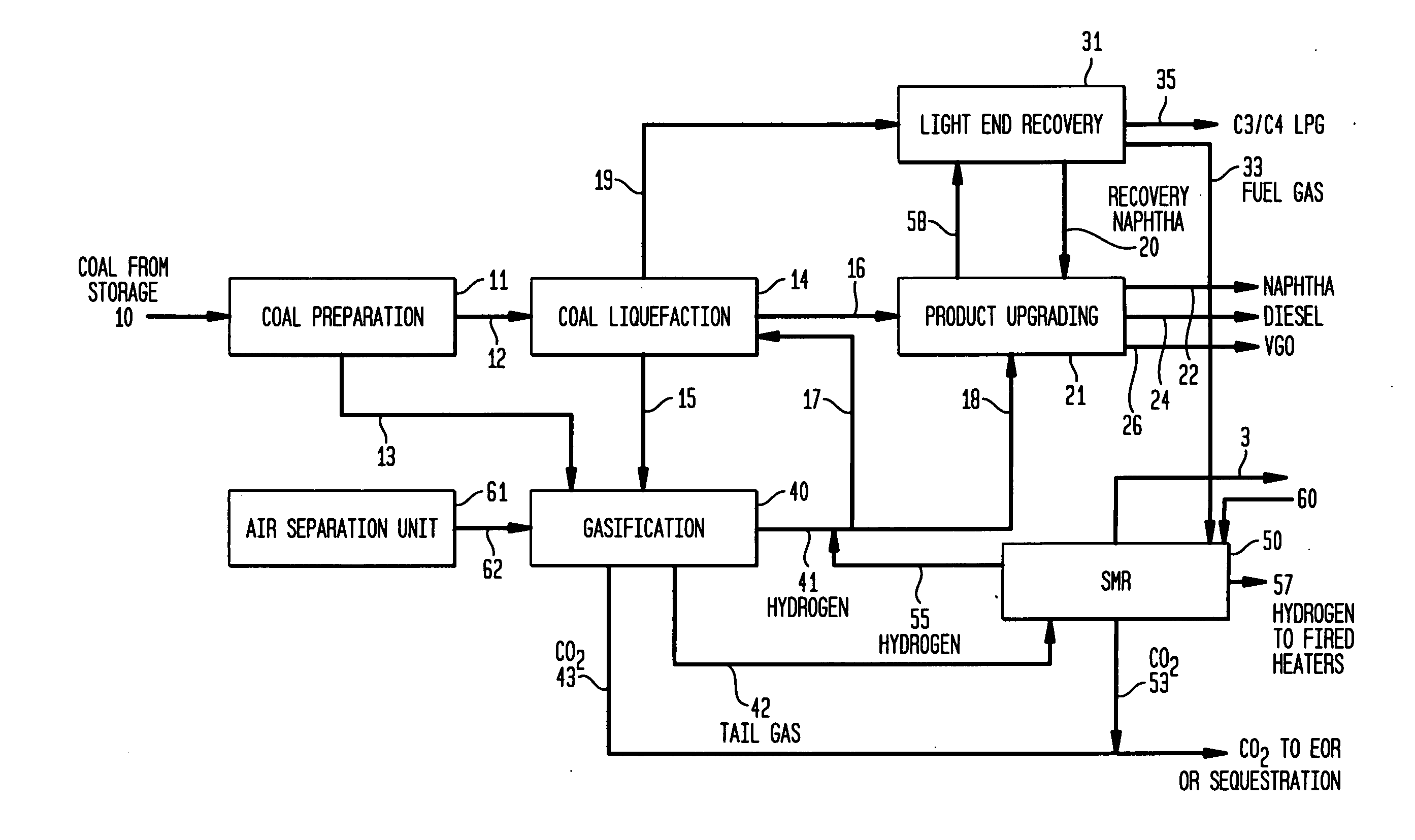
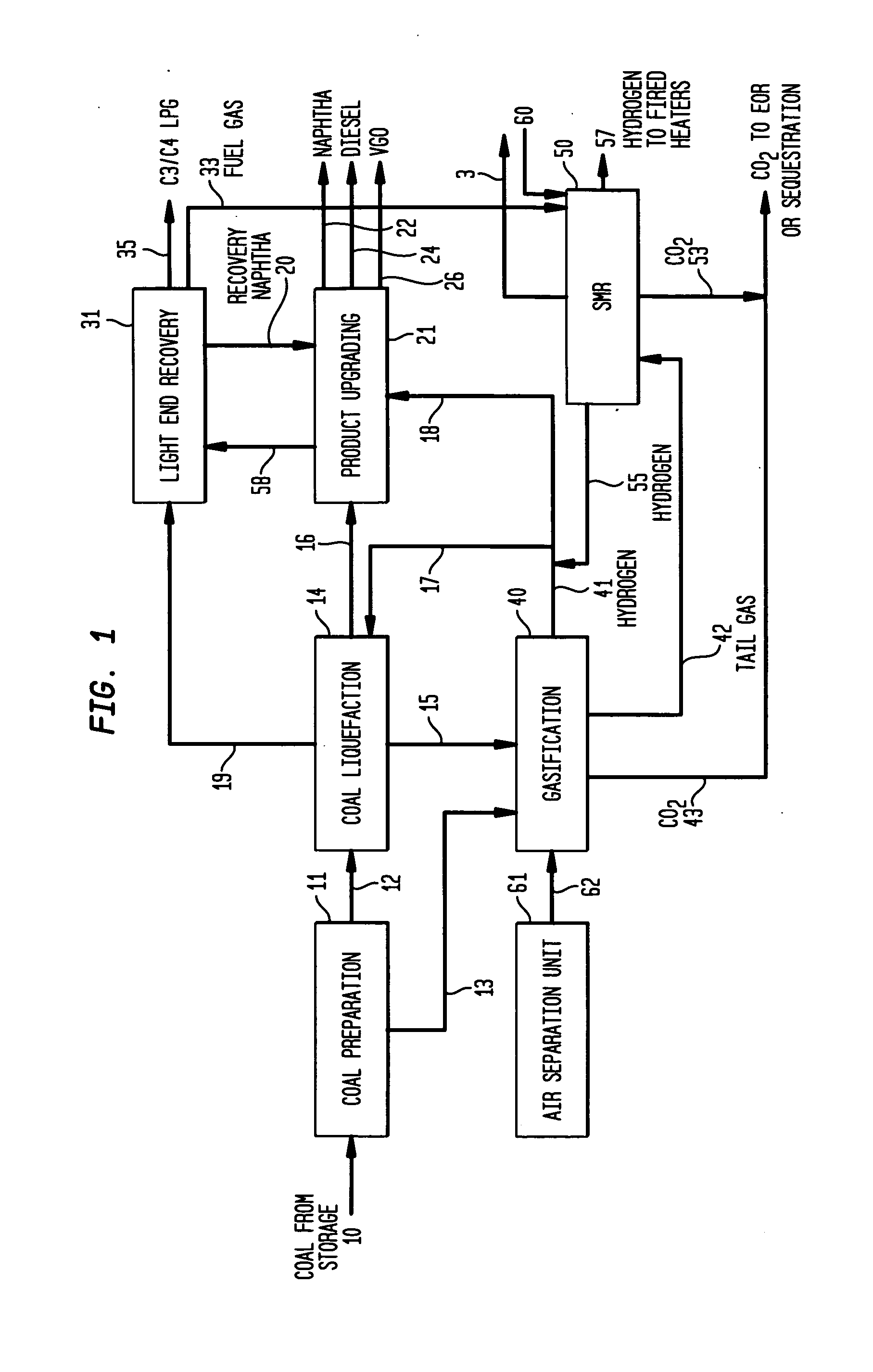
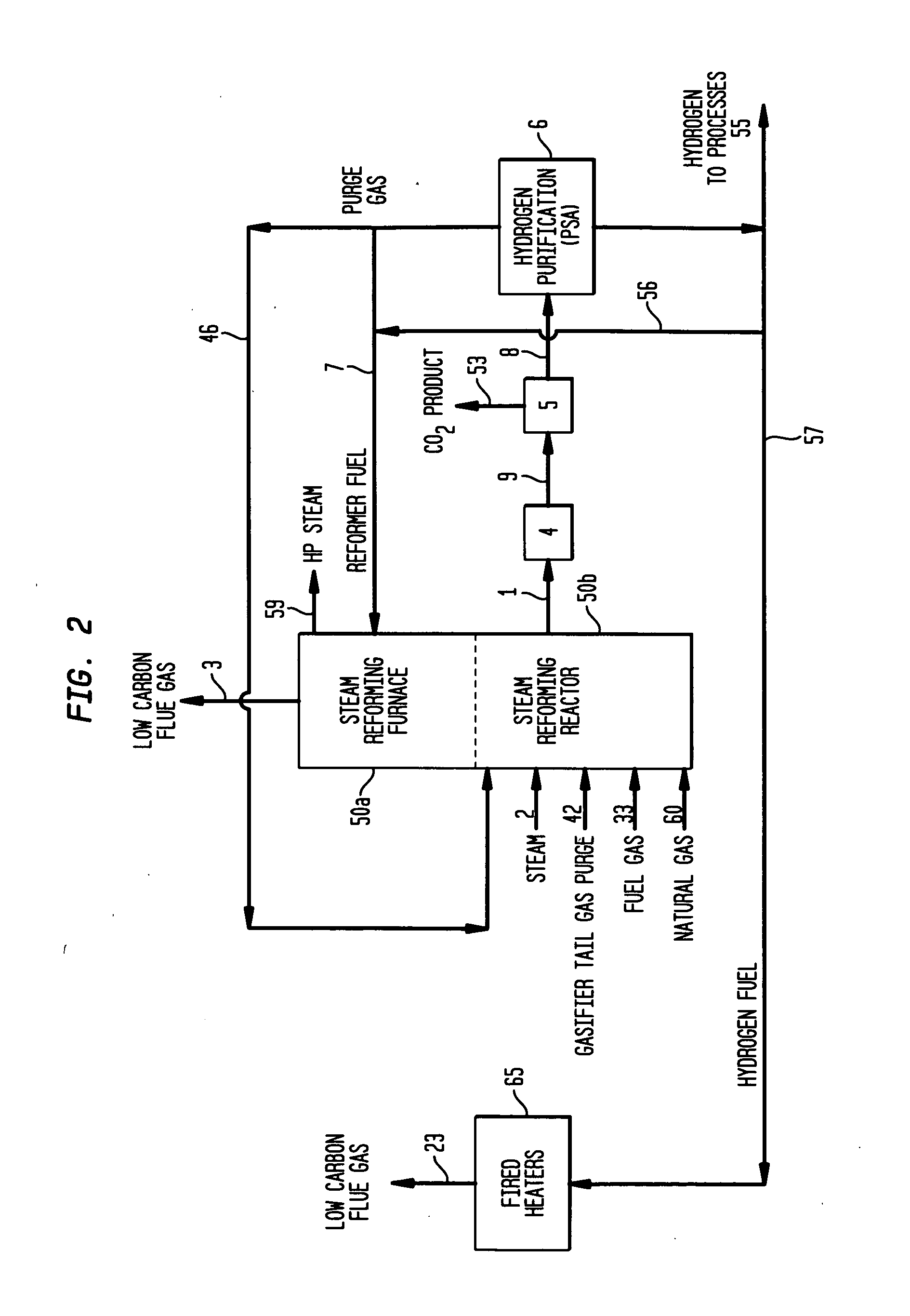
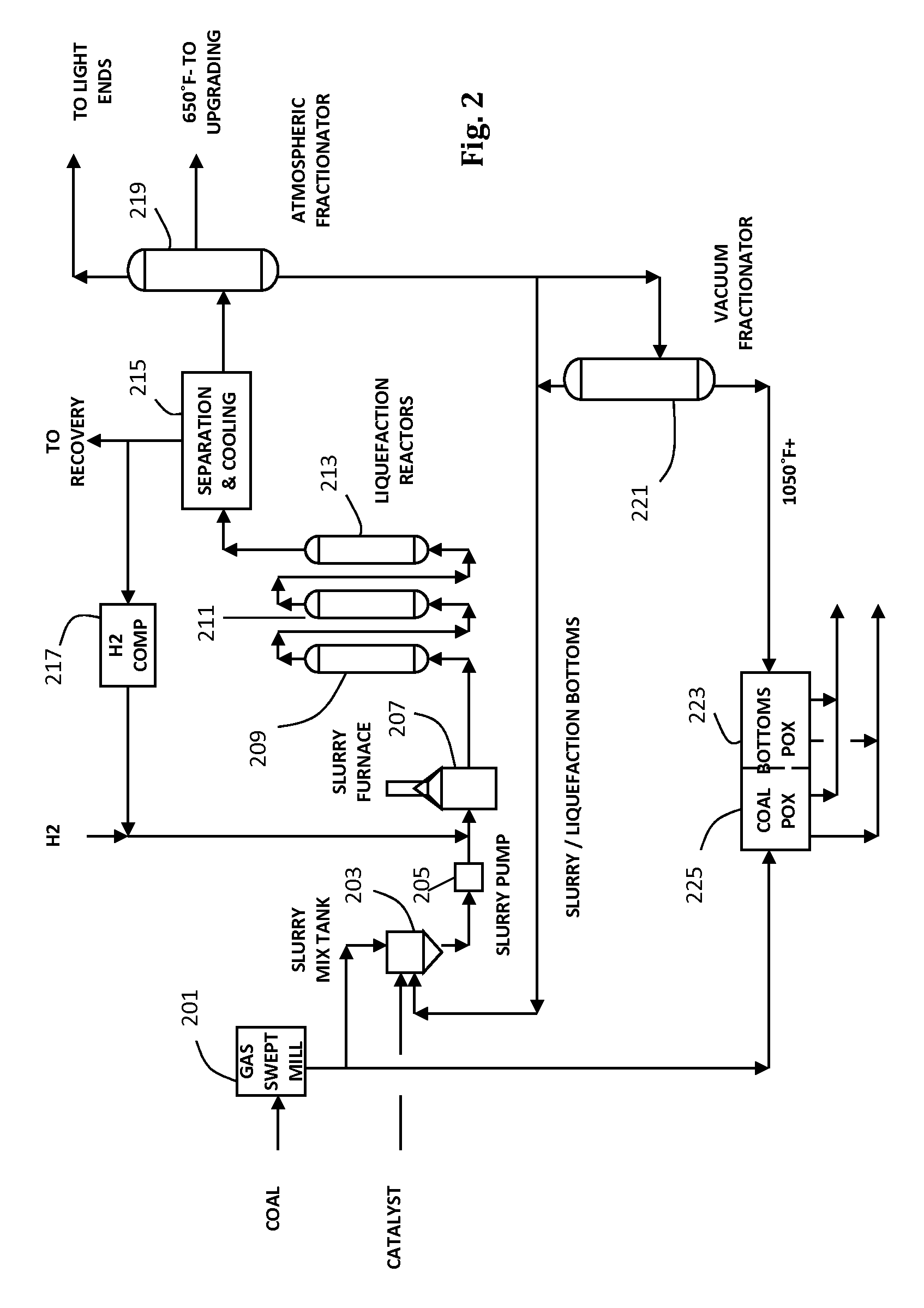
Coal liquefaction complex with minimal carbon dioxide emissions
ActiveUS20110290703A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsEnhanced overall recoveryMethane captureCarbon compoundsMethane reformerHydrogen
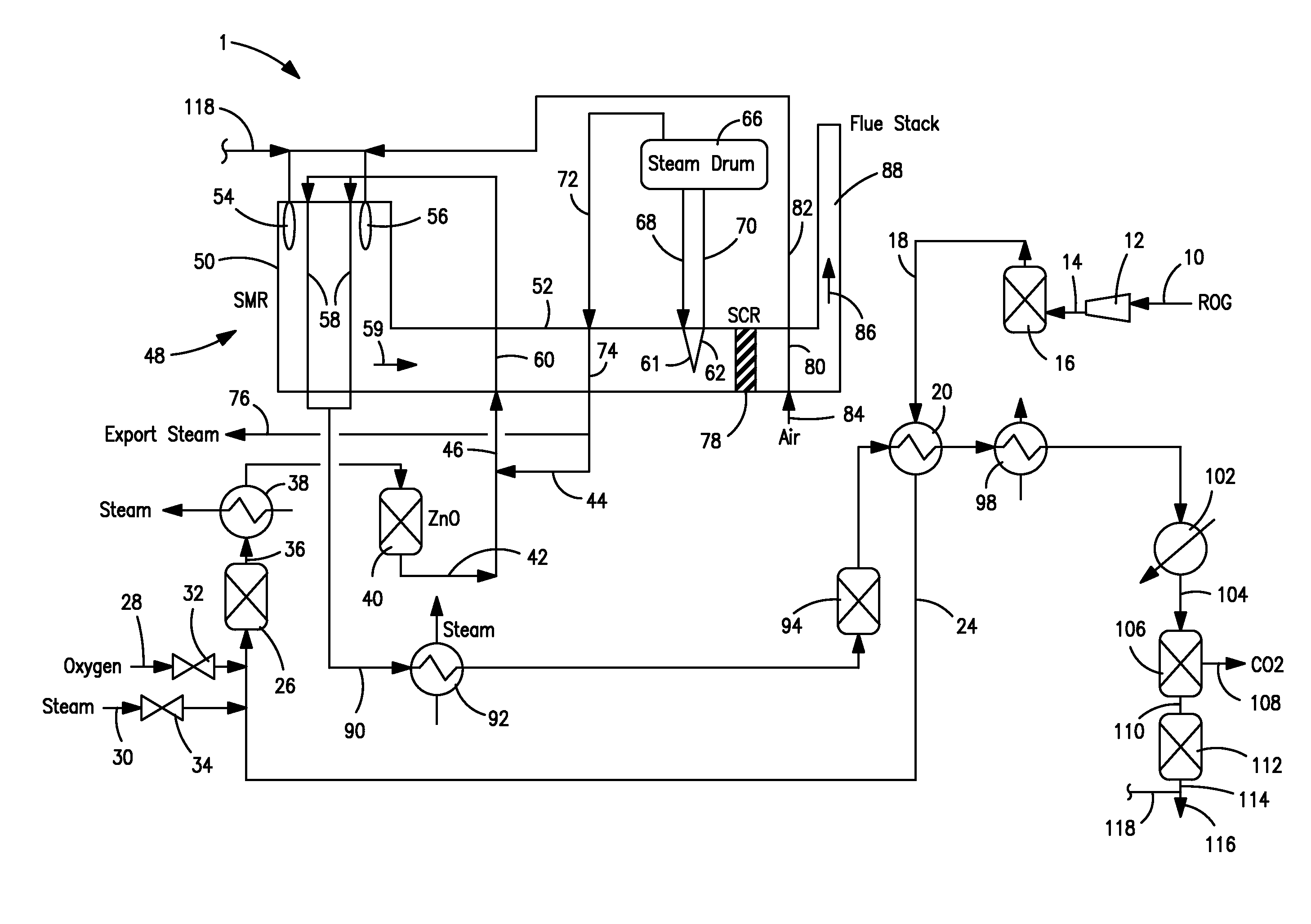
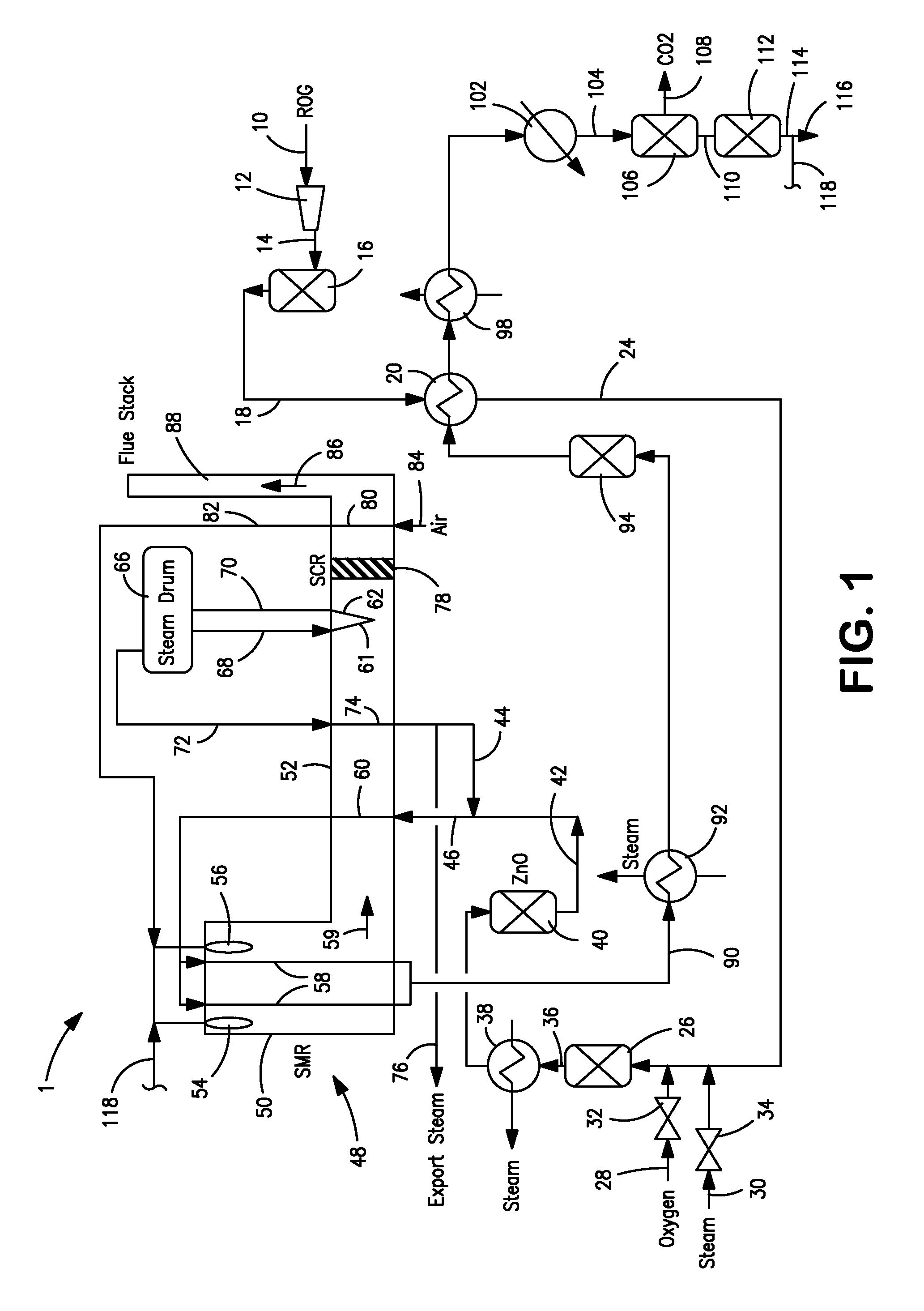
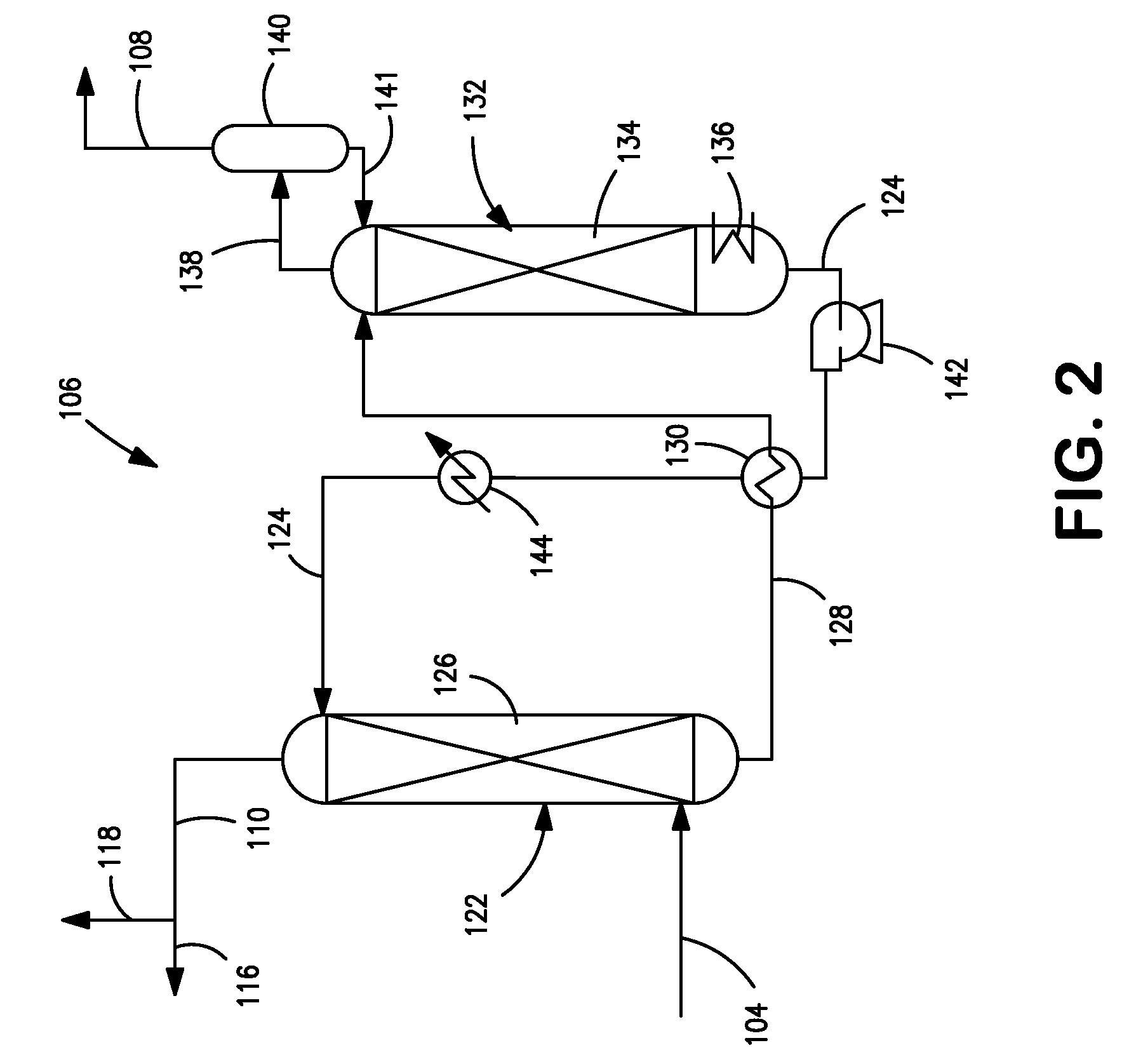
The invention described herein relates to a novel process for reducing the carbon dioxide emissions from a coal and / or biomass liquefaction facility by utilizing a steam methane reformer unit in the complex designed to produce additional hydrogen which can be thereafter utilized in the process, as required for the plant fired heaters (including the SMR furnace), and for the production of plant steam. The plant light ends (C1, C2, etc.), which are normally utilized as fuel gas streams are the primary feeds to the SMR Unit along with the tail gas purge from a gasification complex within the facility.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Integrated coal to liquids process and system
InactiveUS8148435B2Efficient use ofEmission minimizationUrea derivatives preparationProductsCarbonylationNegative carbon dioxide emission
An integrated coal-to-liquids process is provided to minimize carbon dioxide emissions and efficiently make use of carbon resources, by recovering carbon dioxide emissions from Coal-to-Liquids (CTL) facilities, using the recovered carbon dioxide in at least one carbonylation reaction step for converting ammonia to urea and then converting urea into dimethyl carbonate.
Owner:ACCELERGY CORP
Carbon dioxide adsorbent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103691398AImprove adsorption capacityControl pore sizeProductsCarbon compoundsHigh concentrationSorbent
The invention provides a carbon dioxide adsorbent and a preparation method thereof. The carbon dioxide adsorbent is a metal organic skeleton containing two mixed ions, and the ions comprise iron ions and cobalt ions. The adsorbent prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of high adsorption capacity and high carbon dioxide selectivity, so that low-concentration carbon dioxide in flue gas can be enriched to a higher concentration so as to meet the treatment requirements of carbon dioxide waste gas in flue gas in industry, the carbon dioxide emission is reduced and the resource utilization of the carbon dioxide is realized at the same time.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Reduced carbon dioxide emission system and method for providing power for refrigerant compression and electrical power for a light hydrocarbon gas liquefaction process
ActiveUS7243510B2Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsSolidificationLiquefactionProcess engineeringNegative carbon dioxide emission
A reduced carbon dioxide emission system and method for providing power for refrigerant compression and shared electrical power for a light hydrocarbon gas liquefaction process.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Deep-lying storage method of carbon dioxide
InactiveCN101788106AEmission reductionSolve processing problemsContainer filling under pressureGas phaseEngineering
The invention discloses a deep-lying storage method of carbon dioxide, which comprises the following steps of: (1) separating the output end of a carbon dioxide storage tank into two ways of a gas phase and a liquid phase reaching an inlet of a high-pressure pump; (2) enabling liquid-phase carbon dioxide to enter the high-pressure pump and a high-pressure pipe manifold and a low-pressure pipe manifold of the high-pressure pump and swiping off air in the pipe manifold so that the same pressure is established in the high-pressure pipe manifold and the low-pressure pipe manifold of the high-pressure pump as that in the carbon dioxide storage tank; (3) starting a shielding pump, carrying out low-pressure leakage to the high-pressure pipe manifold and the low-pressure pipe manifold again and establishing the output pressure of the shielding pump in normal working conditions; (4) circularly cooling the high-pressure pump; and (5) heating the liquid-phase carbon dioxide entering a heat exchanger to about 10-15 DEG C and pumping the carbon dioxide to the position of an underground sealing level by the high-pressure pump until the sealing level is saturated to affuse cement to seal a well. The invention radically solves the problem of processing carbon dioxide emission, and a device adopting the method has simple structure, compactness, lightness and low use cost so that a discarded mined or a low-yield oil well can be recycled.
Owner:江苏恒源碳创环境技术有限公司
Methods of sequestering carbon dioxide
InactiveCN102942006BEmission reductionSimple and fast operationCarbon-dioxide storageStorage devicesWell drillingProduct gas
The invention discloses a method for sequestering carbon dioxide. The method includes the following steps: (1) selecting the injection layer which includes an unworkable seam and / or a coal seam gob; (2) drilling a well according to the position where the injection layer is located; (3) performing perforating for a fissure zone of a top plate of the unworkable seam and / or the coal seam gob; (4) sequentially injecting carbon dioxide from bottom to top layer by layer when the number of the needed injection layer is larger than one, and performing injecting and sealing storage for the next injection layer after completing injecting and sealing storage for the former injection layer; and (5) burying the drilled well and sealing a cover on the drilled well. The method for sequestering carbon dioxide aims at solving the problems of large carbon dioxide emission, obvious greenhouse effect, complex processing procedures, high expanse and the like of the existing coal power generation mode, and achieves the purposes of permanently sequestering carbon dioxide and reducing carbon dioxide treatment expanse by adopting the carbon dioxide sequestering method of injecting carbon dioxide gases into the unworkable seam or the coal seam gob to sequester carbon dioxide.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
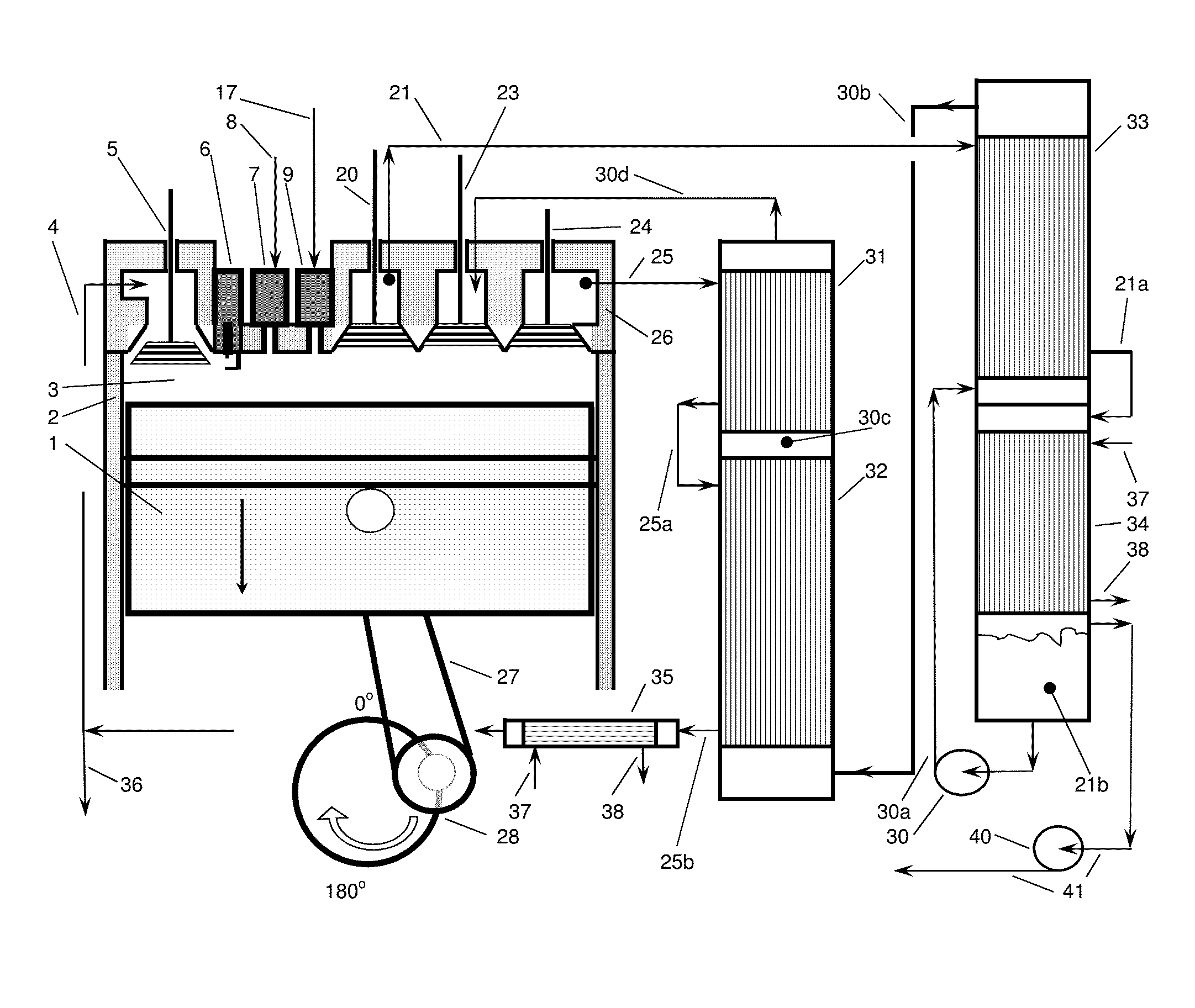
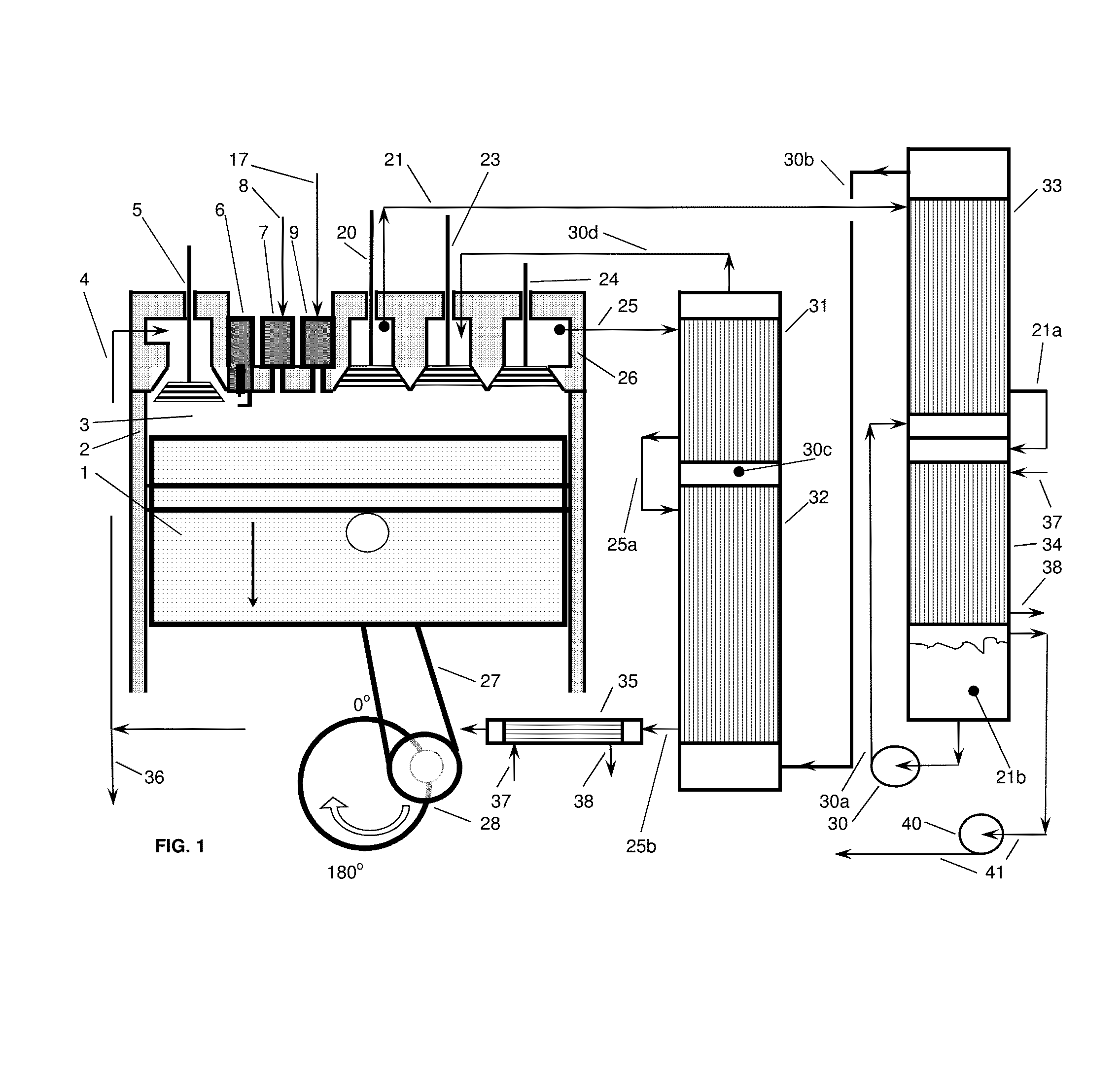
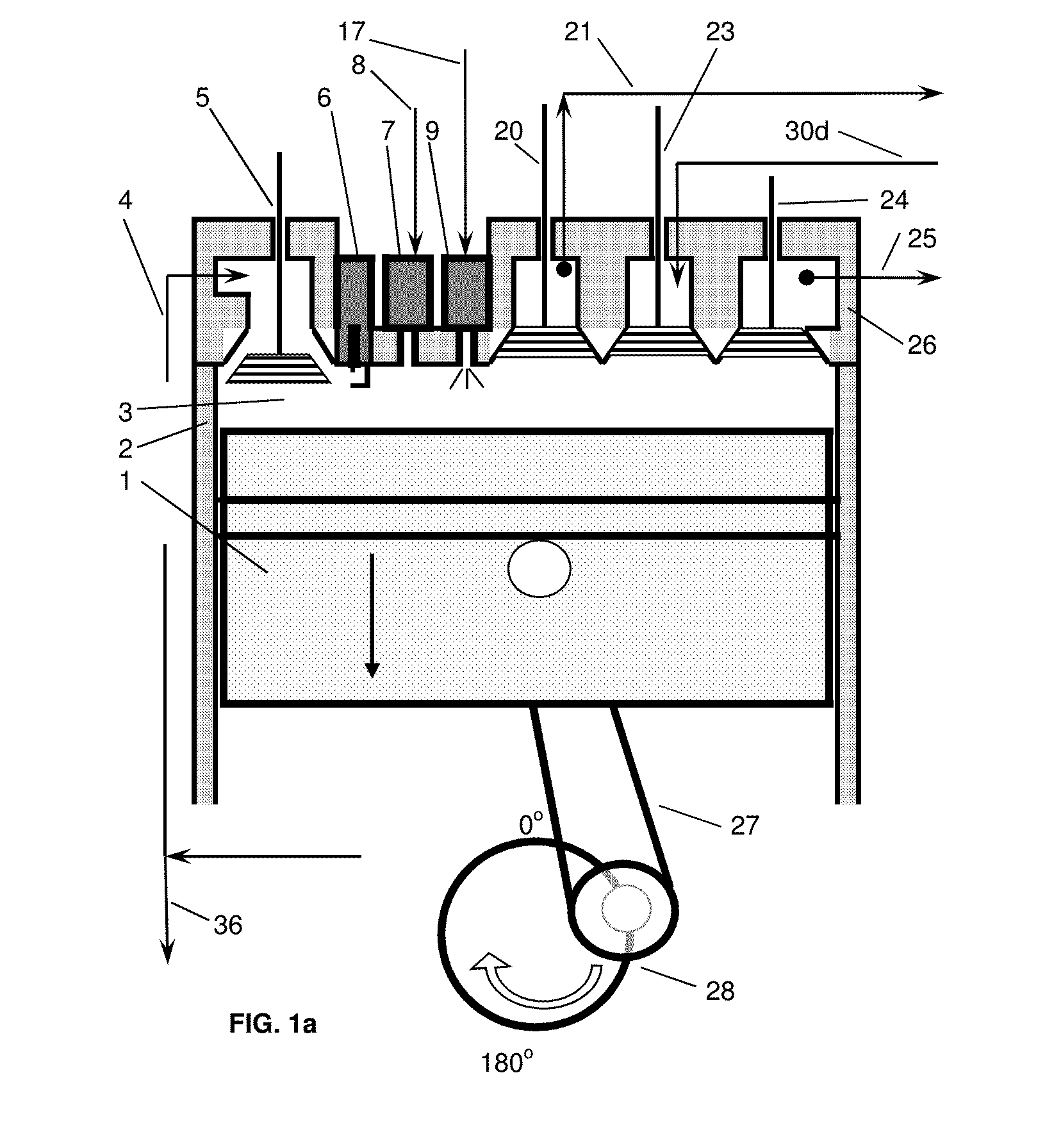
High Thermal Efficiency Six Stroke Internal Combustion Engine with Heat Recovery
ActiveUS20160245235A1Increase work outputReduce heat lossNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesEngineering
A six stroke high thermal efficiency engine and a method for operating such an engine are disclosed. Oxygen or oxygen-enriched air is used as the oxidizer, heat is recovered from the two exhaust strokes, superheated steam is used in the second power stroke, and high levels of exhaust gas from stroke four are recirculated. Lean burn combustion is utilized to produce an oxygen rich exhaust which results in very low levels of particulates, unburned hydrocarbons, and carbon monoxide. Due to high thermal efficiency, carbon dioxide emissions are reduced per unit of power output. Use of oxygen or oxygen-enriched air as the oxidizer produces an exhaust containing very low levels of nitrogen oxides. The engine is insulated to conserve heat, resulting in reduced engine noise. An engine with high thermal efficiency, quiet operation, and low emissions is the result.
Owner:JUNG PHILIP OWEN
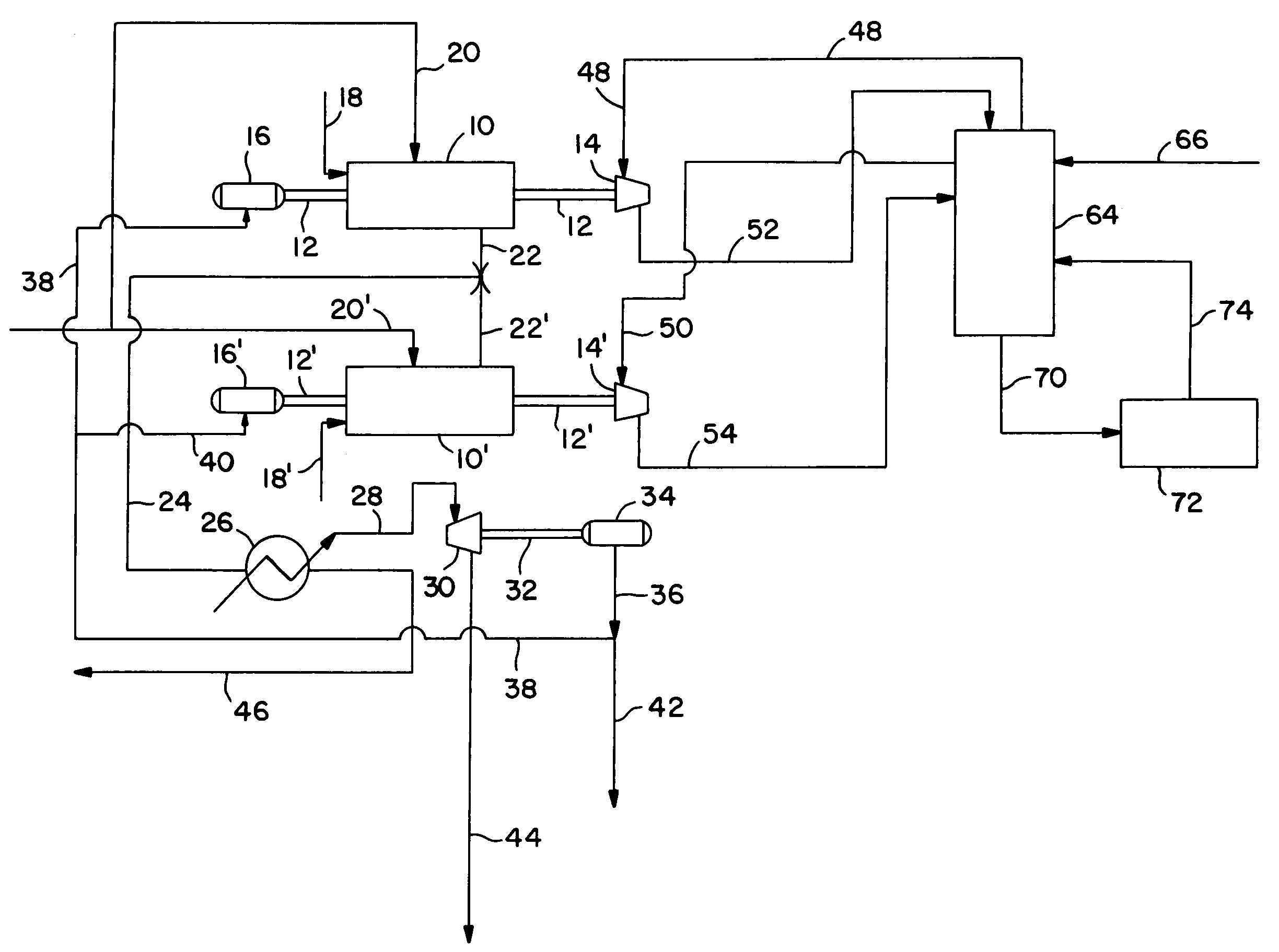
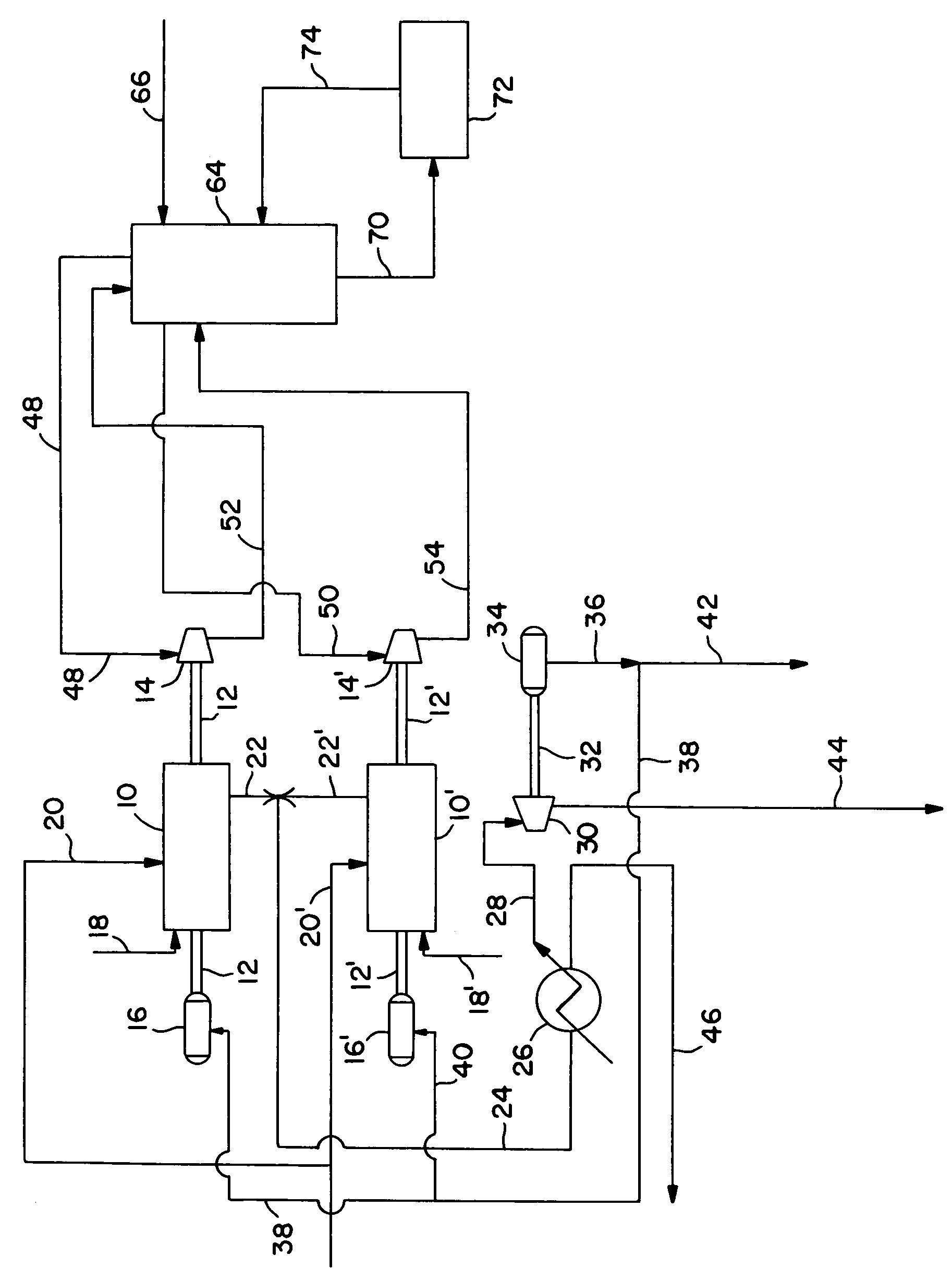
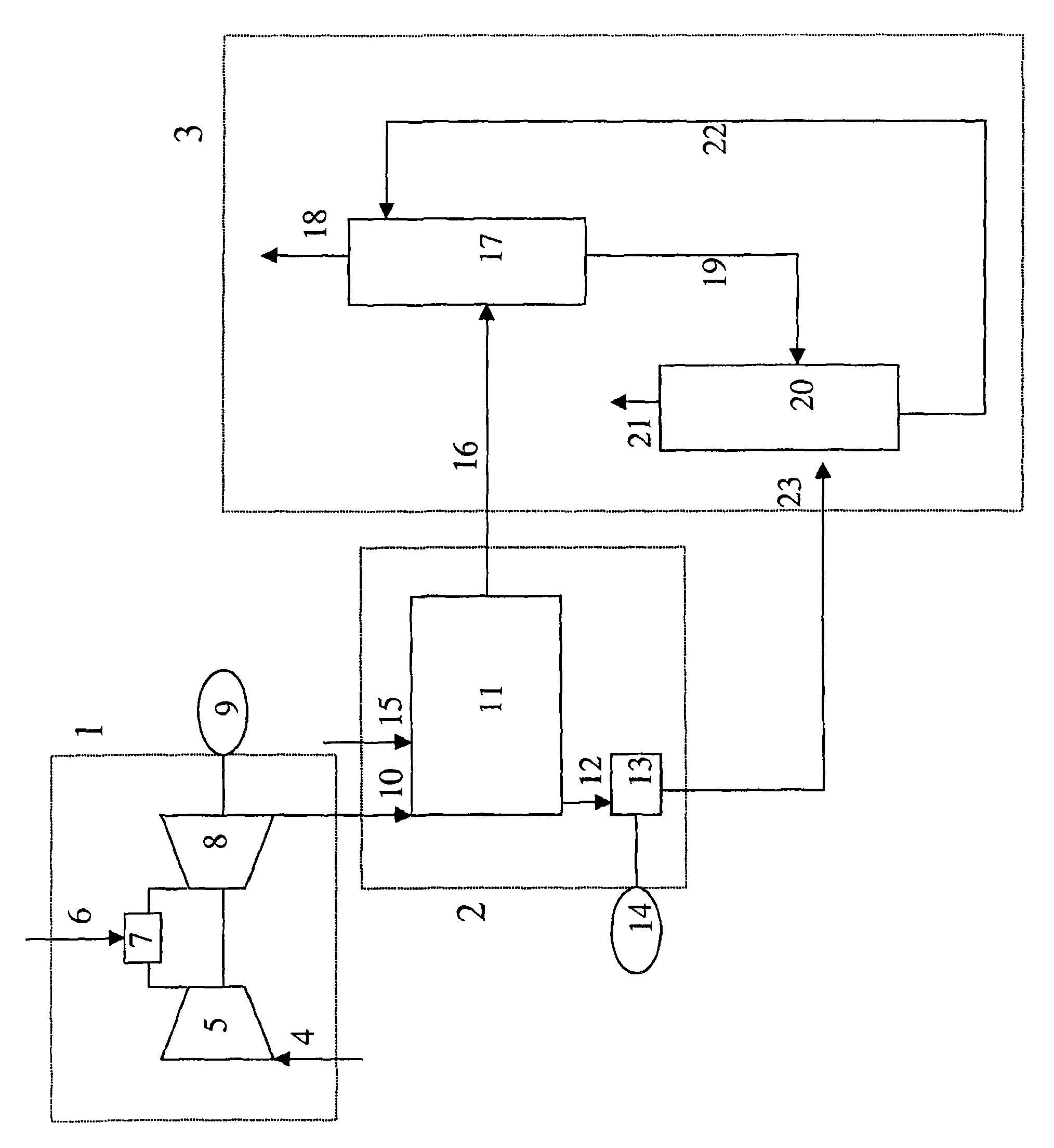
Process for reducing carbon dioxide emission in a power plant
A process for reducing CO2 emission in a power plant, wherein the power plant comprises at least one gas turbine coupled to a heat recovery steam generator unit and the CO2 capture unit comprises an absorber and a regenerator, the process comprising the steps of: (a) introducing hot exhaust gas exiting a gas turbine having a certain elevated pressure into a heat recovery steam generator unit to produce steam and a flue gas stream comprising carbon dioxide; (b) removing carbon dioxide from the flue gas stream comprising carbon dioxide by contacting the flue gas stream with absorbing liquid in an absorber having an elevated operating pressure to obtain absorbing liquid enriched in carbon dioxide and a purified flue gas stream, wherein the settings and / or construction of the gas turbine are adjusted such that the hot exhaust gas exiting the gas turbine has a pressure of at least 40% of the elevated operating pressure of the absorber.
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
Mitigating or eliminating the carbon footprint of human activities
InactiveUS20090285739A1Neutralizing and reducing carbon footprint from carbon dioxide emissionIncrease carbon dioxide levelsCarbon compoundsBiofuelsCombustionCarbon footprint
A method for neutralizing or reducing the carbon footprint from carbon dioxide emissions due to human activities related to the combustion or use of carbon containing fuels. This method includes an initial step of capturing carbon dioxide and then chemically recycling it to form and provide a permanent inexhaustible supply of carbon containing fuels or products, which subsequently can be combusted or used without increasing the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere. Thus, the current lifestyles that rely extensively on conventional carbon containing fuels and products can continue indefinitely without harming the environment to preserve and even improve the earth's atmosphere for the benefit of future generations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
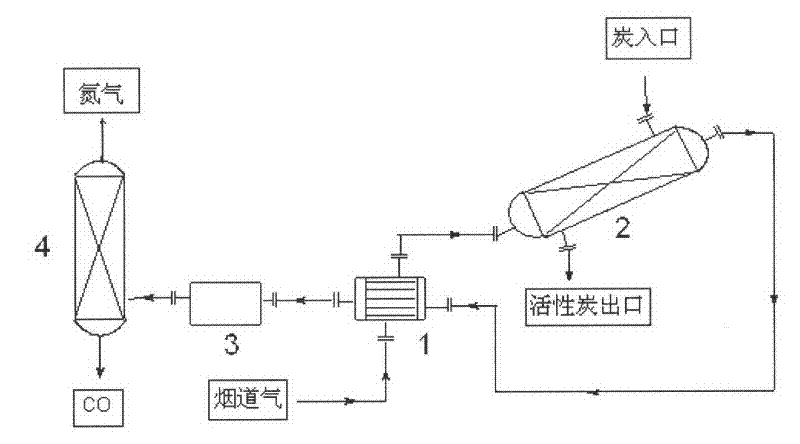
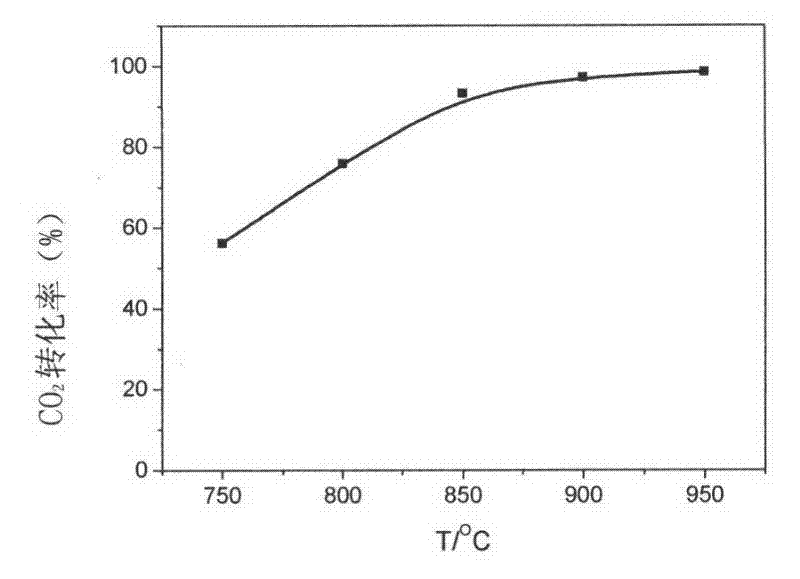
Carbon Reduction Method for Coal-fired Power Plant Tail Gas Emission Reduction
InactiveCN102266717AAvoid huge feesReduce environmental costsDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementNitrogen gasSoot
The invention relates to a carbon reduction method for tail gas emission reduction of a coal-fired power plant, which mainly includes the steps of gas heating, carbon reduction reaction, gas cooling and gas separation. The method of converting CO2 into CO to reduce carbon dioxide emissions not only avoids the huge cost of carbon dioxide capture, transportation and landfill, but also produces CO as an important raw material for one-carbon chemical industry, which has good economic benefits and can Save a lot of gas. During the carbon reduction process, the sulfur and nitrogen oxides in the flue gas are reduced to elemental sulfur and nitrogen, and the decarbonization, desulfurization and denitrification of the flue gas are realized simultaneously, which greatly reduces the environmental protection cost of the power plant. The invention can meet the needs of carbon emission reduction in industries such as power generation, cement, steel and oil refining, especially the control and utilization of carbon dioxide emission from tail gas of coal-fired power plants.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
System and method of reducing carbon dioxide emissions in a fluid catalytic cracking unit
InactiveUS20080153689A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsReduce carbon dioxide concentrationCatalytic crackingOther chemical processesUnit systemInlet pressure
Systems and methods of reducing carbon dioxide emissions in a fluid catalytic cracking unit having a reactor and a regenerator at gasification conditions are disclosed. In one example, a method comprises compressing a first gas at an inlet pressure to a predetermined high pressure to define a compressed gas and combusting a second gas with the compressed gas to a predetermined temperature to define a heated gas. The method further comprises expanding the heated gas to a predetermined low pressure to define a feed gas. The method further comprises introducing the feed gas to the regenerator. The feed gas, now at an elevated temperature, provides heat to the regenerator to burn coke off spent catalyst from the reactor, achieving a proportion of carbon monoxide in a flue gas. In turn, this reduces the concentration of carbon dioxide in the flue gas.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC +1
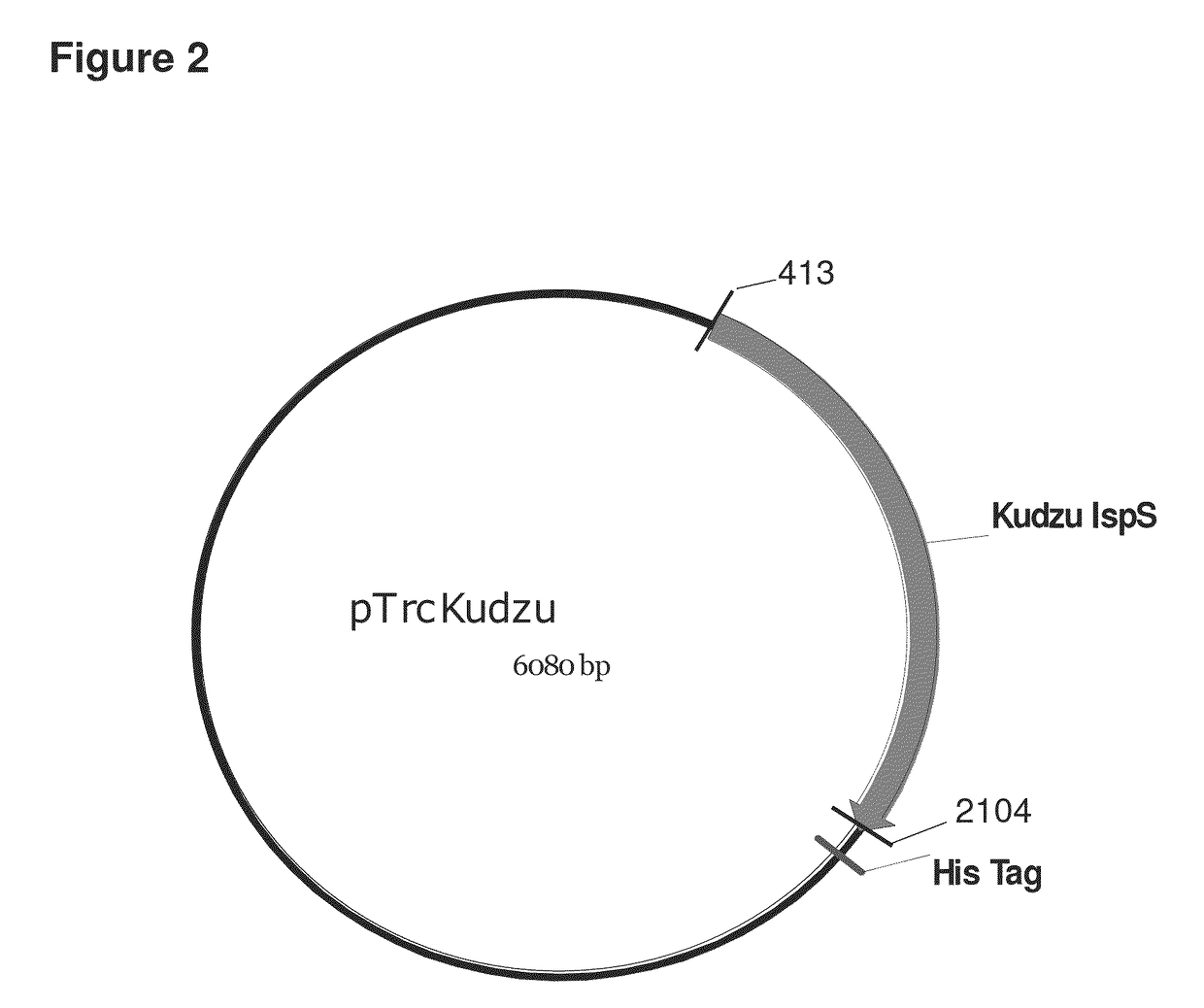
Reduction of carbon dioxide emission during isoprene production by fermentation
The present invention provides methods for increasing the amount of isoprene produced by cultured cells with only a minimal increase in carbon dioxide emitted, thereby resulting in process having a greater yield of isoprene relative to carbon dioxide. In addition, the present invention provides compositions that include the cultured cells or isoprene produced there from.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Method for reducing flue gas carbon dioxide emissions
InactiveUS20140109575A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsEmission preventionDirect carbon-dioxide mitigationFlue gasFlue-gas stack
Plants, devices, and methods are presented which economically and effectively reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from flue gases by converting heat derived from one or more sources of flue gas to drive a heat engine, which generates power, energy, and / or work that is utilized by a CO2 capture unit coupled to the stream of flue gas. CO2 captured from the flue gas stream may be sequestered and / or utilized for commercial purposes.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
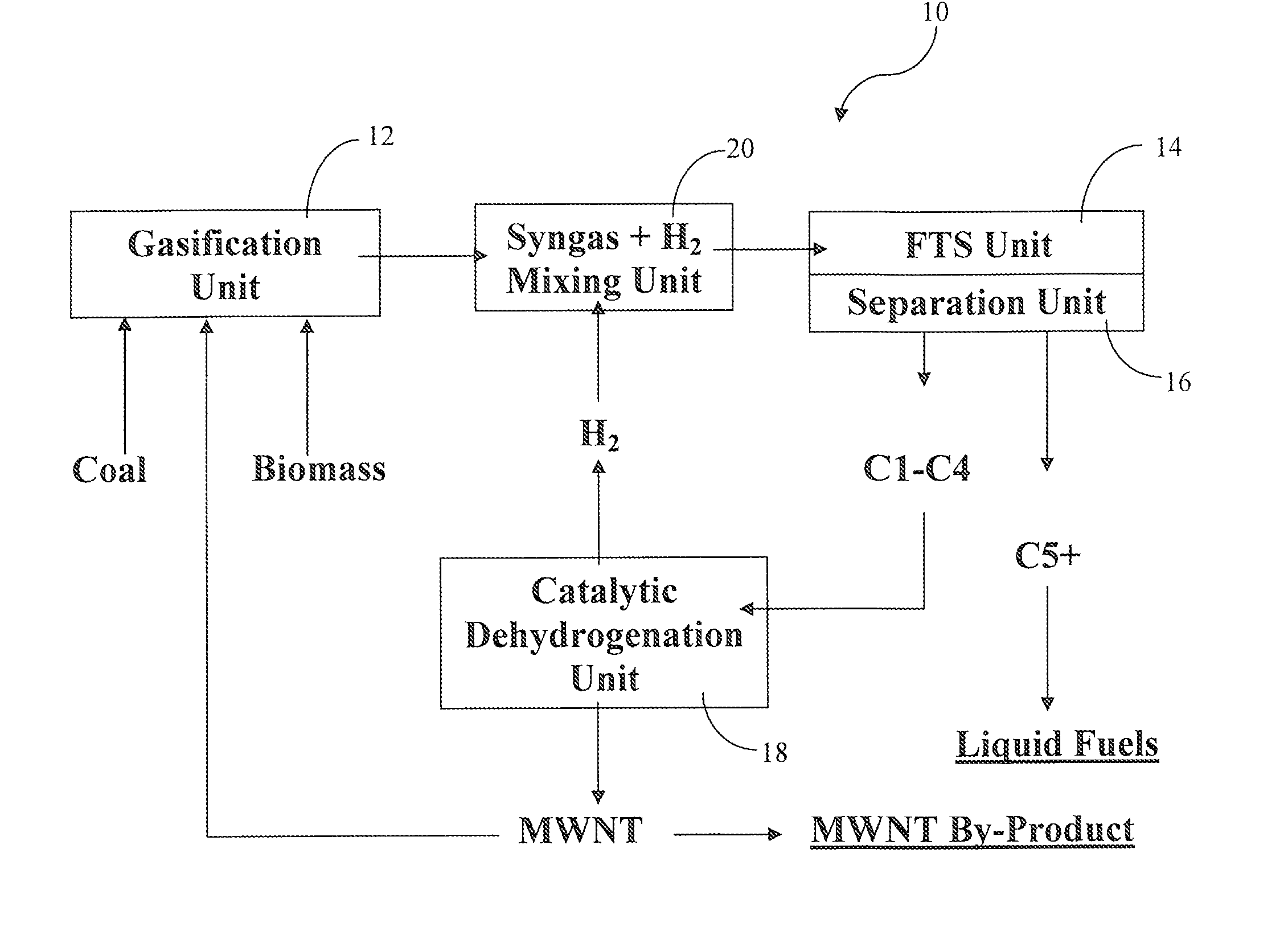
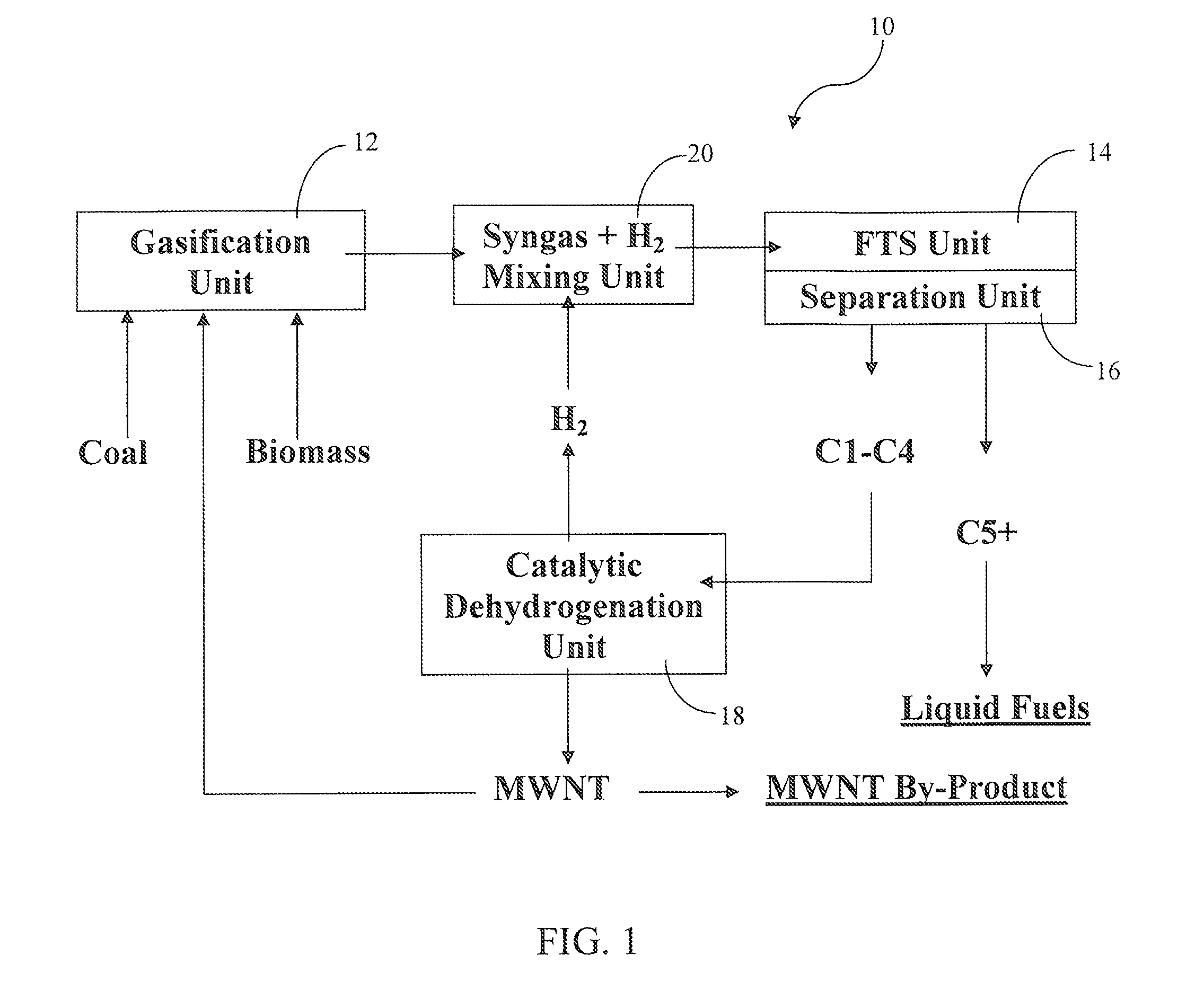
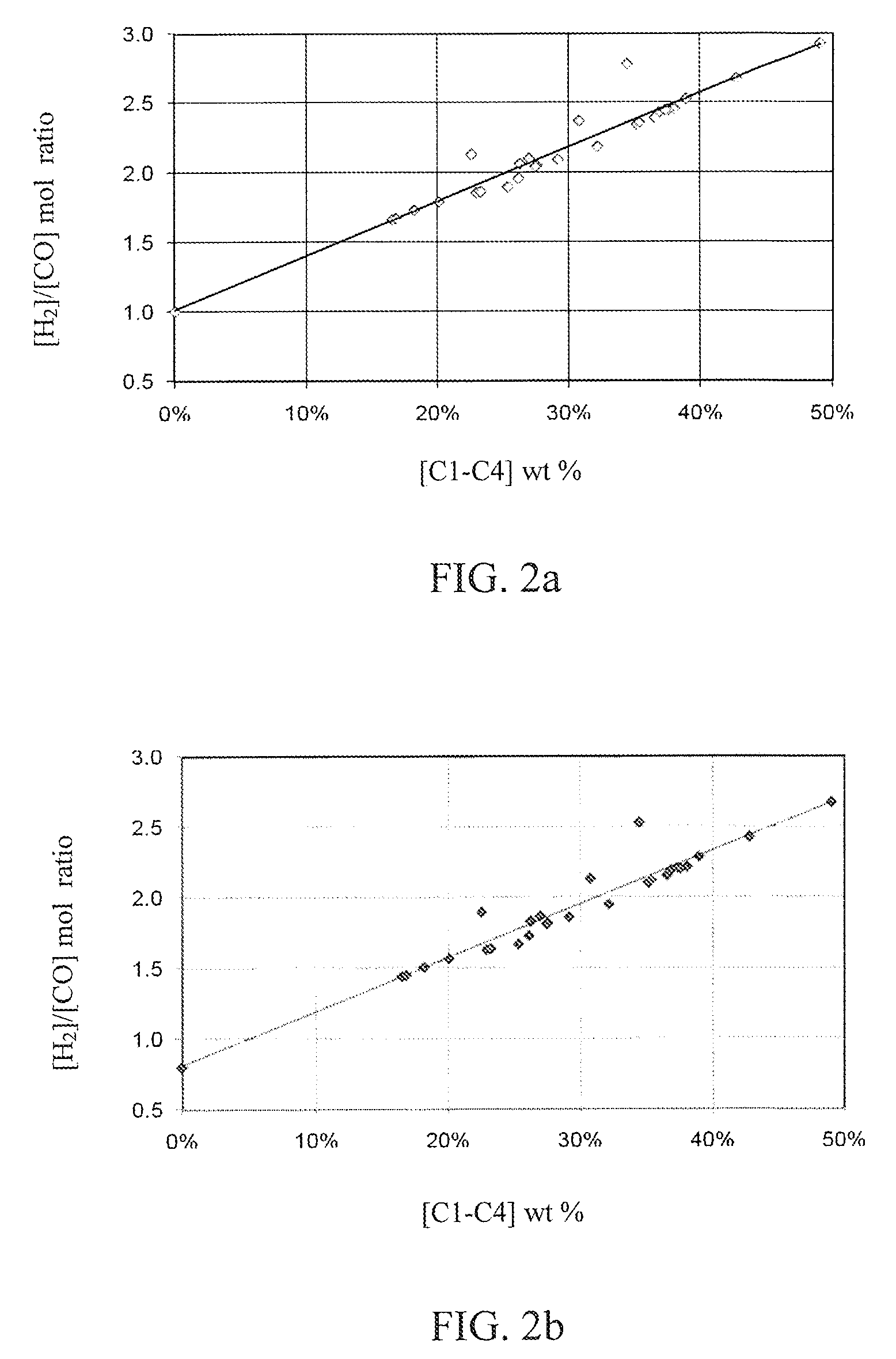
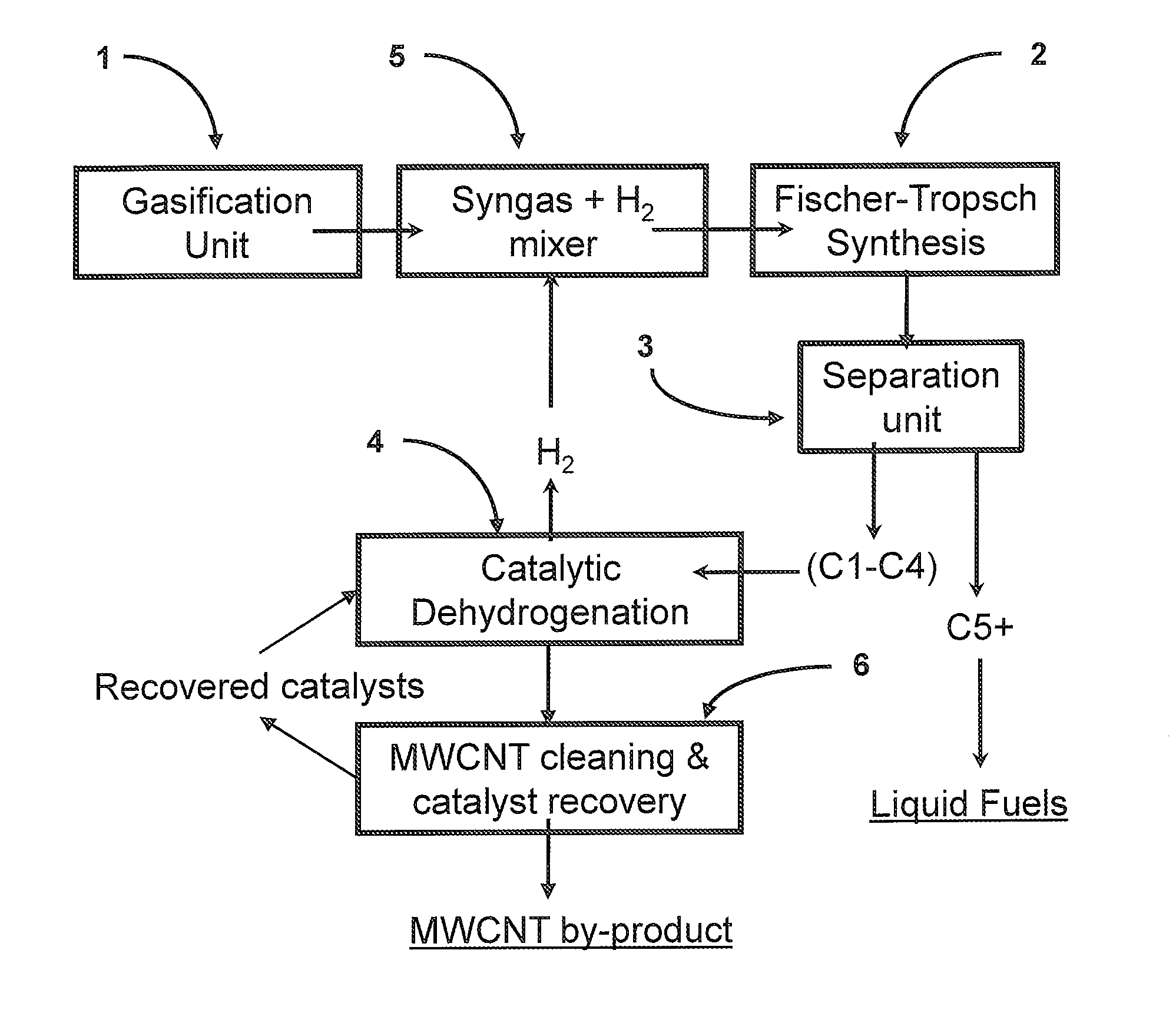
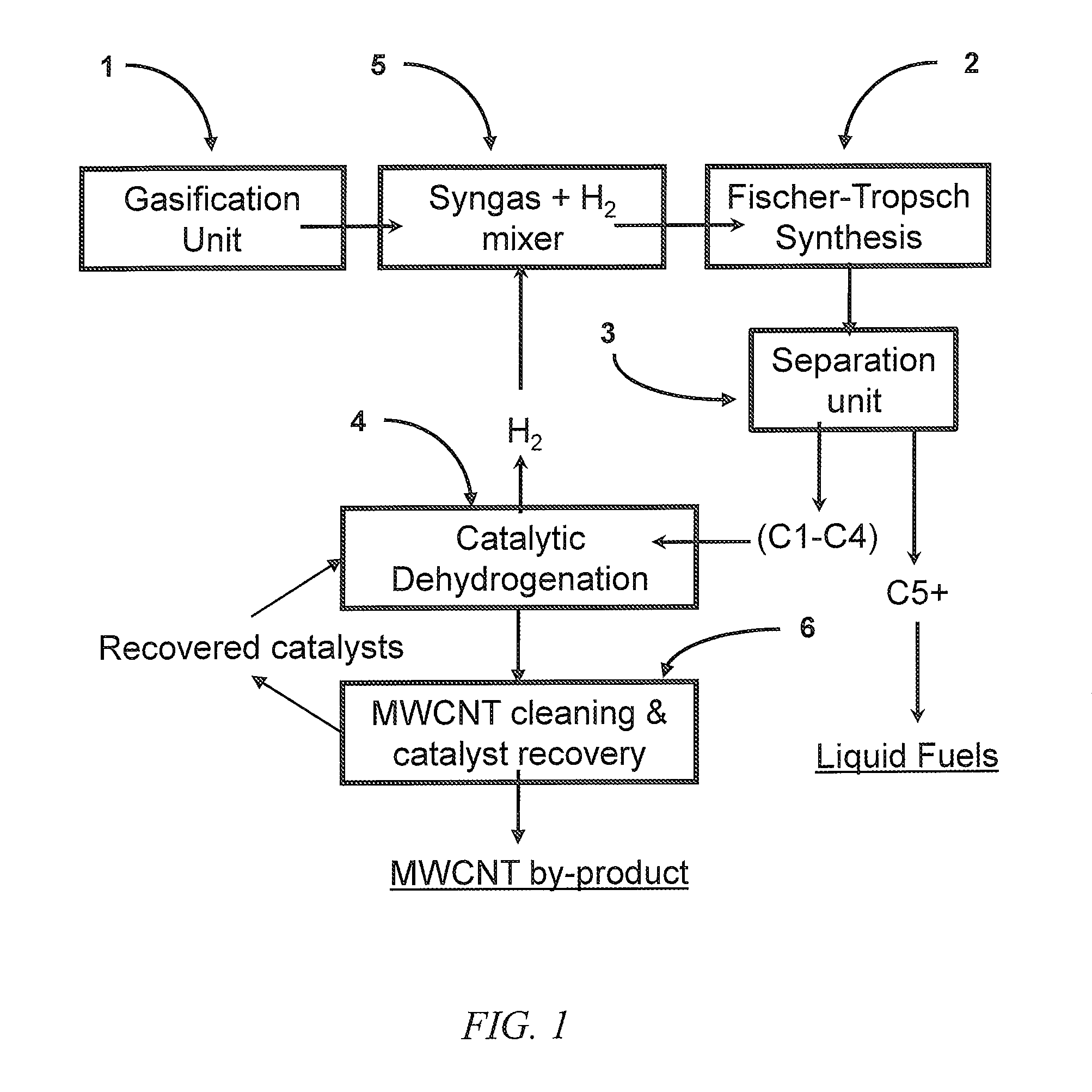
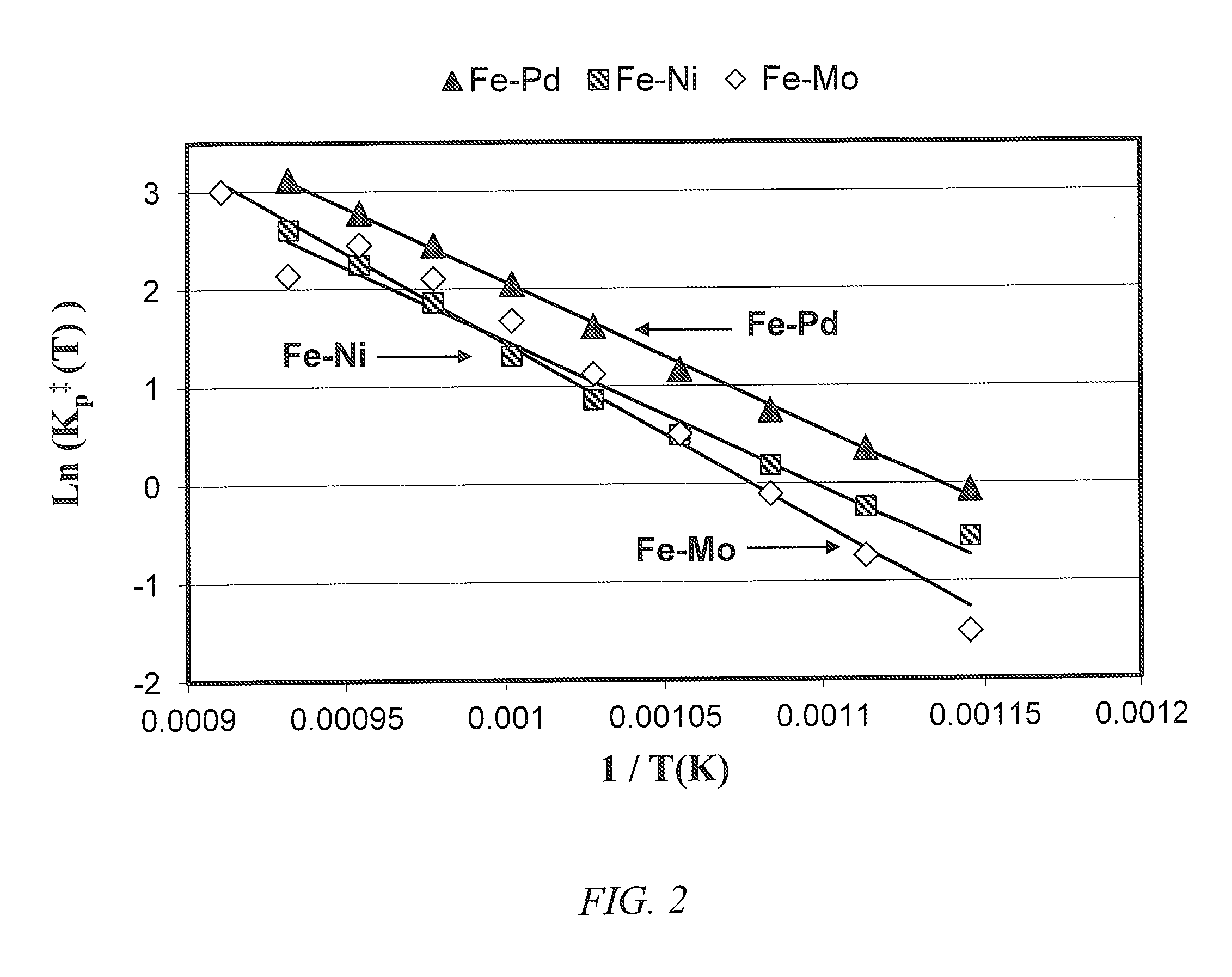
Incorporation of catalytic dehydrogenation into Fischer-Tropsch synthesis to lower carbon dioxide emissions
InactiveUS8268897B2Organic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionDehydrogenationCarbon nanotube
A method for producing liquid fuels includes the steps of gasifying a starting material selected from a group consisting of coal, biomass, carbon nanotubes and mixtures thereof to produce a syngas, subjecting that syngas to Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (FTS) to produce a hyrdrocarbon product stream, separating that hydrocarbon product stream into C1-C4 hydrocarbons and C5+ hydrocarbons to be used as liquid fuels and subjecting the C1-C4 hydrocarbons to catalytic dehydrogenation (CDH) to produce hydrogen and carbon nanotubes. The hydrogen produced by CDH is recycled to be mixed with the syngas incident to the FTS reactor in order to raise the hydrogen to carbon monoxide ratio of the syngas to values of 2 or higher, which is required to produce liquid hydrocarbon fuels. This is accomplished with little or no production of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas. The carbon is captured in the form of a potentially valuable by-product, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNT), while huge emissions of carbon dioxide are avoided and very large quantities of water employed for the water-gas shift in traditional FTS systems are saved.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Incorporation of catalytic dehydrogenation into fischer-tropsch synthesis to significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions
A new method of producing liquid transportation fuels from coal and other hydrocarbons that significantly reduces carbon dioxide emissions by combining Fischer-Tropsch synthesis with catalytic dehydrogenation is claimed. Catalytic dehydrogenation (CDH) of the gaseous products (C1-C4) of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (FTS) can produce large quantities of hydrogen while converting the carbon to multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT). Incorporation of CDH into a FTS-CDH plant converting coal to liquid fuels can eliminate all or most of the CO2 emissions from the water-gas shift (WGS) reaction that is currently used to elevate the H2 level of coal-derived syngas for FTS. Additionally, the FTS-CDH process saves large amounts of water used by the WGS reaction and produces a valuable by-product, MWCNT.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
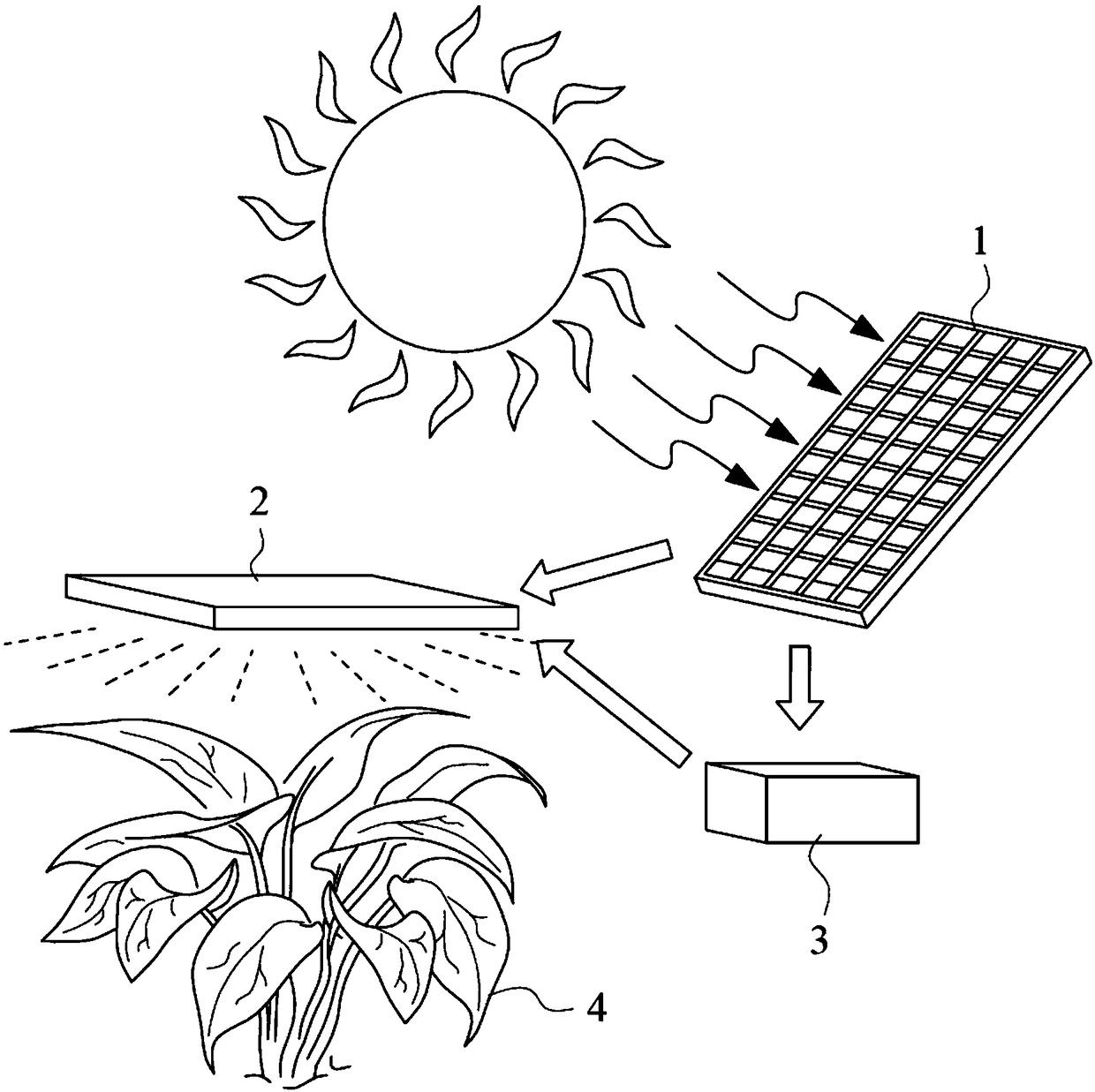
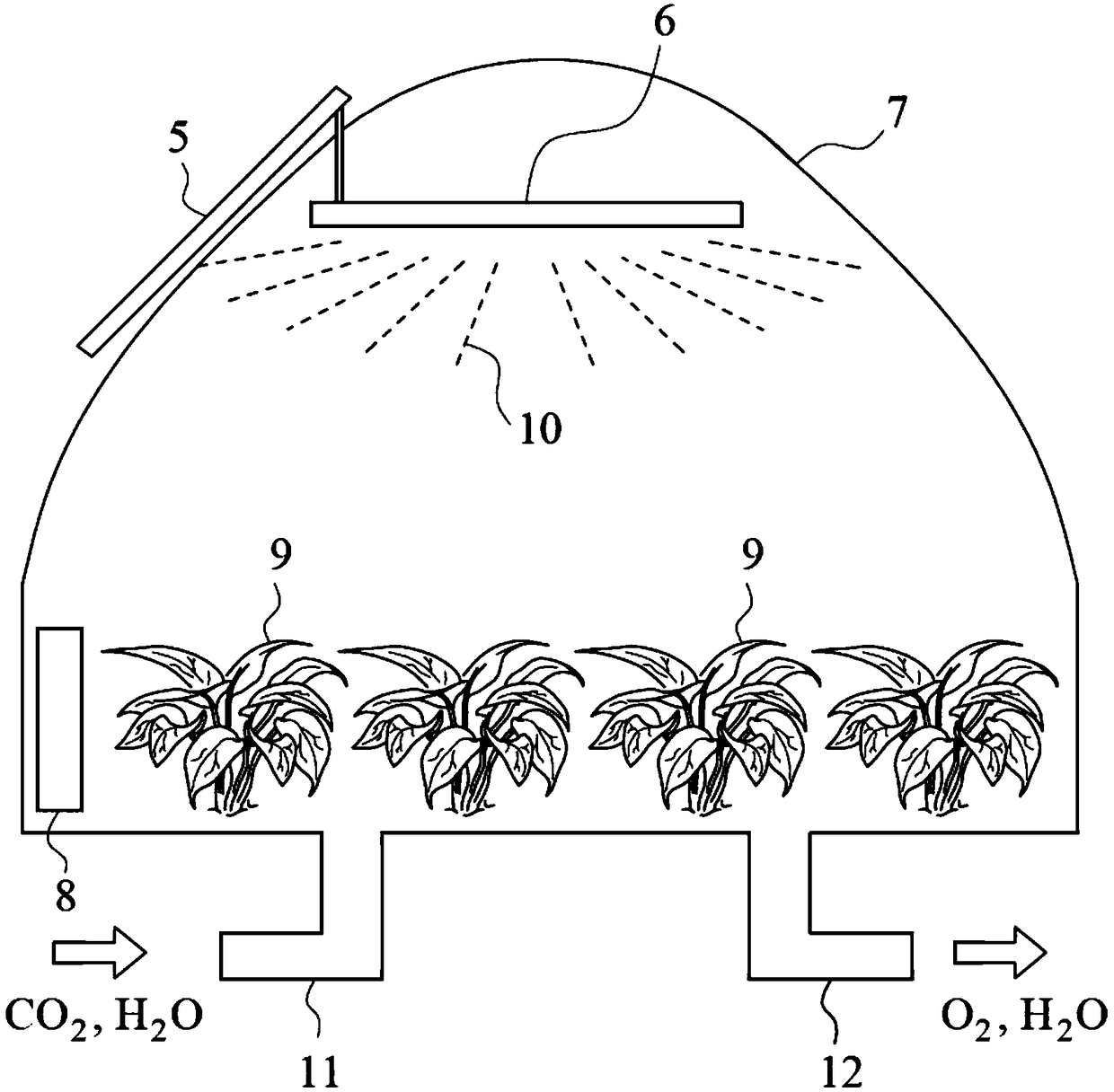
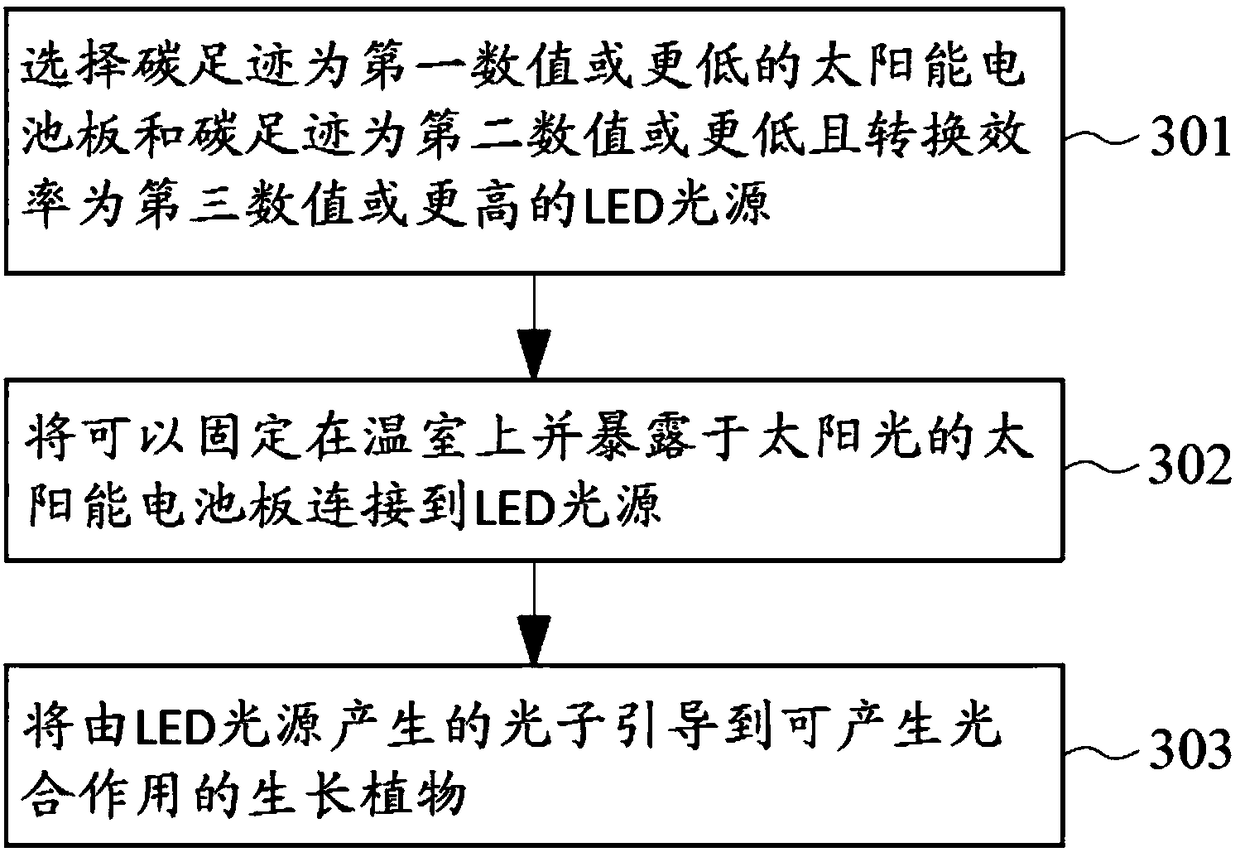
Negative carbon emission system and method thereof
The invention discloses a negative carbon emission system and a method thereof. Carbon dioxide molecules can be fixed by growing plants through plant photosynthesis. When the wavelength of photons that cause the plant synthesis are properly designed to enhance plant photosynthesis of plants. A LED light source, whose carbon footprint is lower than a threshold value and the conversion efficiency ishigher than a threshold value, is adopted. A low carbon power supply with carbon footprint lower than a threshold value such as a solar panel is used. When the combination is realized, carbon dioxidemolecules absorbed by plants through photosynthesis are more than emitted carbon dioxide molecules, long term negative carbon emission is realized, and the system can be used to capture carbon dioxide.
Owner:刘容生
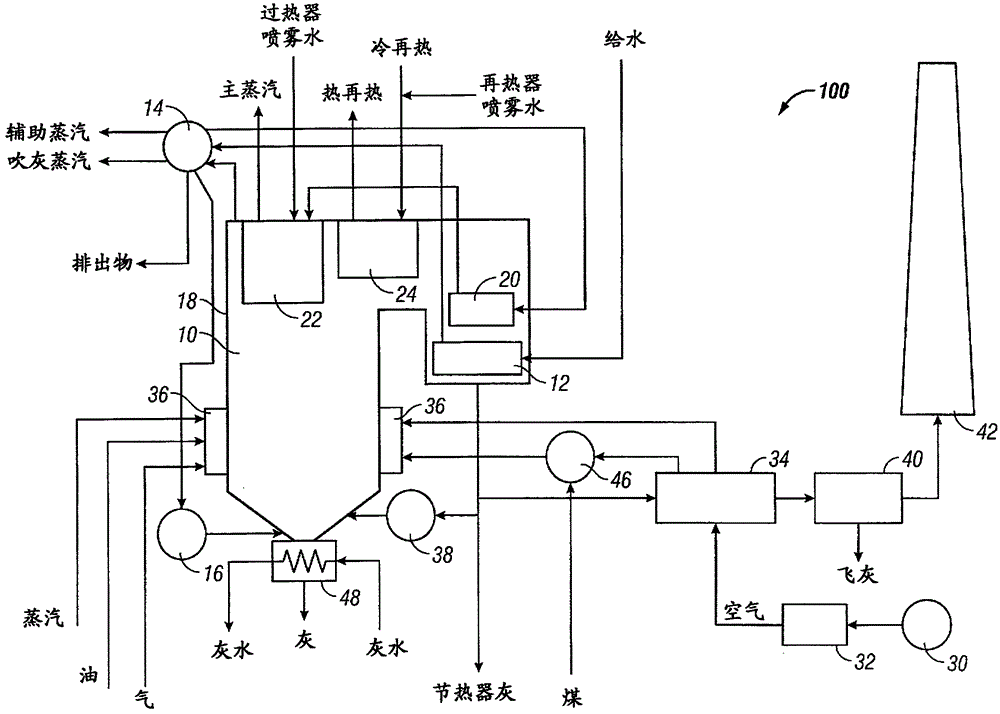
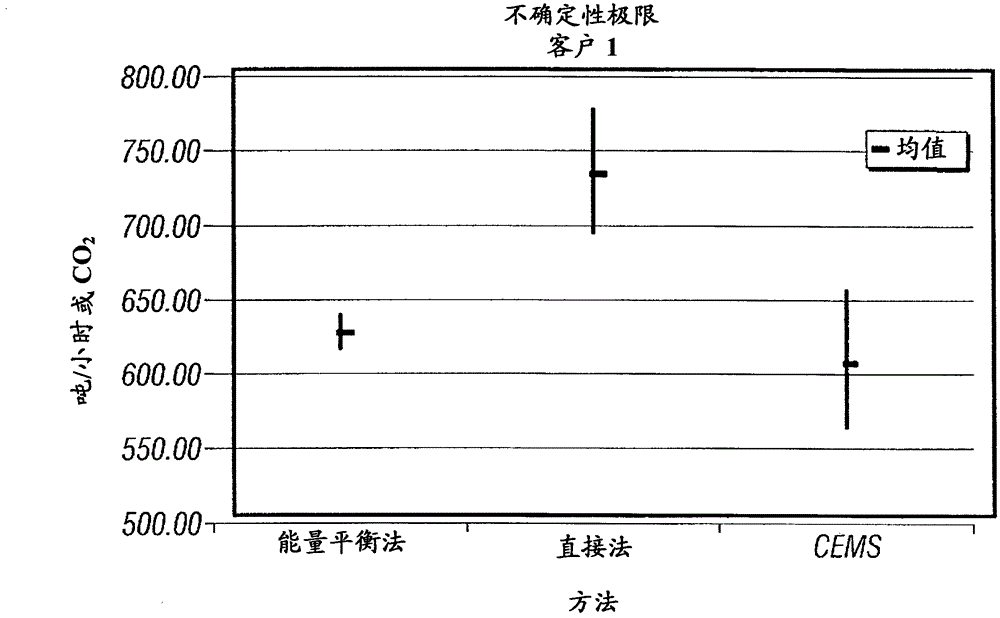
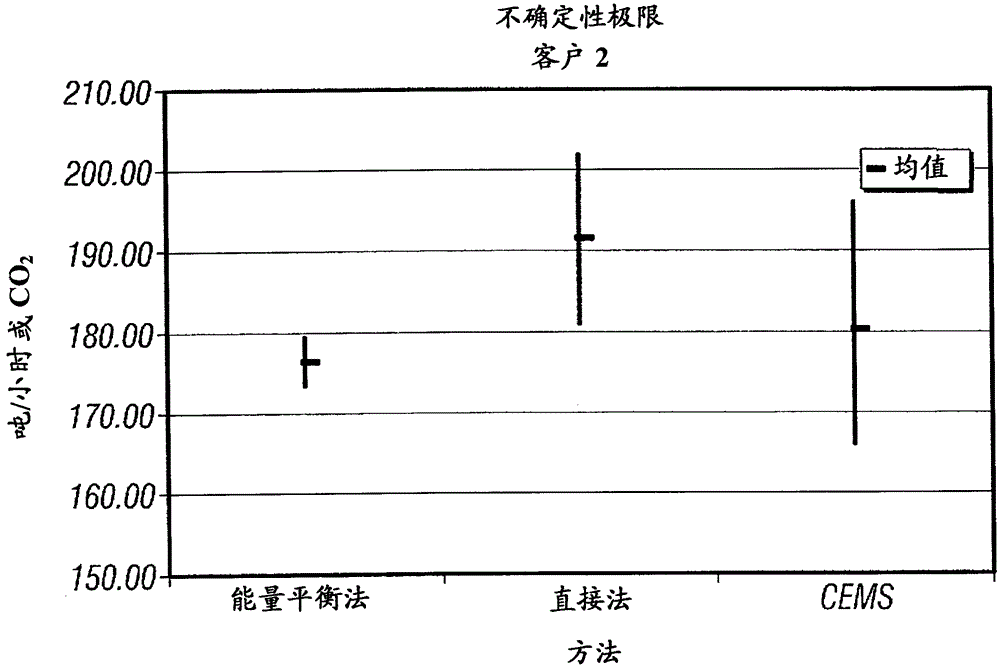
Method for determination of carbon dioxide emissions from steam generation systems
InactiveCN102803847ABoiler indication operationsEnergy industryEngineeringNegative carbon dioxide emission
A method for determining carbon emissions from a steam generation system (100) is disclosed. It includes measuring a first energy of feedwater entering into a steam generation system (100) and measuring a second energy of steam exiting the steam generation system (100). The first energy is subtracted from the second energy to determine a total energy absorbed by the steam generation system (100). The total energy absorbed by the steam generation system (100) is divided by the total energy to determine a heat input to the steam generation system (100). The heat input is used to determine the carbon emissions from the steam generation system (100).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
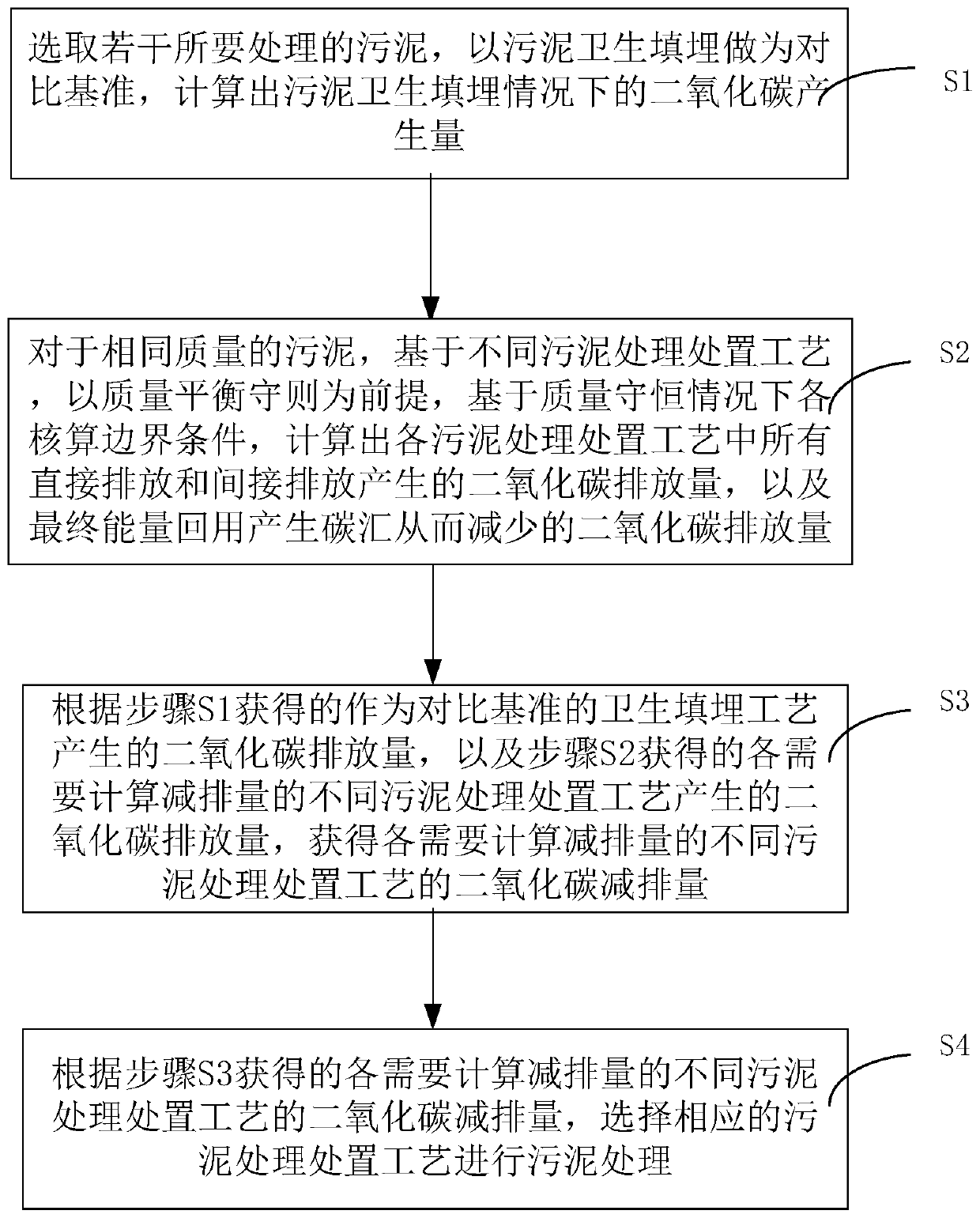
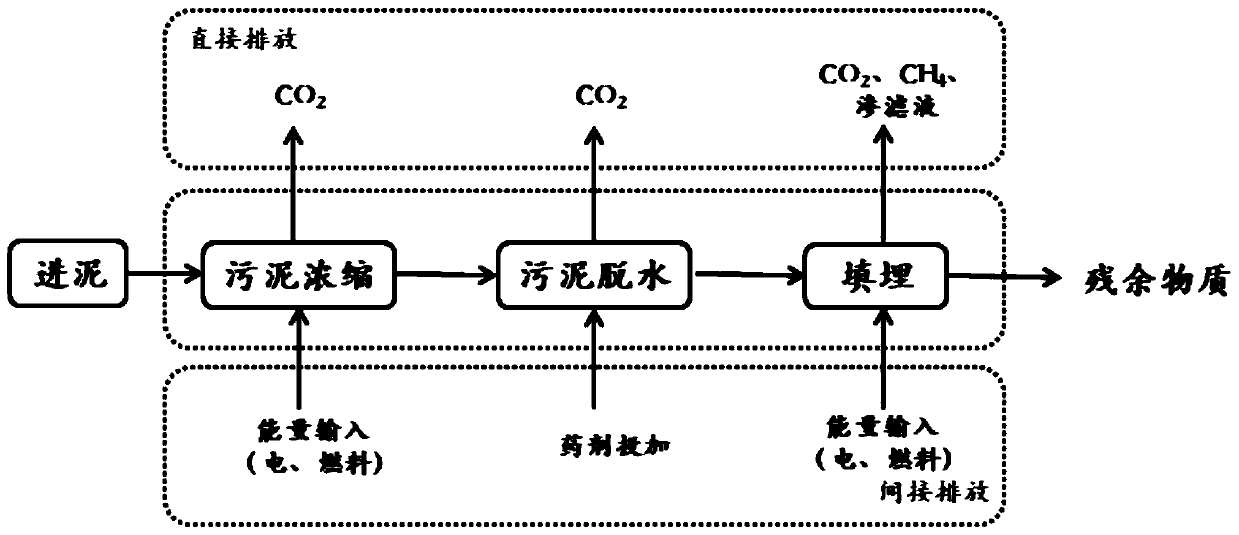
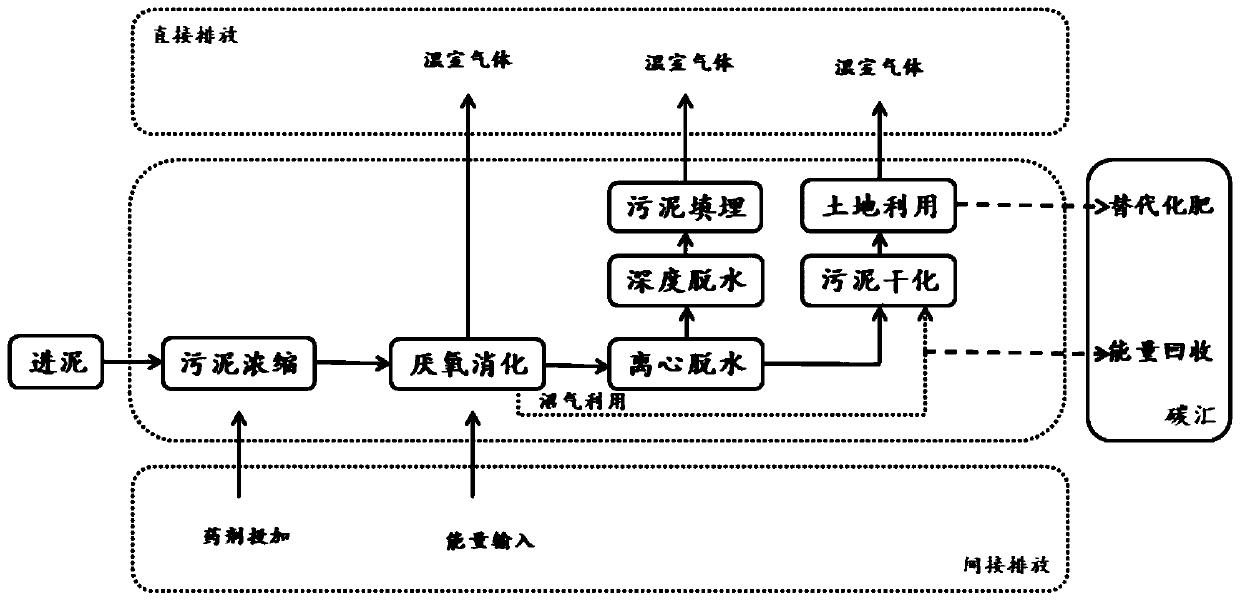
Sludge treatment method based on carbon dioxide emission reduction
InactiveCN110590093AEmission reductionReduce pollutionWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsIndirect emissionsSludge
The invention discloses a sludge treatment method based on carbon dioxide emission reduction. The method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting a certain amount of sludge to be treated, and calculating the carbon dioxide generation amount under the sludge sanitary landfill condition by taking sludge sanitary landfill as a comparison reference; step S2, based on different sludge treatment anddisposal processes, on the premise of mass balance conservation, based on each accounting boundary condition under the condition of mass conservation, calculating carbon dioxide emissions generated by all direct emissions and indirect emissions in each sludge treatment and disposal process, and carbon emission reduction caused by carbon sink generated by final energy reuse; S3, according to the carbon dioxide generation amount btained in the step S1 and the carbon dioxide emission amount obtained in the step S2, obtaining carbon dioxide emission reduction amounts of different sludge treatmentand disposal processes with requirements on emission reduction amount calculation; and S4, according to the obtained carbon dioxide emission reduction amount of each process, selecting a corresponding sludge treatment process to carry out sludge treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL WATER RESOURCES DEV & UTILIZATION NAT ENG CENT
Biomass gasification power generation system and method
PendingCN109337715AImprove power generation efficiencyCompact structureGasification processes detailsBulk chemical productionCombustion chamberOxygen
The invention provides a biomass gasification power generation system. The biomass gasification power generation system comprises a biomass gasification subsystem and a semi-closed supercritical carbon dioxide circulation subsystem, wherein the biomass gasification subsystem comprises a feeding device, a biomass gasifier, a fuel gas purification and cooling device, an oxygen source, a gasifier oxygen feeding compressor, a combustion chamber oxygen feeding compressor, a hydraulic turbine, a fuel gas compressor and the like; and the supercritical carbon dioxide circulation subsystem comprises afirst carbon dioxide pump, a middle cooler, a second carbon dioxide pump, a heat regenerator, a combustion chamber, a turbine, a power generator, a cooler, a water separator, a condenser, a carbon dioxide collection device and the like. The invention further provides a biomass gasification power generation method. The biomass gasification power generation system is high in efficiency, semi-closedsupercritical carbon dioxide is circulated under high-temperature and high-pressure parameters, so that the power generation efficiency is high; negative carbon dioxide emissions are achieved, so thatan additional carbon capturing device is avoided; and the system is simple, compact in structure and flexible to operate, so that a small or large chimney-free biomass gasification power plant can beestablished.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER EQUIP RES INST
Graphene oxide modified coal pitch binder and preparation method thereof
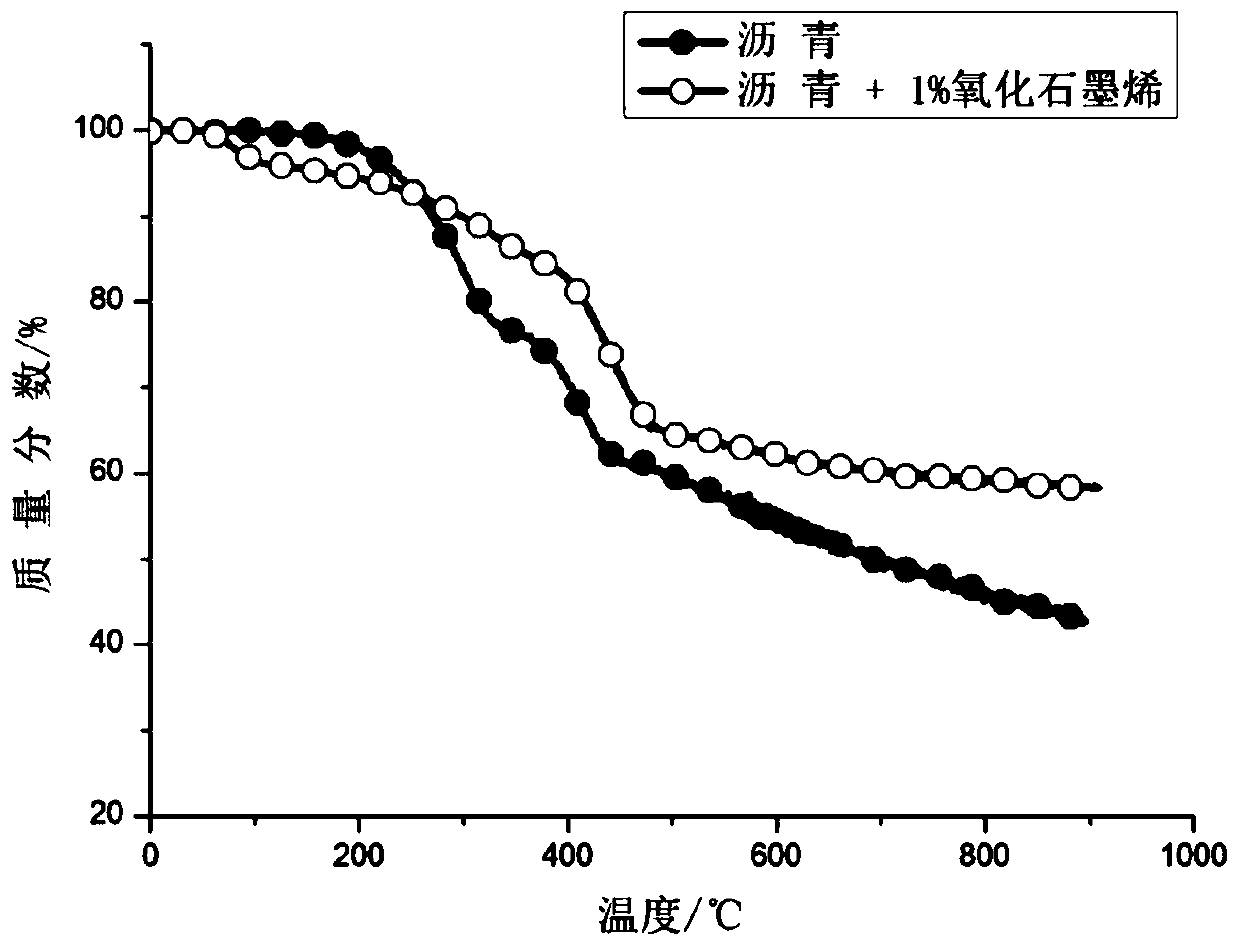
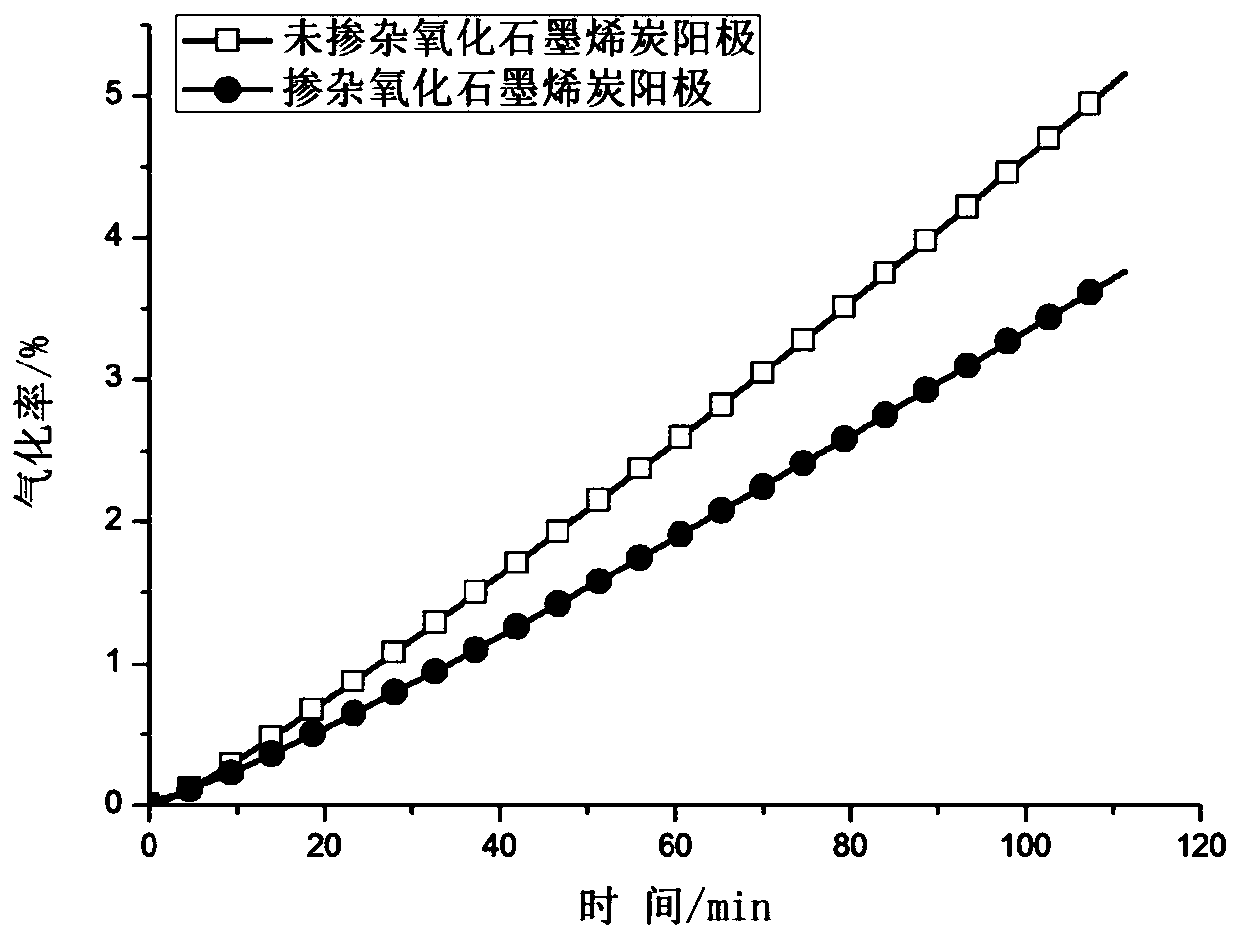
ActiveCN109768277AImprove antioxidant capacityReduce consumptionElectrode manufacturing processesSolid carbonEcological environment
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene oxide modified coal pitch binder, The method comprises the following steps: fully mixing coal pitch serving as a basic raw material and graphene oxide serving as an additive (in a mass ratio of 0.2-2.0%) in an inert liquid medium, separating and purifying to prepare a modified coal pitch binder, and mixing the modified coal pitch binder with a solid carbon component by kneading according to the following ratio (15-30):(70-85) and performing high-temperature roasting to obtain the carbon electrode. The method has the advantages that the oxidation resistance of the carbon electrode prepared by the graphene oxide modified coal pitch binder is improved, so that the carbon consumption during the use of the electrode can be reduced, andthe carbon dioxide emission is reduced, which will be beneficial to the protection of the ecological environment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com